Alcohol use (and abuse) has historically been less frequent among middle-aged and older adults relative to young adults, yet the frequency of alcohol use among middle-aged and older individuals is increasing
(1,
2) . In the 2001 to 2002 National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, 37% of women and 55% of men who were ≥65 years of age reported that they currently used alcohol
(3) . Just over 1% of elderly women and 4.8% of elderly men were thought to have a 12-month DSM-IV diagnosis of alcohol abuse or dependence
(2) . However, results from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging yielded estimates of alcohol abuse of 8.9% among persons who were ≥65 years of age in a clinical sample
(4) . Reasons for the increasing prevalence in this age group may be that alcohol use in moderate quantities has not been found to lead to a significant increase in adverse health outcomes and might (arguably) improve health and that the rising cohorts in this age group have consumed more alcohol than past cohorts during the 20th century. For example, Balsa and colleagues
(3) found that light to moderate alcohol consumption by older women (≥65 years of age) was associated with better self-perceived health status, improved cardiovascular health, and lower rates of hospitalization. No significant negative or positive associations were found for older men.
In the 2001 to 2002 National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, binge drinking was identified in 14% of men and in 6% of women (i.e., one binge drinking episode in the past year)
(5) . Binge drinking could be a significant potential health hazard that is not as frequently recognized in middle-aged and elderly adults. In another community survey
(6), binge drinking was found to be more common among adults aged ≥26 years than previously estimated and carried some significant risks. Seventy-three percent of all respondents who reported binge drinking drank moderately not heavily (although those who drank heavily were more likely than those who drank moderately to binge drink). Additionally, individuals who reported binge drinking were 14 times more likely to drive while impaired by alcohol compared with individuals who did not binge drink. Among adults ≥55 years old who reported consumption of alcohol, 15% of men and 4.7% of women reported an episode of binge drinking during the past 30 days. Frequency overall increased between 1993 and 2001. Caucasians and Hispanics were more likely than African Americans and men were more likely than women to binge drink. Further, college graduates had a slightly lower prevalence of binge drinking than those who did not attend college.
Binge drinking may vary across cultures, yet it is a potential problem in many cultures. In Denmark, binge drinking is typical among youth and decreases with increasing age. For example, in a national survey in Denmark, 38% of men and 18% of women drank heavily in episodes. In a general health survey of 513 Swedish women aged 50 to 59 years old
(6), 56.6% of respondents who reported alcohol consumption affirmed binge drinking within the past year and 39.4% affirmed binge drinking during the past month. A survey in Brazil among subjects ≥60 years of age
(7) estimated that 12% of respondents were individuals who drank heavily, 10.4% reported binge drinking, and 2.9% were alcohol dependent. Predictors of binge drinking and heavy drinking were male sex and younger age but not educational level or depression, and binge drinking was more frequent in the higher income group. These results suggest that at-risk and binge drinking may be hidden from many clinicians because the usual correlates of alcohol use disorders may not apply to binge drinking. In addition, binge drinking may be much more common in middle-aged and elderly women than what is usually assumed.
Data from the Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey in 2003 (N=12,413) revealed that 9% of elderly beneficiaries reported unhealthy drinking (men, 16%; women, 4%)
(8) . Higher education and income; better health status; male sex; younger age; smoking; being Caucasian; and being divorced, separated, or single were associated with an increased likelihood of unhealthy drinking. Hispanic ethnicity was associated with heavy episodic drinking (four or more drinks in a single day during a typical month in the previous year). Heavy episodic drinking was found in 1.2% of women and 3.5% of men. Drinking to relieve tension was affirmed by 7.2% of women (perhaps a risk for binge drinking). These women reported more mental symptoms and less contact with friends relative to the remainder of the sample.
Adverse health effects of binge drinking are unintentional injuries, intentional injuries (e.g., domestic violence), sexually transmitted diseases, high blood pressure, stroke, other cardiovascular diseases, liver disease, neurological damage, and poor control of diabetes. Despite these health hazards, most people who binge drink are not alcohol dependent and therefore may not be recognized clinically as engaged in at-risk drinking
(9) . These health hazards clearly present more negative consequence in later life when natural body defenses decrease and multiple illnesses from other causes may be aggravated by binge drinking. For example, binge drinking has been associated with impairments in instrumental activities of daily living
(10) . In addition, binge drinking has been associated with gambling among older adults
(11) .
