Antipsychotic medications are the primary pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia. They are effective for ameliorating positive symptoms and reducing relapse risk. However, they have limited efficacy for negative symptoms and cognitive impairments. The development of effective treatments for these psychopathological domains is of critical clinical importance, since they account for much of the long-term morbidity and poor functional outcome in schizophrenia
(1 –
6) . The relative lack of efficacy for these domains has led to the search for alternative pathophysiological hypotheses and treatments of negative symptoms and cognitive impairments. The most compelling hypothesis involves the glutamatergic system and
N -methyl-
d -aspartate (NMDA) glutamatergic receptor hypofunction
(7 –
10) .
The hypoglutamatergic hypothesis is largely based on the pharmacology and behavioral effects of phencyclidine and ketamine
(7,
11 –
14) . These agents bind to a site within the NMDA receptor channel and block cation flow through the channel. Behavioral effects include positive and negative symptoms and cognitive impairments. The hypoglutamatergic hypothesis is further supported by magnetic resonance spectroscopy, postmortem, and gene association and expression data suggesting alterations in glutamate metabolites and receptors in schizophrenia
(15) .
The hypoglutamatergic hypothesis predicts a therapeutic effect for compounds that increase NMDA receptor transmission. Heresco-Levy et al. conducted several small sample studies with glycine, an obligatory cotransmitter with glutamate at the NMDA receptor. Glycine 0.8 g/kg/day was the most effective dose, with an average reduction in negative symptom scores of 30% among subjects receiving glycine and 2% among subjects receiving placebo
(16 –
18) . The negative symptom improvement was more robust than that observed with positive symptoms and did not appear to be explained by improvement in depressive or extrapyramidal symptoms. The hypothesis that negative symptoms were the primary therapeutic target was supported in a post hoc analysis, which demonstrated a slightly better response in patients with primary negative or deficit symptoms relative to patients with secondary negative symptoms
(19) . These studies did not include formal measures of cognition.
Another approach is to use a partial agonist:
d -cycloserine. In a dose-finding study, Goff et al. found an inverted-U dose response curve, with maximum therapeutic efficacy at 50 mg/day and loss of efficacy with doses below 50 mg/day or above 100 mg/day
(20) . In subsequent studies, positive results have been observed in patients who received
d -cycloserine (50–100 mg/day) and who were treated with conventional antipsychotics
(21,
22) . Negative results have been observed when patients were treated with doses other than 50 mg/day or when
d -cycloserine was added to clozapine
(23 –
26) . Goff et al. also found that the observed therapeutic effect was mainly on negative symptoms, including patients with deficit or primary negative symptoms. One study used the Sternberg working memory paradigm and reported a benefit for
d -cycloserine
(21) .
Interest in glycine-modulated therapeutic effects has been reinforced by recent studies of two other glycine site agonists (
d -serine and
d -alanine) and a glycine reuptake inhibitor (sarcosine)
(27 –
30) . These studies reported significant benefits for negative symptoms but also for psychotic and depressive symptoms. The latter finding is consistent with the ability of NMDA antagonists, such as phencyclidine to induce positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia but argues against a unique primary negative symptom effect. There is one negative
d -serine study in patients treated with clozapine
(31,
32) .
Method
CONSIST was a multicenter 16-week double-blind, double-dummy, parallel group, randomized clinical trial of adjunctive glycine, d -cycloserine, or placebo for the treatment of negative symptoms and cognitive impairments. It was conducted at four sites in the United States and one site in Israel. The protocol was approved by institutional review boards at each participating site and a central Data and Safety Monitoring Board. The Data and Safety Monitoring Board also conducted periodic reviews of subject safety, including adverse events, and one interim review of cumulative extrapyramidal symptoms and neuropsychological data for evidence of potential neurotoxicity.
Subjects
Eligible subjects were between the ages of 18 and 64 and met DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, based on a best-estimate diagnosis that utilized a structured diagnostic interview (Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV
[33] ), family informants, and medical records. Inpatients and outpatients were included. Two sites (NKI and Israel) recruited exclusively inpatients, while all but one patient at the other three sites (Zucker Hillside, Maryland Psychiatric Research Center, and UCLA) were outpatients. Subjects met retrospective and prospective criteria for persistent moderate to severe negative symptoms. The retrospective determination of persistence was based on the best-estimate diagnosis and/or therapist report. The prospective definition of persistence used negative symptom assessments completed at the beginning and end of the 4-week evaluation phase. A Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms
(34) (SANS) total score ≥20 or SANS affective flattening or alogia subscales global item score ≥3 (i.e., moderate) was required. There was no cognitive impairment inclusion criterion. In order to select a subject cohort with persistent negative symptoms, enriched for primary negative symptoms, and to minimize potential improvement in negative symptoms or cognition secondary to improvement in severe or unstable positive and depressive symptoms or extrapyramidal symptoms, subjects were required to have a Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale
(35) positive symptom item (conceptual disorganization, hallucinations, suspiciousness, and unusual thought content) total score ≤18, a Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale anxiety/depression factor (somatic concerns, anxiety, guilt, and depression) total score ≤14, and a Simpson-Angus Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale
(36) total score ≤8. These symptom domains were stable by history at study onset and confirmed stable during the 4-week evaluation period. Subjects were excluded if they had a DSM-IV alcohol or substance dependence diagnosis (within the last 6 months); an alcohol or substance abuse diagnosis (within the last month); an organic brain disorder; or a medical condition in which pathology or treatment could alter the presentation or treatment of schizophrenia, including active tuberculosis or tuberculosis treatment, kidney stones, and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Subjects could receive any antipsychotic except clozapine. Subjects treated with clozapine were excluded because of reported adverse effects of
d -cycloserine in clozapine-treated subjects
(23 –
26) . Subjects were also allowed to remain on concomitant anticholinergic, beta-blocker, mood stabilizer, antidepressant, antianxiety, or anticonvulsant medication regimens. They were required to receive stable doses of these medications during the evaluation and double-blind study phases. Female subjects were required not to be pregnant and to use a documented method of contraception. Monthly pregnancy tests were performed during study treatment.
