Many studies have attempted to identify and clarify the roles of specific brain regions and networks in the pathogenesis of cognitive and affective symptoms of depression. Particular emphasis has been placed on the limbic system, specifically the hippocampus and amygdala, which are connected to other cortical areas such as the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and hypothalamus
(1) . The limbic system controls emotion and mood regulation. Specifically, hippocampal formation plays a critical role in the regulation of motivation and emotion, and the amygdala is vital to the interpretation of emotional and motivational experiences
(1) . The hippocampus and amygdala are two brain regions that are thought to underlie dysfunctional affective and cognitive processes in depression.
Although the hippocampus is one of the most studied structures in affective disorders research, data are inconsistent as to whether depressed individuals have smaller hippocampal volume compared with nondepressed individuals. Some researchers have reported decreased hippocampal volume in depressed patients relative to comparison subjects
(2,
3), while others have found no group differences
(4,
5) . Two recent reviews examined the extant literature on hippocampal volume. A meta-analysis conducted by Videbech and Ravnkilde
(6) confirmed hippocampal volume loss in patients with depression and found a significant correlation between the number of depressive episodes and right hippocampal volume. Similarly, Campbell and MacQueen
(7) reported decreased volume of the hippocampus in depressed subjects but no alterations in amygdala volume. Thus, both reviews suggested smaller hippocampal volume in patients with recurrent depression relative to age- and sex-matched comparison groups.
Few studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have examined hippocampal volume in subjects with major depression with psychosis. Kim et al.
(8) examined the amygdala-hippocampal complex in older depressed subjects and found no differences between depressed subjects with or without psychosis. However, they did not include a healthy comparison group. More recently, Velakoulis et al.
(9) examined various types and stages of psychosis. Their sample of affective patients with psychosis (N=34), which included patients with bipolar and unipolar disorders, did not demonstrate hippocampal reduction in patients with depression relative to comparison subjects. Hence, although hippocampal volume reduction has been noted in nonpsychotic depression—albeit inconsistently—the few available studies have suggested that a comparable volume reduction may not be present in psychotic depression.
Several investigations have examined the amygdala in depressed patients, with mixed results. Increased amygdala volume has been observed in first-episode major depression
(10) and dysthymia
(11) . However, amygdala atrophy has been reported in female but not male depressed patients
(12) and in chronic depression
(13), and it has been suggested that depressed individuals have a smaller core amygdala nucleus relative to individuals who have never been diagnosed as depressed
(12,
13) . Furthermore, smaller amygdala volume, but intact hippocampal volume, has been reported in pediatric depression
(14) . A recent study found that patients with first-episode psychosis (including schizophrenia, psychotic depression, and other psychotic disorders) had a larger mean amygdala volume relative to healthy comparison subjects
(9) . In contrast, the study did not find any amygdala reduction in patients with first-episode schizophrenia, chronic schizophrenia, or chronic affective psychosis. Other studies did not find altered amygdala volume in nonpsychotic depression
(15,
16) or in geriatric psychotic depression
(8) .
Demographic and clinical variables may be crucial in determining which patients are at greatest risk for reduced hippocampal volume. A number of variables have been found to be correlated with hippocampal volumetric changes, including age, gender
(17), recurrence
(18), duration of illness
(19), refractoriness
(16), history of abuse
(3), age of depression onset
(7), and cortisol dysregulation
(19) . However, many brain volume studies have not examined the relationship of these clinical variables with volume reduction. Furthermore, most studies have not differentiated subtypes of depression (e.g., psychotic depression), although differing results have been found in subjects with unipolar depression relative to subjects with bipolar depression. These variables may play important roles in the mixed results regarding hippocampal and amygdalar volumes in unipolar major depression.
