It is commonly suggested that there has been an epidemic in depression in recent decades. Any prevalence increase could be artifactual, reflecting changes in attribution, definition, destigmatization, help seeking, or other factors. Alternatively, there may have been a real increase. Klerman and Weissman
(1) considered increased rates in Western societies and concluded that such changes could not be explained by changing diagnostic criteria, changing attitudes of health professionals and societies, reporting biases, differential mortality rates, or other obvious artifactual influences. For any true increase, numerous determinants could be proposed, including genetic factors, greater use of illicit drugs, and many social and environmental factors. In relation to the last, there has been considerable interest in a dietary contribution, particularly involving omega-3 fatty acids.
Omega-3 fatty acids are long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids found in various plant and marine life
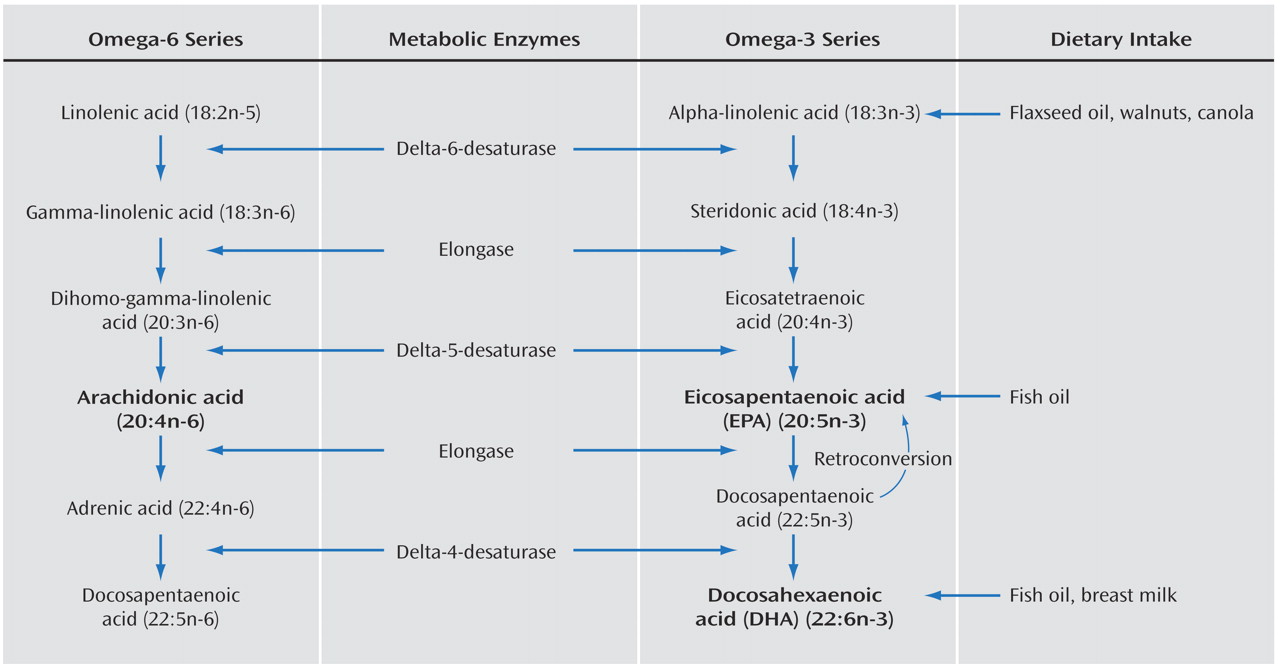
(2) . The marine-based omega-3 fatty acids primarily consist of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and appear to be highly biologically active. In contrast, those from plants (flaxseed, walnuts, and canola oil) are usually in the form of the parent omega-3 fatty acid, alpha-linolenic acid. Although dietary alpha-linolenic acid can be endogenously converted to EPA and DHA (see the metabolic pathways in
Figure 1 ), research suggests that this occurs inefficiently to only 10%–15%
(3) .
In the last 150 years, rapid expansion in Western populations has been associated with a change in diet, with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids from fish, wild game, and plants being replaced by saturated fats from domestic animals and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids from common vegetable oils (corn, safflower, and soybean) and other sources. These changes have resulted in a large increase in the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids in the general diet from 1:1 to more than 10:1
(4,
5) . This has resulted in a high proportion of the common omega-6 fatty acid arachidonic acid, rather than EPA, in the cell membranes of most tissues, leading in turn to a high proportion of inflammatory eicosanoids
(6) . As shown in
Figure 1, an increase in arachidonic acid also affects the production of EPA and DHA, owing to competition for metabolizing enzymes.
