Childhood Maltreatment and Psychopathology: A Case for Ecophenotypic Variants as Clinically and Neurobiologically Distinct Subtypes
Abstract
Objective
Method
Results
Conclusions
Epidemiology of Maltreatment Trauma

Supporting Methodology
Maltreatment and Associated Psychopathology
Major Depressive Disorder
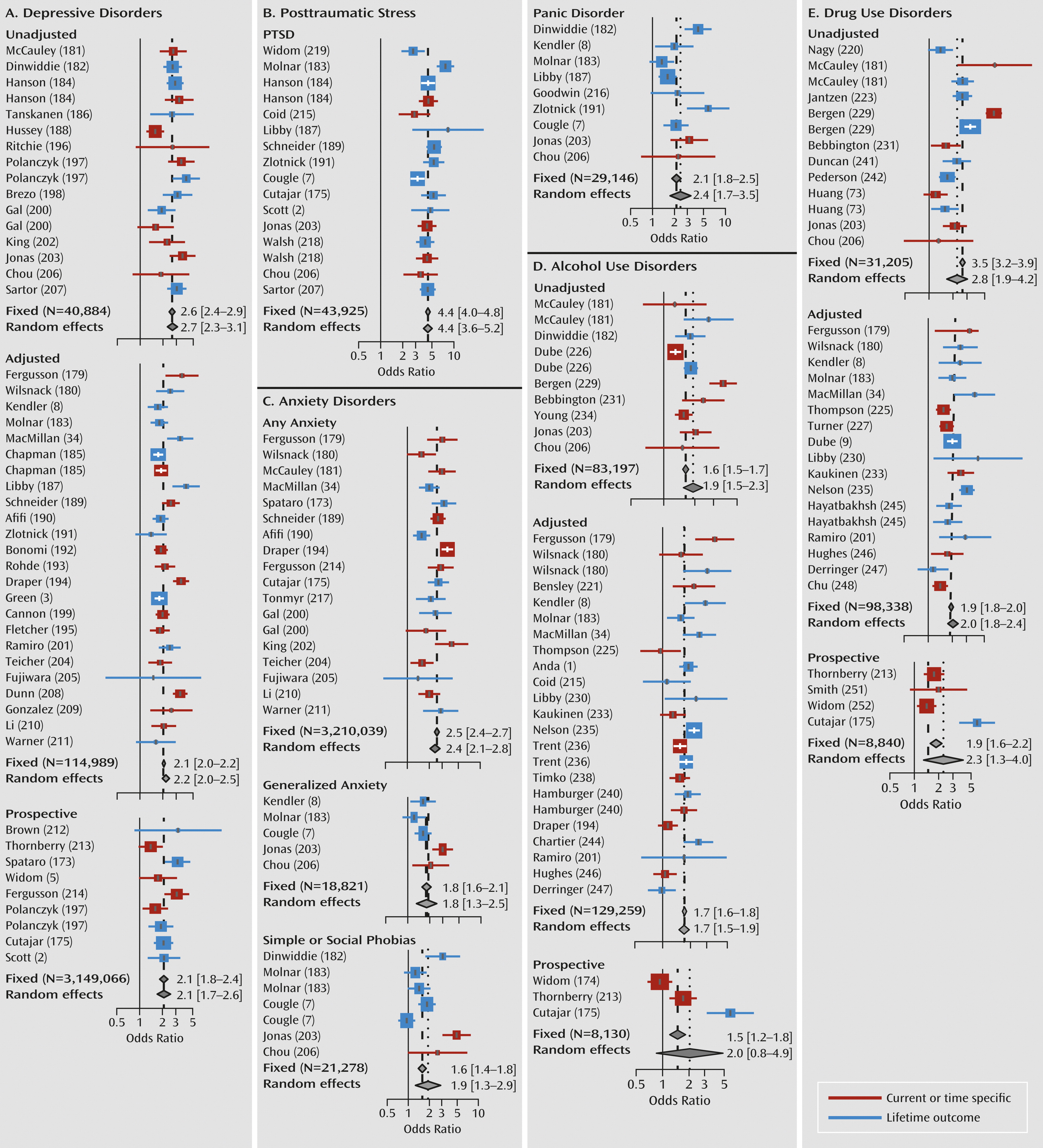
PTSD
Anxiety Disorders
Substance Use Disorders
How Does Maltreatment Increase the Likelihood of Developing So Many Different Psychiatric Disorders?