In the present study, we demonstrate the prevalence and distribution of alcohol use, including at-risk drinking and binge drinking, in a national representative sample of U.S. men and women aged ≥50 years old (approximately 40% of whom were ≥65 years of age) from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. To increase the sample size, we combined 2 years (2005 and 2006) of data. Given that alcohol use and problematic alcohol use among middle-aged and older adults are predicted to increase over time as a result of the aging baby boomer population
(12), we examined self-reported use of alcohol, with a focus on binge drinking. Binge drinking is defined by the National Survey on Drug Use and Health as the consumption of five or more drinks on the same occasion (i.e., at the same time or within a couple of hours apart) on at least 1 day in the past 30 days
(13,
14) . We demonstrate the prevalence and correlates of alcohol use and binge drinking among all respondents, with specific attention to women. Among the subset of respondents who reported alcohol use in the past year, we examined the factors associated with at-risk drinking and binge drinking.
Method
Sample
The present study is based on data from the public use files of the 2005 to 2006 National Survey on Drug Use and Health
(13,
14) . This annual survey provides population estimates of substance use and health status of civilian non-institutionalized individuals aged ≥12 years old in the United States. The survey’s sampling frame covers approximately 98% of the total U.S. population aged ≥12 years old and uses multistage area probability methods to select a representative sample of the civilian non-institutionalized population. Individuals included in the sample are household residents; residents of shelters, rooming houses, college dormitories, migratory workers’ camps, and halfway houses; and civilians residing on military bases. Individuals excluded from the sample are active military personnel, residents of institutional group quarters (e.g., prisons, nursing homes, mental institutions, long-term hospitals), and homeless persons not living in a shelter at the time of the survey. The methods for survey sampling and data collection are the same for both 2005 and 2006, and thus we combined the 2 years in order to increase power.
Respondents were interviewed privately at their places of residence. Confidentiality was stressed in all written and oral communications, and the names of potential respondents and respondents were not collected with the data. The data collection method involved the combination of computer-assisted personal interviewing and audio computer-assisted self-interviewing in order to increase the validity of respondents’ reports of drug use behaviors
(15) . Demographic items were administered by the field interviewer via computer-assisted personal interviewing. The interview was then transitioned to the audio computer-assisted self-interviewing mode, which provided respondents with a highly private and confidential setting in which to answer sensitive questions (e.g., use of alcohol and/or drugs). Specifically, questions were displayed on a computer screen and read through headphones to the respondents, who entered their answers directly into the computer.
A total of 68,308 respondents completed the survey in 2005, and 67,802 respondents completed the survey in 2006. Weighted response rates for interviewing were 76% in 2005 and 74% in 2006. The study sample for each annual independent survey is considered representative of the U.S. general population aged ≥12 years old. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health design and data collection procedures are reported in detail elsewhere
(13,
14) . We combined the de-identified public-use data files from the two survey years, analyzed data from the same questionnaire items of the 2 years, and restricted our analyses to the 10,953 respondents who were ≥50 years of age (men: N=4,952; women: N=6,001). The sample size of each age year (e.g., respondents 64 years of age) was not available from the public-use data files. Within the sample (N=10,953), 54% of respondents were women and 22% were members of non-Caucasian groups.
Study Variables
Social and demographic variables
We examined respondents’ age, sex, race/ethnicity, educational level, current marital status, current employment status, and annual family income. We also created a categorical survey-year variable in order to examine yearly variations in the distribution of demographic and substance use variables.
Alcohol use variables
Alcohol use was defined as consuming at least one drink of any type of alcoholic beverage, and it excluded the use of only a sip or two from a drink
(13) The definition of “a drink” was explicitly described to respondents as a can or bottle of beer; a wine cooler or a glass of wine, champagne, or sherry; a shot of liquor; or a mixed drink with liquor in it. Survey respondents were asked about their use of alcohol during the past year. Individuals who reported using alcohol also reported “the usual number of drinks” they consumed on a drinking day during the past 30 days and the number of days they consumed five or more drinks on the same occasion. The definition of “same occasion” was explicitly stated to respondents as being at the same time or within a couple of hours apart.