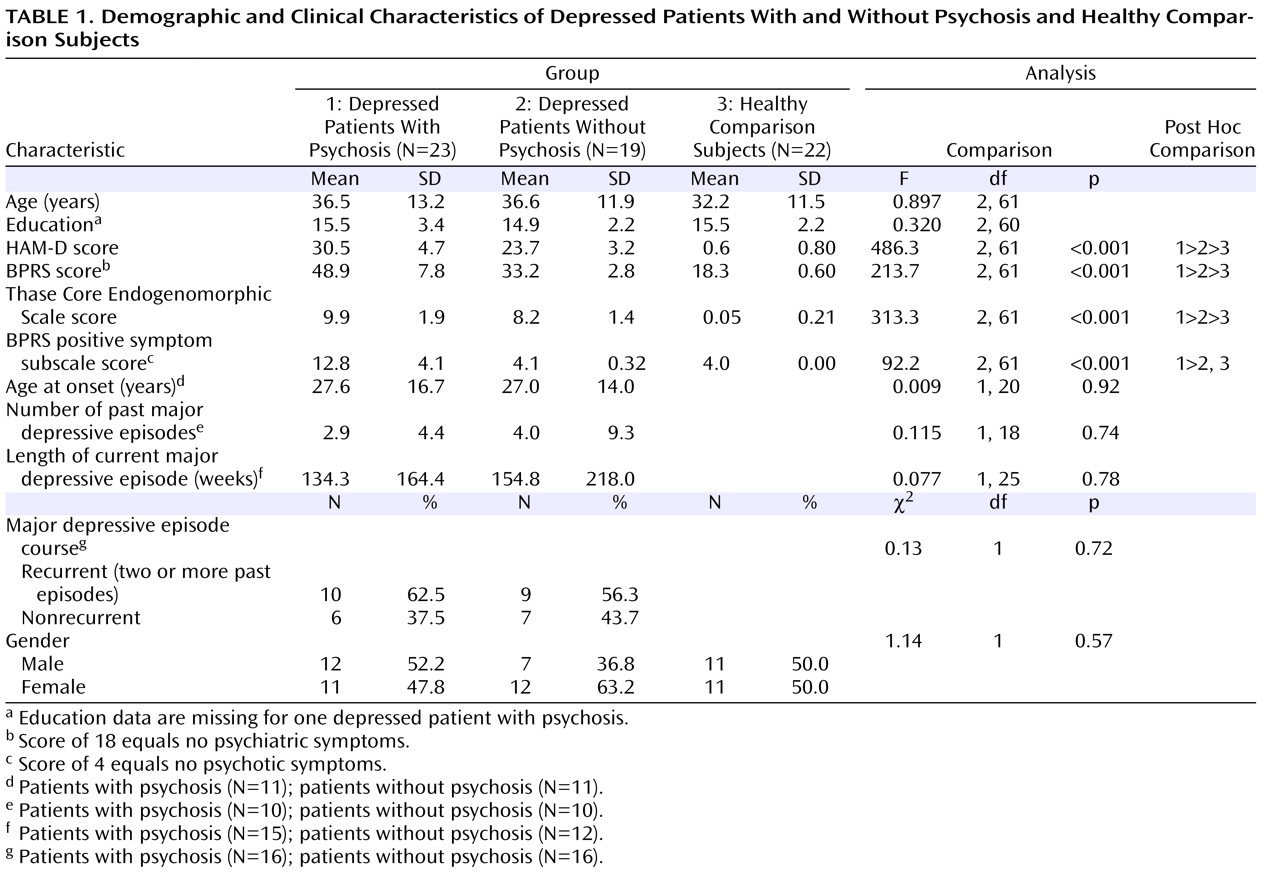
The primary objective of the present study was to compare hippocampal and amygdalar volumes in patients with psychotic and nonpsychotic depression and in healthy comparison subjects. To our knowledge, none of the extant structural imaging studies has examined psychotic depression in nonelderly subjects. Based on our previous studies that examined cognition in depression
(20,
21), which found significant memory impairment in depressed patients with but not without psychosis, we predicted that hippocampal volume differences would be present in patients with major depression with psychosis, relative to comparison subjects, but not in patients with major depression without psychosis.
Method
Participants
Participants were either recruited from outpatient facilities at Stanford University or self-referred via online and print advertisements. Twenty-three patients with psychotic depression and 19 patients with nonpsychotic depression participated in the study and provided usable data. Subjects with major depression with psychosis were diagnosed with the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID)
(22) . The diagnoses were confirmed by consultation with the subjects’ treating psychiatrists. Subjects with major depression without psychosis were also assessed using the SCID.
