Although biological, psychological, social, and cultural factors all have a significant impact on the risk of suicide, over 90% of suicides in the United States are associated with psychiatric illness
(1 –
5) . The most common psychiatric diagnostic class associated with suicide is mood disorders, accounting for about 60% of all suicides
(1 –
6) . Most depressed persons who eventually commit suicide seek professional help within 1 month before death
(7) . However, most are not on antidepressant medication at the time of death
(8 –
10), which suggests that lack of treatment contributes to suicide risk and that more widespread antidepressant treatment might reduce suicide rates. At the same time, concerns have been raised about the potential of some medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and non-serotonergic-specific antidepressants (such as bupropion, mirtazapine, nefazodone, and venlafaxine), to increase the risk of suicide in mood disorders, especially in youths.
Taken as a whole, these ecological data on suicide rates suggest that a decrease in the number of prescriptions written for the newer antidepressants (SSRIs and non-serotonergic-specific antidepressants) will lead to an increase in the suicide rate. In this article, we examine the question of whether the public health warnings in the United States and Europe led to decreases in SSRI prescription rates for children and adolescents in the United States and the Netherlands and whether these decreases in prescription rates were associated with increases in suicide rates in children and adolescents.
Method
Annual U.S. antidepressant prescription rate data for 2003–2005, by zip code, were drawn from a random sample of 20,000 pharmacies (stratified by type, size, and region) from the 36,000 pharmacies in the IMS Health database (IMS Health, Plymouth Meeting, Pa.), which represents over half of all retail pharmacies in the continental United States. These data do not include hospital prescriptions. To provide an estimate of the magnitude of the contribution of hospital prescriptions, we used data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Evaluation Survey and the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Evaluation Survey to compute the ratio of hospital to nonhospital prescriptions for SSRIs by year. Hospital prescriptions for SSRIs ranged from a low of 11.0% in 2000 to a high of 12.8% in 2004, which suggests that the IMS Health data account for nearly 90% of U.S. SSRI prescriptions.
For each zip code, the total number of prescriptions and the number of new prescriptions for SSRIs (citalopram, paroxetine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, and sertraline) were obtained by age group and aggregated to the entire U.S. population. Data for U.S. suicide rates in 2003 and 2004 were obtained from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) WISQARS Injury Mortality Report (http://webappa.cdc.gov./cgi-bin/broker.exe). Data for suicide rates from 1988 through 2002 were obtained from the CDC WONDER Compressed Mortality database (http://wonder.cdc.gov/mortSQL.html). Data on suicide rates for 2005 will not be available until the end of 2007.
Data on national suicide rates in the Netherlands from 1998 to 2005 for children up to age 15 and teenagers 15–19 years of age came from the Central Bureau of Statistics. Prescription data in the Netherlands were obtained from the PHARMO database (www.pharmo.nl). The database consists of a representative sample of more than 200 pharmacies in more than 50 regions that are representative of the Netherlands; over 2 million residents (irrespective of insurance type) are included, representing 12% of the Dutch population. At the time our analyses were conducted, data through the end of 2005 were available.
Poisson regression analyses were performed to determine the overall association between antidepressant prescription rates and suicide rates, adjusted for sex and age, from 1998 to 2005 in the Netherlands, as well as changes from 2003 to 2005 in children and adolescent suicide rates in the Netherlands and from 2003 to 2004 in the United States.
Discussion
We found that the rates of SSRI prescriptions for children and adolescents decreased substantially in both the United States and the Netherlands after U.S. and European regulatory agencies issued warnings of an increased risk of suicide in pediatric patients taking antidepressants. In the United States, the reduction in SSRI prescriptions spilled over to affect prescriptions for adults up to age 60 as well.
