Evidence for Network-Based Cortical Thickness Reductions in Schizophrenia
Abstract
Objective:
Methods:
Results:
Conclusions:
Methods
Participants
| First-Episode Psychosis | Chronic Schizophrenia | Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Patient Cohort (N=70) | Healthy Control Group (N=57) | t or χ2 | Patient Cohort (N=153) | Healthy Control Group (N=168) | t or χ2 | Patient Cohort (N=47) | Healthy Control Group (N=54) | t or χ2 | ||||||
| N | % | N | % | χ2 | N | % | N | % | χ2 | N | % | N | % | χ2 | |
| Male | 50 | 71.4 | 34 | 59.6 | 2.43 | 110 | 71.9 | 81 | 48.2 | 18.64** | 35 | 74.5 | 36 | 66.7 | 0.47 |
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | t | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | t | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | t | |
| Age (years) | 21.49 | 3.38 | 21.36 | 3.66 | 0.21 | 38.11 | 9.82 | 39.74 | 13.97 | 1.22 | 38.79 | 9.44 | 39.23 | 10.56 | 0.22 |
| Current IQ | 87.07 | 13.56 | 109.38 | 10.49 | 9.34** | 105.26 | 13.59 | 117.32 | 11.06 | 8.67** | –18.42 | 18.42 | 113.47 | 12.15 | 8.68** |