Depressed patients with and without psychosis were required to have a minimum score of 18 on the 21-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D)
(23) and a minimum score of 7 on the Thase Core Endogenomorphic Scale
(24), an assessment scale derived from the HAM-D. The latter was administered to ensure that patients with major depression without psychosis demonstrated considerable endogenous symptoms. Subjects with major depression with psychosis were also required to have a minimum score of 5 on the positive symptom subscale of the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS
[25] ), which consists of the following four items: conceptual disorganization, suspiciousness, hallucinations, and unusual thought content. A score of 4 indicates no positive symptoms. All patients met DSM-IV criteria for a current unipolar major depressive episode, with or without psychotic features. Subjects with major depression without psychosis had no history of psychotic symptoms. Participants were allowed to continue their psychiatric medication but were required to maintain a stable medication regimen for at least 1 week prior to the start of the study.
Twenty-two healthy comparison subjects were recruited through online and print advertisements. Comparison subjects were required to have a score of less than 6 on the HAM-D and have no psychotic symptoms. Additionally, they were required to have no current or past axis I psychiatric disorders according to SCID criteria.
Exclusion criteria for all three groups were major medical illnesses, history of seizures or major head trauma, abnormal clinical laboratory tests, pregnant or lactating women, and individuals under age 18. Participants were excluded if they had unstable or untreated hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or endocrine disorders. Subjects being treated with steroids or hormone replacement therapy were also not included. Additionally, patients who were actively suicidal or met DSM-IV criteria for obsessive-compulsive disorder or bipolar disorder were excluded as well as those patients with a history of substance abuse or electroconvulsive therapy within the 6 months prior to the start of the study. All participants were compensated $250.
Procedure
After complete description of the study was given, written informed consent was obtained. Eligibility screening procedures included the following: SCID, HAM-D, BPRS, clinical laboratory tests (with complete blood count examination), comprehensive metabolic panel, urine drug screening, and urine screening for pregnancy in female subjects. If participants met inclusion criteria at the eligibility screening, they were asked to return for baseline procedures. All eligible participants underwent structural and functional MRI. In addition, all eligible subjects participated in neuropsychological testing, psychological interviews, and blood sampling for 2 days (these findings are reported elsewhere [
20,
26 ]).
MRI Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
Structural images were acquired on a 3T GE Signa scanner, using a standard GE whole-head coil. The scanner runs on an LX platform, with gradients in “Mini-CRM” configuration (35 mT/m, SR 190 mT/m/second), and has a Magnex 3T 80-cm magnet. The following three-dimensional, volumetric radio frequency, spoiled-gradient echo parameters were used: TR=35 msec, echo time=6 msec, flip angle=45°. The field of view was 240×240 mm
2, and the acquisition matrix size was 256×192. One hundred twenty-four scan locations were acquired at 1.5-mm slice thickness. MRI scans were imported into BrainImage software for semiautomated whole-brain segmentation and quantification in the coronal plane
(27,
28) .
The amygdala and hippocampus were manually delineated in the coronal plane for each participant according to previously described methods
(29), using grayscale volume stacks derived from whole-brain analysis. These data sets were standardized in their orientation, parallel to the axial plane passing through the anterior and posterior commissures, using a six-parameter rigid-body transformation. A Talairach-based grid
(30) was subsequently fit to each data set in order to provide an additional method for subdividing regions of interest. The resolution of the standardized coronal data sets was then increased from 256×256 to 512×512, using a bicubic interpolation algorithm to increase visualization accuracy. The gray and white matter constituent volumes of the resulting amygdala and hippocampus regions of interest were quantified by projecting these regions of interest (derived from a nonsegmented grayscale image) on to the segmented gray and white matter fraction stacks of each subject. The reliability of the hippocampus and amygdala regions of interest was established by achieving an intraclass correlation coefficient of >0.90.
The anterior border of the amygdala was defined as the coronal plane where the anterior commissure first crossed the midline of the brain and where the amygdala was clearly present. The entorhinal sulcus and a white matter tract comprised the superior and inferior borders, respectively. Medial and lateral borders were defined by CSF in the medial margin of the temporal lobe and a lateral white matter tract. The posterior border of the amygdala was defined by the appearance of the hippocampus.
The anterior border of the hippocampus was defined by the alveus or the hippocampal sulcus. The alveus marked the superior border, and white matter defined the inferior border. The temporal horn demarcated the lateral border, and the ambient cistern demarcated the medial border. Measurement of the hippocampus proceeded posteriorly until the corpus callosum first fused with the fornix. Anterior and posterior subdivision of the hippocampus were achieved using the Talairach E3/F coronal plane
(30), which was located approximately midway along the length of the hippocampus.
