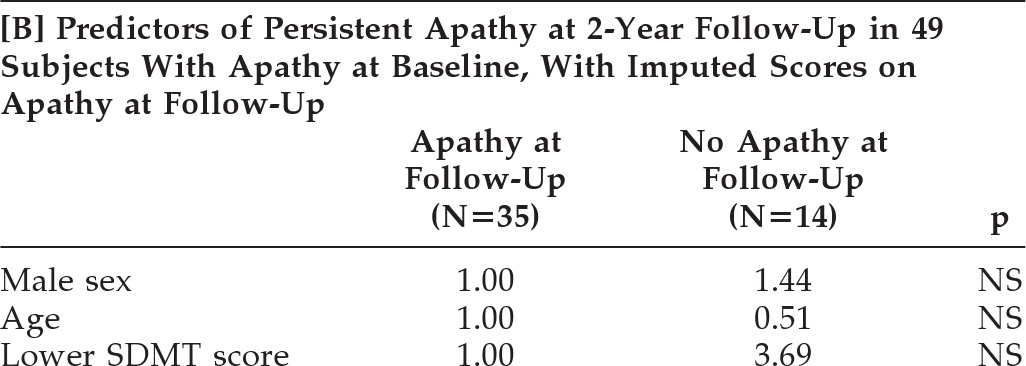Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant, neurodegenerative disorder caused by an expanded trinucleotide C-A-G repeat on the Htt gene on Chromosome 4. Clinical features include motor, neuropsychiatric, and cognitive symptoms. Neuropsychiatric and cognitive symptoms often precede the motor symptoms of HD.
1,2 Particularly, the presence of psychopathology has an important negative impact on daily functioning and quality of life for patients and caregivers, which also increases the risk of institutionalization.
3,4Apathy is a common neuropsychiatric symptom in neurodegenerative disorders such as HD, Parkinson's disease (PD), and Alzheimer's disease (AD). It is defined as a disorder of motivation, with diminished goal-directed behavior, cognition, and emotion.
5–7 Reported prevalences of apathy in HD range from 34%–76% depending on the disease stages examined and assessment methods used.
8 Prevalence and severity of apathy in HD increase with disease progression.
9Cross-sectional studies in HD have found a correlation between apathy and cognitive impairment as well as with functional decline.
9,10 Furthermore, we earlier demonstrated that in HD mutation carriers, apathy was cross-sectionally associated with male sex, presence of depression, and use of psychotropic medication.
11 However, longitudinal studies that may identify temporal relationships between apathy and possible predictors for apathy in HD are lacking.
12 The present study investigates the incidence, course, and predictors of apathy in HD mutation carriers with and without apathy at baseline.
METHOD
Subjects
In this longitudinal study, subjects were recruited between May 2004 and August 2006. A total of 343 genetically tested subjects at initial 50% risk of HD were contacted via the departments of Neurology and Clinical Genetics of the Leiden University Medical Centre and the long-term care facility, Overduin (the Netherlands). Of these, 192 subjects were willing and able to participate in the study. Subjects with a neurological condition other than HD or with juvenile HD were excluded. An additional 18 subjects were recruited through other means (such as the Dutch HD Association). In total, 2 subjects were lost to follow-up; the remaining 208 subjects were divided into three groups on the basis of 1) their genetic test result, which was obtained from their medical records; and 2) on their Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS) confidence level (CL) into premotor-manifest mutation carriers (N=55) and HD patients (N=97). Gene-negative subjects (N=56) were excluded from further analysis.
The present study includes 152 HD mutation carriers, comprising 55 premotor-manifest subjects and 97 motor-symptomatic HD patients. Two years after their initial visit, all subjects were approached for a second measurement. Of the 152 baseline subjects, 3 were deceased, and 27 subjects refused to participate or were excluded because of severe dysarthria; this left 122 subjects for the present analysis. The study was approved by the Medical Ethical Committee of the LUMC, and all subjects gave written informed consent.