Such dietary changes in fatty acid intake have been held to have numerous pathological consequences. For example, epidemiological evidence from the U.S. Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial for 12,866 middle-aged men identified significant inverse relations between omega-3 levels and cardiovascular disease
(7) . In relation to depression, both Smith
(8) and Hibbeln and Salem
(9) suggested that the sharp rises in rates of depression and other neurological disorders in the 20th century are being fueled by increased consumption of vegetable oils rich in omega-6 fatty acids. Indirect support for that hypothesis emerges from data indicating high levels of inflammatory eicosanoids derived from arachidonic acid in both patients with unipolar depression and those with bipolar depression
(10) .
As epidemiological research
(11) has shown wide variation in the annual prevalence of major depression across countries, a dietary determinant has been considered; several epidemiological studies have examined possible links between fish consumption and mood disorders. The study results have been intriguing, and there have now been sufficient studies pursuing deficits in omega-3 fatty acids and treatment implications to encourage fine-focused etiological and treatment studies. As further evidence of the research domain’s importance, the National Institutes of Health conducted a workshop on the links between omega-3 fatty acids and psychiatric disorders in 1998
(12) . We now examine the possible contribution of omega-3 fatty acids to both the onset and treatment of mood disorders, by reviewing relevant studies.
Seafood Consumption and Community Rates of Mood Disorders
Depression
Hibbeln
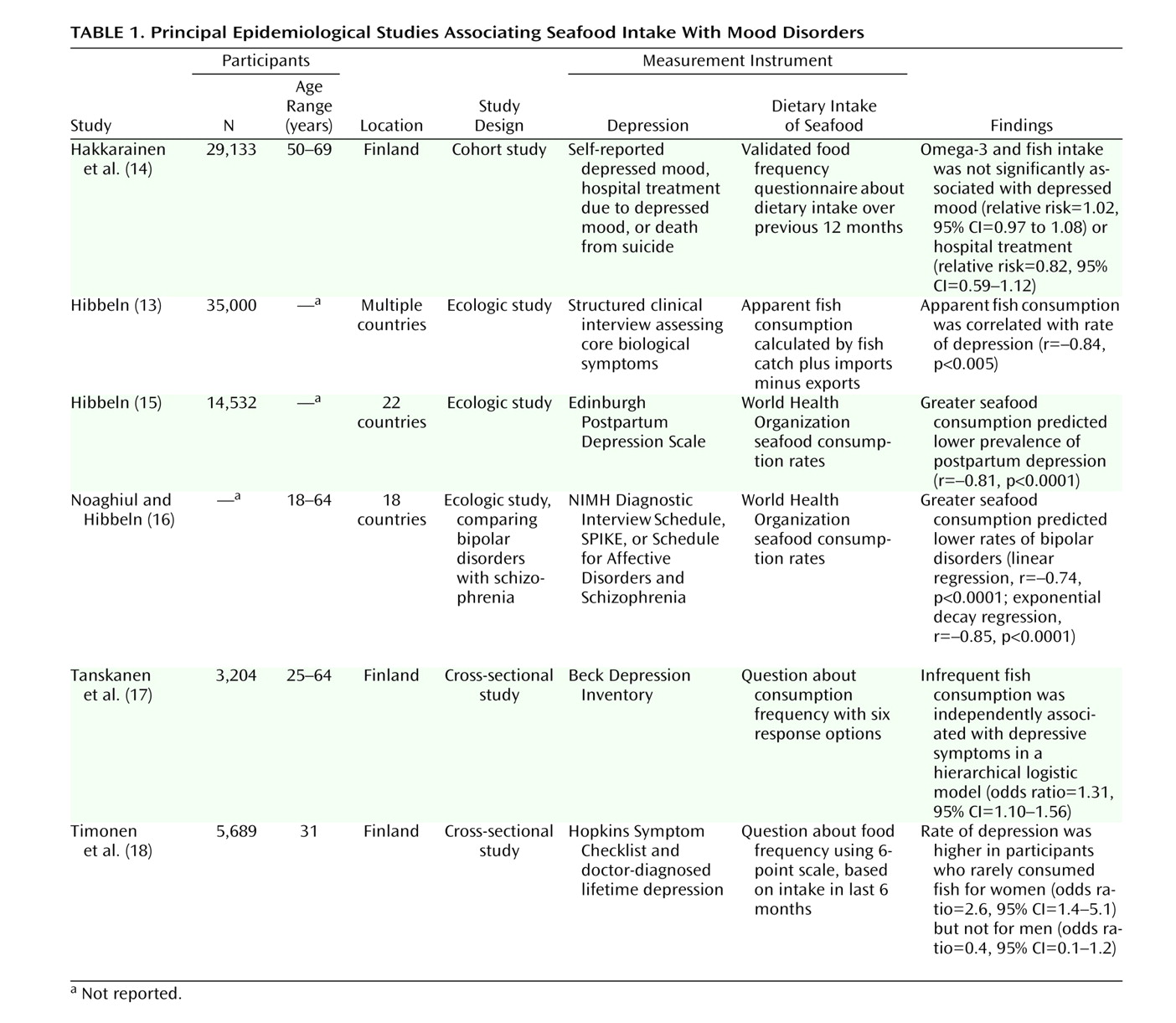
(13) reported a very strong negative correlation (r=–0.84) between fish consumption and major depression in a cross-national depression database. Several other studies (
Table 1 ) have provided indirect support for a link between seafood consumption and depression. For instance, the prevalence of seasonal affective disorder appears unexpectedly low in Iceland
(19) . The authors of that report found no difference between winter and summer scores for depression and anxiety for either sex in their sample, arguing against any seasonality effect, and they proposed that it might reflect some “unique features of the Icelandic population.” Cott and Hibbeln
(20) suggested that this could be the high consumption of fish (225 lb/person per year), as Japan (with a fish consumption of 147 lb/person per year) also had an unexpectedly low rate of seasonal affective disorder. Other countries, with average intakes of 50 to 70 lb, had much higher rates of seasonal affective disorder, despite receiving more winter sunlight. In support, McGrath-Hanna et al.