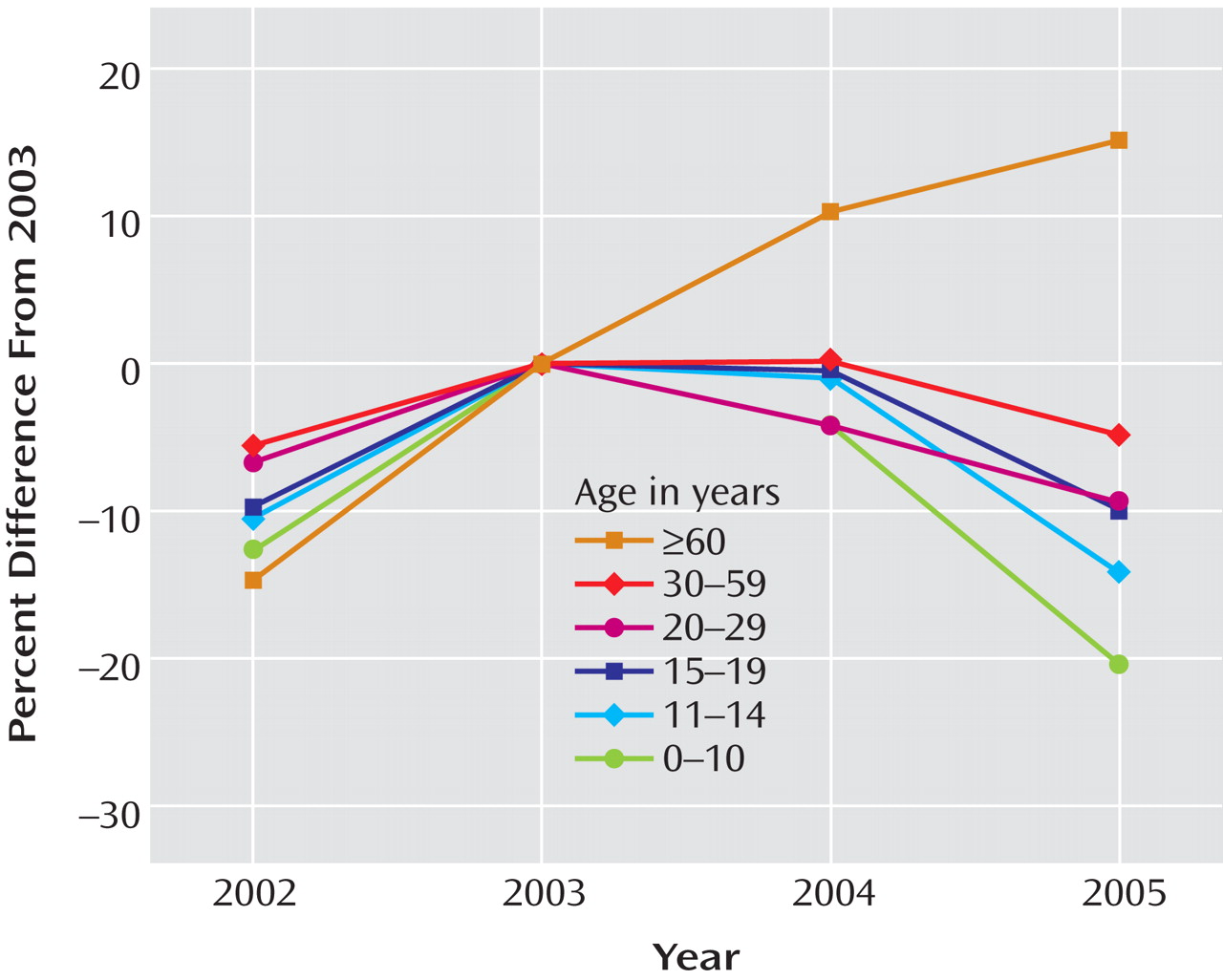
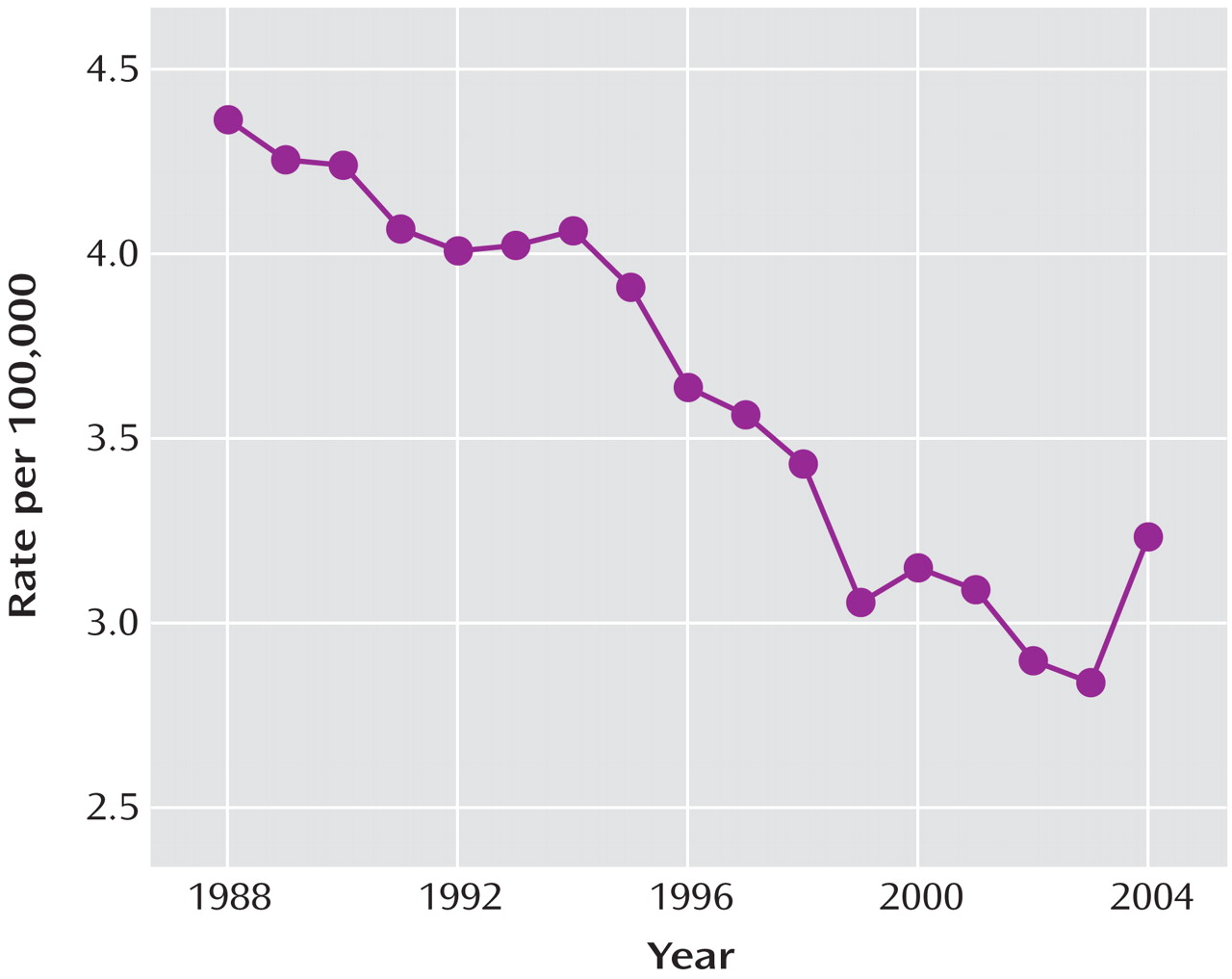
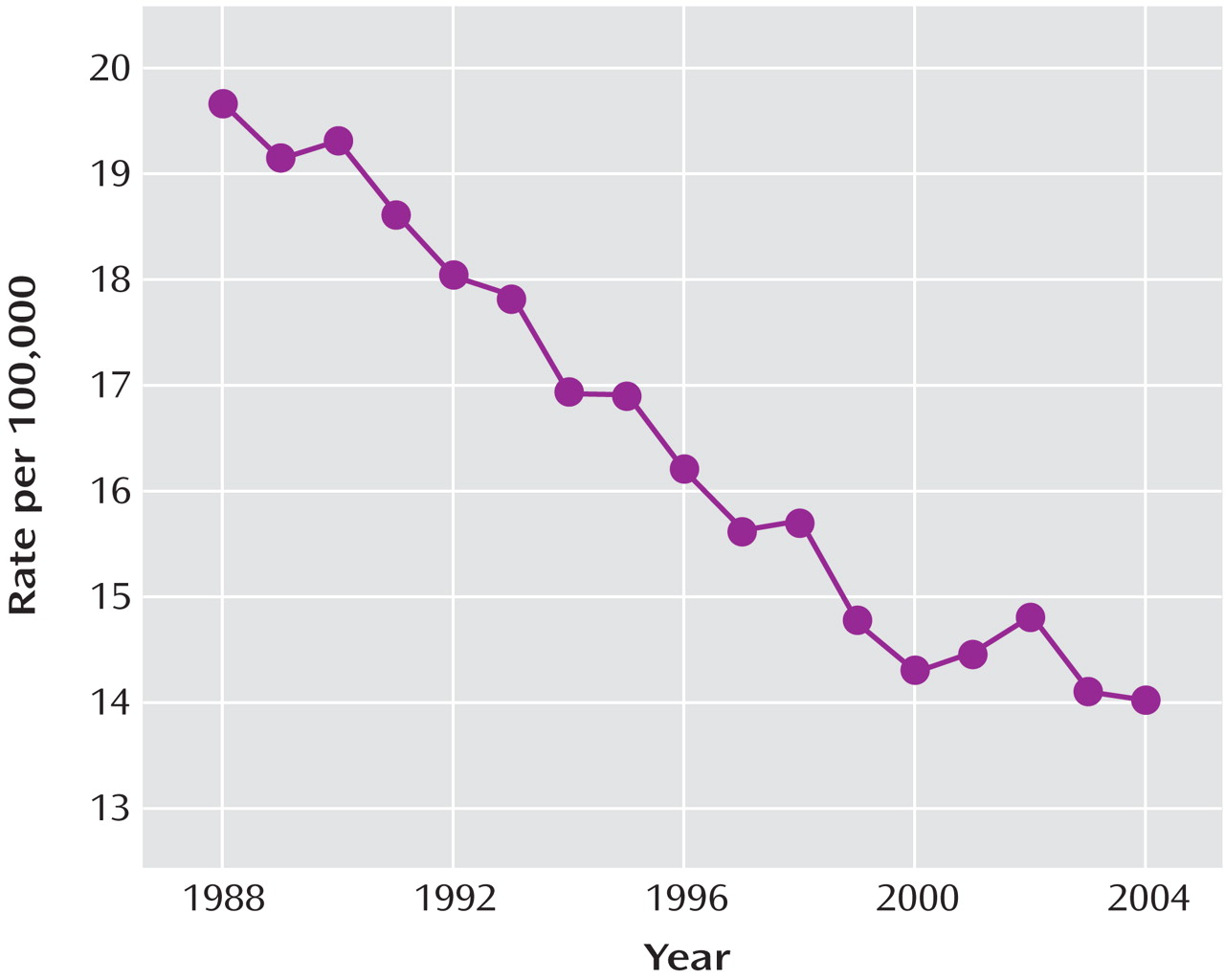
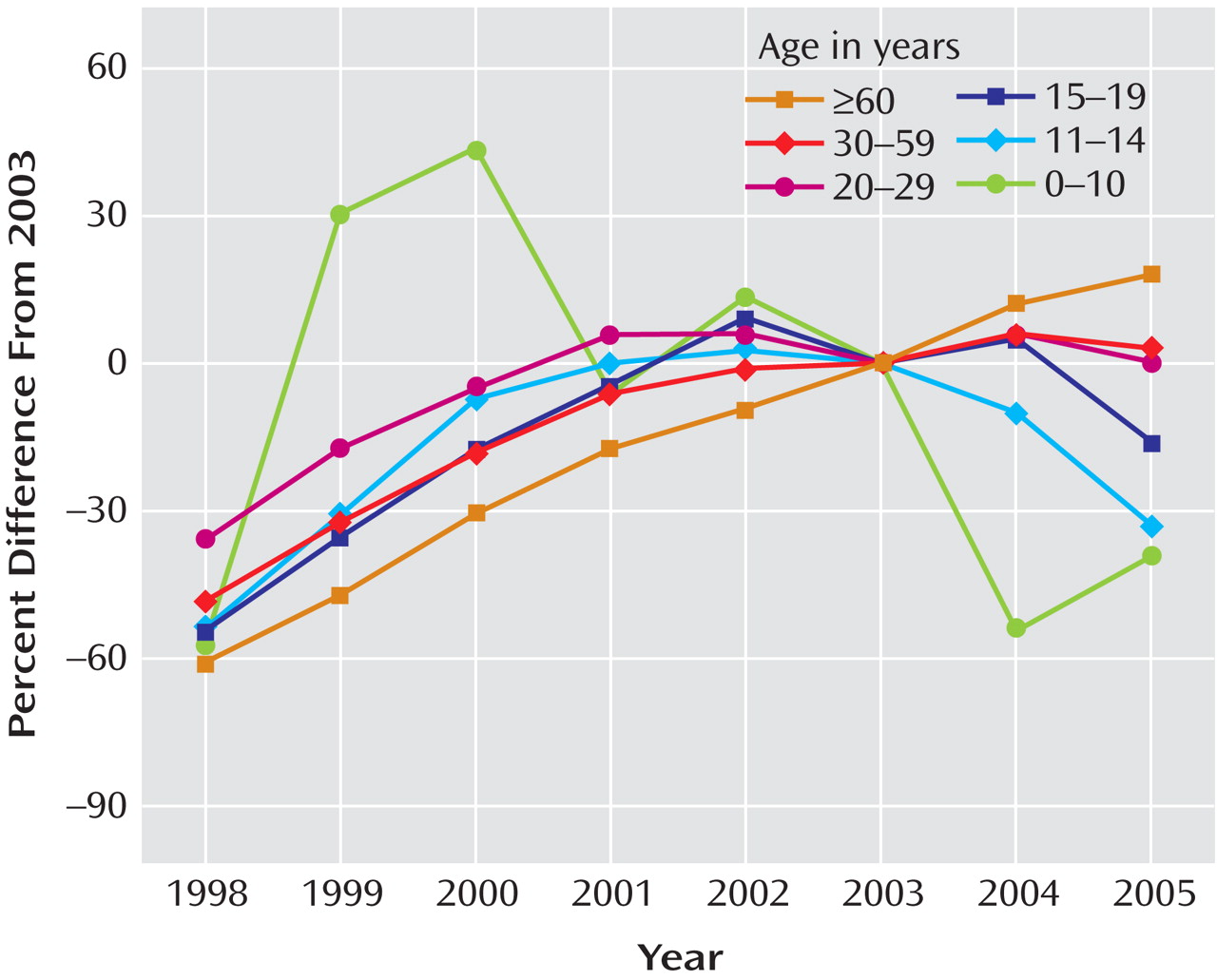
After substantial increases in SSRI prescription rates and substantial decreases in suicide rates in children and adolescents in both countries from 1998 to 2003 (in the United States, a 91% increase in prescription rates and a 33% decrease in suicide rates, and in the Netherlands, a 120% increase in prescription rates and a 31% decrease in suicide rates), the trends for both prescription rates and suicide rates reversed direction in both countries. Furthermore, an overall inverse relationship between the SSRI prescription rate and the rate of completed suicide was identified for the period 1998–2005. The strongest effect was for boys under age 15, which was statistically significant despite the smaller sample size. The data available from the CDC on U.S. suicide rates at the time of the study (through 2004) revealed that there was already a 14% increase in child and adolescent suicide rates from 2003 to 2004. Since 1988, the U.S. child and adolescent suicide rate has consistently decreased, with two exceptions—a 1% increase in 1994 and a 3% increase in 2000. The 14% increase