Instruments
Sociodemographic and Clinical Characteristics
Information on sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of mutation carriers was collected in a standardized manner. Use of medication was categorized into use of antidepressants, neuroleptics, benzodiazepines, and other. Neurological examination was performed according to the motor section of the Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS–M) by a neurologist with extensive experience in HD. Global functioning was assessed with the Total Functional Capacity (TFC) scale of the UHDRS. The estimated duration of disease was calculated with the Vassos formula (ln[age at onset] = 6.18–0.054 [C-A-G repeats]), in accordance with earlier research.
13Assessment of Apathy
Apathy was assessed with the semistructured Apathy Scale (AS).
14 The AS is a modified version of the Apathy Evaluation Scale (AES);
5 it consists of 14 questions, measuring different features of apathy in the 2 weeks before the interview. Since patients with apathy may lack insight into their behavior, we also included caregivers' information and judgment of the interviewer. The total score of the AS ranges from 0 to 42 points, with higher scores indicating more apathy. The AS has shown good interrater reliability and good test–retest reliability, as well as high internal consistency in patients with PD, with a score of ≥14 points being indicative of the presence of apathy.
15 Therefore, in the present study, a total score ≥14 points was used to characterize subjects as apathetic, and those scoring below this cutoff score as nonapathetic.
11,15The Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI) was used to assess Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-IV diagnosis of depressive disorder (Major Depressive Disorder [MDD] or dysthymia), using a computerized questionnaire, Version 2.1.
16 The CIDI was not administered in subjects with a Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE) score <18 points, since it cannot be reliably administered to patients with severe cognitive dysfunction.
Neuropsychological Assessment
The MMSE, Symbol Digit Modalities Test (SDMT), Verbal Fluency Test (VFT) and Stroop Color–Word Test were administered to assess cognitive functioning. The MMSE was used to assess global cognitive functioning.
17 The SDMT examines attention, working memory, and visuoverbal substitution speed.
18 The VFT is sensitive to frontal executive dysfunction and subtle degrees of semantic memory impairment.
19 The Stroop Color–Word Test was used to measure a person's sustained attention in three conditions: color-naming, word-reading, and naming the color of the ink of an incongruous color name (interference).
20Statistical Analysis
The SPSS 17.0 for Windows package was used for the statistical analysis. Data are presented as N (%), or mean (standard deviation; [SD]) when appropriate. Because of substantial withdrawal of participants between the two measurements, selection bias could not be excluded. Therefore, dropouts at the second wave were compared with the participants for baseline characteristics. Because of non-normal distribution of number of C-A-G repeats, TFC score, UHDRS Motor score, AS score, and MMSE scores, these data were dichotomized in order to reduce potential bias caused by outliers (the cutoff scores of the variables are shown in the legend of
Table 1). A composite variable for executive cognitive functioning (ExCog) was computed because of a strong collinearity between the SDMT, VFT, and Stroop Color–Word Test (r >0.80). The variable was computed by averaging the standard
z-scores of the five tests (i.e., subtracting the mean from an individual raw score and then dividing the difference by the SD).
In subjects without apathy at baseline, univariate and multivariate logistic-regression analyses were performed, with the presence or absence of incident apathy as the dependent variable, and baseline characteristics as the independent variables, to determine the predictive variables. In subjects with apathy at baseline, univariate and multivariate logistic-regression analyses were used to analyze potential predictors of persistent apathy at follow-up. Subsequently, we repeated all logistic-regression analyses, using the continuous independent variables to examine potential effects of dichotomization.
In both multivariate logistic-regression analyses, all variables from the univariate analysis with p <0.10 were entered, and the model was adjusted for sex and age. Diagnostic statistics were calculated with the Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness-of-fit tests (H&L). For these analyses, the independent variable ExCog was inverted in order to make results better interpretable; that is, the odds ratios (ORs) correspond to a decrease of 1 SD in ExCog. Also, in subjects with apathy at baseline, multivariate regression analysis was repeated after multiple imputations (5 times) for the 15 missing data of the dropouts, to account for potential selection bias (i.e., bias caused by attrition due to loss of participants who may have been more apathetic). Imputation of the missing variables was based on the distribution of the apathy score and cognitive variables at baseline.