Neurobiological Correlates of Childhood Maltreatment
| Number of Subjects | Age (Years) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Author (Reference) | Types of Maltreatment | Diagnostic Requirement | Exposed | Comparison | Mean | SD | Gender | Medication | Main Corpus Callosum Findingsb |
| Teicher (90) | Sexual, physical, or neglect | Inpatients with versus without abuse | 28 | 23 | 12.9 | 2.9 | Both | No | Decrease in regions IV, III; males more affected than females |
| De Bellis (91) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 44 | 61 | 12.1 | 2.3 | Both | No | Decrease in regions IV, V–VII; males more affected than females |
| De Bellis (92) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus SES-matched controls | 28 | 66 | 11.5 | 2.9 | Both | No | Decrease in regions VII, IV–VI |
| De Bellis (144) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus SES-matched or typical controls | 61 | 122 | 11.7 | 2.6 | Both | No | Decrease in regions VII, I, VI; males more affected than females; reanalysis |
| Teicher (94) | Sexual, physical, or neglect | Inpatients with versus without abuse and controls | 28 | 23 inpatients, 115 controls | 12.2 | 3.4 | Both | No | Decrease in regions IV, V–VII; males affected by neglect, females by sexual abuse; partial reanalysis |
| Zanetti (145) | Physical or sexual | BPD with versus without physical or sexual abuse and controls | 10 (4 without physical or sexual abuse) | 20 controls | 29.1 | 9.1 | Both | No | BPD versus controls NS; increase in regions V, VII in BPD with versus without abuse |
| Rusch (146) | Sexual | BPD with versus without sexual abuse and controls | 20 (10 without physical or sexual abuse) | 20 controls | 27.6 | 6.8 | Female | No | Decrease in region V in BPD versus controls; decrease in regions V, VI in BPD with versus without abuse |
| Kitayama (147) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 9 | 9 | 37.3 | 9.4 | Female | Yes | Decrease in region V and total area |
| Jackowski (95) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 17 | 15 | 10.6 | 2.3 | Both | No | Decreased FA in middle and posterior |
| Andersen (93) | Sexual | No diagnosis required; 27% with history of PTSD | 26 | 17 | 19.8 | 1.4 | Female | No | Decrease in region III; sensitive period, ages 9–10 |
| Carrion (148) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms versus controls | 24 | 24 | 11.0 | 2.2 | Both | Yes | NS 8.7% decrease in region VII |
| Mehta (120) | Early deprivation, 24 months | Romanian orphans versus controls | 14 | 11 | 16.1 | 0.8 | Both | No | NS 6.5% decrease in absolute volume |
| Teicher (96) | Peer verbal abuse | No psychopathology | 63 | Used ratings, not groups | 21.9 | 1.9 | Both | No | Decreased FA in region VII; males and females affected to the same degree |
| Frodl (149) | CTQ score | Unaffected relatives with major depression, controls | 6 relatives, 4 controls | 15 relatives, 20 controls | 36.3 | 12.9 | Both | No | Decreased FA in region VII controls with versus without abuse; increase in FA in region VII, relatives with versus without abuse |
| Number of Subjects | Age (Years) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Author (Reference) | Types of Maltreatment | Diagnostic Requirement | Exposed | Comparison | Mean | SD | Gender | Medication | Main Hippocampus Findingsb |
| Adults | |||||||||
| Bremner (97) | Physical or sexual | PTSD versus healthy controls | 17 | 17 | 41.3 | 6.6 | Female | Yes | L decreased 12% |
| Stein (99) | Sexual | PTSD or dissociative identity disorder versus SES-matched controls | 21 | 21 | 31.1 | 6.4 | Female | Yes | L decreased 5% |