Subjects who met preliminary screening criteria based on clinician referral underwent an informed consent process and provided written informed consent before performing any study assessments. Subject ability to provide valid informed consent was documented using site-specific procedures.
Clinical Assessments
The Schedule for the Deficit Syndrome
(37) was used to categorize subjects into deficit and nondeficit subgroups. A modified version of the SANS was used to assess negative symptoms as follows: the affective flattening subscale items were rated following published criteria; the alogia subscale items were rated as published, but poverty of content of speech was not included in the subscale total score; the avolition/apathy subscale was expanded by rating impersistence in work or school as two items (level and quality of role function); the asociality/anhedonia subscale was modified to directly rate anhedonia and asociality rather than rating recreational activities and relationships with friends and peers; and the attention subscale was not included. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale positive symptom items and the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale anxiety/depression factor were used to assess positive and affective symptoms, respectively. The Clinical Global Impression (CGI) severity of illness item was used to assess global severity. Master’s- and doctoral-level clinicians conducted the clinical assessments. Assessments were completed at the beginning and end of the 4-week evaluation phase and at weeks 4, 8, 12, and 16 of the double-blind phase. The Simpson-Angus Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale and the Abnormal Involuntary Movements Scale
(38) were used to assess extrapyramidal symptoms and dyskinetic movements, respectively. The Side Effect Checklist, consisting of 22 common side effects rated on a 1 (none) to 4 (severe) scale, was used to assess adverse effects. Vital signs and weight were measured at all assessment points.
To the extent possible, each participant was assessed by the same rater throughout the course of the study. All raters were blind to treatment assignment and deficit/nondeficit categorization.
Blood and urine laboratory tests were collected at the beginning and end of the double-blind phase. Glycine and
d -cycloserine plasma levels were assessed at weeks 0, 4, 8, and 16 of the double-blind phase. Antipsychotic doses were converted to haloperidol equivalents
(39) .
Rater Training and Interrater Reliability
Interrater agreement (intraclass correlation coefficient [ICC] was assessed using a standard set of tapes. The SANS total score ICC was 0.71, and subscale total score ICCs were 0.64 (alogia and anhedonia), 0.80 (avolition), and 0.81 (affective blunting). The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale positive symptom items and anxiety/depression factor ICCs were ≥0.80. Simpson-Angus Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale and Abnormal Involuntary Movements Scale raters underwent common training in the administration and scoring of the instruments and were reliable within each site. Schedule for the Deficit Syndrome raters participated in a day-long workshop and subsequently participated in monthly conference calls to maintain interrater reliability.