RESULTS
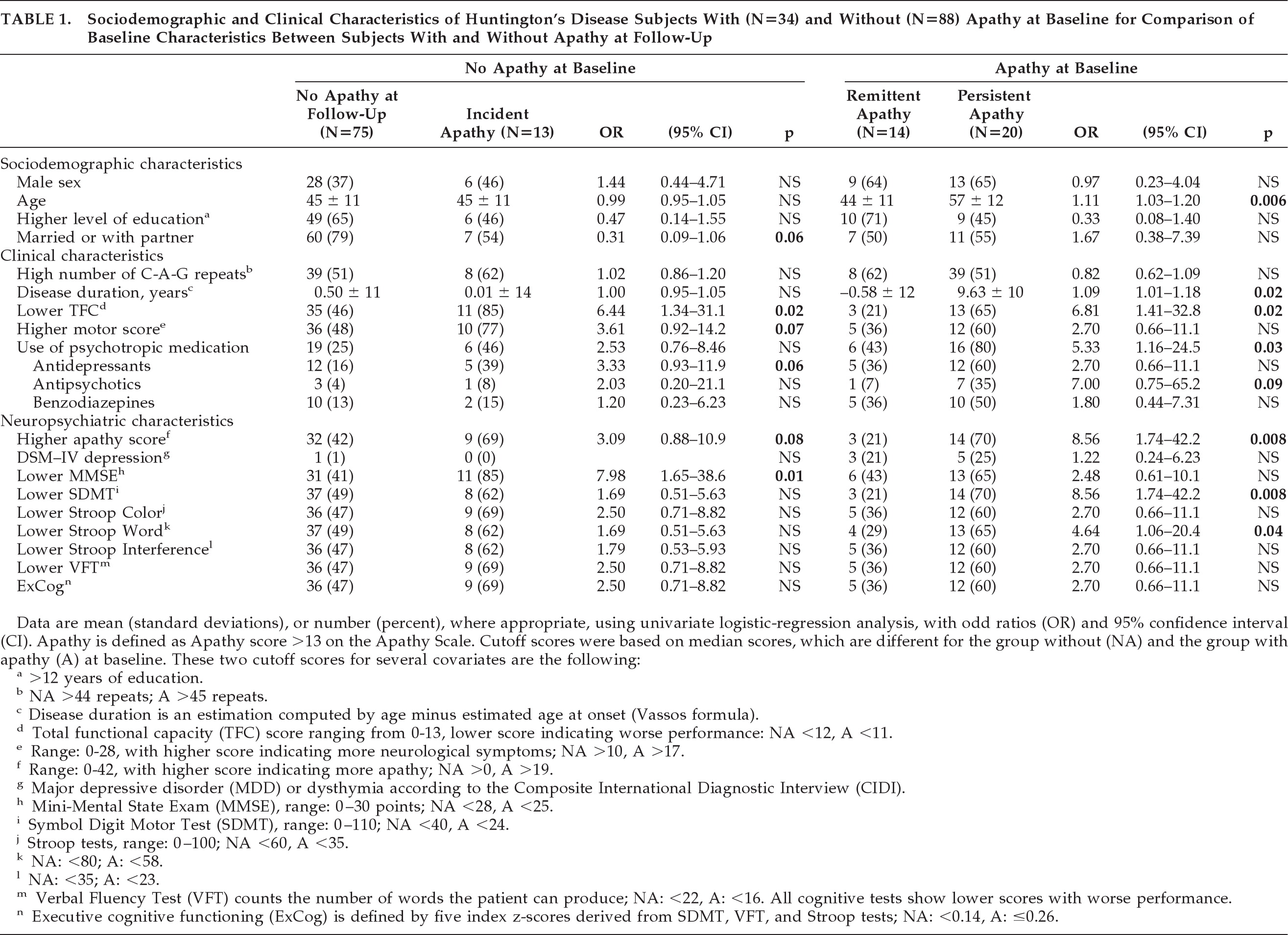
At baseline, the 88 HD subjects without apathy did not differ in their education level, marital status, number of C-A-G repeats, and estimated duration of disease from the 34 subjects with apathy. However, the apathetic subjects performed worse on all clinical and neuropsychiatric characteristics (data not shown).
At 2-year follow-up, 13 (14%) of the 88 subjects without apathy at baseline had developed apathy. Of the 34 subjects with apathy at baseline, 14 (41%) no longer met the criteria for apathy 2 years later, whereas 20 (59%) subjects remained apathetic.
