Antipsychotic Polypharmacy and Metabolic Syndrome in Schizophrenia: A Review of Systematic Reviews
Abstract
Background:
Methods:
Results:
Conclusions:
Background
Aims of the study.
Methods
Inclusion criteria for reviews.
Identification and selection of reviews.
Data extraction and quality assessment of included reviews.
Data synthesis.
Analysis of subgroups or subsets.
Assessment of certainty of evidence.
Results
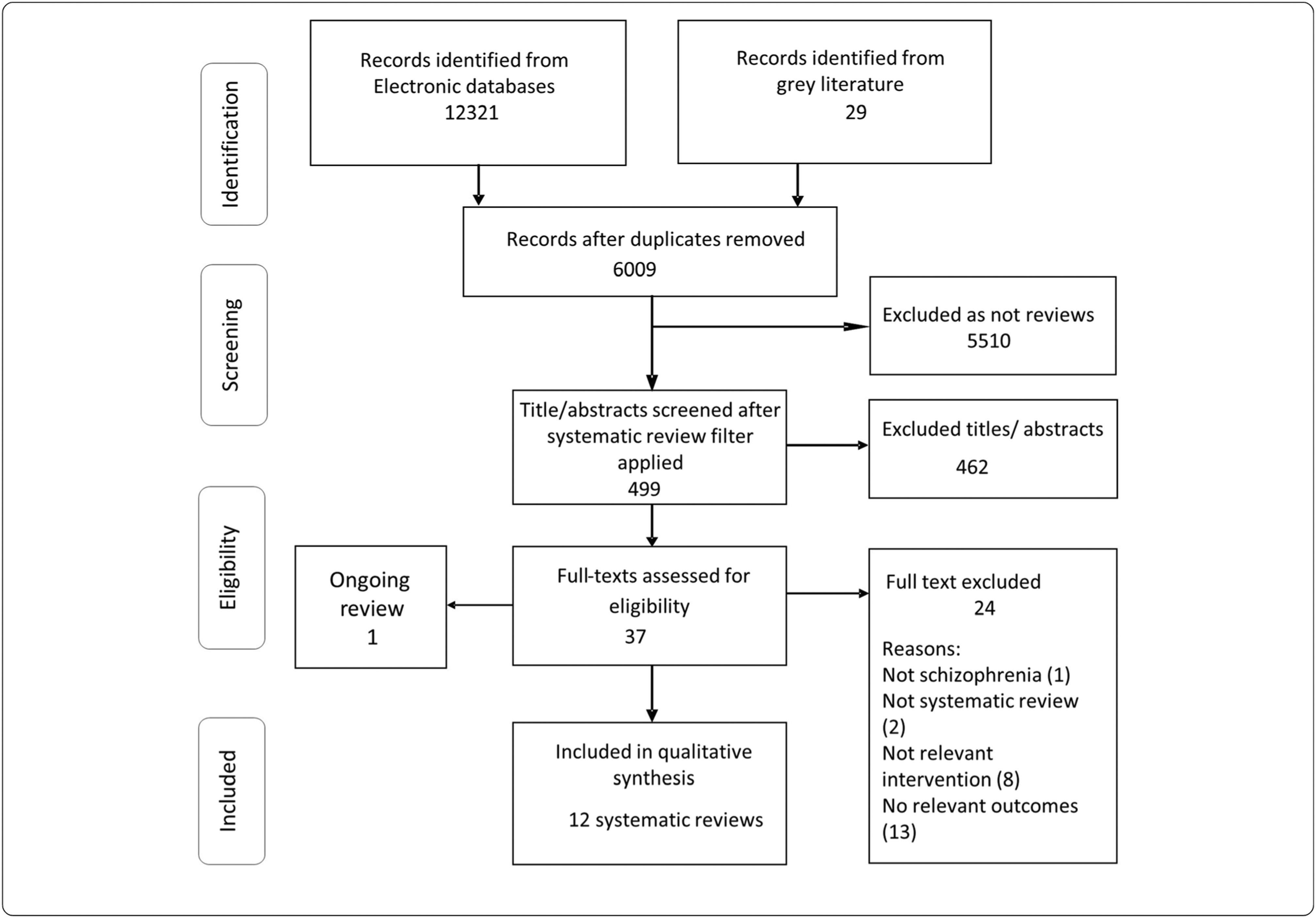
Description of included reviews.