Neuropsychological Battery
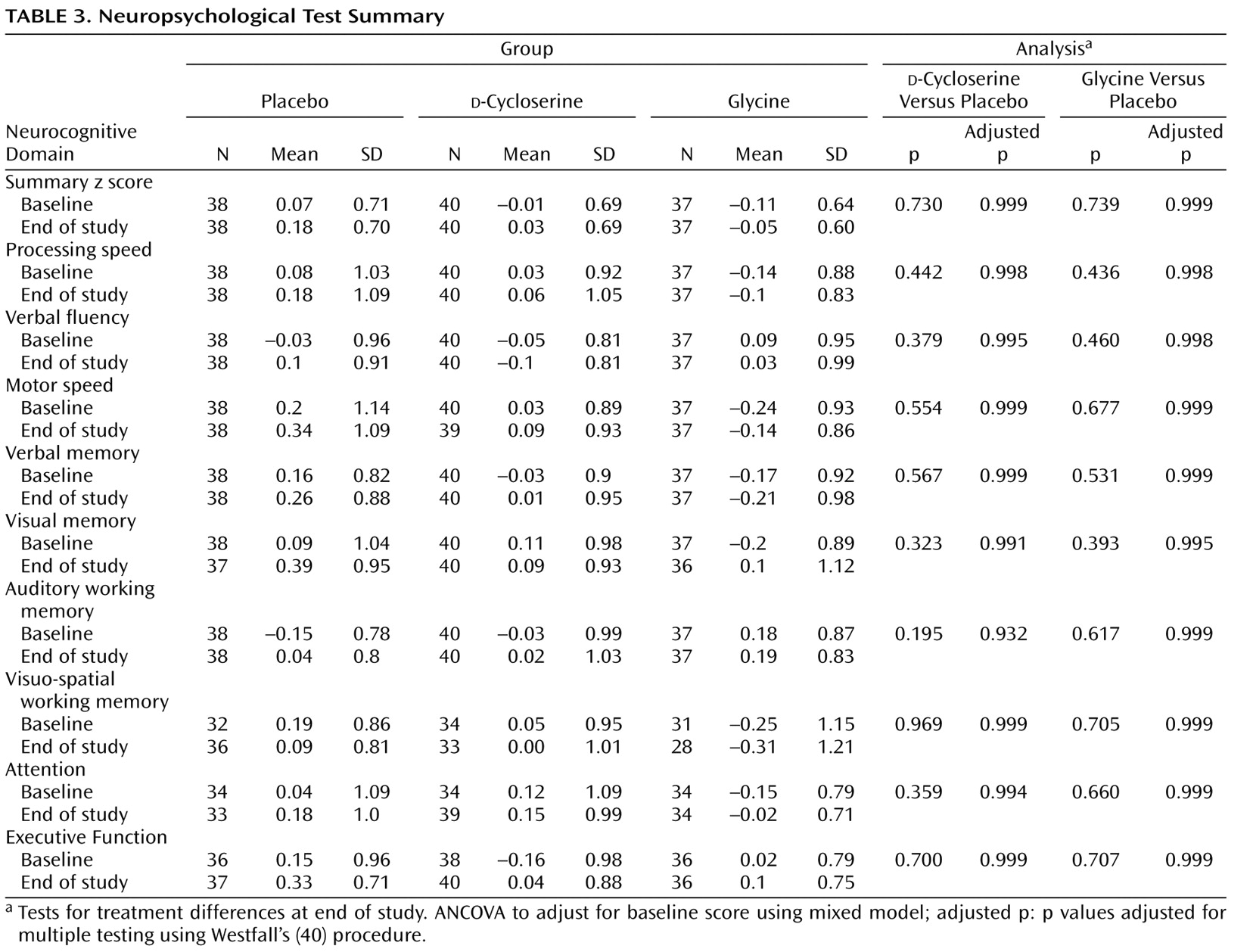
Subjects were administered a neuropsychological battery at baseline and at the end of the 16-week double-blind phase. The battery could not be completely administered at the Israeli site because of language issues. Therefore, only neuropsychological data from the four U.S. sites were used in the analyses. Neuropsychological tests were grouped into the following domains: processing speed, verbal fluency, motor speed, vigilance, auditory memory, visual spatial memory, auditory working memory, visual spatial working memory, and executive function. ICCs for summary scores for each domain ranged from 0.59 to 0.93. (For a detailed list of tests in each domain and achieved domain ICCs, see the table in the data supplement accompanying the online version of this article.)
Study Design
Subjects who met retrospective and prospective criteria for persistent, moderate to severe negative symptoms were randomly assigned to one of three treatment regimens: active glycine and placebo d -cycloserine, placebo glycine and active d -cycloserine, or placebo glycine and placebo d -cycloserine. Glycine dose was titrated over the first 2 weeks from 15 g/day to the target dose of 60 g/day. Glycine and placebo glycine were administered dissolved in water. For 7 days, d -cycloserine was administered at 25 mg/day, increased to 50 mg/day on day 8, and maintained at that dose thereafter unless the subject was unable to tolerate the prescribed dose. Dose was based on prior studies suggesting efficacy. In the event of adverse reactions, the dose could be lowered or titration slowed.
Study treatment adherence was assessed by a pill count and medication review at the biweekly visits. In addition, all subjects had an adherence plan that included medication checks by family, residence staff, or mental health care providers who had extensive contact with the subjects. All subjects who were judged to have received 75% or more of their assigned study medication were considered adherent. A subject could be withdrawn from the study if they met a priori criteria for clinically significant symptom exacerbation.
Statistical Analyses
Treatment assignment was random and used a permuted block design with randomly varying block sizes, stratified within site, deficit/nondeficit categorization, and antipsychotic regimen (conventional antipsychotics only versus at least one second-generation antipsychotic). Because of pharmacy error, one subject assigned to placebo received d -cycloserine throughout the study and one placebo subject received open-label d -cycloserine before final double-blind assessments were completed. Statistical analyses revealed virtually identical results, whether the two subjects were treated “as randomized” or the first of these subjects was treated as assigned to d -cycloserine rather than placebo and the final visit for the second subject was dropped. The results of the latter analysis are presented in this article.