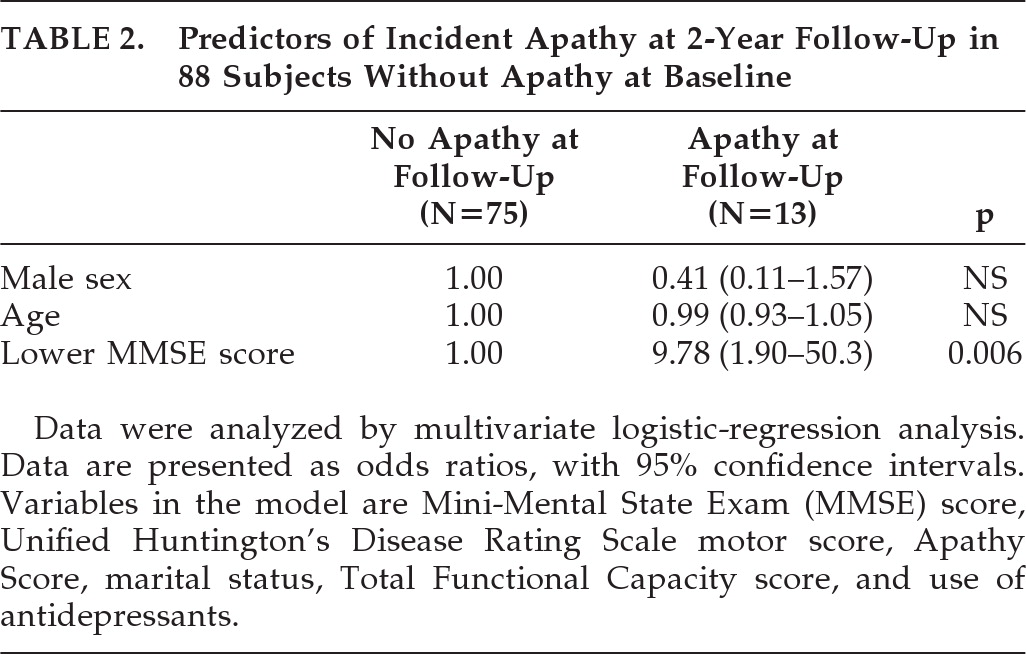
Table 1 shows that, of the 88 subjects without apathy at baseline, the 13 subjects with incident apathy differed significantly from the 75 subjects without apathy at follow-up in more often having a lower TFC score (OR: 6.44; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.34–31.1; p=0.02) and a lower MMSE score (OR: 7.98; 95% CI: 1.65–38.6; p=0.01). Using forward logistic regression, with adjustment for sex and age, a lower MMSE score at baseline remained the only predictor for incident apathy (OR: 9.78; 95% CI: 1.90–50.3; p=0.006; H&L test: 0.72;
Table 2). When we repeated this logistic-regression analysis with continuous UHDRS–M, TFC, and MMSE scores, the MMSE score remained the only independent predictor (OR per 1-point decrease in MMSE: 1.34; 95% CI: 1.09–1.65; p=0.006). The influence of a depressive disorder on apathy in subjects without apathy at baseline was not analyzed, since only one of the baseline subjects and none at follow-up had a depressive disorder.
