The safety of antidepressant drugs during pregnancy is a significant public health concern. Depressive disorders cause a tremendous burden of personal suffering and functional impairment
(1–
3). The prevalence of depression is approximately twice as great among women as men and is greatest during the childbearing years
(4,
5). Furthermore, depression is increasingly recognized as a chronic or recurrent condition requiring long-term treatment
(6,
7). Consequently, women with more severe or recurrent depression face complex choices regarding use of antidepressants during pregnancy
(8).
Previous research leaves significant uncertainty regarding the effects of antidepressants on the embryo and fetus. All antidepressants are classified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as in risk category B, indicating that safety has not been established and use during pregnancy should be avoided unless it is “clearly needed.” Four controlled studies
(9–
12) have evaluated malformations after prenatal antidepressant exposure. None found a greater risk for major malformations, while one
(9) reported a greater risk for minor malformations after exposure to fluoxetine. Three controlled studies
(9–
11) have examined perinatal outcomes after antidepressant exposure; two
(9,
10) found a greater risk of neonatal complications (including premature delivery) after fluoxetine exposure, and one
(11) found no effect. The one controlled study that examined early childhood development
(11) found no effect of exposure to either fluoxetine or tricyclic antidepressants. Two meta-analyses of the studies just described
(13,
14) also found no greater risk of major malformations after antidepressant exposure. One of these meta-analyses
(13) also considered perinatal complications (premature delivery, low birth weight) but reached no definite conclusion regarding outcome. Among studies not included in these meta-analyses
(15–
18), none found a greater risk of congenital malformation after antidepressant exposure. A large Swedish birth registry study
(18), however, found that antidepressant use reported at the first prenatal visit was associated with premature delivery.
Methodological shortcomings in previous studies further increase uncertainty regarding outcomes. First, the samples may have been unrepresentative. All of the controlled studies
(9–
12) selected mothers who called referral centers regarding exposure to possible teratogens. Women seeking care probably differ from the general population of exposed and unexposed pregnant women. Only the Swedish birth registry study
(18) examined a population-based sample of exposed women. Second, selection of unexposed infants may have introduced bias. Comparison groups were typically selected from women calling the same referral centers because of concerns about exposure to nonteratogens (e.g., penicillin). Women using antidepressants during pregnancy certainly differ from women exposed to nonteratogens in the severity of current depression, a known risk factor for premature delivery and consequent low birth weight
(19–
21). Finally, in three of the four controlled studies
(9,
10,
12), clinical examiners and investigators were not blind to exposure, which allowed the possibility of ascertainment bias.
We describe here a cohort study of outcomes after prenatal antidepressant exposure in a systematically identified nonvolunteer sample. We attempted to address methodological shortcomings of previous work with population-based ascertainment of exposure, matching for maternal depression treatment history, and blinding of data collection and data analysis. The infants’ medical records were used to examine perinatal outcomes, congenital malformations, early childhood neurological illness, and developmental delay.
Method
The study sample was drawn from the Group Health Cooperative, a prepaid health plan serving approximately 400,000 members in Washington State. The membership is generally representative of the area’s population
(22) in terms of age, sex, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. Because of contracts between Group Health Cooperative and the state of Washington, the 1996 membership included approximately 25,000 individuals covered by Medicaid and 12,000 covered by the Basic Health Plan, a state-subsidized program for low-income residents. Group Health Cooperative’s computerized information systems record outpatient prescriptions, outpatient visits, and hospital discharges. Except for Medicare members, all Group Health Cooperative plans include prescription drug coverage. Previous surveys have indicated that over 95% of exposure to antidepressants is captured by computerized pharmacy records
(23).
Hospital discharge records were used to identify all live births between January 1, 1986, and December 31, 1998. To ensure availability and uniformity of outpatient records, the sample was limited to those enrolled at primary care facilities owned by Group Health Cooperative. To ensure complete capture of drug exposure, the sample was further limited to mothers continuously enrolled in Group Health Cooperative for 360 days before delivery.
Pharmacy records were used to identify all antidepressant prescriptions filled or refilled during the 360 days before delivery. Mothers with no antidepressant prescriptions during this period were considered unexposed. Those with any antidepressant prescriptions during the 270 days before delivery were considered exposed. The remaining patients (i.e., those with antidepressant prescriptions filled in the period between 270 and 360 days before delivery) were classified as indeterminate and excluded from further analysis. This report considered only mothers exposed to tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, desipramine, doxepin, imipramine, nortriptyline, or protriptyline—hereafter called tricyclic antidepressants) or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants (fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline—SSRIs).