Negative Symptoms
A mixed-model analysis of variance for unbalanced repeated measures was used to test for group differences in the average “rate of change” (slope) of SANS total scores over time. All subjects with postbaseline SANS ratings were included. The SANS total score was divided by the number of items rated to obtain a measure of average negative symptom severity. The two SANS evaluation phase assessments were averaged for the baseline SANS score. An overall test for differences in slopes among the three treatments at alpha=0.05 was followed up by pairwise tests of glycine or d -cycloserine versus placebo. A priori hypotheses tested with appropriate interaction terms were that treatment effects would be moderated by deficit/nondeficit categorization, type of antipsychotic medication, and site. Nonsignificant interaction terms with these moderators were dropped from the final model. Significant interactions of treatment with prespecified moderators were followed by exploratory analysis to clarify these effects. Comparable analyses were conducted for Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale total, positive symptom, and anxiety/depression factor scores and CGI ratings.
Neurocognition
Individual test raw scores at baseline and end of study were converted to z scores relative to the overall baseline mean and standard deviation. If necessary, z scores were multiplied by –1 so that higher z scores represented better performance. Z scores were averaged within nine cognitive domains. Test reliability was computed by calculating ICCs of baseline and follow-up measurements within the placebo group. The Delayed Match to Sample Test was dropped because of an unacceptably low ICC (0.31 [
Table 1 ]).
The primary outcome analysis used a mixed model for repeated measures analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) to calculate the average (across cognitive domains) difference between glycine and placebo or
d -cycloserine and placebo in baseline-adjusted z scores. In addition, baseline-adjusted endpoint z scores were compared for each cognitive domain, at overall alpha=0.05, with Westfall’s multiple testing procedure
(40,
41) . ANCOVA with treatment-by-moderator interaction terms was used to examine treatment interactions with site, deficit versus nondeficit schizophrenia, and conventional versus second-generation antipsychotic treatment.
Analysis of Adverse Effects
