Up to one-fifth of women suffer from depression, and the highest prevalence is during childbearing years. Of pregnant women, 10%–16% fulfill the DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for major depression, and they often need pharmacotherapy. Although it was thought that pregnancy protects against depression, a recent population-based study
(1) showed that depression during gestation is more common than in the postnatal period; scores on measures of depressive symptoms are higher at 32 weeks of gestation than at 8 weeks postpartum. Untreated depression is associated with higher rates of mortality and morbidity. Discontinuation of antidepressant drug therapy in women with medication-responsive illness carries a high risk for relapse and suicide attempts
(2). The Food and Drug Administration has not approved any of the antidepressant medications for use during pregnancy. There is a need to balance the risk of exposure to an antidepressant medication with the impact of untreated maternal disease on pregnancy outcome and child development
(3). The first trimester of pregnancy, in particular weeks 2 to 8 after conception, is the most critical period for drug-induced dysmorphology. The human fetal brain develops throughout gestation, and injury may occur at various critical times of exposure. A number of studies
(4–
11) have suggested that tricyclic antidepressants and fluoxetine may be safe when taken during the first trimester of pregnancy. Although a large number of women need antidepressants throughout pregnancy, the lack of information about their safety may deter women from taking these medications, even when clinically indicated
(12). While neither tricyclic antidepressants nor fluoxetine appear to cause major malformations or neurobehavioral problems when used in the first trimester, the long-term effects on the developing CNS when these drugs are taken throughout gestation is not known.
The present study was designed to assess prospectively the neurodevelopment of children exposed to tricyclic antidepressants or fluoxetine throughout fetal life.
Method
The Motherisk Program
The Motherisk Program provides information and consultation to women, their families, and health professionals on the risk/safety of drug, chemical, radiation, and infectious exposures during pregnancy and lactation. Women with major depression who seek help are invited to a clinic visit to be counseled by a physician.
Subject Selection
We recruited prospectively three groups of mother-child pairs; mothers were approached during the first trimester of pregnancy. The first two groups included all women who had been counseled by the program regarding therapy with either tricyclic antidepressants (since the inception of the program in September of 1985) or fluoxetine (since its introduction in Canada in 1988) and who had continued taking these medications throughout gestation. All subjects receiving antidepressant medications and enrolled in the study had been diagnosed as having major depression after an independent psychiatric evaluation and found to require pharmacotherapy. We also studied a comparison group, also recruited prospectively, that comprised women who had no history of a psychiatric disorder or depressive symptoms and were unexposed to any drug, chemical, radiation, or infection known to affect the fetus adversely. Mothers in the comparison group were chosen randomly from a list of women who had visited our clinic within the 2 months before or after the visits by the study groups and who were not depressed, as indicated by a score less than 16 on the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D Scale)
(13).
Eighteen mother-child pairs exposed to fluoxetine and 36 exposed to tricyclic antidepressants who were part of our original study
(10) and who were exposed to these drugs throughout gestation were included in the present study. The original study focused on first-trimester exposure to antidepressants and did not have a sufficient number of patients to address exposure throughout gestation.
We excluded from the study group women whose antidepressant drug therapy was discontinued before conception or during pregnancy and women who were exposed to more than one antidepressant drug or to known teratogens. We also excluded from the comparison group women with medical conditions that may adversely affect fetal outcome, women with depressive symptoms (indicated by a score of 16 or higher on the CES-D Scale), and those who refused to participate in our follow-up program. In total, six such women were excluded.
The study was approved by the hospital research ethics board. A written informed consent statement was obtained from each woman.
Assessments
Measurement of mother’s depressive symptoms
The CES-D Scale is a short self-report scale designed to measure depressive symptoms in the general population. The scale has been found to have a high internal consistency and adequate test-retest repeatability. The scale is based on symptoms of depression as seen in clinical cases, it discriminates between patients and the general population, and it correlates with other scales designed to measure depression. The scale is widely used in research and is a valid tool for identifying and studying the relationships between depressive symptoms and many other variables. This 20-item scale, which takes 15 minutes to complete, has been extensively tested for reliability and validity. Scores on the CES-D Scale range from 0 to 60, and a score of 16 or above indicates a clinically significant level of depressive symptoms
(13).