| Premorbid IQ | 92.58 | 13.33 | 101.28 | 10.27 | 3.99** | 99.95 | 13.89 | 107.44 | 10.79 | 5.35** | 91.36 | 13.52 | 106.36 | 9.72 | 5.84** |
| Positive symptoms (DIP) | 1.76 | 2.6 | |||||||||||||
| Positive symptoms (PANSS) | 22.78 | 6.56 | 16.2 | 5.71 | |||||||||||
| Negative symptoms (SANS) | 25.8 | 17.34 | 45.64 | 17.57 | |||||||||||
| Negative symptoms (PANSS) | 20.62 | 7.21 | 18.39 | 6.12 | |||||||||||
| Illness duration (years) | 0.16 | 0.27 | 14.16 | 8.83 | 16.64 | 8.77 | |||||||||
| Mean cortical thickness (mm) | 2.49 | 0.08 | 2.54 | 0.1 | 3.40** | 2.5 | 0.1 | 2.6 | 0.1 | 4.66** | 2.42 | 0.09 | 2.52 | 0.08 | 5.84** |
| Total antipsychotic dose (CPZ equivalent: mg) | 216.86 | 117.37 | 915.59 | 324.16 | |||||||||||
Imaging Data Acquisition
Image Processing and Cortical Thickness Estimation
Statistical Analysis
Cortical thickness differences.
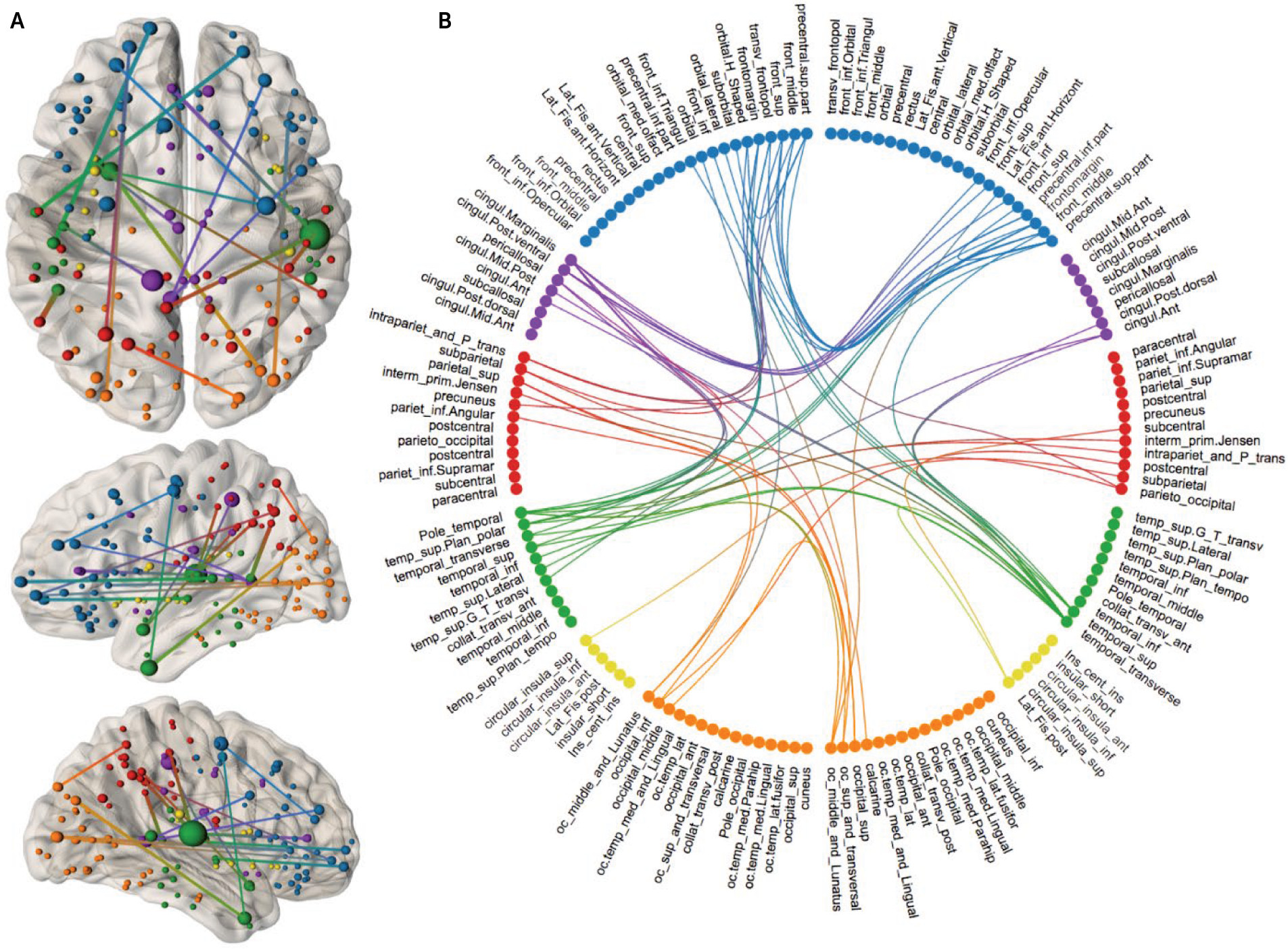
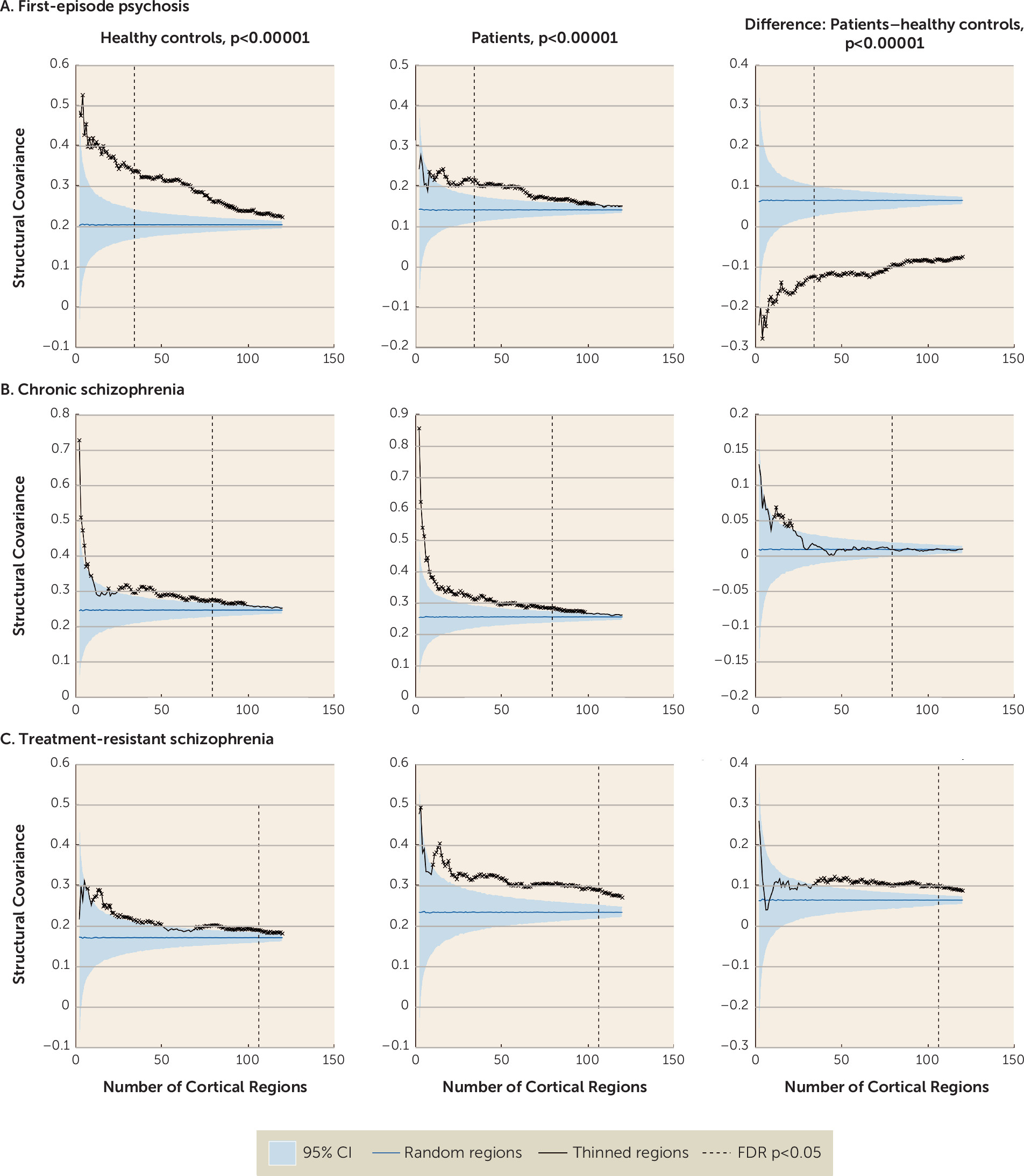
Whole-brain structural covariance analysis.