According to the American Geriatric Society’s clinical guidelines for low-risk (no more than one drink per day) and at-risk (two or more drinks per day on average) alcohol use
(16), we classified respondents into the following four mutually exclusive groups: no use of alcohol in the past year; low-risk use (no more than one drink on a usual drinking day within the past 30 days); at-risk use (two or more drinks on a usual drinking day within the past 30 days); and binge drinking (five or more drinks on the same occasion on at least 1 day within the past 30 days
[13] ). We created the binge drinking category using the official definition of the National Survey on Drug Use and Health
(13) to identify subgroups of individuals who used alcohol and whose drinking pattern may have put them at a greater risk for harm relative to individuals in the other groups.
Mental health variable
Assessment of the past-year status of serious psychological distress was measured using K6-screening scale questions
(17,
18) . The K6-scale questions assessed symptoms of psychological distress during the one month within the past 12 months when respondents were at their worst emotionally. These questions have strong psychometric properties and have demonstrated adequate sensitivity and specificity in discriminating DSM-IV diagnoses
(19) .
Data Analysis
To control for potential sex-related biological and psychosocial differences in the risk for alcohol use, analyses of alcohol use patterns were stratified by sex
(20) . We examined the frequency of key demographic and alcohol use variables by survey year and found little yearly differences in these variables. In the combined sample (N=10,953), we first examined the prevalence of alcohol use by sex and found significant sex differences in all four categories of alcohol use. This finding provides support for sex-specific analysis. We then generated sex-specific prevalence of alcohol use patterns by age group, race/ethnicity, and education. Bivariate associations were determined using chi-square tests.
In the full sample, multinomial logistic regression procedures were conducted to determine correlates of low-risk, at-risk, and binge drinking relative to no alcohol use. To better understand whether individuals who reported binge drinking were distinct from individuals in the low-risk and at-risk groups by demographics, substance use, and mental health, additional multinomial logistic regression procedures were conducted in order to estimate their differences in the subsample of individuals who reported alcohol use (N=6,564). Survey year was included in the multinomial logistic regression models to control for potential yearly variations in the study variables. We examined interactions between sex and each covariate to assess the findings of sex-specific logistic regression models. Significant interactions by sex were observed for age group (p<0.01), race/ethnicity (p=0.01), educational level (p<0.01), and illicit drug use (p=0.047). All analyses were conducted using SUDAAN
(21), a software designed specifically for the analysis of survey data from complex designs such as the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. All estimates in the presented study are weighted except for sample sizes, which are unweighted. Levels of significance at both 0.05 and 0.01 are provided in the article tables. However, given the large sample size, those findings at the 0.01 level are discussed in the results and conclusions.