Antenatal and postnatal assessments
During the initial consultation, during early pregnancy, a detailed medical, genetic, and obstetric history was obtained from each mother. We also collected information about alcohol consumption, tobacco and recreational drug use, sexually transmitted diseases, and maternal medical care. Details concerning the time and duration of exposure to tricyclic antidepressants or fluoxetine, the dose of the antidepressant drug, and the doses of any other concomitant medications were recorded.
The first postnatal assessment was performed at 6 to 9 months after delivery. During this interview the mother was questioned about the course of her pregnancy after the first meeting, including verification of the duration and dose of tricyclic antidepressant or fluoxetine treatment during gestation, maternal illnesses, and perinatal and/or postnatal complications. Information about delivery methods and the perinatal period, the child’s ages at developmental milestones, and a written report from the physician caring for the child were collected.
Neurobehavioral testing of child
Between the ages of 15 and 71 months the children were assessed by a psychometrist who was blinded to the nature of the intrauterine exposure. To test for neurodevelopment, children between 15 and 30 months of age were given the Bayley Scales of Infant Development—II
(14). Older children were tested with the McCarthy Scales of Children’s Abilities
(15). The infant’s temperament and behavior were evaluated by using the age-appropriate Toddler Temperament Scale
(16,
17) and, for toddlers older than 24 months, the age-appropriate Achenbach Child Behavior Checklist
(18). Language skills were assessed in all infants and children with the Reynell Developmental Language Scales
(19).
Follow-up testing of mother
Maternal IQ was assessed with the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Revised
(20), and socioeconomic status was measured with the Hollingshead Four Factor Index of Social Status
(21).
The mother’s level of functioning from the birth of the infant to the time of the psychological assessment was measured by using the Global Assessment of Functioning Scale
(22), which rates the woman’s lowest level of functioning by selecting the lowest range that describes her functioning on a continuum of mental illness. At the follow-up assessment we also administered the CES-D Scale and the Index of Parental Attitudes, a 25-item scale designed to measure the extent, severity, or magnitude of parent-child relationship problems as seen and reported by a parent
(23). These maternal assessments were conducted at the time of examination of the offspring. As part of these assessments we also recorded whether the mother continued drug therapy in the postpartum period and, if so, for how long.
Statistical Analysis
The recruited study group was large enough for detection of a medium effect of antidepressant treatment on the child’s IQ (10.6-point difference between the study and comparison groups) with a power of 80% and alpha of 0.05. In a similar manner, it had 80% power for detection of a medium effect on language achievements (measured by the Reynell Developmental Language Scales) and behavior.
Outcome measures in each group (tricyclic antidepressants, fluoxetine, and comparison) were compared by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s honestly significant difference test. All tests were two-tailed. Differences in proportions among the groups were compared by the chi-square test.
Subsequently, correlations and multiple regression analyses were conducted in order to determine the effects of potential confounders on the outcome measures.
Results
In total, 46 mother-child pairs were tested after being exposed throughout gestation to a tricyclic antidepressant, and 40 mother-child pairs were tested after exposure to fluoxetine. The comparison group consisted of 36 mothers and their children not exposed to teratogenic drugs and not suffering from depression as measured by the CES-D Scale
(13).
Among the subjects given tricyclic antidepressants, 18 took amitriptyline, 12 imipramine, seven clomipramine, three desipramine, three nortriptyline, two doxepin, and one maprotiline. The tricyclic antidepressants were taken for an affective disorder in 32 cases, for pain control in 11 cases, and for an anxiety disorder in three cases. The doses of tricyclic antidepressants were in the therapeutic ranges in all cases. Thirty-six mothers took fluoxetine (20 to 80 mg a day) for depression, and the other four took the drug for an anxiety disorder.