Exposed infants were then stratified into 432 potential cells according to the following maternal characteristics: age, year of delivery, lifetime number of antidepressant prescriptions filled or refilled, lifetime history of outpatient psychiatric treatment, lifetime history of inpatient psychiatric treatment, and length of Group Health Cooperative enrollment. For each cell of exposed infants, an equal number of unexposed infants was randomly selected from the corresponding cell of unexposed infants.
Data sources included the following:
1.
Standardized forms from maternal prenatal visits for data regarding alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, or cocaine use during pregnancy.
2.
Standardized birth records for data regarding birth weight, head circumference, Apgar scores, and estimated gestational age.
3.
Newborn nursery records for results of standardized physical examinations.
4.
Standardized physical examination records from pediatric health-monitoring (“well-baby”) visits from birth to age 2 for data regarding congenital malformations and developmental delay.
5.
Records of all other outpatient visits and, where appropriate, hospital admissions for data regarding congenital malformations, neurological disorders, and developmental delay.
6.
Results of at least one detailed physical examination (in the newborn nursery or the first “well-baby visit”) was required for inclusion.
For each infant, all relevant records were photocopied after masking all identifying information and information regarding any prenatal exposures. Two chart reviewers received an initial 6 hours of training from the investigators (G.E.S. and M.L.C.), followed by approximately 40 hours of supervision during the course of the project. Reviews were conducted by using a structured abstraction form available from the first author on request. All records with any suspected abnormalities (malformation, developmental delay, etc.) were also reviewed by the investigators (G.E.S. and M.L.C.) for diagnostic classification. Final classification of malformation diagnosis and malformation severity (major versus minor) was performed by a pediatrician specializing in diagnosis and treatment of congenital malformations (M.L.C.). Final diagnosis of speech or motor delay required both a physician diagnosis and confirmation by a formal developmental evaluation. Final diagnosis of seizure disorder required neurological diagnosis and an EEG. Febrile seizures only were excluded from the seizure category. To confirm sensitivity of the initial review, the first author independently reviewed the first 200 records initially classified as normal as well as a 10% random sample of the remainder. Chart reviewers and investigators remained blind to exposure status throughout chart reviews and primary data analyses (as identified in this report).
Primary outcomes designated a priori were gestational age, birth weight, head circumference at birth, Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes, any major malformation, any minor malformation, motor delay, and speech delay. All analyses were conducted by using the SPSS software package (SPSS, Inc., Chicago). Percentages were compared by using chi-square statistics and odds ratios computed by means of logistic regression analysis. Continuous measures were compared by using t tests (for unadjusted comparisons) and analysis of covariance (for adjusted comparisons). A priori power calculations indicated 80% power to detect either a twofold increase in prevalence of minor malformations (expected base rate=10%) or a 2.5-fold increase in prevalence of major malformations (expected base rate=4%). All procedures were approved by institutional review boards at both the Group Health Cooperative and the University of Washington.
Results
The procedures described identified 209 infants exposed to tricyclic antidepressants during pregnancy, including 66 exposed to amitriptyline, 49 exposed to imipramine, 36 exposed to doxepin, 33 exposed to nortriptyline, and 22 exposed to desipramine. A total of 185 were exposed to SSRIs, including 129 exposed to fluoxetine, 32 exposed to sertraline, and 28 exposed to paroxetine (with some exposed to two different drugs).
Consequent to the matching procedure, maternal age, year of delivery, lifetime use of antidepressants, and lifetime history of psychiatric treatment did not differ between exposed and unexposed groups. In both the SSRI and tricyclic antidepressant groups, there were no significant differences between exposed and unexposed infants in the mothers’ reported use of alcohol, tobacco, or marijuana. In the tricyclic antidepressant group, self-reported cocaine use was significantly higher in the exposed group (4%, N=8) than in the unexposed group (0%) (χ2=8.2, df=1, p=0.004).