Results
Prevalence of Alcohol Use
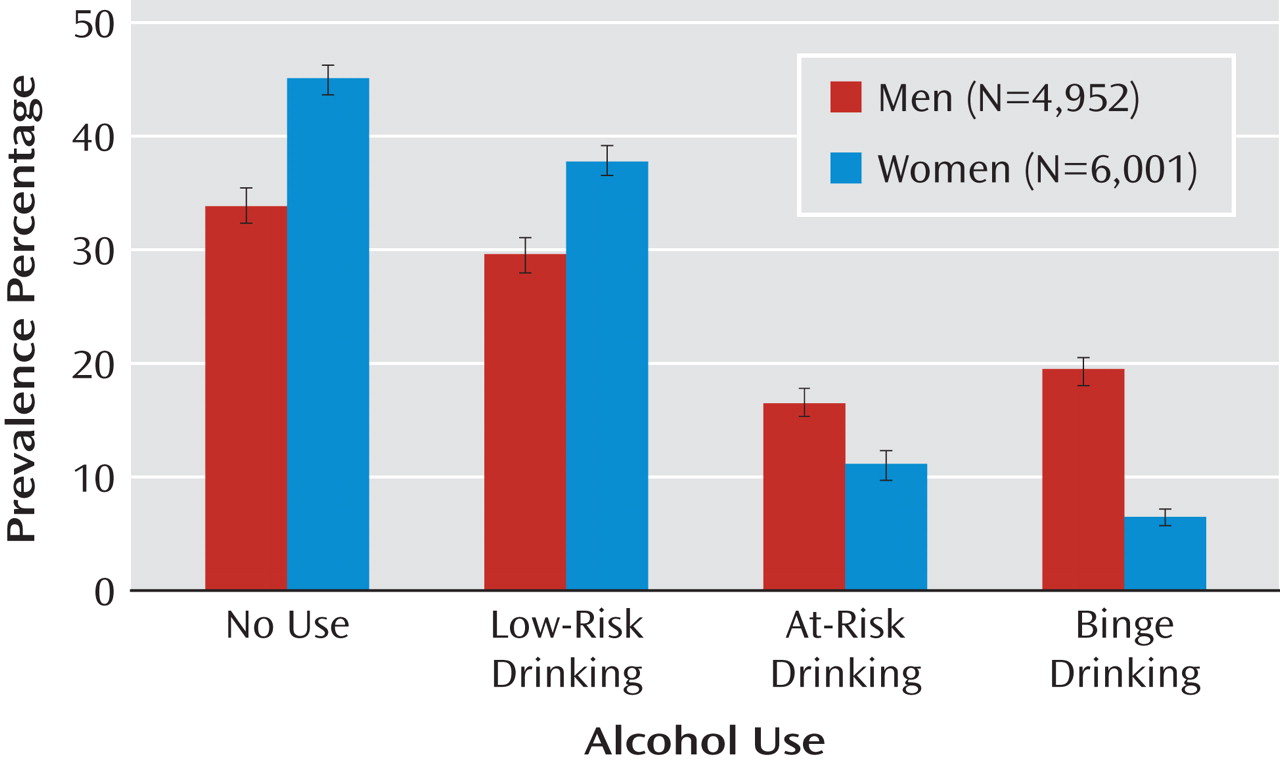
Overall, 66% of male respondents and 55% of female respondents reported alcohol use during the past year. As illustrated in
Figure 1, men showed a higher prevalence of at-risk drinking relative to women (17% versus 11%), as well as a higher binge drinking prevalence (20% versus 6%), but a lower prevalence of low-risk drinking (30% versus 38%) (χ
2 =334.52, df=3, p<0.001).
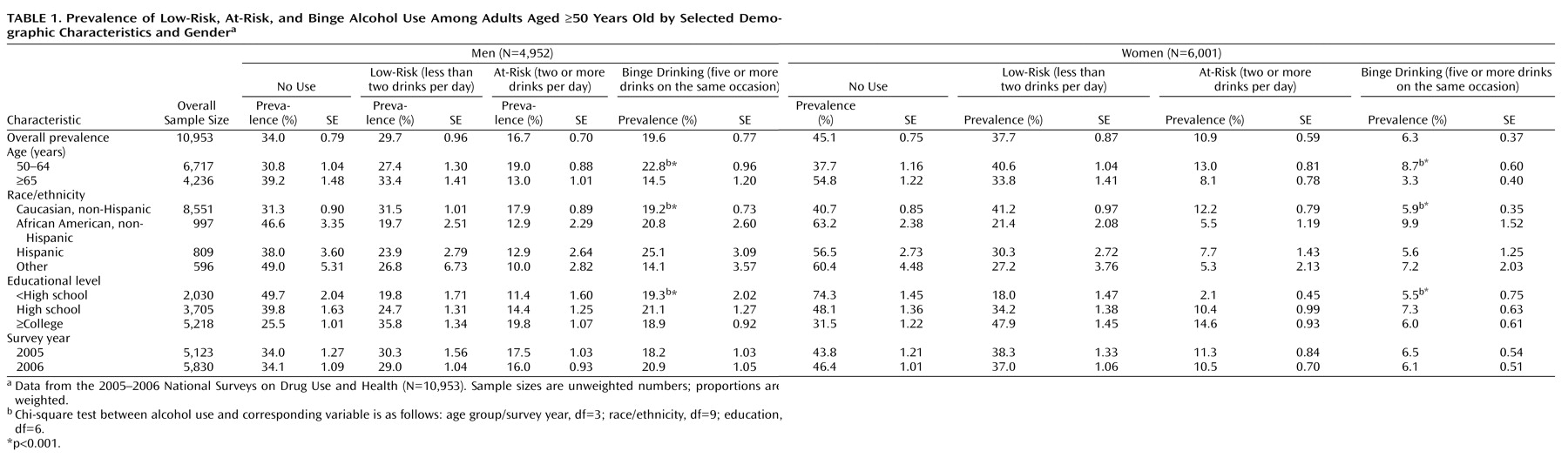
In both sexes, significant bivariate associations of alcohol use with age group, race/ethnicity, and education were observed (
Table 1 ). Overall, any alcohol use was more prevalent among Caucasians and more educated respondents. However, when the frequency of alcohol use was taken into account, we found that men who were Caucasian (19%), African American (21%), or Hispanic (25%) had a higher prevalence of binge drinking relative to other ethnic groups (14%). Among female respondents, African American women had a higher prevalence of binge drinking relative to Caucasian women (10% versus 6%). In both sexes, higher prevalences of low- and at-risk drinking were noted among more educated respondents relative to the least educated respondents, while the prevalence of binge drinking was similar across all educational levels.