Statistical Analyses
For all statistical tests, a two-tailed alpha of 0.05 was chosen as the threshold for statistical significance. Initial data analyses consisted of univariate analysis of variance and chi square analyses examining basic demographic differences between the three groups. Univariate analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was then used to detect group differences in hippocampal and amygdala volumes. A custom model was established based on literature suggesting that age and gender are variables that may contribute to volume differences in brain regions. Independent factors were gender and diagnostic group, and covariables were total brain volume and age. In addition to the full model examining the interaction of group-by-gender, we added the group-by-age interaction to our model. Group-effect differences were then examined using simple-effects ANCOVAs.
Next, we examined the effects of clinical and chronicity variables on brain volume. Clinical variables included the total scores for the following assessments: HAM-D, BPRS, and the BPRS positive symptom subscale. Unfortunately, chronicity data were only available for approximately one-half of our sample, equally distributed across the major depression with psychosis and major depression without psychosis groups. Post hoc analyses comparing the depressed groups were conducted using available chronicity data, including age at onset, number of past major depressive episodes, length of current major depressive episode, and number of patients with recurrent depression.
Discussion
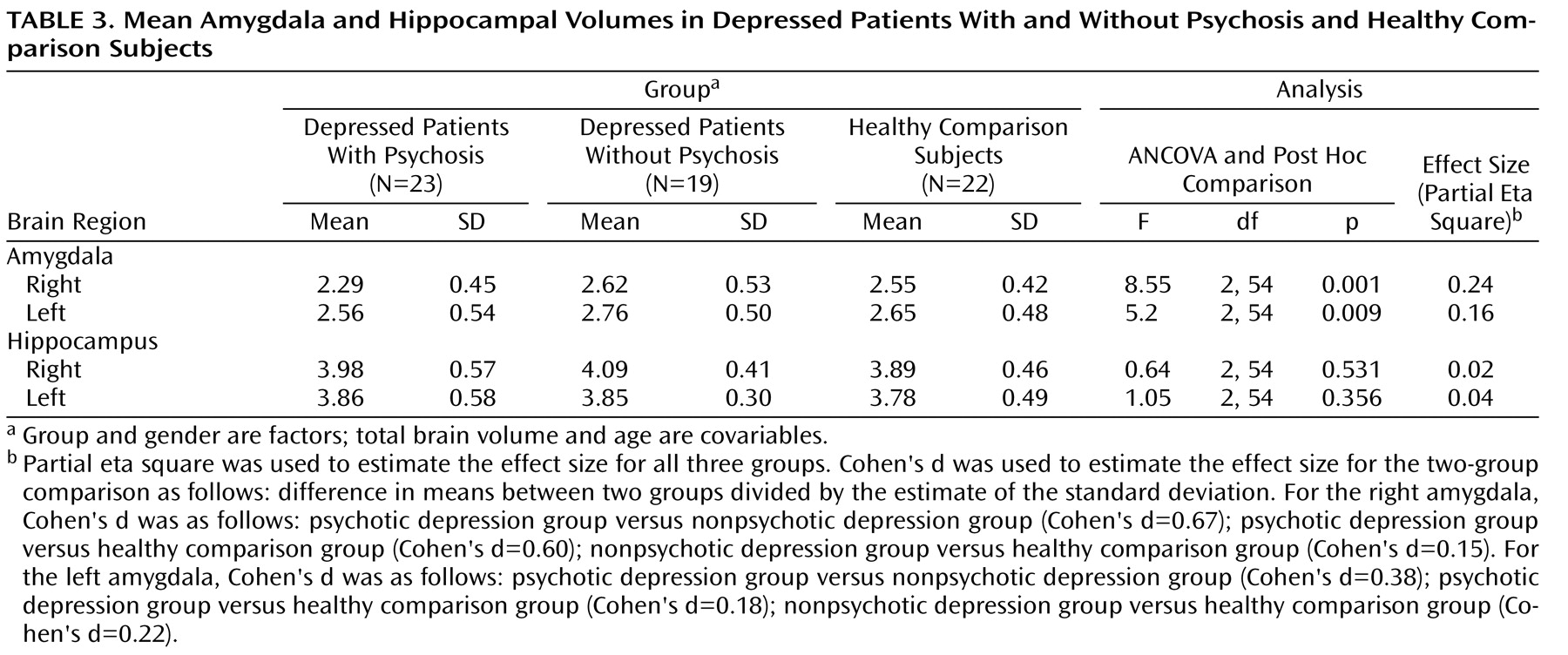
To our knowledge, this is the largest study to examine amygdalar and hippocampal volume differences separately in nonelderly subjects with major depression with psychosis relative to nonelderly subjects with major depression without psychosis. Although the depressed patients with psychosis in our study were more severely depressed compared with those patients without psychosis, the two depressed groups did not differ on measures of chronicity or age at onset of depression. Contrary to the conclusions of recent meta-analyses
(6,
7), we did not find left or right hippocampal volume differences in patients with psychotic or nonpsychotic depression relative to healthy comparison subjects. Our effect sizes suggest that this finding was not simply the result of a lack of statistical power. One meta-analysis
(6), which examined nonpsychotic depression, found recurrent chronic depression to be an important variable that influences brain volume. Our samples did not differ on measures of recurrent chronic depression, which may be one reason that we observed no differences in hippocampal volume between the two depressed groups. Alternatively, it is possible that the finding of no group differences in our study, as well as in the data reported by other investigators, may be related to the rating scales used for sample assessment or the sensitivity of the methodology used in quantifying hippocampal size.