from 2003 to 2004 is the first increase of this magnitude in the child and adolescent suicide rate since the CDC began systematically collecting suicide data in 1979. While only a small decrease in the SSRI prescription rate for U.S. children and adolescents occurred from 2003 to 2004, the public health warnings may have left some of the most vulnerable youths untreated. By contrast, SSRI prescription rates continued to increase for adults age 60 and over, and suicide rates continued to decrease in this age group, reaching a record low since the CDC began collecting suicide data.
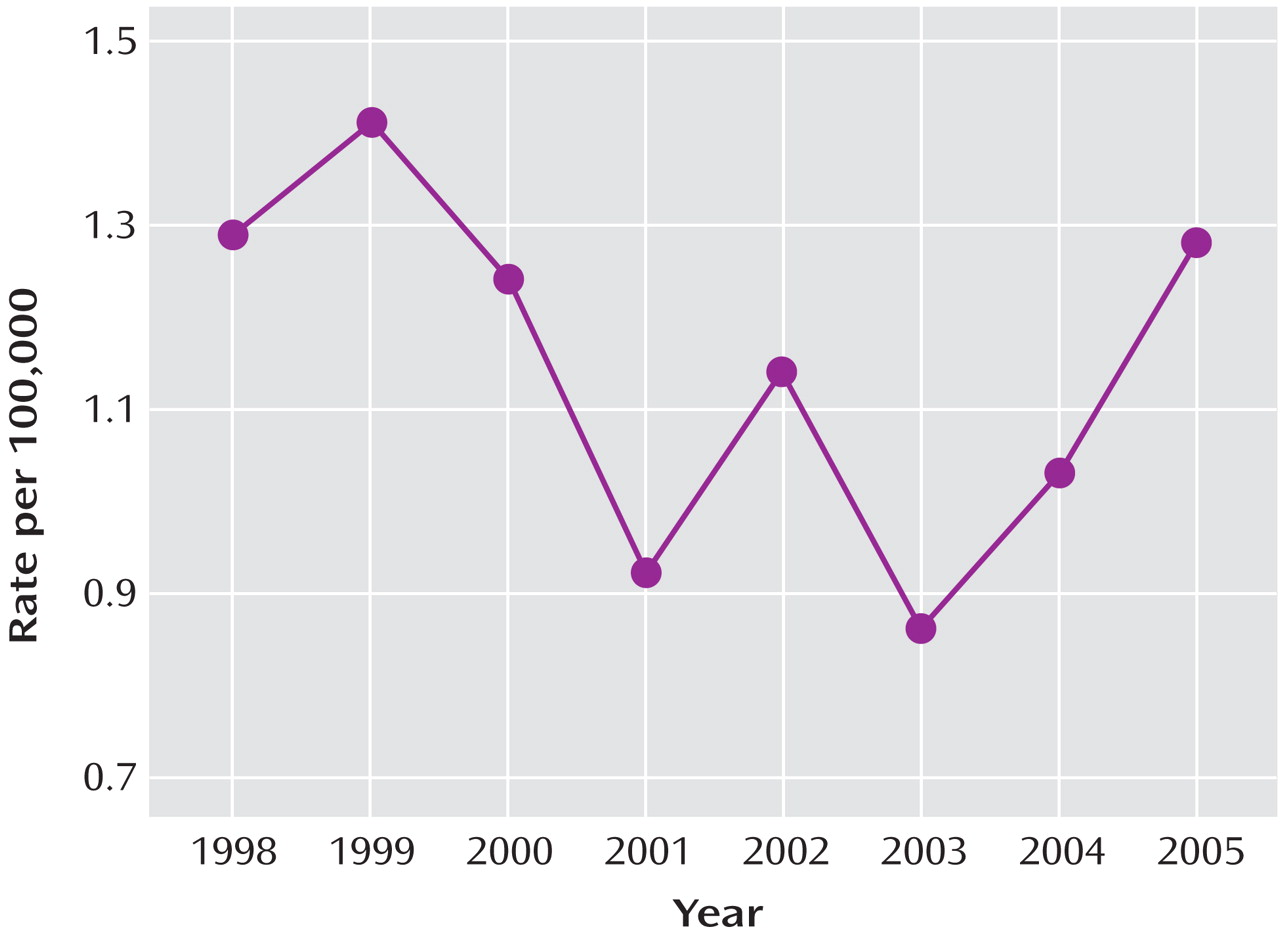
In the Netherlands, there was a 22% decline in child and adolescent SSRI prescription rates and a 49% increase in suicides in this age group from 2003 to 2005. Note that the estimates for the Netherlands are less stable than those for the United States because of the smaller population size (in 2003, some 290 million overall in the United States versus some 10 million overall in the Netherlands). Nevertheless, our findings are consistent with earlier work that identified significant inverse associations between SSRI prescriptions and suicide rates in the United States—in adults
(17), in children ages 5–14