| Study | Studies (N) included | Date of latest search | Study Settings (Primary/Secondary care) | Included Study Designs | Participants | Intervention/Exposures | Comparison | Outcomes | Quality assessment in the review | Meta-analysis | Findings/effectaon metabolicmarkers/conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galling 2016 (32) | 67 | 05/25/2015 | Both | RCTs | Schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder | Any APP; APP with D2 antagonists; APP with partial D2 agonists | AP monotherapy | Total cholesterol; LDL cholesterol; | No formal assessment; all studies considered at high risk; sensitivity analysis done for blinding. | Yes | APP was associated with lower total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol |
| Young 2015 (25) | 53 | June 2013 | NR | Case control; cohort; cross-sectional | All diagnostic groups. Children and adults | Any AP | AP monotherapy | Prevalence of: Metabolic disorder; diabetes mellitus; hypertension; | Author defined criteria used to give scores and only highest scoring studies summarised. | No | APP was associated with increased prevalence of AE: metabolic syndrome, dyslipidaemia, diabetes. A longer duration of treatment was associated with greater severity; Clozapine strongly associated with metabolic disturbance |
| Tranulis 2008 (26) | 51 | 23 Aug 2006 | NR | All | Schizophrenia | APP specific combinations | NR | Safety | NR | No | No synthesisb/effect estimate on metabolic outcomes. |
| Tracy 2013 (27) | 72 | 6 January 2013 | NR | All | Schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder or related diagnoses | APP | NR | Any functional outcome or adverse effect | NR | No | No synthesis/effect estimate on metabolic outcomes. They report that there is consistent emerging data supporting aripiprazole for reregulate lipid profiles. |
| Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health 2012 (35) | 30 | June 16, 2010 | NR | RCT | schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder inadequately managed with one or more AAPs at recommended doses | High dose AP/APP | AP Low dose/monotherapy | AE (endocrine/metabolic markers for glucose, prolactin, | Modified SIGN checklist assigned a rating (very good, good, or poor); 27/30 rated poor. Low quality tested in sensitivity analyses | Probably yes but results NR | Total cholesterol and LDL were statistically significantly lower with Clozapine +AP. |
| Zheng 2016 (24) | 55 | June 2015 | NR | RCT | Patients using antipsychotic drugs | Aripiprazole + AP | Placebo + AP or AP alone | No outcome of interest | Cochrane Risk of bias tool: 2 trials at low risk | Yes | No effect estimate on metabolic outcomes. |
| Mizuno 2014 (29) | 50 | November 5, 2013 | NR | RCT | schizophrenia or related psychotic disorders | NR; likely any APP | AP plus placebo or AP monotherapy | HbA1C, LDL, total cholesterol | Cochrane Risk of bias tool: results NR | Yes | Add-on aripiprazole compared to monotherapy led to l better HbA1C control, and better lipid profile. |
| Lerner 2004 (31) | 29 | 2003 | Both | All | Treatment-resistant t schizophrenic/schizoaffective patients on combinations atypical antipsychotics | Typical AP + Atypical AP | AP | AE | NR | No | No synthesis; No effect reported for metabolic outcomes. |
| Srisurapanont 2015 (28) | 5 | July, 2014 | NR | RCT | Schizophrenia patients with unsatisfactory response to clozapine | Aripiprazole + clozapine | Clozapine alone (AP) | AE (LDL) | Cochrane Risk of bias tool: 1 trial at low risk in all domains | Yes | LDL reduction effects favoured APP with aripiprazole addition compared to monotherapy. |
| Gallego 2012 (33) | 16 | NR | NR | All | NR | APP in general; specific APP combinations | NR | AE (glucose and lipid metabolism effect/metabolic syndrome)(not defined) | NR | No | No synthesis; expert opinion presented: APP carries an increased side effect burden compared to monotherapy; Aripiprazole augmentation was associated with a decrease in dyslipidaemia. |
| Lochmann van Bennekom 2013 (30) | 46 | April 2012 | NR | RCT; SR | Schizophrenia | APP | NR | AE | NR | No | No synthesis; no effect on metabolic outcomes. |
| Correll 2013 (34) | 8 | NR | NR | RCT | schizophrenia | APP | Placebo | glucose and lipid metabolism; cardio metabolic outcomes (not defined) | NR | Yes | Aripiprazole + clozapine/olanzapine led to: Significant reduction in total and LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, but not in HDL cholesterol or glucose. No significant cardio metabolic effects were found with risperidone/fluphenazine + clozapine, aripiprazole + quetiapine/risperidone, or aripiprazole + haloperidol. |
Quality of included reviews.
| Review ID AMSTAR Questions | Galling et al. 2016 (32) | Young et al. 2015 (25) | Tranulis et al. 2008 (26) | Tracy et al. 2013 (27) | Anonymous 2012 | Zheng et al. 2016 (24) | Mizuno et al. 2014 (29) | Lerner et al. 2004 (31) | Srisurapanont et al. 2015 (28) | Gallego et al. 2012 (33) | Lochmann van Bennekom et al. 2013 (30) | Correll et al. 2013 (34) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Was an ‘a priori’ design provided? | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | U | N | N | U |
| Was there duplicate study selection and data extraction? | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | U |
| Was a comprehensive literature search performed? | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | U |
| Was the status of publication (i.e. grey literature) used as an inclusion criterion? | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | U |
| Was a list of studies (included and excluded) provided? | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | U |
| Were the characteristics of the included studies provided? | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | U |
| Was the scientific quality of the included studies assessed and documented? | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | U | N | Y | N | N | U |
| Was the scientific quality of the included studies used appropriately in formulating conclusions? | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | U |
| Were the methods used to combine the findings of studies appropriate? | Y | N | N/A | N/A | Y | Y | Y | N/A | Y | N/A | N/A | U |
| Was the likelihood of publication bias assessed? | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | U |
| Was the conflict of interest included? | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | U |
Metabolic syndrome.