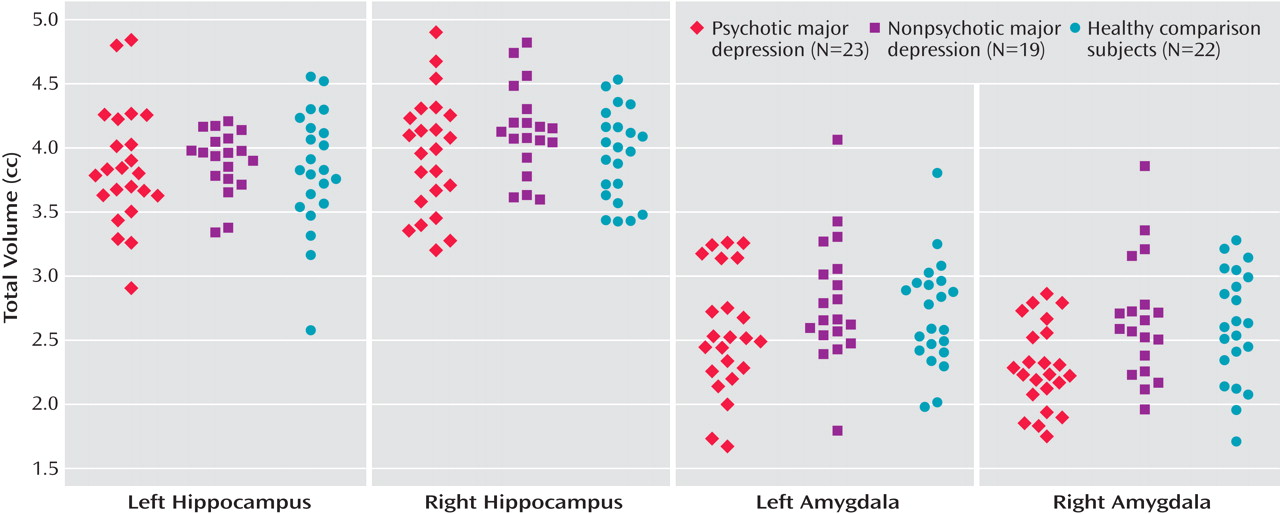
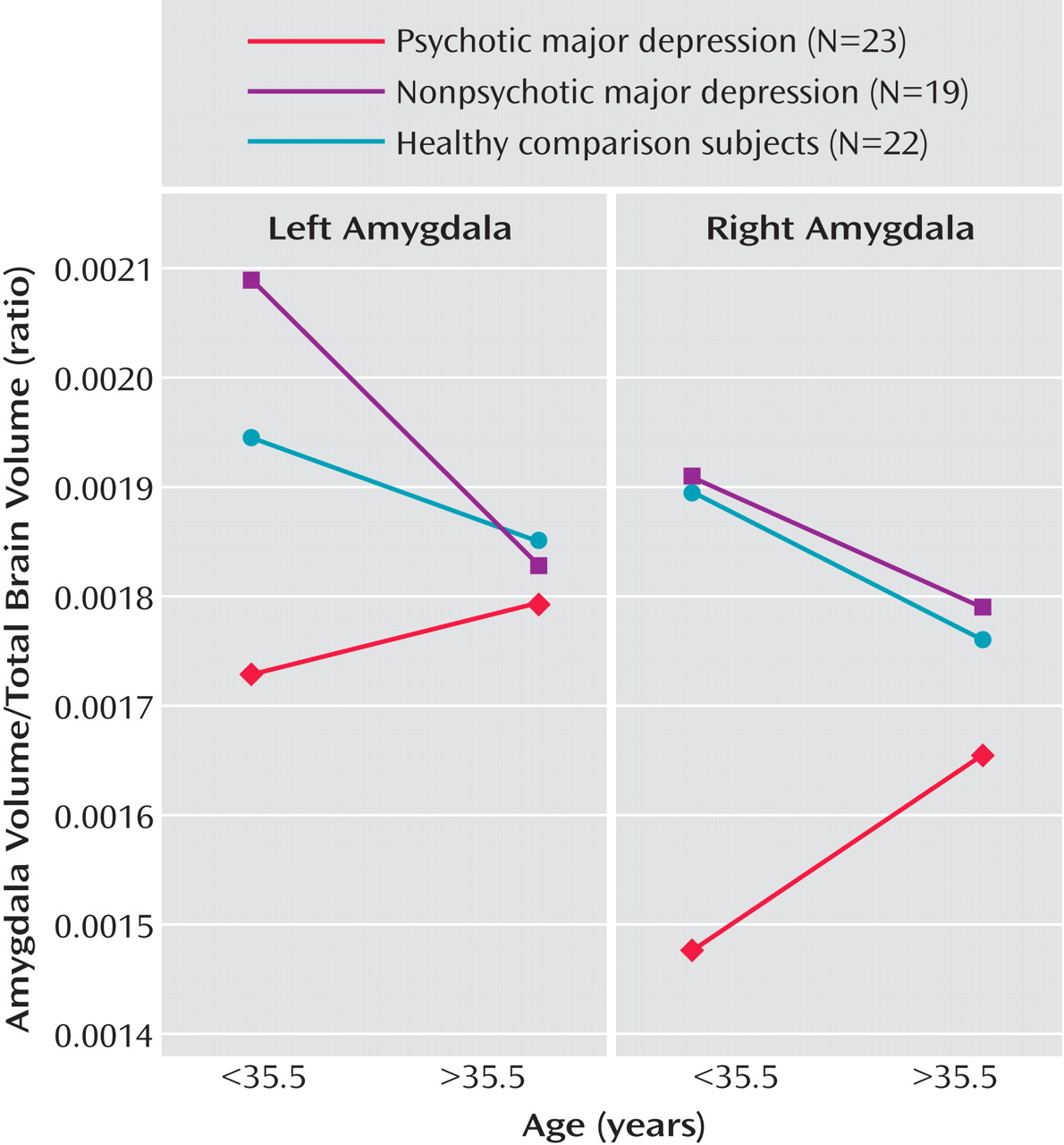
Interestingly, our results suggest that psychotic, but not nonpsychotic, depression is associated with reduced amygdala volume. Depressed patients with psychosis had smaller right and left amygdala volumes relative to depressed patients without psychosis and healthy comparison subjects. In addition, the two latter groups did not differ from one another. Importantly, our statistical models took into consideration gender, age, and total brain volume, since it has been suggested that these variables are central in examining amygdalar and hippocampal volumes
(31,
32) . The amygdala is vital to the accurate interpretation of emotion, emotional memory, and fear conditioning
(33,
34) . Many depressed patients with psychosis have significant anxiety, fear, and apprehension, all of which could be influenced by structural abnormalities in the limbic region. Given the paucity of data pertaining to morphometric findings in psychotic depression, the novel finding in the present study requires replication before being considered a possible phenotypic characteristic of major depression with psychosis. If our data are replicated, further investigation into the functional implications of abnormal amygdala morphology in psychotic depression is warranted.
In order to better understand our findings, we examined whether severity of current psychiatric illness correlated with amygdala volume. Severity of depression and severity of positive symptoms did not correlate with amygdala volume in our two depressed groups. Normal amygdala volume has been seen in patients with chronic schizophrenia
(9), which is consistent with our observation that amygdala volume was not related to psychosis per se. These findings suggest that there is a specific aspect of the diagnosis of major depression with psychosis, other than the severity of illness and presence of psychosis, which accounts for the reduction of amygdala volume.