(16), and in children ages 10–19
(15) —as well as in Europe
(18), Norway
(20), and Sweden
(21) .
Because the period of observation in this study was brief, our findings must be considered preliminary. However, confidence in these findings is increased by the fact that they are the same in two different countries as well as within the United States and that the degree and direction of change in suicide and prescription rates differed in the hypothesized direction across the life span—that is, in the ≥60 age group, the prescription rate continued to increase while the suicide rate continued to decline, whereas in the younger age groups, the reverse was seen, which was also a reversal of a two-decade trend.
We are aware of the important limitations inherent in ecological analyses regarding causation. These ecological results, however, take advantage of a natural experiment in which the likely causal agent (major depression) is affected by an alteration in a moderating factor during the period of observation (SSRI prescription rates), resulting in a change in the outcome measure (suicide rates) in the direction hypothesized by our explanatory model. Furthermore, since data from randomized studies are not available to explore the link between prescription rates and suicide rates, and an enormous number of participants would be necessary to study the question because of the rare nature of suicide
(17), alternative approaches, such as the analysis of large observational databases, can provide preliminary evidence. Although observational evidence has many limitations, it has been suggested
(24) that causal significance can be assessed through the use of coherence with existing theories of how an exposure should behave if it has a given effect. For example, we would assume that if SSRIs caused suicide, a decrease in SSRI use would lead to a decrease in suicide—and the evidence generated in this study is not consistent with the causal assertion that SSRIs lead to suicide.
Our findings are consistent with other data from large administrative and clinical records databases. Gibbons et al.
(25), analyzing person-level suicide attempt data from the U.S. Veterans Health Administration (VA), studied a cohort of 226,866 veterans who had a new diagnosis of depression in 2003 or 2004 (with at least 6 months of follow-up) and no history of depression or antidepressant treatment in the previous 3 years. Complete longitudinal records for all inpatient and outpatient visits and complete pharmacy records were available for all patients. Comparisons of suicide attempt rates were made, both within patients before and after initiation of treatment and between patients taking and not taking antidepressants. The suicide attempt rate observed in patients treated with SSRI monotherapy was just over one-third that of patients who were not treated with any antidepressant (123/100,000 versus 335/100,000, odds ratio=0.37, p<0.0001). These findings may represent a lower bound for the true protective medication effect, since the likelihood that an SSRI will be prescribed (rather than, say, a tricyclic antidepressant) is greater for patients who are more suicidal because of concerns about medication overdose. Similar protective effects were observed throughout the age range, including young adults in the 18- to 25-year-old cohort. This result indicating that suicide attempt rates were reduced with SSRIs was also supported in analyses that took into account the timing of treatment. Within subjects treated with SSRI monotherapy, the rate of suicide attempt was significantly greater prior to treatment (221/100,000) than after treatment (123/100,000) (relative risk=0.56, p<0.0001). Similar results were obtained by Simon et al.