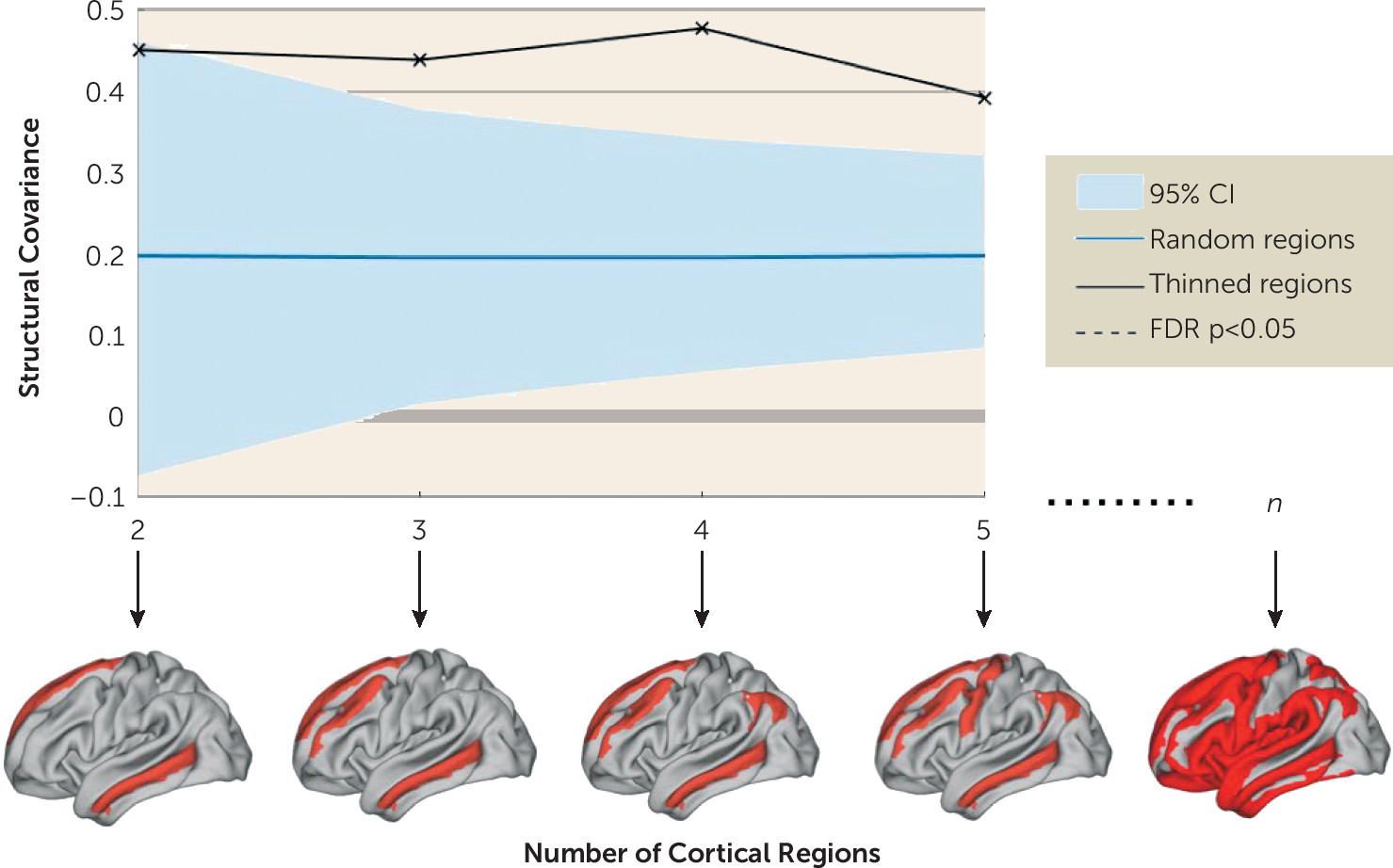
Structural covariance between regions with cortical thickness reductions.