Of the 34 subjects with apathy at baseline (
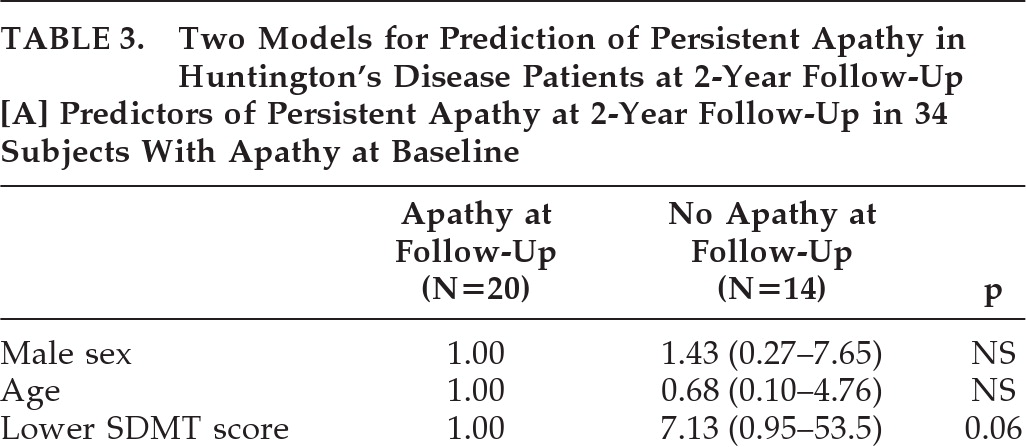
Table 1), the 20 subjects with persistent apathy at follow-up were older (OR: 1.11; 95%CI: 1.03–1.20; p=0.006), had a longer disease duration (OR: 1.09; 95%CI: 1.01–1.18; p=0.02), and showed a significantly decreased TFC score (OR: 6.81; 95% CI: 1.41–32.8; p=0.02), SDMT score (OR: 8.56, 95%CI: 1.74–42.2; p=0.008) and Stroop Word Test score (OR: 4.64; 95%CI: 1.06–20.4; p=0.04) at baseline, versus subjects with remittent apathy. No difference was found in the number of patients with depression between subjects with persistent and remittent apathy (OR: 1.22; 95% CI: 0.24–6.23; p=0.81), although all three subjects with reversible apathy and depression at baseline no longer had depression at follow-up. Also, no incident depression occurred in this group. In contrast, in the 20 subjects with persistent apathy, 5 subjects had depression at baseline, and 4 subjects had depression at follow-up, of whom 3 had persistent depression. In the multivariate logistic-regression analysis, age was additionally dichotomized, to put a similar statistical weight on all included variables in the analysis. By forward logistic-regression analysis, a lower SDMT score at baseline was the only independent predictor of persistent apathy at 2-year follow-up (OR: 7.13; 95% CI: 0.95–53.5; p=0.06; H&L test: 0.51;
Table 3A), but with a very wide CI. When we repeated this logistic-regression analysis with continuous age, SDMT, and TFC scores, the SDMT score was not a predictor of persistent apathy at 2 years (OR per 10-point decrease in SDMT: 1.21; 95% CI: 0.77–1.89; p=0.41). Similarly, after imputation of apathy scores of the 15 dropouts, a lower SDMT score did not remain a significant predictor for persistence of apathy (OR: 3.69; p=0.21;
Table 3B).
For all 122 mutation carriers,
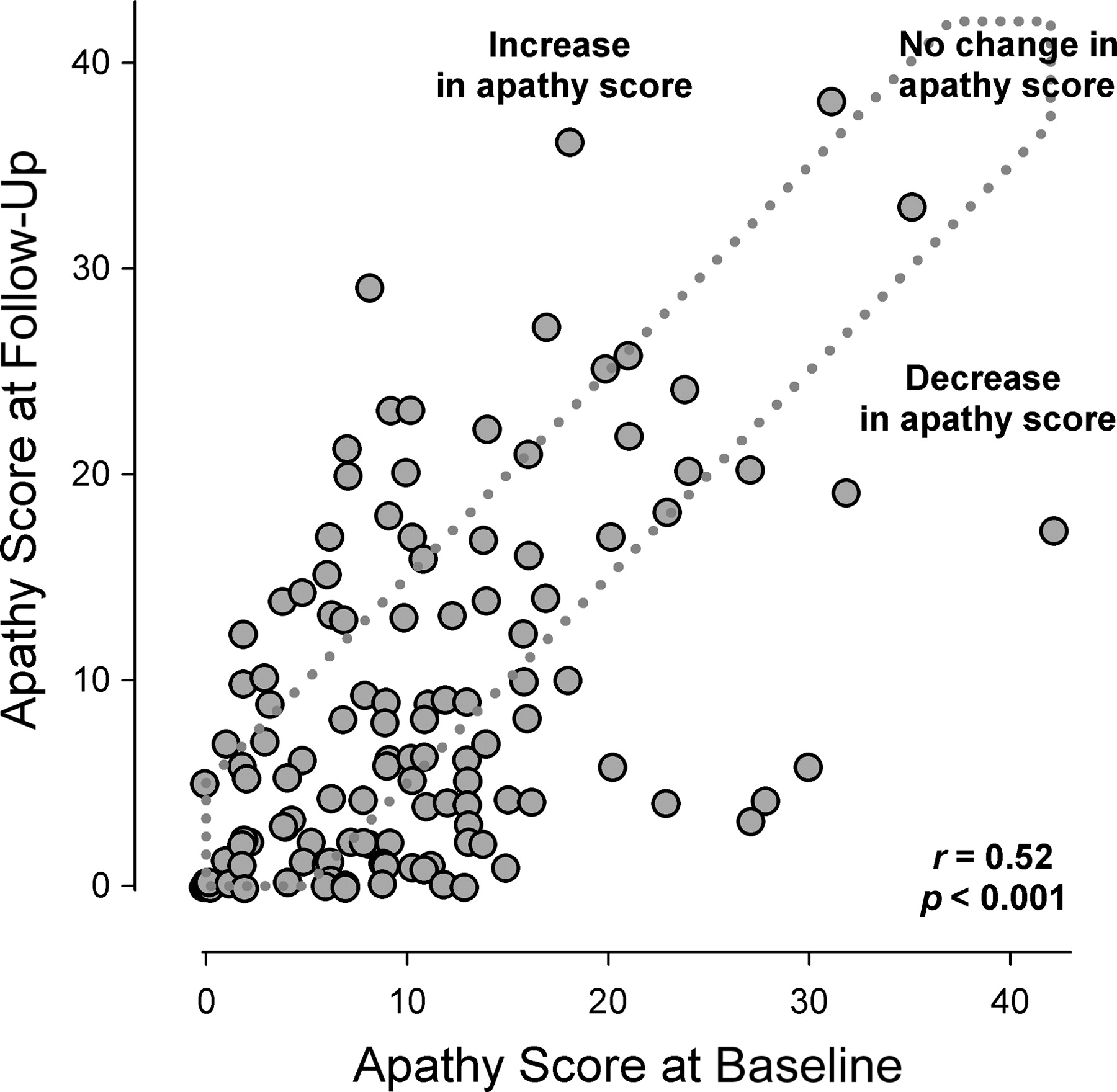
Figure 1 presents the AS scores at baseline versus those at follow-up for the groups with an increasing, equal, and decreasing AS score over time.