| Review ID | Outcome measure | Findings reported | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic syndrome | |||
| Gallego 2012 (33) | Metabolic syndrome | No synthesis or conclusion reported for this outcome | Not applicable (comparison not specified) |
| Young 2015 (25) | Proportion with Metabolic syndrome in APP users | No synthesis or data reported | They report that there is an association between metabolic syndrome and APP but no data reported. |
| Lipid profile outcomes | |||
| Galling 2016 (32) | Mean Total cholesterol mg/dl | SMD −0.27 (95%CI -0.43, −0.10) | APP was associated with lower total and LDL cholesterol compared to monotherapy |
| Mean LDL mg/dl | SMD −0.28 (95%CI -0.45, −0.11) | ||
| Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health 2012 (35) | Mean Total cholesterol | Total cholesterol statistically significantly lower with Clozapine +AP | Adding a second antipsychotic to clozapine was associated with lower total and LDL cholesterol compared to monotherapy with clozapine. |
| Mean LDL | LDL statistically significantly lower with Clozapine +AP | ||
| Tracy, 2013 (27) | NR | Aripiprazole co-treatment reregulates lipid profiles | APP including aripiprazole is associated with good lipid profile (comparison not specified) |
| Srisurapanont, 2015 (28) | Mean LDL mg/dl | MD −11.06 (95%CI -18.25, −3.87) | Aripiprazole + clozapine APP was associated with lower total and LDL cholesterol compared to monotherapy with clozapine |
| Mizuno, 2014 (29) | Mean Total cholesterol mg/dl | MD −12.81 (95%CI -19.35, −6.27) | |
| Mean LDL mg/dl | MD − 11.69 (95% CI -19.12, −4.26 | ||
| Gallego, 2012 (33) | NR | Aripiprazole augmentation was associated with a decrease in dyslipidaemia | APP with aripiprazole is associated with good lipid profile (comparison not specified) |
| Correll, 2013 (34) | Mean Total cholesterol | SMD −0.4 (95% CI -0.7,-0.2) | APP with aripiprazole was associated with lower triglycerides, and total and LDL cholesterol but not HDL cholesterol, compared to clozapine or olanzapine monotherapy |
| Mean LDL | SMD −0.3 (CI -0.6,-0.1) | ||
| Mean triglycerides | SMD −0.4 (CI -0.7,-0.0) | ||
| HDL level | Mean NR; p = 0.95 | ||
| Glucose profile outcomes | |||
| Mizuno, 2014 (29) | Mean HbA1C | MD −0.65 (95%CI -1.25, −0.06) | APP with aripiprazole is associated with lower HbA1C levels than AP monotherapy |
| Correll, 2013 (34) | Decrease in glucose levels | Mean NR; p = 0.41 | APP with aripiprazole was associated with no significant change in glucose levels compared to clozapine or olanzapine monotherapy |
| Gallego, 2012 (33) | NR | No synthesis or data reported. | APP has been associated with Increased diabetes |
| Hypertension | |||
| Galling 2016 (32) | Hypertension (not defined) | SMD/RR (not defined): 0.97, 95%CI 0.32 to 2.98, p = 0.97 | No conclusions drawn. Data indicate no difference between AP monotherapy and APP with D2 antagonists |
Hyperlipidaemias.
Diabetes/ glucose metabolism disorder.
Hypertension.
Certainty of evidence.
| GRADE assessment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | No of reviews | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | GRADE Quality rating |
| Metabolic syndrome | 2 | Seriousa | Seriousb | Seriousb | Seriousb | Publication bias strongly suspectedc | ⊕◯◯◯ VERY LOW |
| Lipid disorder | 8 | Seriousa | Not serious | Seriousd | Seriouse | Publication bias strongly suspectedf | ⊕◯◯◯ VERY LOW |
| Diabetes | 3 | Seriousa | Seriousg | Seriousd | Seriouse | Publication bias strongly suspected strong associationh | ⊕◯◯◯ VERY LOW |
| Hypertension | 1 | Seriousa | Not serious | Not serious | Seriouse | Publication bias strongly suspectedi | ⊕◯◯◯ VERY LOW |
Discussion
Limitations.
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