(21) showed that as the diet of circumpolar people changed from the traditional one, based largely on fish and fish-eating animals, to one of a largely Western nature, so rates of depression, seasonal affective disorder, anxiety, and suicide rose. Further, in a survey of 3,204 Finnish adults, Tanskanen et al.
(17) demonstrated that the likelihood of having depressive symptoms was significantly higher among infrequent fish consumers than among frequent consumers.
Negative studies have, however, also been reported. Hakkarainen et al.
(14) undertook a correlational study nested within a randomized, controlled cancer prevention trial of the antioxidants alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene in 29,133 men (ages 50 to 69 years) in Finland. Intake of fatty acids and fish consumption were calculated from a questionnaire about food use. Self-reported depressed mood was recorded three times annually, data on hospital treatments for major depression were derived from the National Hospital Discharge Register, and suicides were identified from death certificates. No significant association of fish consumption or intake of omega-3 fatty acids with any outcome variable was found. However, as only dietary intake was assessed and not actual levels of omega-3 fatty acids, it is difficult to know whether there was any mechanistic interference from the antioxidant supplementation. Further, the intake of EPA and DHA in this study was less than 0.5 g/day, most of the omega-3 fatty acid intake was alpha-linolenic acid, and as noted earlier, the conversion of alpha-linolenic acid to EPA and DHA is only 10%–15%. A further possible explanation for these negative findings may be the male-only cohort, since a recent prospective cohort study in Finland showed low fish consumption to be significantly associated with depression in women only
(18), possibly reflecting gender differences in neurotransmitter and phospholipid metabolism.
Bipolar Disorder
Noaghiul and Hibbeln
(16) examined possible links between seafood consumption and prevalence rates of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Simple exponential decay regressions quantified links between greater seafood consumption and lower lifetime prevalence rates of bipolar I, bipolar II, and bipolar spectrum disorder, with the strongest association for bipolar II (r=–0.91). The lack of any association between seafood consumption and lifetime rate of schizophrenia was interpreted as reflecting specificity of the association to affective disorders.
Postpartum Depression
Hibbeln
(15) reported a cross-national ecological analysis of seafood consumption, DHA content of mothers’ milk, and the prevalence rate of postpartum depression. The prevalence varied nearly 50-fold, from 0.5% in Singapore to 24.5% in South Africa; the mean prevalence rate worldwide was 12.4%. Both higher national seafood consumption and higher DHA content in the mothers’ breast milk predicted a lower prevalence of postpartum depression. Furthermore, greater apparent seafood consumption predicted a higher DHA content in the mothers’ milk. However, the arachidonic acid and EPA content of the mothers’ milk were unrelated to either prevalence of postpartum depression or apparent seafood consumption.
The median DHA intake of women from Australia has been estimated
(22) at 15 mg/day, whereas the intake in countries with high fish consumption (e.g., Japan, Korea, and Norway) is approximately 1000 mg/day. During the third trimester, the fetus accumulates an average of 67 mg/day of DHA, in excess of the dietary intake of many women
(23) . Such transfer to the baby through the placenta and, subsequently, through breast milk poses a risk to women of significant depletion of omega-3 fatty acids during pregnancy and lactation, thus possibly contributing to perinatal risk for depression. Hibbeln
(15) therefore argued the need for controlled intervention trials to determine whether omega-3 fatty acids could prevent postpartum clinical depression and whether they might provide a viable alternative to pharmacological treatments. If efficacious, any such intervention has other advantages. First, studies in women
(24,
25) and animals
(26,
27) have indicated that omega-3 supplementation during pregnancy and the postpartum period is safe. Second, in a review of omega-3 fatty acids and postpartum depression
(28), we argued that omega-3 supplementation in the perinatal period may have additional benefits for the infant’s neurodevelopment. Third, that same review highlighted the need to explore safe alternatives to antidepressant drug therapies for use in the perinatal period.