To consider possible attrition bias, dropouts with and without apathy at baseline were compared with the HD subjects with and without apathy who had had two assessments, respectively. Of the 27 dropouts, 12 (44%) had apathy at baseline. Dropouts with apathy had lower motor and cognitive functioning as well as higher apathy scores at baseline, as compared with the included 34 apathetic subjects (all p≤0.02). In contrast, dropouts without apathy showed no significant differences from the remaining 88 subjects without apathy at baseline, except for their AS score, which was slightly higher in the dropout group (p=0.05; data not shown).
DISCUSSION
The present study shows that incident apathy occurred in 13 (14%) of the 88 subjects without apathy at baseline. At the same time, 14 (41%) of the 34 subjects with apathy at baseline showed remittance of apathy at 2-year follow-up. Subjects with incident apathy had decreased TFC and MMSE scores at baseline, as compared with subjects without apathy at follow-up. In the subjects with apathy at baseline, those with persistent apathy were older and had a longer disease duration. Furthermore, subjects with persistent apathy had decreased TFC, SDMT, and Stroop Word Test scores, and also a higher AS score at baseline, as compared with subjects with remittent apathy at follow-up. Decreased MMSE score at baseline was the only independent predictor for incident apathy, whereas a lower score on the SDMT predicted persistence of apathy. However, the SDMT score did not remain significant when the analysis was repeated with the continuous variables.
The incidence rate of apathy in HD at 2-year follow-up is 14%, which is relatively low, compared with incidence rates reported in other neurodegenerative disorders. For example, in a study on patients with Parkinson's disease, incidence of apathy according to the Neuropsychiatric Inventory over a 4-year follow-up was 57% (39/68 nonapathetic subjects at baseline).