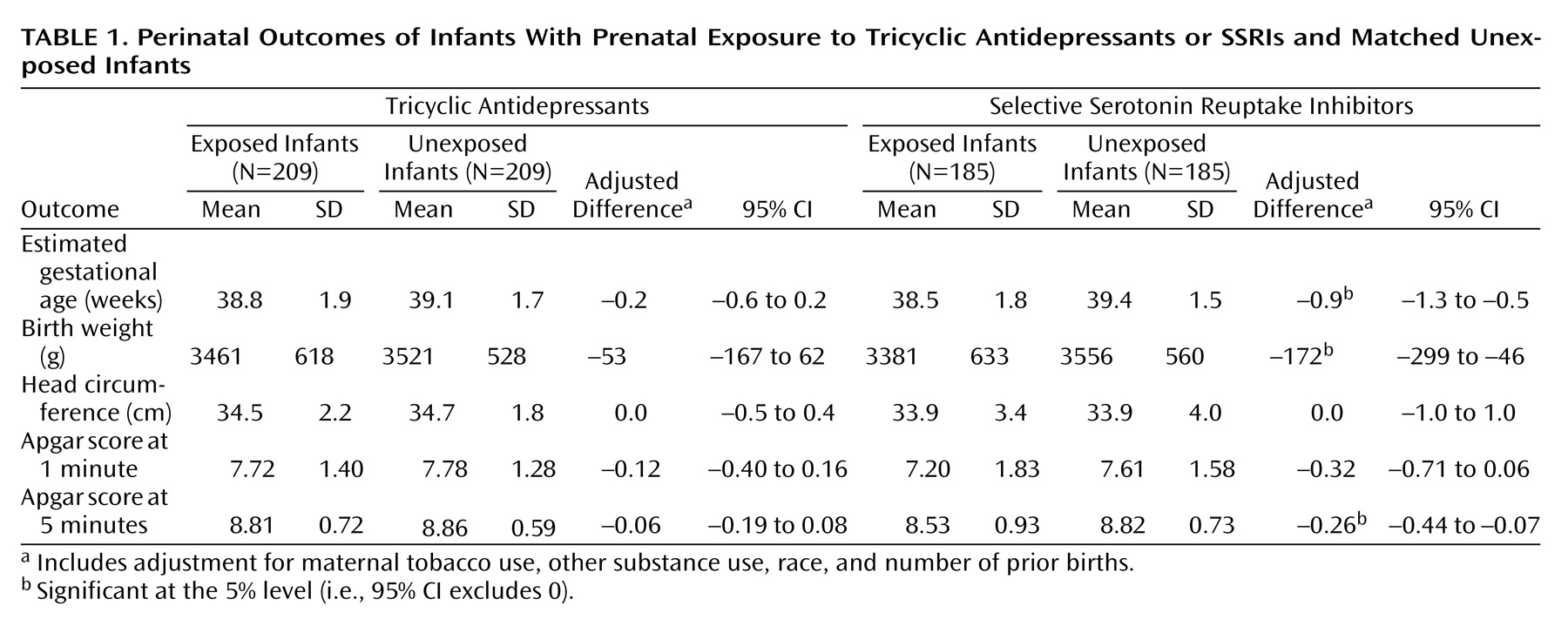
Perinatal outcomes are shown in
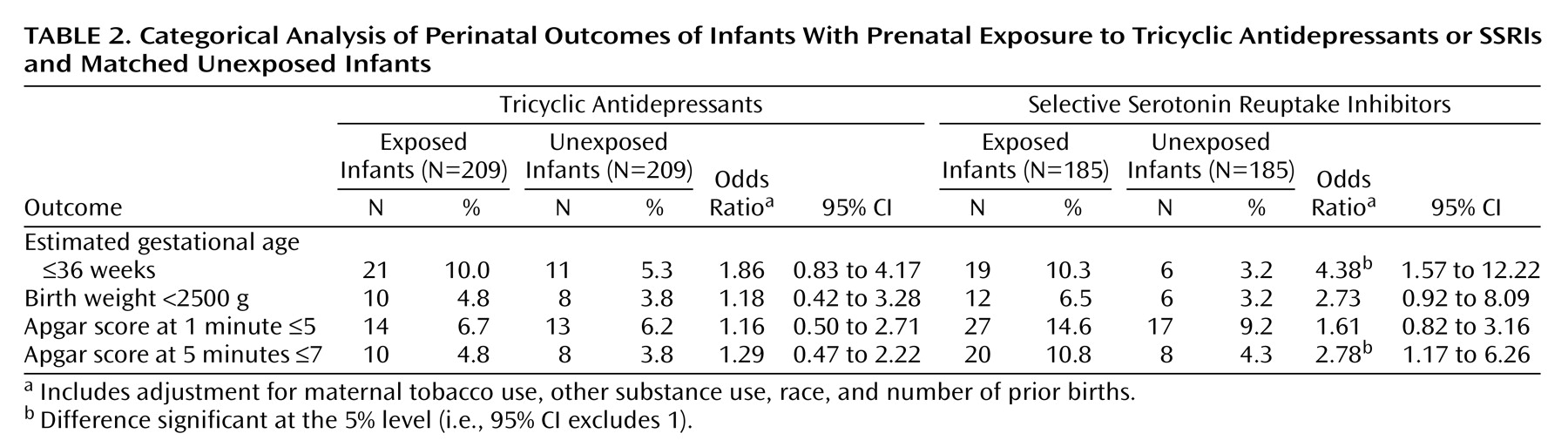
Table 1. For the tricyclic antidepressant group, exposed and unexposed infants did not differ significantly in estimated gestational age, birth weight, head circumference, or Apgar scores. No differences were observed in weight or head circumference at any point from birth to age 2 (data not shown). For the SSRI group, gestational age, birth weight, and Apgar scores were all significantly lower in the exposed group. Significant differences in weight were also observed at the 2-month and 4-month visits, but no significant differences were seen at 6 months or beyond (data not shown). Categorical analyses of perinatal outcomes are shown in