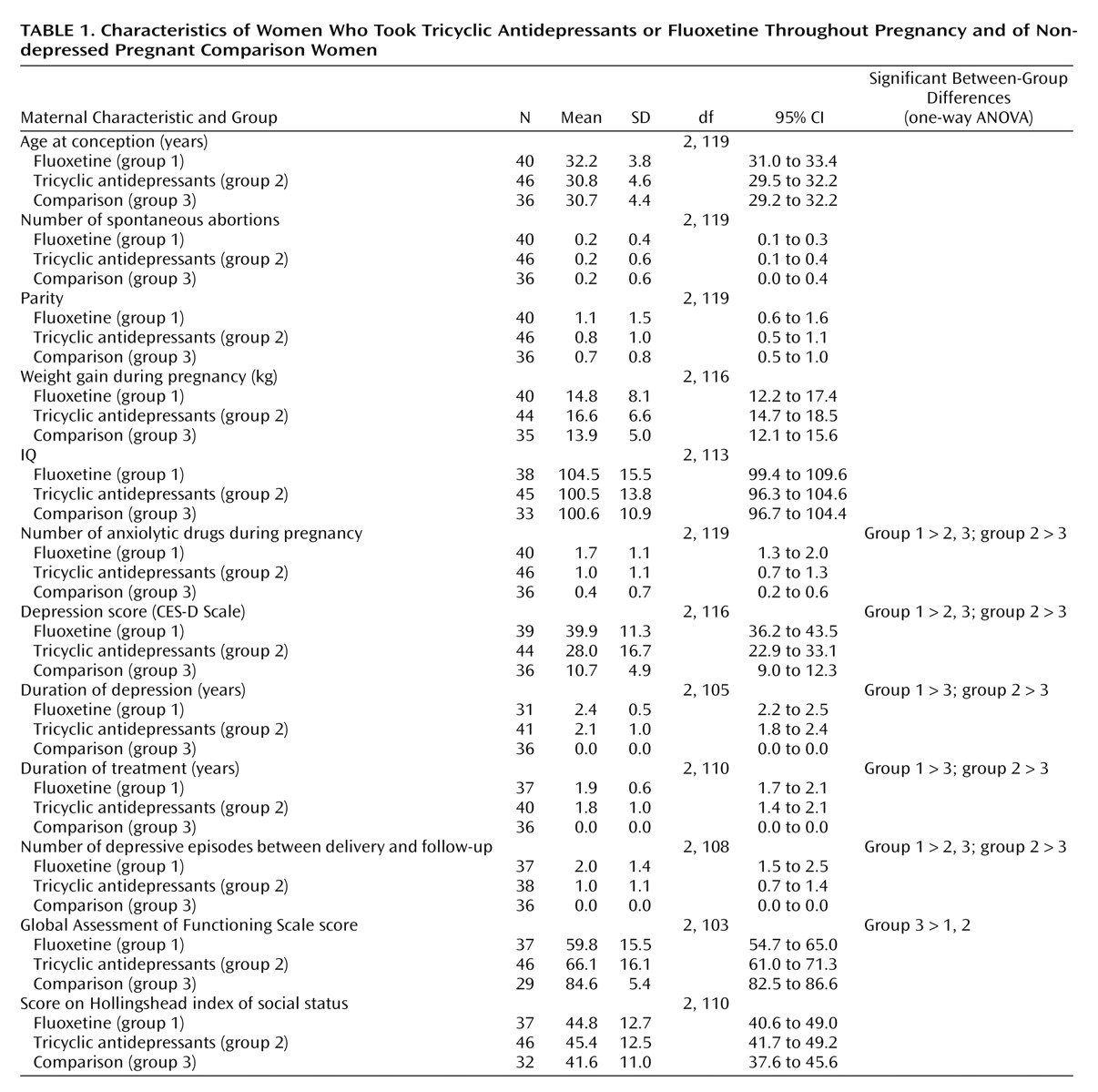
There were no differences among the groups in maternal age, maternal IQ, or socioeconomic status (
Table 1). The women in both antidepressant groups tended to consume more ethanol and to smoke more cigarettes during the index pregnancy than did women in the comparison group (data not shown). The women in the fluoxetine group were significantly more depressed, experienced more depressive episodes after delivery, and used more anxiolytic medications than the comparison women, and both groups of mothers taking antidepressants scored lower on the Global Assessment of Functioning Scale than the comparison women (
Table 1).