Quantifying Omega-3 and Depression Variables
We now review several articles indicating links between key polyunsaturated fatty acids and the level of depression. One intrinsic advantage to this research domain is the capacity to pursue and quantify the proposed biological marker. Adams et al.
(29) investigated relationships between depression severity and the levels and ratios of omega-3 and omega-6 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in plasma and erythrocyte phospholipids in 20 moderately to severely depressed patients. Intakes of arachidonic acid and EPA were calculated from self-reported frequency of intake of a wide variety of foods and use of a locally constructed database of the content of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in different foods. They reported a significant positive relation between depression severity and the ratio of erythrocyte phospholipid arachidonic acid to EPA and a negative relation between erythrocyte EPA and depression. The arachidonic acid/EPA ratio in plasma phospholipids was also significantly correlated with depression.
Tiemeier et al.
(30) screened 3,884 subjects age 60 or older in Rotterdam for depressive symptoms, and they compared 264 with depressive symptoms (including 106 with depressive disorders) against 461 randomly selected reference subjects. The subjects with depressive disorders had significantly lower concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids and a significantly higher ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids. As such associations were not secondary to inflammation, atherosclerosis, or several other possible confounders, a direct effect of fatty acid composition on mood was inferred.
Maes and colleagues
(31) compared 36 subjects with major depression, 14 with minor depression, and 24 nondepressed patients. Those with major depression had a significantly higher ratio of arachidonic acid to EPA in both serum cholesteryl esters and phospholipids and a significantly higher omega-6/omega-3 ratio than did the nondepressed subjects and those with minor depression. Such subjects also had significantly lower alpha-linolenic acid and lower total omega-3 in serum cholesteryl esters and lower EPA in both serum cholesteryl ester and phospholipid fractions. In a study extending these results, Maes et al.
(32) studied 34 inpatients with major depression and 14 normal volunteers. Major depression was associated with lower EPA and total omega-3 levels and a higher omega-6/omega-3 ratio in cholesteryl esters and phospholipids. However, in this study there was no significant effect of antidepressant treatment on any of the polyunsaturated fatty acids. The authors suggested that major depression is associated with a deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids (which may act as a trait marker) and a compensatory increase of monounsaturated fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids in phospholipids.
Edwards et al.
(33) reported a study of 10 depressed patients and 14 comparison subjects in which erythrocyte membrane fatty acids were measured; the authors took account of age, gender, stress level, and smoking habits and included a full dietary analysis. The erythrocyte membrane omega-3 levels were significantly lower in the depressed patients. Peet et al.
(34) undertook a similar study of 15 depressed patients and 15 healthy well-matched comparison subjects, and they found that the erythrocyte omega-3 levels of the depressed patients were significantly lower. Ten of the depressed patients were retested after 6 weeks’ treatment with either lofepramine or amisulpride. Total omega-3 and DHA levels had increased from pretreatment levels but were still significantly below those of the comparison subjects. However, erythrocyte samples from both depressed and comparison subjects were then incubated with hydrogen peroxide, resulting in no significant difference in either total omega-3 or DHA level between any samples. This raises the possibility that the low erythrocyte omega-3 and DHA levels of the depressed patients may have been due to oxidative attack.
Mamalakis et al.
(35) investigated possible relationships between polyunsaturated fatty acids in adipose tissue (an index of long-term or habitual fatty acid intake) and lower mood in a group of 247 healthy adults. The mildly depressed subjects had significantly lower adipose tissue DHA levels than the nondepressed subjects. The authors speculated that, as depression has been reported to be associated with increased cytokine production and as fish oil and omega-3 fatty acids may inhibit inflammatory cytokine synthesis, the observed negative association between adipose DHA and depression may stem from the inhibiting effect of DHA on inflammatory cytokine synthesis.
One study
(36) examined possible abnormalities in patients with bipolar I disorder. The erythrocyte concentrations of polyunsaturated fatty acids in 20 patients and 20 comparison subjects were compared. The bipolar subjects had significantly lower levels of arachidonic acid and DHA, but there were no differences between groups in total omega-3 and omega-6 compositions (or in the omega-6/omega-3 ratio).
Possible Mechanisms for Links Between Fatty Acid Abnormalities and Mood Disorders
Several neurophysiological mechanisms have been proposed to explain the relationship between omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and depression, such as the one proposed by Mamalakis et al.