Table 2. In the SSRI group, exposed infants were significantly more likely to be born prematurely (i.e., at an estimated gestational age of 36 weeks or less) and to have 5-minute Apgar scores of 7 or lower. Because any differences in birth weights or Apgar scores might be explained by different rates of premature delivery, secondary analyses compared these outcomes after adjustment for gestational age. After this adjustment, infants who were exposed and unexposed to SSRIs did not differ significantly in mean birth weights (adjusted difference=–37 g, 95% confidence interval [CI]=–151 to 77) or 5-minute Apgar scores (adjusted difference=–0.18, 95% CI=–0.39 to 0.03).
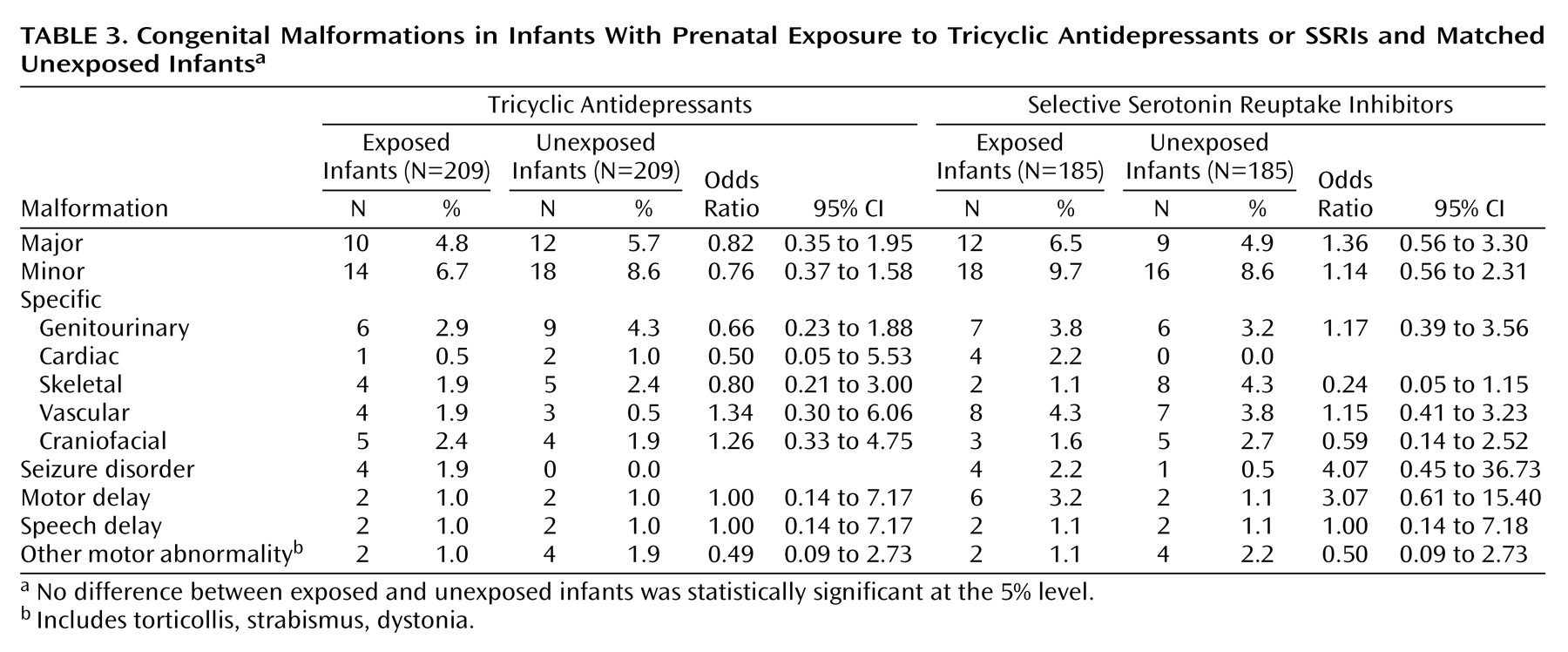
As shown in
Table 3, no significant differences were seen between exposed and unexposed infants in rates of major malformation, minor malformation, specific malformation, developmental delay, or other neurological disorder in either the tricyclic antidepressant or SSRI groups.