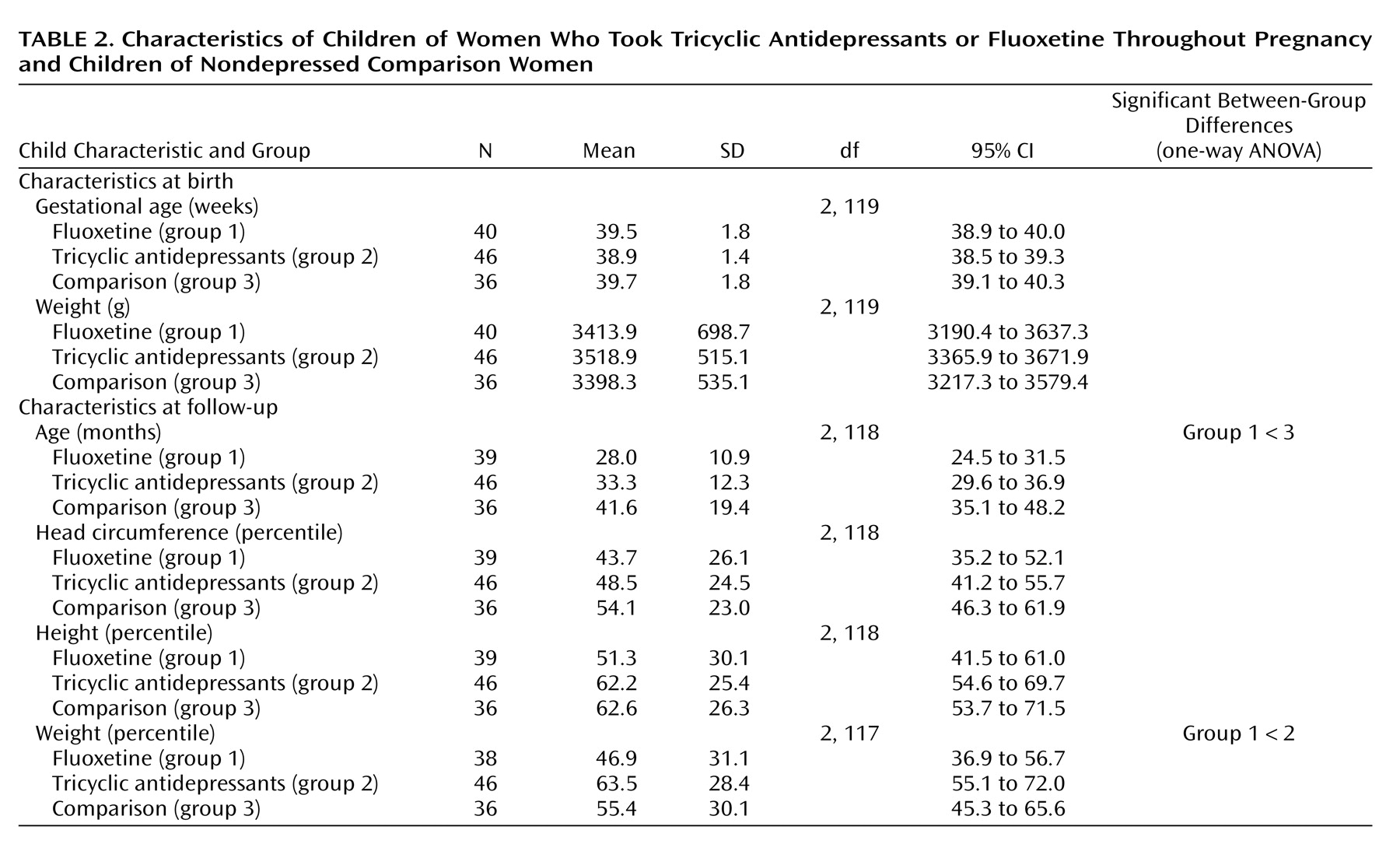
Characteristics of the children are shown in
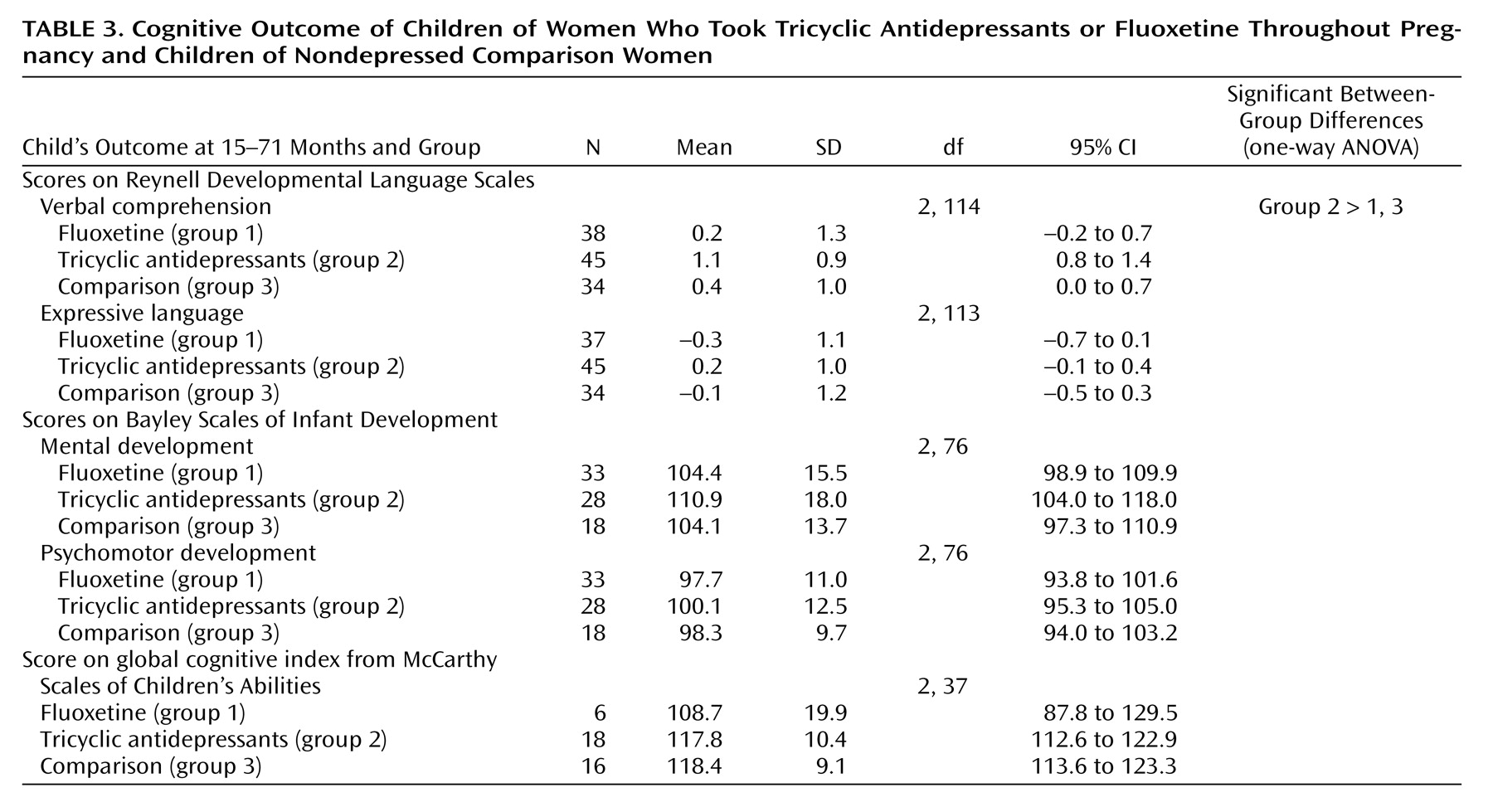
Table 2. At birth and at the time of testing, the weight and head circumference percentiles of the children in both antidepressant groups were similar to those for the comparison group. The children in the fluoxetine group were significantly younger than those in the comparison group. Cognitive characteristics of the children are presented in
Table 3. There were no differences in the children’s global IQ among the three groups (measured by either the Bayley or McCarthy test). Children in the tricyclic antidepressant group scored slightly higher on the Reynell Developmental Language Scales, but all three groups scored within the normal range. Of the 46 children in the tricyclic antidepressant group, 25 were breast-fed while their mothers were taking tricyclic antidepressants. Of the 40 children in the fluoxetine group, 21 were breast-fed while their mothers were taking fluoxetine. Of the 36 children in the comparison group, 32 were breast-fed. Breast-feeding (or lack of) did not affect neurodevelopmental achievements among the study groups.