(26,
27), who found that the highest rate of suicide attempt occurred immediately before initiation of antidepressant treatment. Valuck et al.
(14) examined data from 24,119 adolescents with a first diagnosis of major depression for whom at least 6 months of follow-up data were available. Treatment with antidepressant medication for at least 6 months reduced the likelihood of a suicide attempt compared with 2 months of treatment, both for single and multiple antidepressant prescriptions. These findings from person-level studies further validate observations in other ecological studies examining interventions designed to improve diagnosis of major depression in discrete regions or cities that resulted in increases in antidepressant prescription rates and declines in suicide rates
(28) . These effects are consistent with our results and conclusions regarding the protective effect of SSRIs.
The FDA’s recent report of a meta-analysis of 372 placebo-controlled studies
(12) totaling approximately 100,000 patients showed an overall protective effect of antidepressants on suicidal ideation and behavior (odds ratio=0.83, 95% confidence interval=0.69–1.00, p<0.05). When the data were stratified by age, the FDA researchers found that in patients age 65 and over, the suicide attempt rate was 31/100,000 in those who received test drug (SSRIs or non-serotonergic-specific antidepressants) and 250/100,000 for those who received placebo, compared with 129/100,000 with test drug and 147/100,000 with placebo in patients 31–64 years of age. In patients 18–25 years of age, however, the FDA found a statistically nonsignificant higher rate of suicide attempt in those treated with antidepressants compared with those who received placebo (551/100,000 versus 269/100,000, p<0.12). Gibbons et al.
(25) found a similar suicide attempt rate in VA patients 18–25 years of age who were treated with an SSRI (477/100,000); however, the rate of suicide attempt in untreated depressed patients in this age group (1,368/100,000) was five times higher than that of placebo patients enrolled in the randomized controlled trials the FDA analyzed (269/100,000). This difference points to the much lower risk of suicide attempt in depressed patients enrolled in randomized controlled trials compared with that of depressed patients in the general population.
If the FDA’s conclusion that there may be a causal link between suicide and antidepressants (which was the basis for the black box warning) were correct, we would have expected to see decreases in the suicide rate during the period of declining SSRI prescription rates, but instead we saw an increase in suicide rates, and the increase was greatest in the age range most affected by the decline in SSRI prescription rates. This finding, which is consistent with results of our previous ecological studies of U.S. data
(16,
17), suggests that SSRIs confer a protective effect.
The FDA’s meta-analysis of pediatric studies
(11) had several methodological limitations that could affect its conclusions. First, since no completed suicides were reported in any of these studies, their analysis was based exclusively on nonfatal suicide attempts and suicidal ideation. Attempts and ideation are common in adolescents and children, are often not reported to adults, and serve only as surrogate measures of suicide
(13,
29) . Second, by design, the randomized controlled trials analyzed by the FDA systematically excluded patients who were actively suicidal, and thus the FDA lacks data on those who are at highest risk of suicide. Third, the FDA’s analysis of the only systematic and prospectively collected suicidality measure (item 3 on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and item 10 on the Childhood Depression Rating Scale) revealed no association with treatment. Fourth, the primary evidence of an increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior could be affected by ascertainment bias
(30) . Specifically, the FDA’s conclusion that the risk of suicidal behavior for children treated with SSRIs was double that of those who received placebo was based on suicide-related adverse event reports that were retrospectively abstracted from the research records. However, because active medications generally have more side effects than placebo, the active treatment group will typically have more expansive medical records as a result of greater contact with the treatment team and therefore a greater likelihood of reporting suicidal ideation or behavior. For example, a review of the GlaxoSmithKline data on paroxetine in adults
(31) revealed that 83% of paroxetine-treated patients with major depression had at least one adverse event, compared with 71% of the placebo-treated patients (p<0.001). A second possible ascertainment bias applies to suicide attempts by overdose of study medication, which may go undetected in patients on placebo, whereas among those on active medication, more cases of medication overdose will be symptomatic and result in contact with health care staff in an emergency department or study staff. This ascertainment bias can result in underreporting of suicide attempts in placebo groups and make it appear as if antidepressant treatment were related to a higher rate of suicide attempt. Retrospective reviews of medical records from randomized controlled trials are not insulated from these types of ascertainment biases. Finally, a recent reanalysis of these data (32) revealed that antidepressants are in fact efficacious in the treatment of childhood depression and that the overall benefit to risk ratio is clearly positive.