(35) . The two omega-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA, appear to decrease the production of inflammatory eicosanoids from arachidonic acid by means of two mechanisms
(37) . First, they compete with arachidonic acid for incorporation into membrane phospholipids, decreasing both cellular and plasma levels of arachidonic acid. Second, EPA competes with arachidonic acid for the cyclo-oxygenase enzyme system, inhibiting the production of proinflammatory eicosanoids derived from arachidonic acid (e.g., prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes), and prostaglandin E
2 and thromboxane B
2 have been linked to depression. DHA and EPA also inhibit the release of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-2, interleukin-6, interferon-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor alpha, which depend on eicosanoid release and are also associated with depression
(38) . Further, omega-3 fatty acids affect brain-derived neurotrophic factor, which encourages synaptic plasticity, provides neuroprotection, enhances neurotransmission, and has antidepressant effects
(39) .
Another possible mechanism relates to the abundance of DHA in CNS membrane phospholipids, where it plays a vital role in maintaining membrane integrity and fluidity
(40) . By varying lipid concentrations in cell membranes, changes in fluidity can affect either the structure or functioning of proteins embedded in the membrane, including enzymes, receptors, and ion channels, leading to changes in cellular signaling. Support for involvement of omega-3 fatty acids in receptor functioning, neurotransmitter levels, and the metabolism of monoamines implicated in depression has been provided by animal studies (see references
9 and
38 ).
The hypothesis that omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids can affect cell membrane fluidity is supported by a recent study using magnetic resonance imaging
(41) . Twelve women with bipolar disorder received omega-3 fatty acids for 4 weeks and were contrasted with two nontreatment groups. T
2 whole-brain relaxation times were used to detect changes in membrane fluidity, measured at baseline and 4 weeks after treatment initiation. The bipolar subjects receiving omega-3 fatty acids had significant decreases in T
2 values, with a dose-dependent effect shown by subdividing the treatment group into patients receiving a high dose (10 g/day) and those receiving a low dose (2 g/day).
Another postulated, more direct mechanism involves gene expression and the binding of fatty acids to specific nuclear receptors early in life, leading to genetic transcription
(42) and predisposing to a range of diseases with DHA and EPA depletion later in life, such as Alzheimer’s disease, cardiac disease, and depression.
Treatment Studies
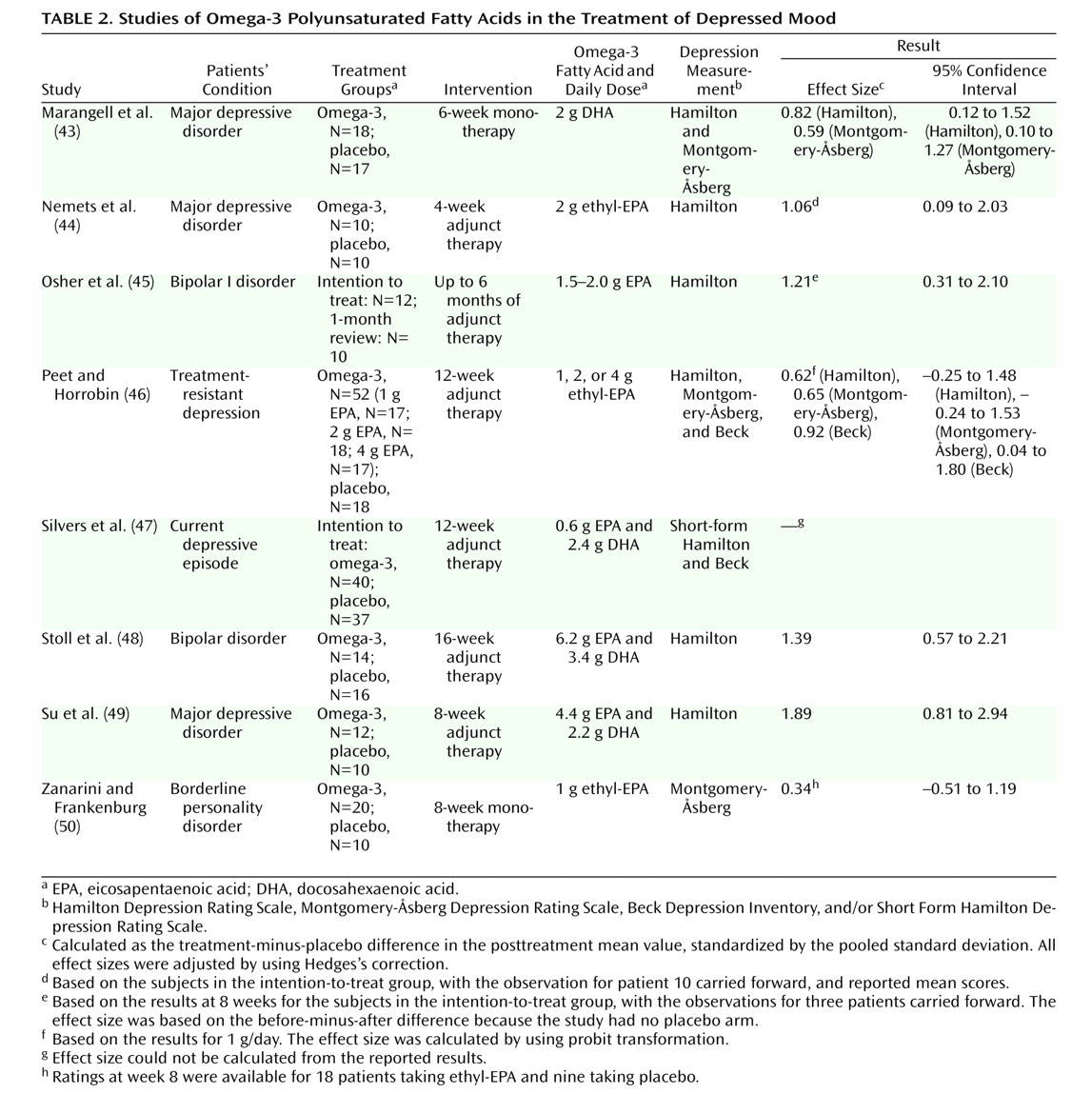
We now review a series of treatment studies, summarized in
Table 2 with effect sizes calculated by us for relevant studies.