Differences in tendencies between experimental treatments and placebo in Simpson-Angus Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale and Abnormal Involuntary Movements Scale scores were assessed using a rank test for differences in the correlation between these scores and the study visit (42). Chi-square tests (or Fisher’s exact tests for rare outcomes) were used for pairwise comparisons of glycine versus placebo or d -cycloserine versus placebo on the frequency of new onset or worsened severity (most severe rating during follow-up) adverse effects.
Results
Subject Characterization and Treatment Implementation
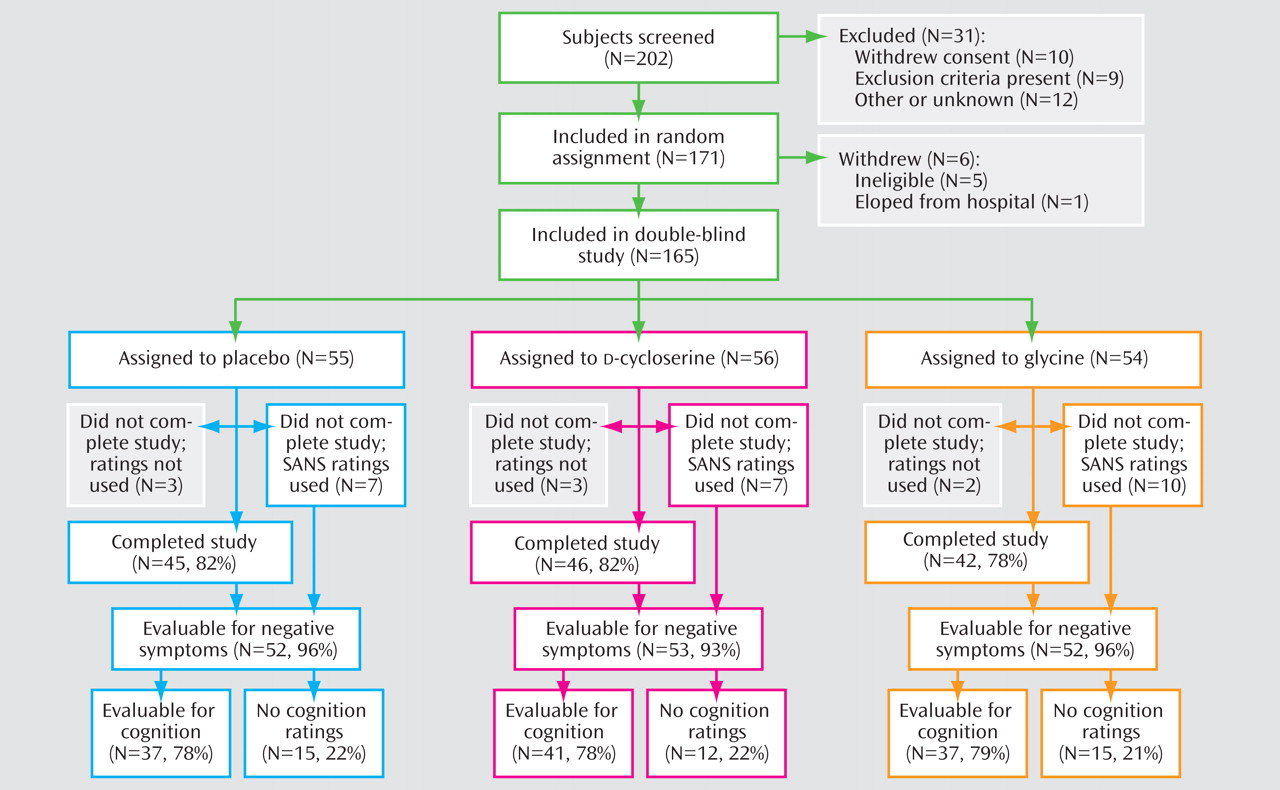
Subject flow through the study is summarized in
Figure 1 . Reasons for early termination included deterioration of psychiatric condition (placebo: two subjects;
d -cycloserine: three subjects; glycine: one subject), noncompliance (placebo: two subjects), side effects of the study medication (placebo: two subjects;
d -cycloserine: two subjects; glycine: five subjects), unrelated medical reason (placebo: three subjects; glycine: one subject), subject request (
d -cycloserine: four subjects; glycine: three subjects), and other (placebo: one subject,
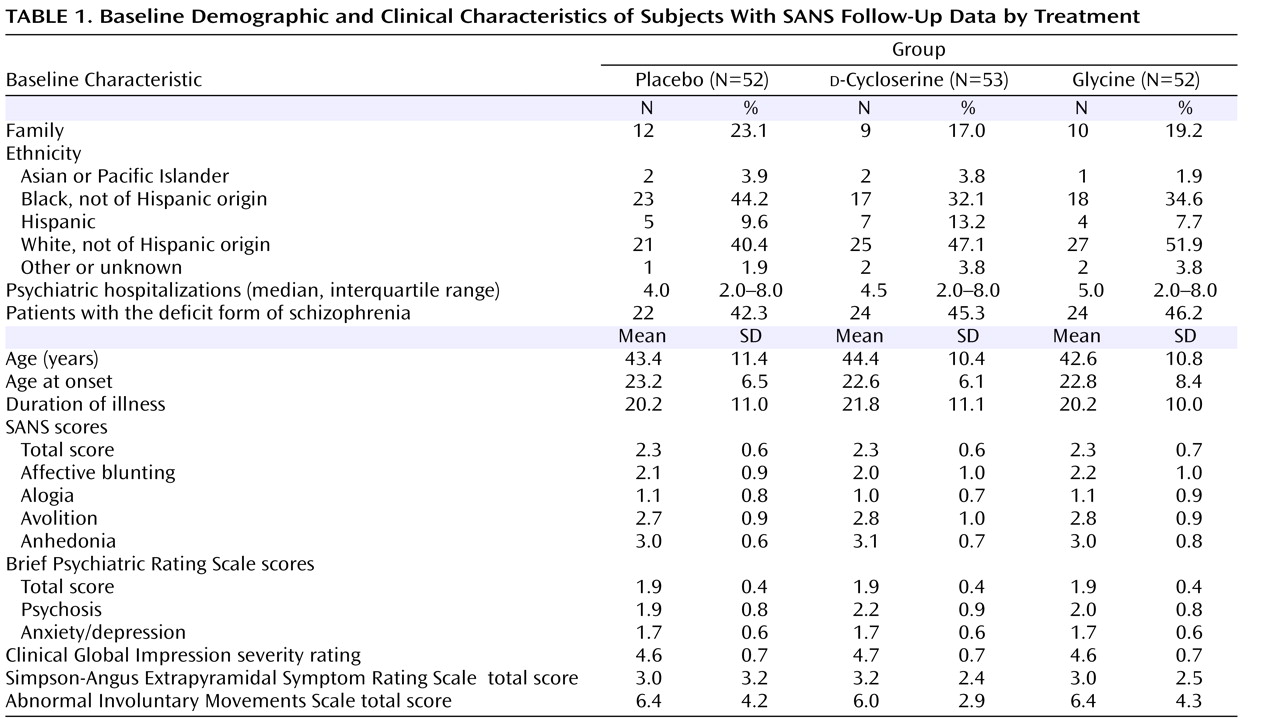
d -cycloserine: one subject, glycine: two subjects). Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics are presented in
Table 1 as well as the data supplement accompanying the online version of this article. Antipsychotic and concomitant psychotropic medications are also presented in the online data supplement.
Treatment Adherence
Compliance with prescribed medication was 90%–100%. At week 16, 78% of glycine subjects and 85% of d -cycloserine subjects were receiving the target dose. The baseline median plasma glycine levels were 182 mmol/liter in the placebo group, 195 mmol/liter in the d -cycloserine group, and 182 mmol/liter in the glycine group. In patients randomly assigned to glycine, the median (interquartile range) increase in plasma glycine was 372 mmol/liter (range=208–620), 237 mmol/liter (range=127–237), and 233 mmol/liter (range=61–453) at weeks 4, 8, and 16, respectively. The median (interquartile range) attained plasma glycine levels were 531 mmol/liter (range=339–869), 432 mmol/liter (range=263–764), and 408 mmol/liter (range=257–845) at weeks 4, 8, and 16, respectively. Plasma serine levels showed a median increase of 105 mmol/liter, 9 mmol/liter, and 85 mmol/liter at weeks 4, 8, and 16, respectively; no significant changes were seen in glutamate or glutamic acid levels. Median increases in glycine and serine were near zero among subjects assigned to d -cycloserine or placebo. In the d -cycloserine group, the median (interquartile range) attained plasma d -cycloserine levels for observed cases were 0.80 mg/dl (range=0.60–1.20) at weeks 4 and 8 and 0.75 mg/dl (range=0.50–1.00) at week 16.