12 An explanation for this high incidence may be that many patients in the latter study were in a more advanced disease stage, when apathy occurs more frequently. Also, many PD patients with persistent or incident apathy had a depressive disorder at baseline (6/11 [55%] and 5/39 [13%], respectively),
12 which may also have caused symptoms of apathy. In Alzheimer's disease, the incidence of apathy during 1 to 4 years of follow-up was 23%, according to the Lille Apathy Rating Scale (41/179 subjects).
21 In this latter study, however, the follow-up visit was not at a fixed time, which hinders determination of the incidence rate and comparison with our study. Another explanation for the lower incidence rate in our study may be attrition bias due to differential dropout of apathetic subjects with worse motor and cognitive functioning, as well as higher AS scores at baseline.
Our results show that global cognitive dysfunction precedes the onset of apathy. Although the association has scarcely been studied in patients with HD, these findings are in line with other studies investigating patients with PD and AD.
12,21–24 Patients with mild cognitive impairment and AD or PD with apathy at baseline were at increased risk for accelerated cognitive decline.
21,24 In patients with PD, poor cognitive functioning and dementia at baseline predicted onset of apathy 1.5 to 4 years later.
12 This study therefore showed results similar to our study, as we found that cognitive dysfunction predicted the occurrence of apathy as well in patients with HD. The previous studies, combined with our findings, point to a strong link between apathy and cognitive impairment. Future studies should try to elucidate the underlying causal pathways.
Remarkably, in the present study, 14 subjects recovered from apathy. A longitudinal study on apathetic patients with AD found a similar phenomenon, but no further information about those AD patients who recovered from apathy is available because they were excluded from further analyses.
21 Since we earlier showed that apathy is cross-sectionally associated with the presence of depression and use of psychotropics,
11 remission from apathy might be related to recovery from a depressive disorder and/or discontinuation of psychotropic medication between the two measurement points. Remission from apathy was predicted by higher scores on the SDMT, indicating that poor cognitive functioning may decrease the chance of remission from apathy in HD. There may be a substantial construct overlap of depression and apathy, which makes it difficult to differentiate between these two neuropsychiatric disorders. This is supported by the data in the present study, where the subjects with reversible apathy and depression at baseline recovered from both disorders at follow-up. Still, these findings might be of clinical importance because this suggests that apathy is reversible, being a symptom of depression. Also, in the present study, the use of psychotropic medication (especially antipsychotics) was related to a lower chance of remission, but not in the multivariate analysis, possibly because of relatively low statistical power. It remains to be established whether psychotropic medication can be a cause or effect of apathy.
The strengths of this study are its prospective design, the relatively large group of HD mutation carriers, and the use of specific validated measurement tools in a standardized interview. Some limitations also need addressing. First, the cutoff score for the presence of apathy has been investigated in PD patients but not in HD patients. Also, a gold standard is lacking for the assessment of apathy, thereby hindering the validation of any apathy scale. Second, many of the subjects who were lost to follow-up had apathy at baseline. Similar to the increased chance of depressed participants dropping out of prospective studies,
25 apathetic HD patients were more likely to withdraw. This probably led to an underestimation of the occurrence of apathy, as well as persistent apathy, at follow-up. Because this attrition bias was probably larger in the analysis for predictors of persistent apathy, we did an additional analysis with multiple imputation of the missing AS scores at follow-up; this indeed supported the idea that the predictive value of a lower SDMT score could partly be ascribed to bias. Third, the CIDI might not be valid in assessing depression in HD, leading to an under-ascertainment of depression and, hence, underrecognition of depression as a major explanatory factor for reversible apathy. Fourth, the strongly skewed distributions of most of the independent variables necessitated the use of categorization, which limits our statistical power. Finally, effects of regression to the mean may have enlarged the changes in apathy found in our subjects, explaining part of the improvement and deterioration of apathy in HD patients.
26In conclusion, the results of the present study support the assumption that cognitive dysfunction contributes to the presence of apathy in HD. However, because apathy can be reversible, we recommend that HD patients with apathy undergo clinical evaluation for treatable causes of apathy, including the presence of depression and/or use of psychotropic medication.