Stoll et al.
(48) undertook a 4-month double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with patients who had bipolar disorder; 14 received omega-3 fatty acids, and 16 received placebo (olive oil). As most were also receiving a mood stabilizer, this was essentially an augmentation strategy, and the principal outcome measure was the duration of time before symptom exacerbation led to study exit. Those in the omega-3 group reported greater symptom reduction and remained in remission for a significantly longer time. Consideration of the noncompleters in the 4-month study is of some interest. In the omega-3 group, three of the 14 were noncompleters because of mania, hypomania, and worsening of a mixed state, respectively. In the placebo group, 10 of the 16 were noncompleters, nine because of worsening depression and one because of a “continued mixed state.” Such indicative data were interpreted as demonstrating an antidepressant effect of omega-3 fatty acids, while the authors noted that the baseline clinical state of their subjects did not allow evaluation of any antimanic effect of omega-3 fatty acids. Thus, while this study is commonly viewed as demonstrating the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for bipolar disorder, it may also be that this study demonstrated more the antidepressant potential of omega-3 fatty acids. Subsequently, Osher et al.
(45) reported an open-label study with patients who had bipolar I disorder and reported depressive symptoms and/or being functionally impaired. Their current pharmacotherapy was maintained during adjunct treatment. Of the 10 patients who attained 1-month follow-up, eight had a 50% or greater reduction in depression score within 1 month.
Su et al.
(49) reported a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of omega-3 fatty acids for major depression in 22 patients, 12 treated with omega-3 fatty acids and 10 with an olive oil placebo, in addition to their existing medication. Participants in the omega-3 group had a significantly lower score on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale from the 4th treatment week. Effects on erythrocyte fatty acid composition were also examined. The mean posttreatment level of DHA in the omega-3 patient group was significantly higher than at pretreatment, whereas the posttreatment level of EPA was not significantly different from the pretreatment level. By contrast, there were no significant differences between pre- and posttreatment levels of DHA or EPA for patients in the placebo group.
Nemets et al.
(44) reported a 4-week parallel-group, double-blind addition of either placebo or ethyl-EPA to ongoing antidepressant therapy for 20 patients with recurrent unipolar depressive disorder. Improvement in the group receiving EPA was significant from week 2 and was highly significant from week 3, and at the end of the 4 weeks the mean reduction in Hamilton score was 12.4 points for the EPA group and 1.6 points for the placebo group. However, in another controlled augmentation trial for community-recruited subjects with moderate levels of depression, Silvers et al.
(47) found no support for 3 g/day of fish oil supplementation of antidepressant medication, despite significant increases in both EPA and DHA in erythrocyte membranes.
Peet and Horrobin
(46) studied the effects of ethyl-EPA in patients with ongoing depression despite apparently adequate treatment with standard antidepressant drugs. The 70 patients (ages 18 to 70, male and female) were divided into four groups of approximately equal size. One group took four capsules of paraffin oil placebo per day, the second group took one capsule containing 1g of ethyl-EPA and three of placebo, the third group received two capsules of ethyl-EPA and two of placebo, and the fourth group took four capsules of ethyl-EPA. Thus, the group members consumed 0, 1, 2, and 4 g of ethyl-EPA per day, respectively. All patients continued to received their antidepressant medications. The group taking 1 g/day showed strong beneficial effects on items rating depression, anxiety, sleep, lassitude, libido, and suicidality. The group taking 2 g/day showed little evidence of efficacy, whereas the group taking 4 g/day showed nonsignificant improvement. The suggested curvilinear dose response (across three depression measures) in this omega-3 augmentation study may reflect the relatively low group numbers or a valid dose difference.