Negative Symptoms
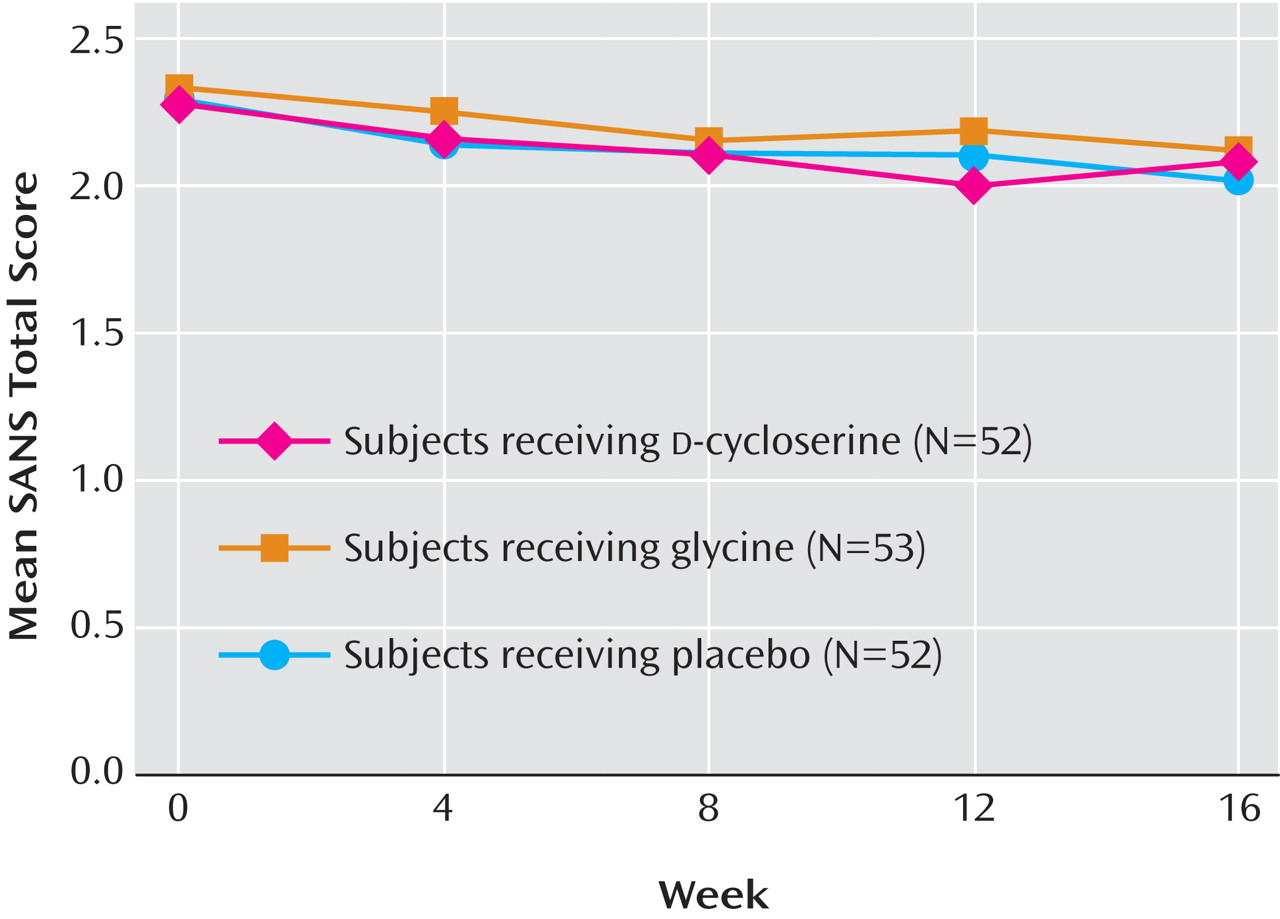
There were no significant SANS total score differences between glycine and placebo subjects (t=0.99, df=550, p=0.32) or
d -cycloserine and placebo subjects (t=0.57, df=550, p=0.57) (
Figure 2 ). At week 16, there were no significant differences in the number of subjects who had a 20% or more reduction in the SANS total score. Twelve out of 43 (28%) placebo subjects met this criterion compared with 11 out of 45 (24%)
d -cycloserine subjects and 11 out of 46 (24%) glycine subjects (p=0.88). The number of responders across groups was also similar at earlier weeks.