We found a significant group-by-age interaction for amygdala volume. Follow-up analyses suggested that younger age was associated with smaller amygdala volume in depressed patients with psychosis. One possible explanation for this relationship is age at depression onset. In our sample of depressed patients with psychosis who had age at onset data, younger patients had a mean age at onset of 19 years, whereas older patients had a mean age at onset of 34 years. Thus, a smaller amygdala volume may be a risk factor for psychotic depression. However, replication of this effect is required to determine whether age or age of depression onset has a mitigating effect on amygdala volume.
There are data to support the hypothesis that chronicity of depression contributes to hippocampal volumetric changes in depressed individuals
(17), but data pertaining to amygdala volume are limited. The fact that we did not have complete chronicity data from all subjects limited our ability to test this hypothesis. However, with chronicity data from approximately one-half of our depressed subjects, we found that increased right amygdala volume was highly correlated with 1) a later age at depression onset, 2) a shorter duration of current depressive episode, and 3) fewer past major depressive episodes. One explanation for this finding is that smaller amygdala volume may be a risk factor for psychotic depression. If this is the case, it would support the hypothesis that smaller volume of mesial temporal limbic structures is associated with a vulnerability to psychopathology rather than the result of psychopathology. Both animal
(35) and human
(36,
37) data have suggested that smaller hippocampal volume may be a risk factor for impaired stress response. For example, Lyons et al.
(35) found that smaller hippocampal volume in adolescent monkeys predicted greater stress responses in adulthood. Gilbertson et al.
(36) reported that smaller hippocampal volume in twins was a risk factor for stress-related psychopathology. In particular, they found that veterans with smaller hippocampal volume were at greater risk for later development of posttraumatic stress disorder after combat. Similarly, Frodl et al.
(15) reported that men with first-episode depression had smaller hippocampal volume relative to healthy comparison subjects. Furthermore, a recent study found reduced amygdala volume in pediatric depressed patients relative to healthy comparison subjects, but no hippocampal volume differences were observed
(14) . These findings suggest a relationship between age at depression onset and amygdala volume, and thus support the hypothesis that smaller amygdala volume may be a risk factor for psychotic depression.
In the general literature, there are some inconsistencies pertaining to neuroimaging and depression. One concern is that the existing literature on depressed samples may contain a mixture of depressive subtypes, and this may confound results. Our study suggests a specific relationship between unipolar psychotic depression and reduced amygdala volume. We did not observe a similar finding in depressed patients without psychosis. More studies need to be conducted in order to understand how psychotic and nonpsychotic depression may differ at the neurobiological and morphometric levels. More broadly, our findings highlight the need to distinguish depression subtypes when investigating brain abnormalities in depression.
The association of chronicity and psychotic subtype with limbic volume may be related. Depressed patients with psychosis are often more chronic, with a longer duration of depressive episodes
(38) and a greater likelihood of recurrence
(39) . Furthermore, the psychosis associated with major depression may be more difficult to recognize than other (nonaffective) psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Dubovsky
(40) concluded that approximately one-half of the depressed patients who are refractory to antidepressants have psychotic symptoms of which their treating physician is unaware. Hence, available morphometric imaging studies of depression could be confounded by the lack of recognition of psychotic subtypes as well as symptom chronicity. Although depression chronicity has received a lot of attention, only a few studies have examined depressive subtypes. It would seem wise for future neuroimaging studies to systematically address both the chronicity of an individual’s condition as well as the individual’s depressive subtype. Only then can we begin to elucidate the neuroanatomical findings of psychotic depression.
