Depressive disorders are associated with low levels of omega-3 plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids and elevated omega-6/omega-3 ratios
(1 –
5), while augmentation with omega-3 plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids is reportedly therapeutic
(6) . However, there is disagreement regarding a possible link between plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid status and suicidal behavior
(7 –
9) . In the present study, we sought to prospectively determine whether plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid status is related to suicide attempt.
METHOD
Adult subjects (N=33) seeking treatment for depression gave written informed consent, approved by our institutional review board, and met criteria for a major depressive episode. Axis I diagnoses were based on the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV. Subjects were excluded for neurological or medical disease or substance dependence and were off antidepressant medications for at least 14 days prior to baseline assessments. The 24-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the Beck Scale for Suicidal Ideation measured depression and suicidal thoughts. Lifetime aggression was assessed using the Brown-Goodwin Aggression History. A suicide-attempt history was also obtained. Baseline fasting plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid composition was analyzed using gas chromatography, and percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids were determined for docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5n-3), arachidonic acid (20:4n-6), and omega-6/omega-3 ratio. Subjects received naturalistic psychopharmacological inpatient (8 weeks) or outpatient (6 months) treatment from the research team, followed by community-based treatment. Research evaluations were performed at 3, 12, and 24 months by raters unaware of the subjects’ plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid status.
Demographic/clinical attributes at study entry were tested for associations with plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid levels using Student’s t test, Pearson’s r, or Spearman’s rho correlations. Plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid status and omega-6/omega-3 ratio were entered separately into Cox proportional regressions, with time to subsequent suicide attempt as outcome measure and variables correlated with plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid status as covariates. In additional, proportional hazards analyses, effects of plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid levels or omega-6/omega-3 ratio on suicide attempt status were adjusted for number of medications prescribed during the follow-up period as a measurement of treatment intensity. For subsequent attempters, only medications prescribed prior to the first attempt were considered. The effects of demographic/clinical attributes regarding time to suicide attempt were likewise analyzed individually, with proportional hazards modeling.
RESULTS
Three of the 33 subjects were lost to follow-up, 23 were nonattempters, and seven made at least one suicide attempt. Two attempts were fatal. Subjects had a mean age of 40.4 (SD=11.9) years, with 16.6 (SD=8.4) years of illness duration and 3.7 (SD=2.3) prior episodes of depression. On admission, most subjects had failed recent treatment. Our clinic has a reputation for suicide research and treatment of suicidal patients, attracting a high proportion of suicide attempters. Fifty-three percent of the present sample had a history of previous suicide attempt. Four subjects had bipolar depression. Among these four, two were subsequent attempters. Six attempters and 13 nonattempters had comorbid axis I diagnoses. Two attempters and eight nonattempters had comorbid cluster B diagnoses.