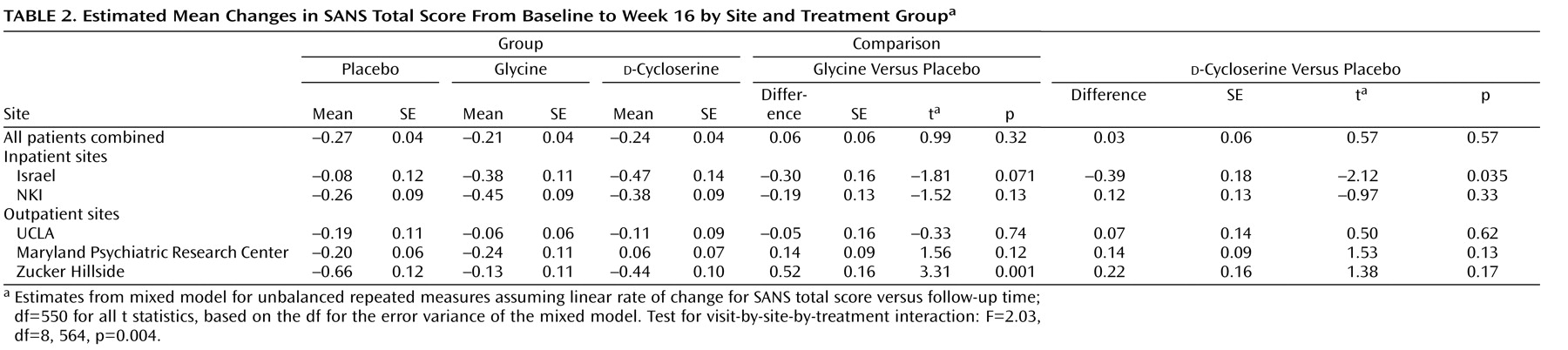
Site Effects
The prespecified test for the site-by-treatment-by-time interaction was significant (F=2.52, df=8, 562, p=0.011). Post hoc tests found one site with significantly greater reduction in the SANS total score for
d -cycloserine patients relative to placebo patients (t=2.12, df=550, p=0.035), while a second site showed significantly greater reduction for placebo patients relative to glycine patients (t=3.31, df=550, p=0.001) (
Table 2 ). Hypotheses accounting for these site differences—medication adherence, unblinding because of side effects, differences in antipsychotic regimens, or differences in negative symptom severity—were not supported by the CONSIST data (see the online data supplement). The other clinical and demographic variables that significantly differed across sites were age of first episode and gender. The inclusion of these variables did not affect the site-by-treatment-by-time interaction.
Antipsychotic Effects
A prespecified test was performed to evaluate the effect of conventional antipsychotics and second-generation antipsychotics on treatment effects. The time-by-treatment-by-type of antipsychotic interaction was statistically significant (F=4.13, df=2, 546, p=0.016), indicating that active treatment/placebo differences in the rate of SANS total score change depended on the type of antipsychotic. Post hoc analyses of the interaction found that among subjects receiving conventional antipsychotics, the eight subjects randomly assigned to glycine had a larger decrease in the SANS total score relative to the seven subjects randomly assigned to placebo (difference in estimated 16-week change: –0.42 [SE=0.15]; t=2.67, p=0.008). In contrast, subjects assigned to glycine in the second-generation antipsychotic stratum improved slightly less than placebo subjects (p=0.14). No statistically significant effects were found for d -cycloserine subjects in either antipsychotic medication group. In view of the baseline imbalances in prescribed second-generation antipsychotics, further exploratory analyses were conducted to compare treatment effects among subjects treated with olanzapine monotherapy, risperidone monotherapy, or polypharmacy with a conventional and second-generation antipsychotic. Glycine and d -cycloserine did not show greater negative symptom reduction than placebo in any of these antipsychotic medication groups (see the table in the online data supplement).
Deficit Status
There was no evidence that the time course of treatment effects differed in deficit versus nondeficit subjects (interaction F=0.04, df=2, 562, p=0.96).
Neurocognition
There were no significant differences between glycine and placebo on the composite cognition summary measure (adjusted average difference in z scores: –0.01 [SD=0.02]; df=112; t=–0.36, p=0.72). Two subjects in the
d -cycloserine group had extreme outlying values (z scores >7.0) on the visuospatial working memory measure. If these outliers were left in the analysis,
d -cycloserine subjects performed more poorly than subjects randomly assigned to placebo (baseline-adjusted difference in z statistics: –0.08 [SD=0.03]; t=2.44, df=112, p=0.032). With these subjects excluded, there was no significant difference between
d -cycloserine and placebo (baseline-adjusted average difference in z scores: –0.01 [SD=0.02]; t=–0.34, df=112, p=0.73). Because the use of a composite cognition score in the primary endpoint analysis could obscure a therapeutic effect on any one of the nine cognitive domains, we conducted pairwise comparisons for each domain. There were no significant glycine/placebo or
d -cycloserine/placebo differences (
Table 3 ).
Other Symptom Ratings
There were no significant treatment effects for Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale positive symptom item (F=0.19, df=2, 574, p=0.82) or Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale anxiety/depression factor (F=0.01, df=2, 578, p=0.99) scores; these results were not significantly different among sites and among deficit versus nondeficit subjects. CGI scores improved by 0.4 points in the placebo and glycine groups and by 0.2 points in the d -cycloserine group ( d -cycloserine versus placebo on difference in tendencies over time: F=8.12, df=1, 710, p=0.004).
