Pharmacotherapy for Anxiety Disorders: From First-Line Options to Treatment Resistance
Abstract
| Medication (brand name) | Starting dosage (mg/day) | Target dose range (mg) | Anxiety disorder FDA indications | Specific notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSRIs | ||||
| Escitalopram (Lexapro) | 5–10 | 10–30 | Generalized anxiety disorder | May prolong QT interval similarly to citalopram |
| Sertraline (Zoloft) | 25 | 50–200 | Panic disorder, social anxiety disorder | |
| Citalopram (Celexa) | 10 | 20–40 | None | FDA warning for QT prolongation at doses>40 mg/day; FDA recommended dose limit 20 mg/day in older adults |
| Fluoxetine (Prozac) | 10 | 20–80 | Panic disorder | Very long elimination half life; CYP2D6 strong inhibitor |
| Paroxetine (Paxil) | 10 | 20–60 | Panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder | Anticholinergic and antihistaminergic side effects; strong CYP2D6 inhibitor; difficult discontinuation, taper slowly |
| Paroxetine CR (Paxil CR) | 12.5 | 25–75 | Panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder | Same as paroxetine |
| Fluvoxamine (Luvox) | 25 | 100–300 | CYP1A2 strong inhibitor; inhibits own metabolism; increases serum levels of clozapine, caffeine | |
| SNRIs | ||||
| Venlafaxine XR (Effexor XR) | 37.5 | 75–300 | Panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder | Monitor BP for patients at doses≥225mg/day; difficult discontinuation, taper slowly |
| Duloxetine (Cymbalta) | 20 | 60–120 | Generalized anxiety disorder | FDA-approved for fibromyalgia and chronic pain |
| Milnacipran (Savella) | 25 BID | 50 BID | FDA-approved for fibromyalgia; may be useful for panic disorder | |
| Novel serotonin-modulating antidepressants | ||||
| Vilazodone (Viibryd) | 10 | 20–40 | Mechanism is SSRI+5-HT1A partial agonist (like SSRI+buspirone) | |
| Vortioxetine (Trintellix) | 5 | 5–20 | Improves cognitive processing speed | |
| TCAs | ||||
| Imipramine (Tofranil) | 10 | 100–300 | Target serum levels 110–140 ng/ml | |
| Clomipramine (Anafranil) | 10 | 50–250 | Strongest evidence for panic disorder; consider in comorbid refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder | |
| Despiramine (Norpramin) | 10 | 100–300 | Consider in comorbid attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder | |
| MAOIs | ||||
| Phenelzine (Nardil) | 15 | 60–90 divided BID–TID | Low-tyramine diet; wash out prior antidepressant 5 half lives | |
| Tranylcypromine (Parnate) | 10 | 30–60 divided BID | See above | |
| Other antidepressants | ||||
| Bupropion (Wellbutrin) | 100 SR; 150 XL | 150 SR BID; 300 XL daily | Lowers seizure threshold; no sexual side effects | |
| Mirtazapine (Remeron) | 7.5–15 QHS | 15–30 QHS | May cause significant weight gain | |
| Nefazodone (Serzone) | 50 BID | 200–600 divided BID | Rare liver toxicity, can be fatal | |
| Trazodone (Desyrel) | 50 QHS | 200–400 divided BID | Metabolite MCPP can cause agitation | |
| Beta blockers (for performance-only social anxiety disorder) | ||||
| Propranolol (Inderal) | 10 PRN | 10–40 PRN | Test dose before performance situation; monitor BP, HR | |