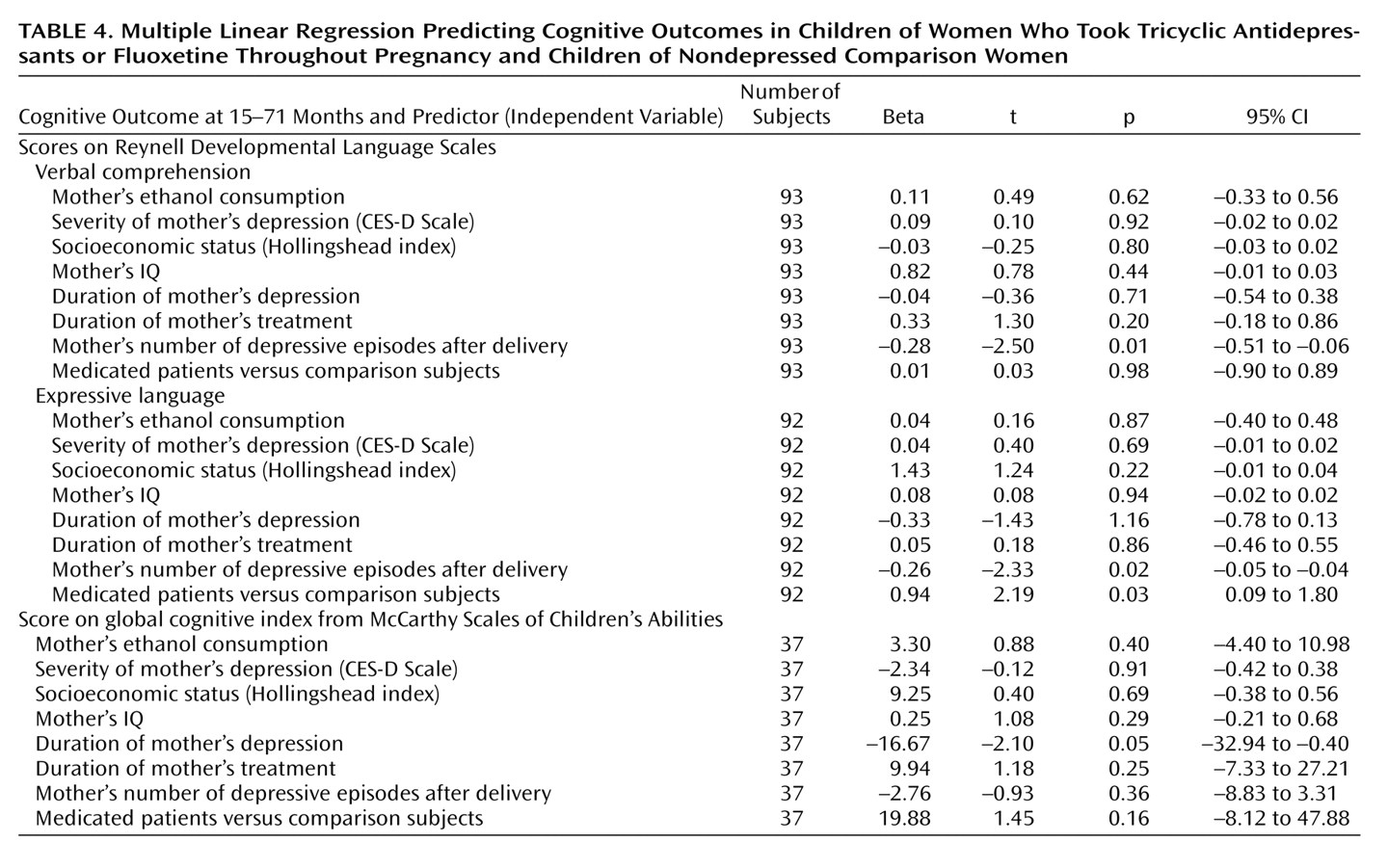
To control for potential confounders that may affect a child’s neurodevelopmental outcome, a regression analysis was performed. The children’s cognitive and language outcomes were entered into the analysis as dependent variables. The mother’s IQ, socioeconomic status, ethanol use and cigarette smoking, depression severity, depression duration, treatment duration, number of depressive episodes after delivery, and medications used for depression treatment were entered as independent variables.
