Enrollment in preexisting condition insurance plans— the temporary insurance pool established under the new health reform law for those denied coverage in private plans due to preexisting conditions—has been considerably lower than expected, according to a report by the Government Accountability Office (GAO).
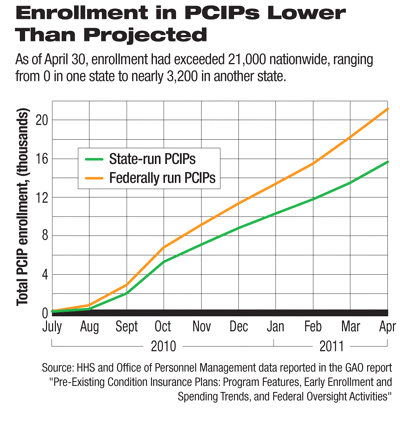
Though enrollment has increased steadily since the program's inception, total enrollment was just 21,454 as of April; initial projections for total enrollment were between 200,000 and 300,000 people, according to the GAO report, "Preexisting Condition Insurance Plans: Program Features, Early Enrollment, and Spending Trends and Federal Oversight Activities."
The GAO noted that five reasons may account for the lower-than-expected enrollment: the statutory requirement that applicants be uninsured for six months prior to applying, affordability concerns, a lack of awareness about the program, the processes used for determining eligibility, and existing state laws or state-supported health insurance programs (see
Reasons for Lower-Than-Expected Enrollment in PCIPs).
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act appropriated $5 billion to create a temporary pool—known as the Preexisting Condition Insurance Plan (PCIP) program—to provide access to insurance for such individuals until new protections take effect in 2014. Twenty-seven states opted to run their own PCIPs, while 23 states and the District of Columbia chose to let the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) run the PCIPs for their residents.
Enrollment in state-run programs ranged from none in Vermont to nearly 3,200 in Pennsylvania. As of April 30, actual enrollment totaled about 15,800 in the state-run PCIPs and about 5,700 in the federally run PCIPs. This represents 5.6 people per 10,000 uninsured living in the 27 state-run PCIP states and 2.5 per 10,000 uninsured living in the 24 federally run PCIP states.
The other main finding of the GAO report is that spending on the program has been significantly lower than expected. State-run PCIPs collectively spent about $78 million as of March 31, and HHS spent almost $26 million for the federally run PCIPs and about $1.6 million for its own administrative expenses, which together represented about 2 percent of the total $5 billion appropriation.
State- and federally run PCIPs generally had similar cost-sharing arrangements, although other features varied. Most states had annual deductibles of between $1,000 and $2,999, with out-of-pocket limits at or near $5,950. Coverage limits were common but varied, both in terms of the benefits affected and the extent of the limits. Monthly premiums ranged considerably—from $240 in Utah to $1,048 in Alaska for a 50-year-old enrollee—and were generally lower in the federally run PCIPs.