Results
Demographic Characteristics
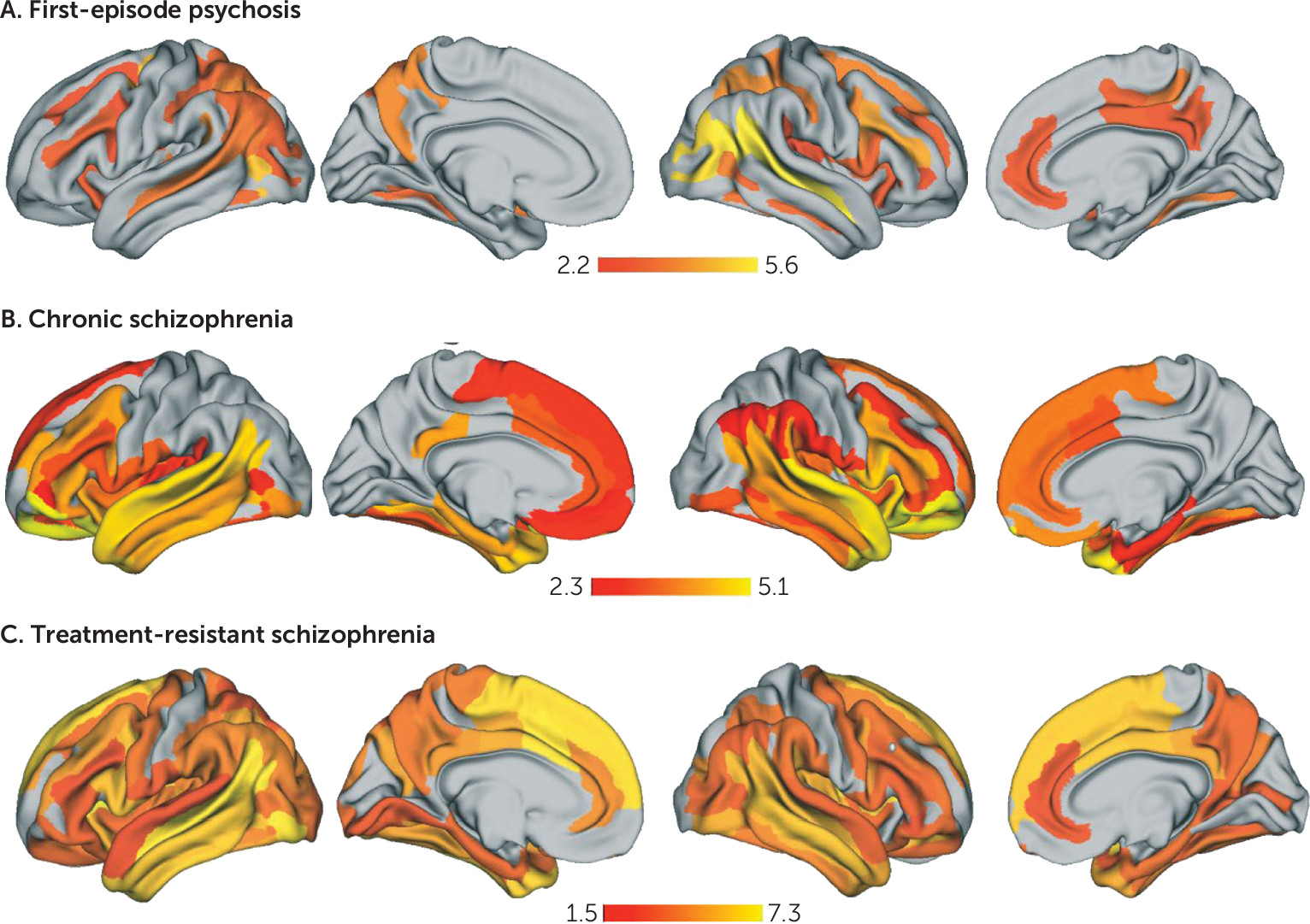
Cortical Thickness Reductions
Whole-Brain Structural Covariance
Structural Covariance Between Regions With Cortical Thickness Reductions
Supplementary Analyses
Discussion
Characterizing Cortical Thickness Reduction Across Distinct Schizophrenia Cohorts
Network-Based Cortical Thickness Reductions
Limitations and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Footnote
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 4.93 MB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