Multinomial Logistic Regression of All Respondents
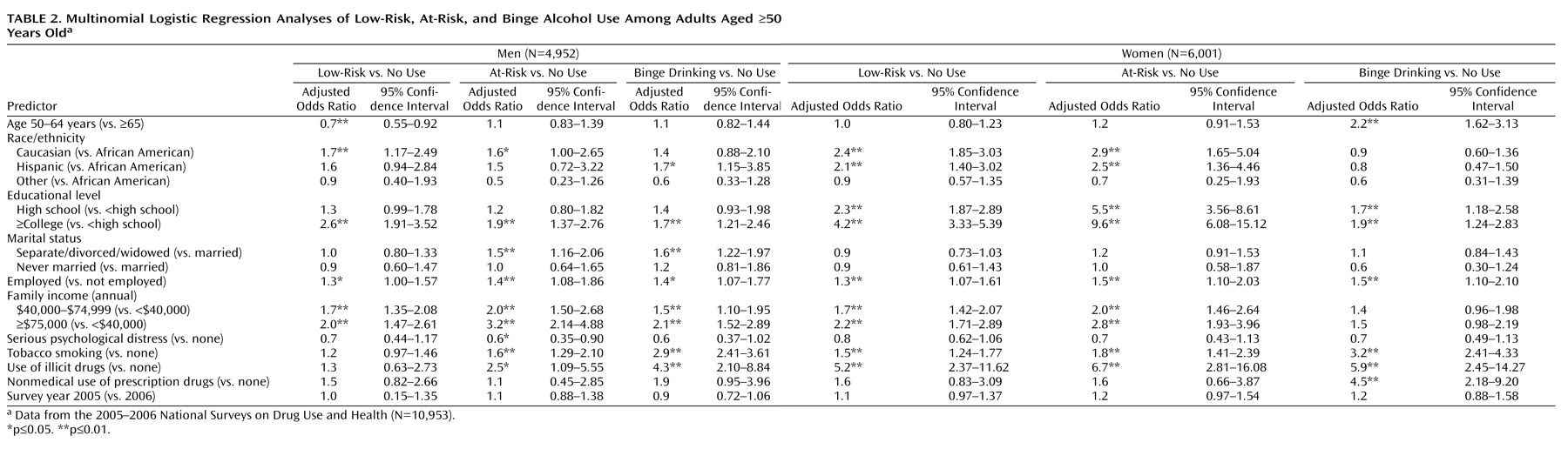
Adjusted odds ratios of low-risk, at-risk, and binge drinking relative to no alcohol use are presented in
Table 2 . In both sexes, having attended college was associated with an elevated odds ratio of low-risk, at-risk, and binge drinking. Also in both sexes, tobacco smoking and illicit drug use were associated with binge drinking. Further, there were unique sex-specific patterns in correlates. For male respondents, Caucasian men were more likely than African American men to report low-risk drinking. For female respondents, both Caucasian and Hispanic women were more likely than African American women to report low- and at-risk drinking. There were no racial/ethnic differences in binge drinking in both sexes. High levels of family income (≥$40,000 annually) were associated with all three categories of alcohol use among men. For women, high levels of family income were associated with low- and at-risk drinking but not binge drinking. Being separated, divorced, or widowed was associated with at-risk and binge drinking among men only, while nonmedical use of prescription drugs was associated with binge drinking among women only. At-risk and binge drinking were not associated with a report of serious psychological distress.