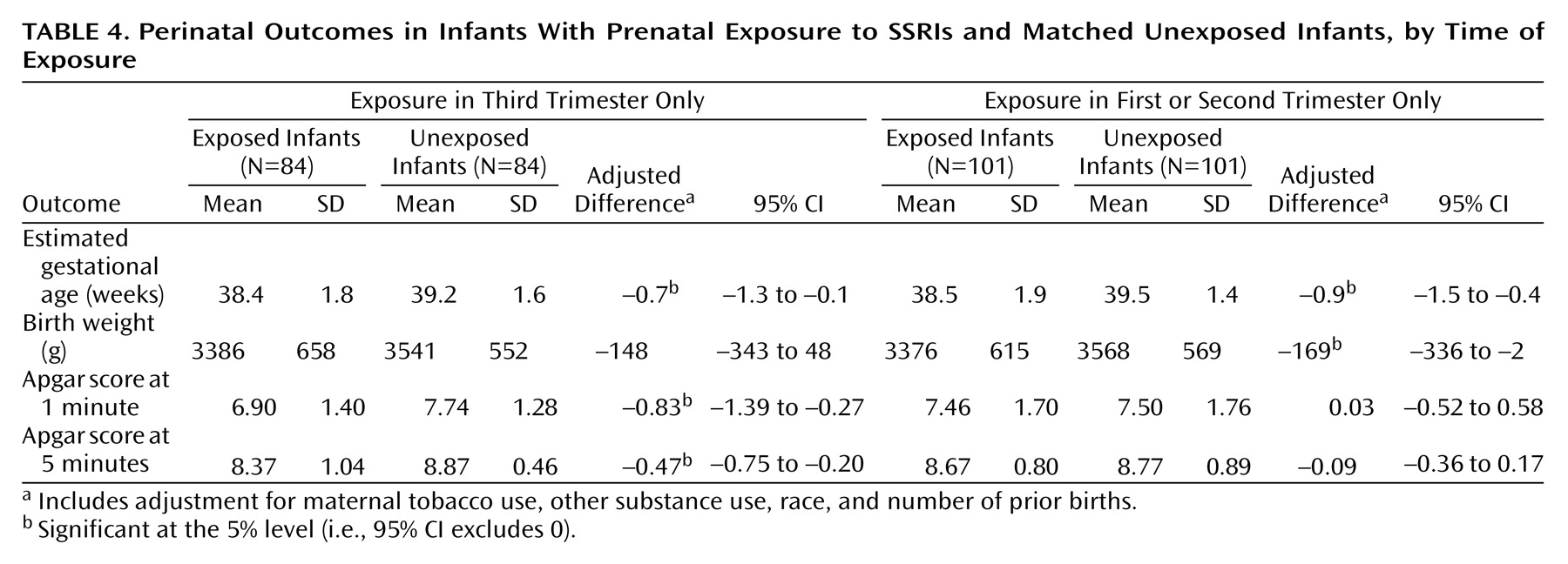
Given previous findings regarding early versus late pregnancy exposure
(9), the final set of primary (a priori) analyses compared perinatal outcomes stratified by timing of exposure (third-trimester exposure versus exposure limited to the first or second trimester). For the SSRI group (
Table 4), differences in gestational age and birth weight were seen in both subgroups (with third-trimester exposure and exposure limited to the first or second trimester only). In contrast, the association between SSRI exposure and lower Apgar scores was confined to the subgroup with third-trimester exposure. Analyses for the tricyclic antidepressant group (not shown) found no significant differences in gestational age or birth weight in the groups with early or late exposure. Apgar scores were slightly (but not significantly) lower among infants with third-trimester tricyclic antidepressant exposure than among those who were unexposed.