Our findings raise concerns about the potential for harm that may result from a decreased use of SSRIs in the pediatric population. Regulatory agency warnings have likely resulted in a decrease in pediatric SSRI prescriptions in the United States and the Netherlands. In the Netherlands, the rate of pediatric and young adult suicides rose 49% after the U.S. and European agency warnings were issued. As noted, the U.S. data for 2004 already indicate a 14% increase over the previous year in suicide rates for children and adolescents (patients up to age 19). Based on our previous U.S. studies
(16,
17), we estimate that if SSRI prescriptions in the United States were decreased by 30% for all patients, there would be an increase of 5,517 suicides per year, or an additional 1.8 suicides per 100,000 people per year. In children 5–14 years of age, a 30% reduction in SSRI prescriptions would lead to an estimated increase of 81 suicides per year, or 0.20 suicides per 100,000. Given that SSRI prescriptions for children under age 15 already underwent a reduction of approximately 17% from 2003 to 2005 (
Figure 1 ), we expect an increase of 0.11 suicides per 100,000 children in this age group. Since there are approximately 40 million children in this age group, we would expect 44 additional deaths by suicide in 2005 relative to 2003, or an increase of 18% in this age group.
Results of current ecological analyses are not sufficient to conclude that there is a definitive causal relationship between decreased SSRI prescription rates (and hence presumably reduced use of SSRIs) and increased suicide rates. Nevertheless, these national data provide an estimate of the population balance between overall benefit and harm of SSRIs in major depression, since most SSRI prescriptions are for major depression
(19) . Two undisputed facts, namely, that pediatric suicide is most common in children with untreated major depression and that SSRIs are rarely found to be present at the time of death in suicide victims
(13), also suggest that SSRIs are not likely to be a causal factor in a substantial proportion of child and adolescent suicides.
Although some might expect that decreases in SSRI prescriptions would have led to increases in alternative antidepressant treatments, such as the newer non-serotonergic-specific antidepressants and tricyclic antidepressants, this does not appear to have been the case: similar decreases were seen in pediatric and young adult prescription rates for both these alternative antidepressant types (approximately 20% in the 5–14 years age range and approximately 10% in the 15–19 years age range). Furthermore, the majority of child and adolescent antidepressant prescriptions are for SSRIs. For example, in 2005, a total of 9,911,743 antidepressant prescriptions were written for the population under age 20, 65% of which were for SSRIs, 20% for non-serotonergic-specific antidepressants, and 15% for tricyclic antidepressants (based on IMS data).
An alternative explanation that has been proposed for the decrease in U.S. child and adolescent suicide rates from the late 1980s to 2003 is a drop in substance use during this period
(33) . However, the fact that national rates of illicit drug use have continued to decline from 2003 to 2004
(34) while suicide rates increased makes this alternative explanation unlikely.
Further support of our findings is provided by recent work showing that SSRI prescription fills were 58% lower than predicted by pre-2004 data and that pediatric diagnoses of major depression were more than 30% lower than predicted for pediatricians and primary care physicians based on pre-2004 historical trends (22). Furthermore, these effects have “spilled over” to the adult population, where significant decreases in the percentage of adults with new depressive episodes have been observed since the black box warning was introduced (23). These authors have also shown that there has been a significant increase in the percentage of depressed patients who did not receive antidepressant treatment (from 20% before the policy action to 30% after the policy action). These findings not only provide an independent replication of the medication effects reported here but also fill in an intermediate step related to the observed decrease in antidepressant prescriptions, namely, a decrease in the rate of diagnosing new episodes of depression in both pediatric and adult populations.
Additional work is needed to determine definitively whether suicide rates are increasing as a result of a decline in SSRI prescription rates. This is a major priority in designing national suicide prevention strategies.
In December 2006, the FDA’s Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee recommended that the black box warning be extended to cover young adults, and in May 2007, the FDA asked drug manufacturers to revise their labels accordingly. If the intent of the pediatric black box warning was to save lives, the warning failed, and in fact it may have had the opposite effect; more children and adolescents have committed suicide since it was introduced. If as a result of extending the black box warning to adults there is a 20% decrease in SSRI prescriptions in the general population, we predict that it will result in 3,040 more suicides (a 10% increase) in 1 year
(17) . If the FDA’s goal is to ensure that children and adults treated with antidepressants receive adequate follow-up care to better detect and treat emergent suicidal thoughts, the current black box warning is not a useful approach; what should be considered instead is better education and training of physicians.