Multinomial Logistic Regression of Individuals Who Use Alcohol
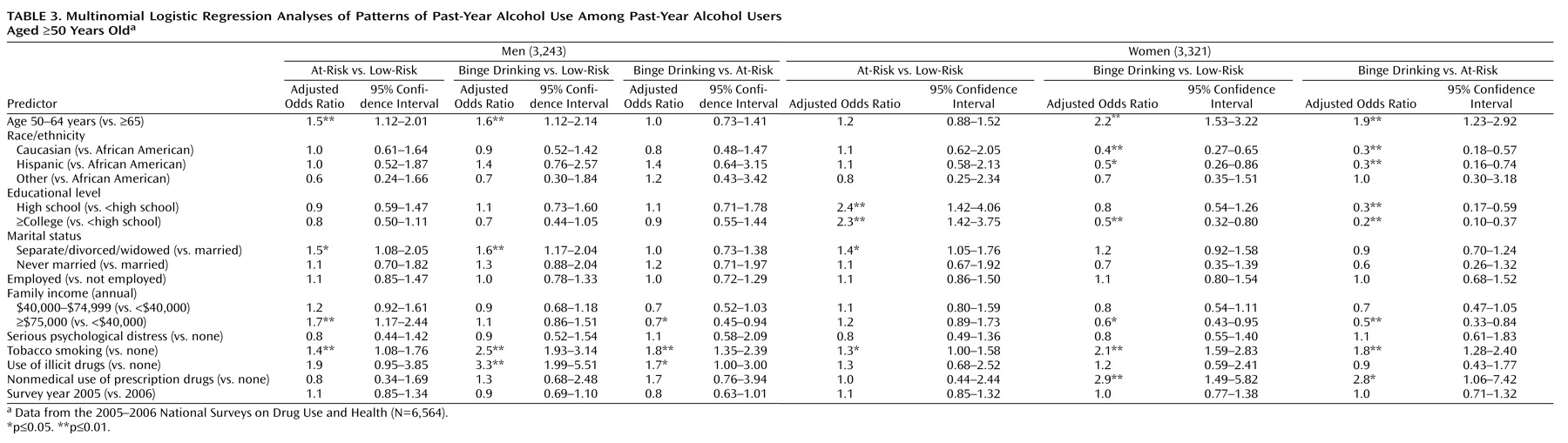
Adjusted odds ratios contrasting different groups of individuals who use alcohol are summarized in
Table 3 .
At-risk versus low-risk drinking
Relative to low-risk drinking, being 50 to 64 years of age, having a family income ≥$75,000 (annually), and tobacco smoking were associated with at-risk drinking among men. Among women, a higher level of education (≥high school) was associated with at-risk drinking.
Binge versus low-risk drinking
Compared with low-risk drinking, being 50 to 64 years of age; being separated, divorced, or widowed; tobacco smoking; and illicit drug use were associated with binge drinking among men. For women, being 50 to 64 years of age, being African American (relative to Caucasian), having less than a high school education, tobacco smoking, and nonmedical use of prescription drugs were associated with binge drinking.
Binge versus at-risk drinking
Relative to at-risk drinking, tobacco smoking was associated with binge drinking among men. For women, being 50 to 64 years of age, being African American (relative to Caucasian and Hispanic), having less than a high school education, having a family income <$40,000 (compared with ≥$75,000), and tobacco smoking were associated with binge drinking.