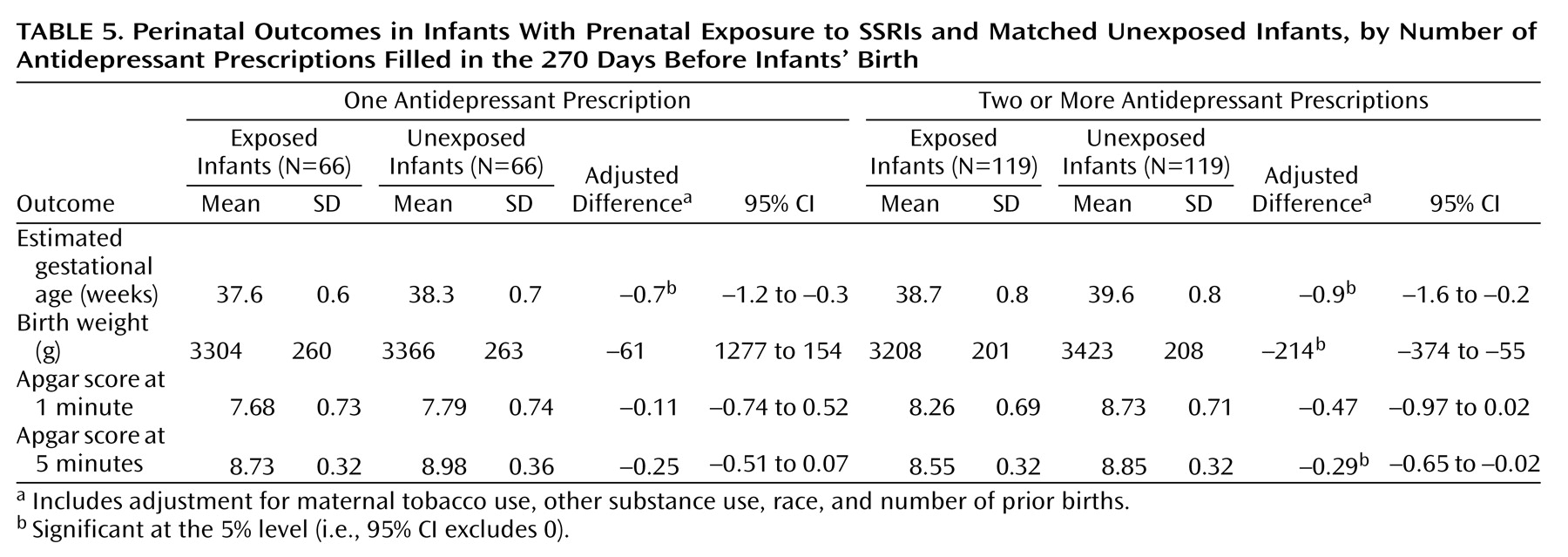
Secondary analyses examined subgroups defined by level of antidepressant exposure or by exposure to individual drugs.
Table 5 shows the results for the SSRI group subdivided by the number of antidepressant prescriptions filled (one versus two or more). In general, the differences were clearer for the subgroup that filled two or more prescriptions, but the differences in gestational age remained significant even in the subgroup that filled only a single prescription. Analyses of perinatal outcomes stratified according to specific SSRI drugs yielded generally similar results for fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine, although subgroups were too small for detection of drug-specific effects. Exclusion of all twins (five in the tricyclic antidepressant group, four in the SSRI group) and of infants exposed to more than one antidepressant (five in the SSRI group, none in the tricyclic antidepressant group) yielded essentially identical results.