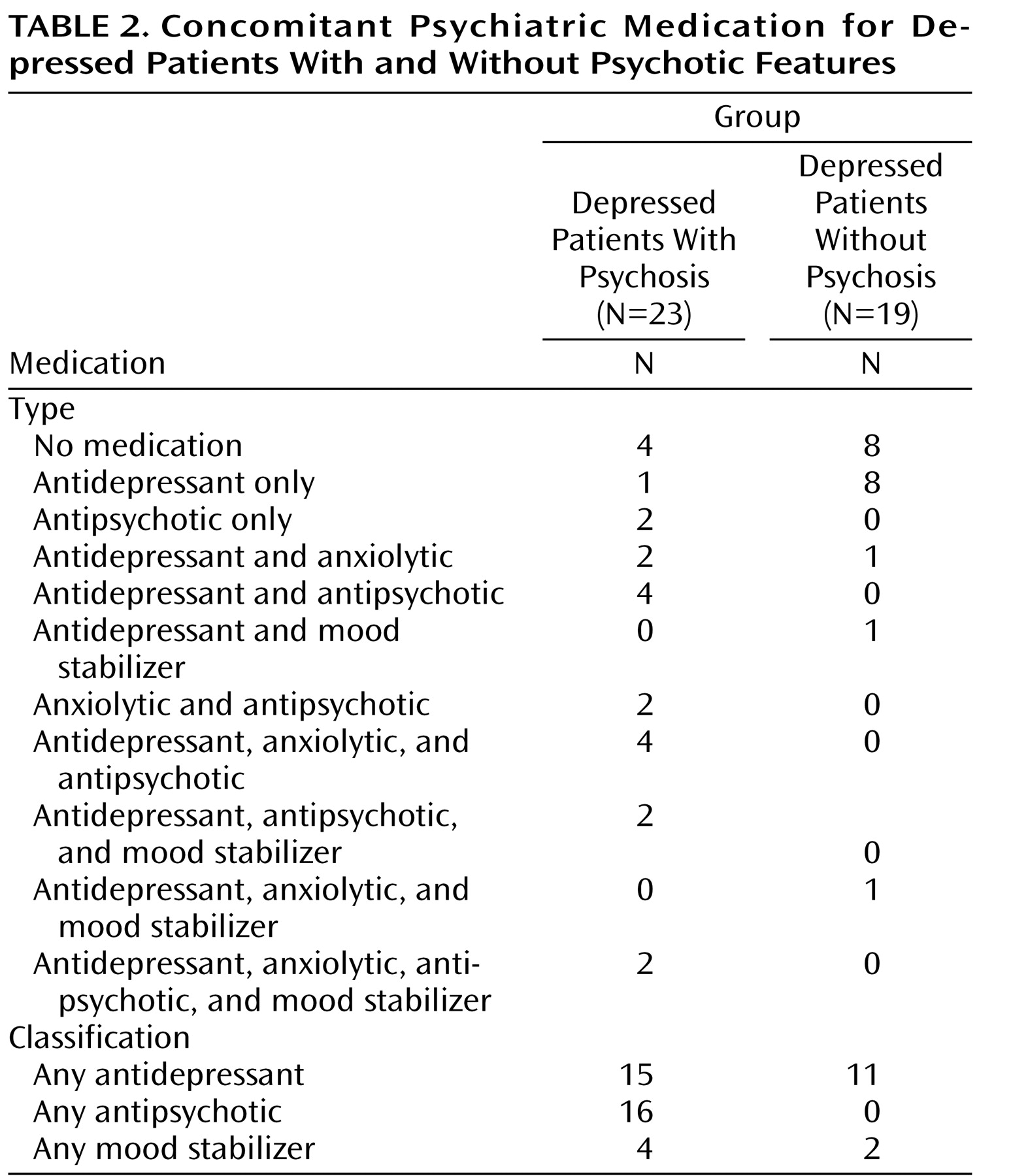
Our study has several limitations. We reported multiple correlational analyses between brain volume and other demographic and chronicity variables. The number of these analyses increased the risk of family-wise type I error. Thus, our findings are in need of replication in order to obtain confirmation. Another limitation of our study is that the majority of the depressed patients (both with and without psychosis) were medicated with antidepressants, and three-quarters of depressed patients with psychosis were medicated with antipsychotic agents. Unfortunately—but out of necessity—the vast majority of studies that have investigated brain volume in depression have included medicated subjects
(6) . We examined the effects of medication use on our findings but did not observe significant relationships between medication use and brain volume. Furthermore, normal amygdala volume has been reported in patients with chronic schizophrenia
(9), individuals who would be more likely to have reduced amygdala volume if such volume reduction was a direct result of antipsychotic medication. In addition, if the effect was primarily the result of antidepressant medication, we would have expected our depressed patients without psychosis to have shown reduced volume as well. Thus, it appears that amygdala volume in psychotic depression is not likely associated with medication effects. Further studies that specifically address the long-term effects of medication on brain volume would be useful to clarify whether volumetric abnormalities can be attributed to major depression, medication, or both.