Adverse Effects
New or worsened nausea was more frequent in glycine subjects (20/52 [38.5%]) versus placebo subjects (7/52 [13.5%]) (χ 2 =8.37, df=1, p=0.004). New or worsened complaints of dry mouth were also more common in glycine subjects (17/52 [32.7%]) compared with placebo subjects (7/52 [13.5%]) (χ 2 =5.36, df=1, p=0.021). The occurrence of side effects was not associated with treatment response (data not shown). There were no significant d -cycloserine/placebo side effect differences (all p values >0.12).
Simpson-Angus Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale and Abnormal Involuntary Movements Scale total scores were low at baseline and declined by similar amounts over the course of follow-up in all treatment groups (minimum p value=0.41 for treatment differences; data not shown).
Discussion
The study results suggest that neither glycine nor
d -cycloserine is superior to placebo for negative symptoms or cognitive impairments. The study conforms to designs advocated for primary negative symptom evaluation
(43,
44) and that address pseudospecificity in evaluating drug effects on cognition
(45) . The experiment-wide results are unequivocal, especially for cognition, but a site-by-treatment-by-time interaction for negative symptoms required further evaluation.
The site-specific negative symptom tendency differences suggested an inpatient versus outpatient treatment-effect difference. There are several possible explanations. First, study medication adherence may be better in inpatients than outpatients. However, adherence rates and mean and highest achieved d -cycloserine and glycine levels did not differ, and achieved plasma glycine levels were not associated with negative symptom response. Second, the higher inpatient baseline negative symptom levels may have increased the potential for improvement. However, baseline negative symptom ratings were lower or the same in inpatient responders versus nonresponders. Third, the estimated antipsychotic dose was higher at inpatient than outpatient sites; however, within each treatment group, negative symptom responders and nonresponders had similar average antipsychotic doses. Furthermore, the concern is that higher doses, especially of second-generation antipsychotics, might interfere with an efficacy signal. Fourth, closer observation of inpatients may introduce unwitting bias in efficacy ratings because of differential observation of known adverse effects, but their side effects and treatment response were not associated. It is possible that clinical factors other than those assessed in the current study underlie the site difference in treatment efficacy.
A major difference between CONSIST and previous studies was the high percentage of patients treated with second-generation antipsychotics. In previous studies, the negative symptom effect was more robust in subjects treated with conventional antipsychotics compared with second-generation antipsychotics
(46), although a glycine/placebo difference was observed in patients treated with olanzapine, risperidone, or clozapine
(16 –
19) . In CONSIST, negative symptom response was better than placebo for glycine but not
d -cycloserine among the small number of subjects treated with conventional antipsychotics.
The overall failure of the two experimental treatments to do better than placebo strongly refutes effectiveness hypotheses for patients with moderate to severe and persistent negative symptoms or with impaired cognition. However, a strict efficacy test would require that a therapeutic dose be delivered. In this regard, the CONSIST data do not support the efficacy hypothesis for d -cycloserine, since it was prescribed at the putative optimal dose, adherence was high, and trial length was adequate.
For glycine, an important qualification is necessary. In three previous studies, glycine dose adjusted for body weight was effective (i.e., 0.8 gm/kg/day in two studies [
17,
19 ]; 0.4gm/kg/day in one study
[47] ). In CONSIST, we aimed to use fixed doses of 60 g/day, which gave an average target dose of 0.7 g/kg/day. This dosing may have resulted in suboptimal glycine levels for heavier patients. Javitt et al. suggested plasma glycine level ≥600 mmol/liter as a threshold for potential efficacy
(48) . In CONSIST, the percentage of treatment responders was similar in glycine-treated subjects above and below the 600 mmol/liter threshold, and the overall correlation between plasma glycine concentration and negative symptom response was near zero. Further, the effect size favoring glycine in the Javitt et al. study
(47) dosed at 0.4gm/kg/day was similar to the overall effect size reported for all studies in a recent meta-analysis
(49) . Nevertheless, it is not known if efficacy would have been achieved at substantially higher serum glycine levels.
These results have straightforward implications for developing
d -cycloserine and glycine for the treatment of negative symptoms and/or cognition in schizophrenia. Partial agonists at the glycine site are not attractive therapeutic candidates. If the glycine site is near saturated, it is difficult to predict a sustained partial agonist benefit. Recent reports do not support
d -cycloserine efficacy
(26,
50) . Glycine administered systemically is problematic, since present formulations of the medication are not well tolerated. However, early studies of other agents, including
d -serine,
d -alanine, and sarcosine, targeting the glycine site have had positive results
(27 –
30), although these studies suggest a broad symptomatic response. The ability of
d -serine to cross the blood-brain barrier and exert either direct effects or conversion to glycine is a distinct advantage for drug delivery. A reuptake inhibitor would likewise have greater potential to increase agonist effect at the glycine site. It seems wise to explore these two approaches and to develop drug targets at other molecular sites in the glutamatergic system.