Conclusions
Overall, 66% of male respondents and 55% of female respondents reported alcohol use during the past year. At-risk use was more frequent in respondents 50 to 64 years of age and among men. In the ≥65 year-old age group, 13% of men and 8% of women reported at-risk use and more than 14% of men and 3% of women reported binge drinking. Compared with no alcohol use, binge drinking was associated with higher income and being separated, divorced, or widowed in men and with the use of tobacco and illicit drugs in all respondents. African American women had a relatively high rate of binge drinking relative to Caucasian women (10% versus 6%). Our findings suggest that the level of alcohol use was positively associated with educational level and family income and that men who reported a high level of family income were likely to have also reported binge drinking in the past month. In both sexes, tobacco smoking and illicit drug use were likely to co-exist with binge drinking. Therefore, individuals who binge drink may benefit from screening for substance use and brief intervention or counseling as appropriate.
Among women who reported using alcohol, greater odds of binge drinking were observed for those who were aged 50 to 64 years old, African American (relative to Caucasian), and less educated. However, among men, greater odds of binge drinking were observed for those aged 50 to 64 years only. In addition, illicit drug use was associated with binge drinking among men, while nonmedical use of prescription drugs was associated with binge drinking among women. Thus, younger individuals who reported using alcohol (ages 50 to 64 years old) and appeared socioeconomically disadvantaged, especially women, and who had used tobacco and other drugs in the past year (e.g., illicit drug use in men and nonmedical prescription drugs in women) were at risk for binge drinking. For both men and women, lack of an association between at-risk drinking and binge drinking and psychological distress may appear surprising. Yet these variables are identified via controlled analyses in which the effect of psychological distress may be effectively accounted for through other variables. In addition, middle-aged and older adults with at-risk drinking and binge drinking behaviors may be especially easy to miss in clinical settings because they do not report overt stress at the time of the interview.
The present findings should be interpreted with some caution. First, the cross-sectional nature of our data precludes drawing causal inference related to the associations reported. Second, substance use behaviors were obtained from respondents’ self-reports, which were subject to a variety of biases associated with memory errors and underreporting
(22) . For example, among emergency department patients, excess undeclared use of illegal substances is more common in the elderly (≥65 years old)
(23), which could generalize to at-risk drinking and binge drinking in this age group. In addition, individuals who were institutionalized (e.g., jail, long-term hospitalization) or homeless on the date of the survey, as well as active military personnel, were not included in the National Survey on Drug Use and Health sampling. Thus, the present findings do not apply to these individuals, and some settings may contain a higher frequency of substance use than the community sample. Finally, individuals who suffer from severe health or psychiatric problems associated with substance use and misuse are unlikely or unable to participate in a household survey such as the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. In addition, as age increases, so do cognitive impairment and dementia risk. This might have affected self-report data in several ways (e.g., by leaving out cognitively impaired people who anecdotally tend to drink less, hence producing overestimates, or by providing inaccurate recalled responses).
Despite these limitations, the National Survey on Drug Use and Health design has noteworthy strengths. The large number of respondents provides one of the largest samples of substance use among late-middle-aged and elderly individuals living in the community. The response rate is certainly respectable given the current state of community-based survey research, and the probes that assessed substance use are quite detailed given the focus of the survey. In addition, the survey used the most advanced audio computer-assisted self-interviewing technology to assess respondents’ substance use behaviors, a technology that has been found to increase reporting of drug use behaviors
(17) .
At-risk drinking and binge drinking are prevalent among middle-aged and elderly adults nationally, and the prevalence of middle-aged and elderly women reporting at-risk (11%) and binge drinking (6%) (although lower than the rate for men) is of public health concern. The potential adverse consequences of at-risk and binge drinking among middle-aged and elderly individuals (who are more susceptible to health problems) may often be overlooked by clinicians, not to mention the potential safety problems. For example, the CAGE questionnaire, which is often used to screen for alcohol problems, is of little value in identifying people who binge drink
(24) . Therefore, clinicians working with middle-aged and older adults who screen for alcohol problems would be well advised to specifically ask about binge drinking. These national findings also suggest the need to screen for illicit drug use among men who binge drink and nonmedical prescription drug use among women who binge drink.