In separate Cox proportional hazards analyses of the effects of demographic/clinical variables on suicide attempt outcome, gender, body mass index, smoking status, income, history of aggression, and average number of medications were not predictors of subsequent suicide attempt. Younger age was a predictor of suicide attempt (hazard ratio=0.91, p=0.034), with trends for prior suicide-attempt history (hazard ratio=6.67, p=0.08) and baseline suicidal ideation as predictors (hazard ratio=1.11, p=0.064); p values were uncorrected for multiple comparisons in this exploratory study.
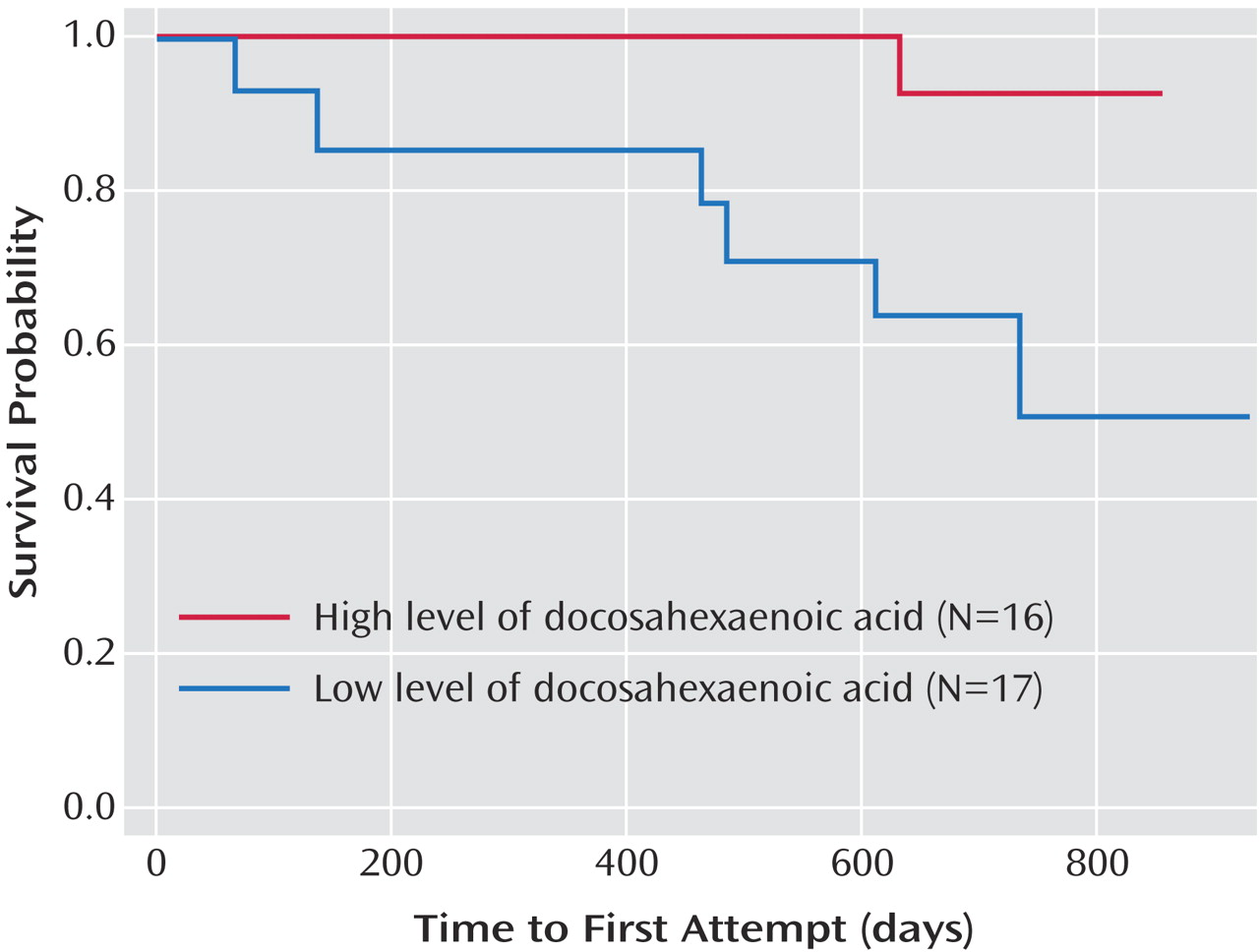
Lower docosahexaenoic acid percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids (
Figure 1 ) and higher omega-6/omega-3 ratio predicted subsequent suicide attempts (docosahexaenoic acid percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids: p=0.002, hazard ratio=0.29; omega-6/omega-3: p=0.008, hazard ratio=1.36). Of the clinical and demographic variables, only age and suicidal ideation had significant correlations with docosahexaenoic acid percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids (age: Pearson’s r=0.41, p=0.02; ideation: Spearman’s rho = –0.43, p=0.02). When entered into the survival analysis, these age and ideation effects lost significance and were removed from the model. The effects of docosahexaenoic acid percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids or omega-6/omega-3 ratio regarding time to suicide attempt were not altered by adjusting for the number of medications prescribed during the follow-up period. Neither arachidonic acid percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids nor eicosapentaenoic acid percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids predicted suicide attempts.
DISCUSSION
Our findings indicate that low docosahexaenoic acid percentages of total phospholipid fatty acids and elevated omega-6/omega-3 ratio predict suicidal behavior in major depression. Moreover, plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid status may mediate effects of age and suicidal ideation on the outcome of suicide attempt. One possible explanation for this is that plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid intake affects neurobiological factor(s) specific to depression. Plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid status has been implicated in the putative serotonin-mediated link between lower cholesterol and suicidality in humans and aggression in primates
(10,
11) . Low concentrations of cerebral spinal fluid serotonergic metabolite 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) are associated with suicide
(12), while cerebral spinal fluid 5-HIAA is positively correlated with long-chain plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid levels in normal subjects
(13) . Increased risk of suicide has also been linked to elevated cerebral spinal fluid corticotropin- releasing factor levels
(14), which have been associated with low plasma docosahexaenoic acid status
(15) . Thus, low omega-3 fatty acids may adversely impact serotonergic and corticotrophic function, resulting in greater vulnerability to suicide.
Strengths of this pilot study include a prospective design and no confound of medications on baseline fatty acid levels. The relatively high number of prior suicide attempters in the study population likely increased the chances of detecting an effect, although our results may not generalize to lower-risk populations. A limitation to the study is that it cannot be determined whether psychopathology affected dietary habits or vice versa. Future studies should include data regarding subjects’ diet.
These preliminary results suggest that reduction of suicide risk through increased intake of omega-3 fatty acids merits investigation in a placebo-controlled study.