Multiple regression analysis revealed that the duration of maternal depression was a significant negative predictor for McCarthy global cognitive index. The antidepressant drugs themselves did not predict cognitive achievements (
Table 4). The number of depressive episodes after delivery had a negative relationship with language scores. In contrast, treatment for maternal depression was a positive predictor for language development.
No differences were detected among the three groups across the nine temperament scales (p=0.83) or three behavioral scales (p=0.83) of the Child Behavior Checklist (data not shown).
Discussion
Our study does not show adverse cognitive, language, or temperament effects on offspring exposed throughout gestation to tricyclic antidepressants or fluoxetine. In contrast, uncontrolled depression was associated with lower cognitive and language achievements. These data are important clinically, because many pregnant women discontinue their antidepressant therapy abruptly, because of fears of adverse fetal effects, thus putting themselves at risk of increased morbidity, adverse pregnancy and fetal outcomes, and disease relapse. Repeated relapse is associated with a risk of treatment resistance and chronicity of depression
(24). Severe stress and depression have been shown to be associated with altered fetoplacental function, premature delivery, impaired fetal growth, perinatal complications, and possible long-term behavioral problems in the children
(25–
27). Substance abuse, suicide attempts, failure to follow prenatal guidelines, and poor prenatal care have been reported in pregnant women with uncontrolled depression
(28).
We have previously shown
(10) that neither tricyclic antidepressants nor fluoxetine tend to affect cognitive and language outcome after first-trimester exposure. Such information, while reassuring, could not support the use of these medications during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. In humans, the fetal brain develops throughout gestation, and therefore fetotoxics (e.g., lead and ethanol) have been shown to adversely affect brain development after first-trimester exposure.
Symptoms associated with pregnancy, such as sleep disturbances, poor appetite, and fatigue, may often mask symptoms of depression. We included in our study group only women who were diagnosed with depression by a psychiatrist before conception and who required treatment with an antidepressant medication. Moreover, we tested women in the comparison group for depressive symptoms, and we identified and excluded six women who scored 16 or above on the CES-D Scale.
Because we measured symptoms of depression from birth to the time of testing, we had the rare opportunity to record potential confounders that may have an impact on children’s cognitive and behavioral functioning. The children in the fluoxetine group were significantly younger, as fluoxetine is newer than tricyclic antidepressants. The neurodevelopmental and cognitive tests we used were age appropriate, with the normal mean for the general population of 100 and a standard deviation of 16. Children in all groups scored within the normal ranges on all tests.
We did not detect differences in cognitive and language test scores between breast-fed and formula-fed children. This may be explained by an insufficient number of subjects and more severe depression among breast-feeding mothers.
Because it was not possible to randomly assign women to the two groups of antidepressants, the prospective observational design may suffer from differences among the groups in confounders that may affect pregnancy outcome. To overcome this shortcoming we conducted a multiple regression analysis, which revealed that the duration of maternal depression and the number of depressive episodes after delivery consistently and adversely affected child achievements. Neither tricyclic antidepressants nor fluoxetine had such effects.
It could be argued that the lack of adverse developmental effects in the preschool and early-school years does not rule out potential later detrimental effects by tricyclic antidepressants or fluoxetine.
Management of depression during pregnancy should depend on the severity of the disease. Psychotherapy should always be incorporated into the management, as it may obviate fetal exposure to antidepressants. Mild or moderate depression may be treated nonpharmacologically, whereas pharmacotherapy is usually indicated for severe depression. Although the power of our study was limited to the detection of a medium effect size, the mean values for the different groups were virtually identical at most endpoints, and all children scored within the normal ranges on all tests used. The results of this study are helpful in the risk-benefit decision and counseling of pregnant women with depression.
In separating the neurodevelopmental effects of antidepressants from those of depression itself, our study supports adequate antidepressant therapy during and after pregnancy.