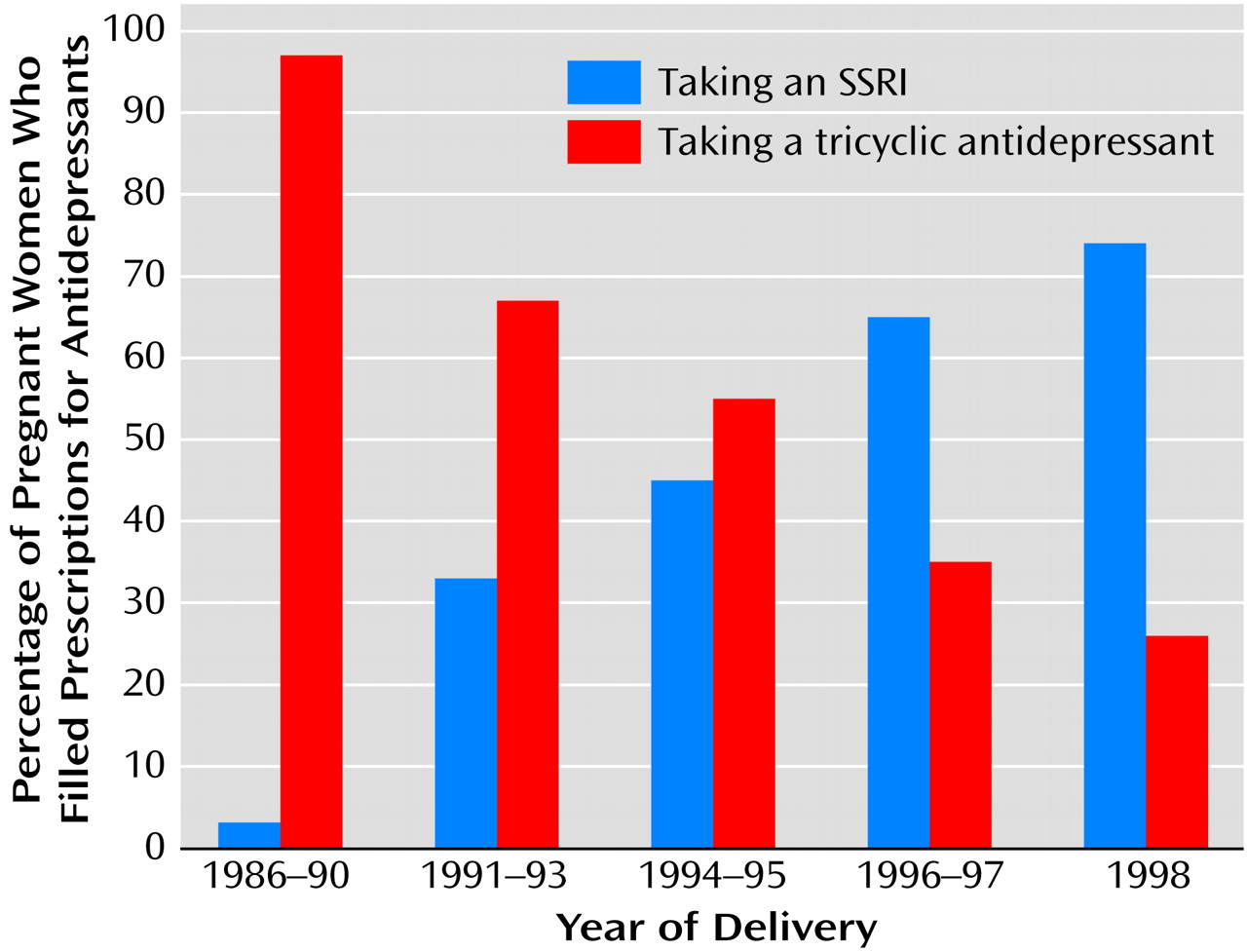
The finding of differential effects on perinatal outcomes for exposure to SSRI and tricyclic antidepressants suggests the possibility of confounding by indication (i.e., different classes of drugs prescribed to different types of patients). This was examined by reviewing predictors of SSRI exposure versus tricyclic antidepressant exposure within the exposed group. Medication selection was not significantly related to prior psychiatric treatment history, maternal age, maternal tobacco use, or other maternal substance use. As shown in
Figure 1, however, medication selection was strongly related to year of delivery (for linear trend, χ
2=84.1, df=1, p<0.001).
Discussion
Consistent with previous research, we found no association between SSRI exposure and congenital malformation or developmental delay in infants. We also found no evidence for teratogenicity of tricyclic antidepressants, a question not addressed by previous controlled studies. Most important, these findings more clearly establish a specific association between premature delivery and SSRI exposure at any point during pregnancy as well as an association between lower Apgar scores and late pregnancy exposure to SSRIs.
The design of this study incorporates elements intended to address the shortcomings of previous research. First, exposed and unexposed infants were systematically selected from a defined population, thus avoiding possible biases due to self-identification of exposure. Second, we attempted to match exposed and unexposed infants for factors associated with gestational age, low birth weight, malformation, or developmental delay, including maternal history of depression, maternal age, and year of delivery. Third, data collection and primary data analyses were completed without knowledge of exposure status. We suspect that most examining physicians were also unaware of prenatal exposure, but we have no specific documentation of this knowledge.