Marangell et al.
(43) reported a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of DHA monotherapy for patients with a major depressive episode. The patients were randomly assigned to receive either DHA (N=18) or placebo (N=17) for 6 weeks. The response rates were 27.8% in the DHA group and 23.5% in the placebo group, and the difference was not formally significant. The differing results across the last three studies have been interpreted as possibly reflecting differential antidepressant efficacy of EPA and DHA.
Zanarini and Frankenburg
(50) studied the comparative efficacy of EPA and placebo in female subjects meeting formal criteria for a borderline personality disorder, not in receipt of any psychotropic medication, and not formally meeting criteria for a current major depressive episode. In contrast to the trial of Marangell et al.
(43), the 8-week study (20 participants taking ethyl-EPA and 10 taking mineral oil placebo) established that those treated with EPA experienced a significantly greater reduction in depressive symptoms—as well as in overall aggression.
Earlier, we noted the suggested link between seafood consumption and postpartum depression. Llorente et al.
(51) reported a double-blind intervention study in which they sought to determine the effect of DHA supplementation on plasma phospholipid DHA content and on depression indices. Mothers planning to breast-feed were randomly assigned to receive either DHA (≈200 mg/day) or placebo for 4 months after delivery, with depression levels assessed at baseline (delivery), 3 weeks, 2 months, and 4 months. At baseline, the mean plasma phospholipid DHA level was 3.15 mg/dl in the DHA-supplementation group and 3.31 mg/dl in the placebo group. At 4 months, the plasma phospholipid DHA levels were 8% higher (3.40 mg/dl) in the supplementation group and 31% lower (2.27 mg/dl) in the placebo group. While there were no group differences on depression measures at 4 months, this was a prevention study and the women did not have depression when recruited.
Do Omega-3 Fatty Acids Induce Switching?
As examined in controlled trials and reported in case study series, all antidepressant drugs appear to have some capacity to induce manic “switching,” although such a propensity appears less evident with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and dual-action drugs than with tricyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors
(52) . In fact, it was long held by many clinicians that an “effective antidepressant” should induce switching.
Kinrys
(53) reported the case of a woman with a history of major depressive disorder who had not taken antidepressants for 8 months. Five days after she began taking a daily dose of 1980 mg of DHA and 1320 mg of EPA, she became hypomanic, but after the cessation of this treatment she was euthymic in 2 days. In response to the suggestion that omega-3 fatty acids might have mood-elevating effects, Stoll et al.
(54) replied that their group had treated more than 300 patients with various open-label omega-3 preparations, including high DHA/low EPA fish oil, high EPA/low DHA fish oil, and flaxseed oil, which contains alpha-linolenic acid (a shorter-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid), and they observed “fewer than 10 cases of apparent omega-3-induced hypomania or mania, almost all from flaxseed oil preparations.”
Do Omega-3 Fatty Acids Link Depression to Cardiovascular Disease?
Earlier we noted a large epidemiological study
(7) identifying inverse relationships between omega-3 levels and cardiovascular disease. A number of studies have examined the nature of those associations in societies where there is a high dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids. In one such study
(55), Newman et al. established that the extent of atherosclerotic lesions was lower in Alaska natives than in nonnatives and judged that their lipid profiles were related to their diet (reflecting the high intake of omega-3 fatty acids by Eskimos) and not genetic in origin.
It is not surprising then that the well-known association between depression and cardiovascular disease has been interpreted
(56,
57) as reflecting a common factor—a deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids. Severus et al.
(56) noted numerous studies showing that omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of primary cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death (presumably through their antiarrhythmic properties and impact on heart rate variability) and that a high ratio of arachidonic acid to DHA (omega-6/omega-3) ratio has been reported
(58) in the heart muscle of men following sudden cardiac death. Low heart rate variability is a risk factor for sudden cardiac death and has been shown to be associated with a reduced content of omega-3 fatty acids in platelet membranes of patients following myocardial infarction
(59) . In addition, fish oil supplementation led to an increase in heart rate variability in these patients
(60) . Severus et al.
(57) concluded that the higher rate of cardiovascular disease in patients with depression may be the result of one or more still-unrecognized underlying physiological factors predisposing to both depression and cardiovascular disease, with omega-3 deficiency and a high homocysteine level being two possible determinants. A recent article is therefore of some relevance.
Frasure-Smith et al.