| Atenolol (Tenormin) | 25 PRN | 25 | Test dose before performance situation; monitor BP, HR | |
| Azapirones | ||||
| Buspirone (Buspar) | 5 BID–TID | 10–20 BID–TID | Generalized anxiety disorder | No efficacy as monotherapy except in generalized anxiety disorder |
| Antihistamines | ||||
| Hydroxyzine (Vistaril, Atarax) | 25 QHS | 12.5–50 BID–TID | Evidence for efficacy in generalized anxiety disorder at total daily dose of 50 mg | |
| Benzodiazepines | ||||
| Lorazepam (Ativan) | 0.5 QD–TID | 0.5–2 QD–TID | Anxiety disorders | Not reliant on CYP450-mediated hepatic metabolism |
| Clonazepam (Klonopin) | 0.25–0.5 BID | 0.5–1 BID (maximum 4 daily) | Panic disorder | No proven increased efficacy advantage but increased side effects at doses>2mg/day |
| Alprazolam (Xanax) | 0.25 TID–QID | 2–6 mg divided TID–QID | Anxiety disorders | Prone to rebound anxiety; most misuse liability |
| Alprazolam XR | 0.5–1 | 2–6 daily or divided BID | Panic disorder | Less risk of rebound anxiety; slow onset |
| Diazepam (Valium) | 2–5 | 40 divided BID–QID | Anxiety | Accumulates active metabolites with very long half life |
| Anticonvulsants, including gabapentinoids | ||||
| Gabapentin (Neurontin) | 100–300 QHS | 900–3,600 divided TID | Best evidence for social anxiety disorder; likely requires near-maximal doses | |
| Pregabalin (Lyrica) | 75–150 QHS | 300–600 divided BID | Social anxiety disorder requires higher doses (450–600) | |
| Valproic acid (Depakote) | 250 QHS | 500–2,500 daily or divided BID | No target therapeutic serum level; requires periodic monitoring of CBC, LFTs, and drug levels | |
| Second-generation antipsychotics | ||||
| Quetiapine (Seroquel) | 25 QHS | 50–150 QHS | Mostly studied in XR formulation | |
| Risperidone (Risperdal) | 0.25 daily | 0.25–1 daily | Best evidence for panic disorder | |
| Olanzapine (Zyprexa) | 2.5 QHS | 5–10 QHS | Very high risk of metabolic adverse effect | |
| Aripiprazole (Abilify) | 2–2.5 daily | 2–15 mg daily | Less likely to cause metabolic effects |
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Review of Specific Agents and Their Efficacy and Tolerability in Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs).
Buspirone.
Anticonvulsants.
Benzodiazepines (BZDs).
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
Miscellaneous antidepressants.
Antihistamines.
Neuroleptics.
Rational Pharmacologic Approach to Generalized Anxiety Disorder
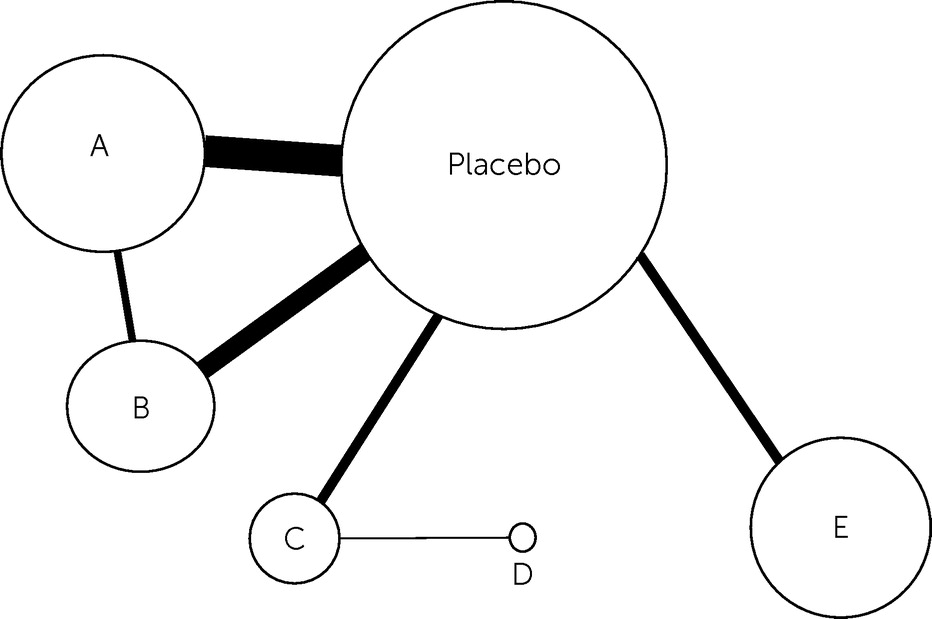
Panic Disorder
Review of Specific Agents and Their Efficacy and Tolerability in Treatment of Panic Disorder
SRIs.
BZDs.
TCAs.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
Other antidepressants.
Anticonvulsants.
Second-generation antipsychotics.
Rational Pharmacologic Approach to Panic Disorder
Social Anxiety Disorder
Review of Specific Agents and Their Efficacy and Tolerability in Treatment of Social Anxiety Disorder
SRIs.
Beta-adrenergic blockers.
BZDs.
Anticonvulsants.
MAOIs.
Miscellaneous medications: other antidepressants, buspirone, and neuroleptics.
Rational Pharmacologic Approach to Social Anxiety Disorder
Conclusions and Future Directions
Footnote
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