Despite these strengths, we must acknowledge several significant limitations of this study. First, pharmacy records indicate drug dispensing rather than actual use. Misclassification of drug exposure (i.e., medication dispensed but not taken) would reduce the likelihood of detecting true effects. Second, we relied on routinely collected clinical data rather than specific examinations for malformation or developmental delay. Examinations at outpatient pediatric visits are relatively crude screening measures. Use of these data may reduce bias in ascertainment of malformation or developmental delay, but it sacrifices sensitivity by limiting our analyses to abnormalities detected during routine medical care. Third, we sampled live births rather than pregnancies, so we were unable to examine the risk of spontaneous abortion. Fourth, a 270-day period to define pregnancy exposure may lead to some misclassification in instances of premature delivery (i.e., in which the gestation period was significantly shorter than 270 days). Any such misclassification could have biased our analyses of premature delivery and antidepressant exposure in the first trimester but would not have explained the association between premature delivery and exposure in the second or third trimester. Fifth, we have no data on antidepressant exposure during breast-feeding or other postnatal exposures, which might influence rates of developmental delay or early childhood neurological illness. Finally, marginally significant results should be interpreted cautiously, given the large number of comparisons performed.
We should also acknowledge that our matching for depression treatment history may not have completely accounted for differences between exposed and unexposed infants in risk factors for poor perinatal outcomes, such as severity of maternal depression or other psychiatric disorders
(19–
21). Women using antidepressants during the index pregnancy (our exposed group) may have been more severely depressed at the time than were women with identical treatment histories who were not currently treated (our unexposed group). Such a bias, however, should have had the same effect on the results for the two drug classes (SSRIs and tricyclic antidepressants) and would not have been consistent with a specific effect of SSRI exposure. Furthermore, the relative proportion of SSRI versus tricyclic antidepressant use among pregnant women was strongly related to year of delivery, suggesting that choice of drug class reflected time trends in prescribing rather than maternal clinical characteristics (i.e., confounding by indication). In addition, SSRI antidepressants may have been prescribed more often for anxiety disorders, while tricyclic antidepressant drugs may have been more often used for pain or insomnia. Indications for antidepressant use may have also changed over time. We would not, however, expect a difference in indications between exposed and unexposed mothers within the tricyclic antidepressant or SSRI groups.
While we found no association between antidepressant exposure and malformation or developmental delay, we cannot exclude the presence of modestly greater risk. As shown by the confidence intervals in
Table 2 and
Table 3, we can exclude from concern twofold differences in rates of minor or major malformations, but we cannot exclude five- or tenfold differences in rare outcomes, such as specific malformations. Our findings, however, add to those of previous studies in finding no detectable effect of antidepressant exposure on overall rates of malformation or developmental delay.
We found an association between SSRI exposure and lower gestational age with a consequent effect on birth weight. For both measures, significant differences were seen in the SSRI group but not in the tricyclic antidepressant group, suggesting a specific effect of SSRI exposure rather than a confounding effect of maternal depression. Effects on gestational age and birth weight were not limited to the infants exposed late in pregnancy. A similar finding was reported by Pastuszak et al.
(10) and Ericson et al.
(18), while Chambers et al.
(9) found that only third-trimester fluoxetine exposure was associated with a greater risk of premature delivery. An effect of early exposure on premature delivery raises the possibility of antidepressant effects on development or maintenance of the maternal-fetal interface. Human placental tissue contains both norepinephrine
(24) and serotonin
(25,
26) transporters—the presumed sites of action of antidepressant drugs. Such a mechanism, however, would not account for a specific effect of SSRI antidepressants.
Effects of SSRI exposure on Apgar scores were entirely attributable to third-trimester exposure, and infants with third-trimester tricyclic antidepressant exposure showed lower (but not statistically significant) Apgar scores. These findings are consistent with the report by Chambers et al.
(9) of neonatal complications after third-trimester fluoxetine exposure and suggest a direct effect of exposure near the time of delivery. Several case reports
(27–
31) have described transient neonatal toxicity or withdrawal among infants exposed to tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs late in pregnancy.
Our results cannot resolve all questions regarding the safety of antidepressant use during pregnancy, but they do provide additional information to women facing a complex decision. We found no evidence that tricyclic antidepressant or SSRI exposure is associated with congenital malformation or developmental delay. Taken together with previous studies, our findings offer additional reassurance in these areas. Exposure to SSRI antidepressants late in pregnancy was associated with lower Apgar scores, although the long-term clinical impact of this difference is not clear. While any effect of late pregnancy exposure might be avoided by tapering antidepressants during the third trimester, patients and physicians considering such a decision should consider the high risk of depression during the postpartum period. Finally, SSRI exposure at any time in pregnancy was associated with a twofold increase in premature delivery, but the absolute risk was still only 10%. Women considering use of SSRI antidepressants during pregnancy may weigh any greater risk of premature delivery against the risk of persistent or recurrent depression and the availability and acceptability of alternative treatments.