(61) recruited 812 individuals experiencing an acute coronary syndrome and contrasted a subset of 54 who had major depression with another subset of age- and sex-matched nondepressed subjects. The depressed patients had significantly lower concentrations of total omega-3 and DHA than the matched comparison subjects and higher arachidonic acid/DHA, arachidonic acid/EPA, and omega-6/omega-3 ratios. The authors noted that to their knowledge, while there had been many studies demonstrating low omega-3 levels in people who later develop coronary artery disease, this was the first study showing lower omega-3 levels in plasma phospholipids of depressed patients with coronary artery disease. They reviewed studies indicating that depression is associated with lower total omega-3 levels; some of these studies identified significantly lower DHA, others indicated lower EPA, and others found a lower DHA-EPA combination. In addition, they noted that, while there were some variations in the studies examining omega-3 fatty acids as risk factors for coronary artery disease, “the most consistent results parallel those for depression” (p. 894), and they argued the need for trials of dietary supplementation with long-chain omega-3 fatty acids in both patients with coronary artery disease and patients with depression.
As a relative deficiency in essential omega-3 fatty acids has been strongly implicated as providing an increased risk for coronary artery disease and for depression, a deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids may act as a higher-order variable increasing their independent risk and creating a spurious association.
Conclusions
There are now several cross-sectional studies showing associations between seafood consumption and rates of both depression and bipolar disorder. Such research postulates a plausible etiological factor. Further, and unusual in any pursuit of a psychiatric disorder, the biological risk factor can be measured, with several studies identifying lower concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids in patients with depression. Most, but not all, studies have examined levels in plasma rather than red blood cells.
In terms of intervention, there are now several studies supporting omega-3 supplementation as having a distinct antidepressant role. Predictably, because of the complexities intrinsic to the domain, much work will be required to determine which omega-3 fatty acid (and in what ratio to omega-6 fatty acids) is likely to have the greatest benefit and at what dose. Currently, there appears to be somewhat stronger support for EPA than for DHA in terms of antidepressant strength. However, this is of theoretical interest principally, as the two omega-3 fatty acids are not normally separated but given together as fish oil. It presently remains unclear whether omega-3 supplementation alone has antidepressant properties or whether omega-3 fatty acids may have greater potential as augmenters of standard antidepressants. Finally, while there are two studies indicating efficacy of omega-3 supplementation for patients with bipolar disorder, it remains to be further investigated whether its identified benefits derive from a mood-stabilizing propensity or an antidepressant effect.
Our review therefore suggests a raft of possible studies, as now noted. First, measurement issues need further clarification. Specifically, what is the most useful modality for measuring polyunsaturated fatty acids (i.e., adipose tissue, red blood cells, plasma), while there is a need to refine and calibrate questionnaires on food frequency and diet to ensure their links to measured levels of the biological markers (e.g., DHA, EPA, and arachidonic acid). Second, placebo-controlled trials require careful selection of an appropriate placebo, given the possible influence of some oils (e.g., olive oil) on mood, the ethical considerations of using a proinflammatory omega-6 placebo, and the obvious fish aftertaste in intervention groups, risking identification. Third, clarification of the risk factor is required. Specifically, which omega-3 fatty acid deficiency (DHA or EPA) or what ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 provides the greatest risk for mood disorders in general and for subsets of disorders (bipolar, unipolar, postpartum), what factors influence that risk factor (e.g., diet, maternal depletion during pregnancy), and what duration of dietary supplementation is required to correct any anomaly in polyunsaturated fatty acids. Fourth, further treatment studies should examine whether supplementation is beneficial—and which omega-3 fatty acid (EPA, DHA, or some combination) is optimal and whether there is specificity to differing mood disorder types. Fifth, does such supplementation have general effects on mood state or is it weighted toward antidepressant or mood-stabilizing effects, and therefore preferentially relevant to unipolar or bipolar disorder, or does it have even wider benefits (e.g., for anxiety or sleep disorders)? Sixth, treatment studies should identify whether such supplementation is of relevance only if there is an established omega-3 deficiency and whether supplementation has primary mood effects or is more an augmentor requiring a primary drug, such as an antidepressant. Thus, the study designs would broadly be compatible with those of standard pharmacotherapy trials but would have the advantage of being able to measure process issues, such as the biological markers. Seventh, if benefits from short-term treatment are demonstrated, extension studies would need to pursue their prophylactic potential. Eighth, treatment studies should be associated with pursuit of likely mechanisms, by means of functional MRI (as noted earlier) or other technologies. Ninth, the hypothesis that abnormal levels of omega-3 fatty acids may act as a higher-order variable that independently increases risk for coronary artery disease and for depression (and so suggesting a causal link between those two outcome variables) would benefit from refined studies.
In this article we have reviewed components of an intriguing hypothesis linking a dietary contribution to variable rates of mood disorders. There is now a clear hypothesis linking disorder diathesis and variation with an identifiable risk factor and allowing a rational treatment approach. There is great opportunity for more specific etiological and treatment intervention studies. Further research into the essential polyunsaturated fatty acids and their relevance to psychiatric, cardiac, and more general health areas would benefit from fast tracking and enhancement of coordinated research endeavors.