| Driessen (103) | CTQ score | BPD versus healthy controls | 21 | 21 | 29.6 | 6.5 | Female | Yes | L, R decreased 16% |
| Vythilingam (16) | Physical or sexual | Major depression with versus without abuse and controls | 21 | 11 major depression, 14 controls | 31.4 | 6.9 | Female | No | L decreased 15% in major depression with physical or sexual abuse versus control; NS for major depression without physical or sexual abuse versus control |
| Schmahl (104) | Physical or sexual | BPD with abuse versus comparison without BPD | 10 | 23 | 30.3 | 8.0 | Female | Yes | L decreased 11%, R 16% |
| Bremner (63) | Sexual | Abuse with PTSD, abuse without PTSD, and controls | 10 with PTSD, 12 without PTSD | 11 | 34.9 | 7.5 | Female | No | L, R, decreased 19% for sexual abuse with PTSD versus control; NS for sexual abuse without PTSD versus control |
| Brambilla (102) | Physical or sexual | BPD versus healthy controls | 10 | 20 | 33.0 | 8.9 | Both | No | L, R decreased 6.8%, most marked in BPD with abuse |
| Pederson (150) | CTQ severe to extreme, pubertal | Abuse with PTSD, abuse without PTSD, controls | 17 with PTSD, 17 without PTSD | 17 | 25 | 6 | Female | ? | NS 2.8% decrease on L for abuse with PTSD versus control; NS 6.3% decrease on L for abuse without PTSD versus control |
| Vermetten (100) | Physical or sexual | Dissociative identity disorder with PTSD versus comparison | 15 | 23 | 37.8 | 9.0 | Female | Yes | L, R decreased 19.2% |
| Cohen (114) | ELSQ high versus low, 0–12 years | No psychopathology | 122 | 84 | 39.9 | 17.2 | Both | No | L, R decreased (p=0.07 and p=0.06) |
| Zetzsche (151) | Physical or sexual | BPD with versus without physical or sexual abuse and controls | 14 BPD with 11 BPD without physical or sexual abuse | 25 | 26.7 | 6.7 | Female | Yes | L decreased 5% (p=0.07), R decreased 6% (p=0.03) for BPD versus control; NS for BPD with versus without physical or sexual abuse |
| Andersen (93) | Sexual | No diagnosis required; 27% with history of PTSD | 26 | 17 | 19.8 | 1.4 | Female | No | Decreased 6.8% bilaterally; sensitive periods, ages 3–5, 11–13 |
| Bonne (152) | Sexual, physical, emotional | PTSD with versus without abuse, controls | 11 | 11 PTSD, 22 controls | 35.9 | 10.4 | Both | No | Decreased 9% bilaterally for PTSD versus control; NS for PTSD with versus without abuse |
| Weniger (153) | Physical or sexual | PTSD, dissociative disorders, and controls | 10 PTSD 13 dissociative disorders | 25 | 32. | 7.1 | Female | Yes | Decreased 18% bilaterally for PTSD versus control; NS for dissociative disorders versus control |
| Lenze (154) | CECA score | Remitted major depression with versus without abuse, controls | 19 | 12 Remitted major depression, 24 controls | 48.5 | 14.9 | Female | Yes | Decreased L for remitted major depression versus control; abuse NS contribution |
| Soloff (155) | Physical or sexual | BPD with versus without physical or sexual abuse, controls | 20 with 14 with-out physical or sexual abuse | 30 | 26.6 | 7.9 | Both | No | Decreased R, L for BPD versus control; NS for BPD with versus without physical or sexual abuse |
| Weniger (101) | Physical or sexual | BPD, controls | 24 | 25 | 32.5 | 6.5 | Female | Yes | Decreased 12% bilaterally (with or without comorbid PTSD) |
| Gatt (156) | ELSQ score | No psychopathology | 89 | Used ratings, not groups | 36.2 | 12.7 | Both | No | Decreased gray matter volume R, L with ELSQ ratings and MET polymorphism of BDNF |
| Frodl (98) | CTQ score | Major depression, healthy controls | 43 | 42 | 44.1 | 12.4 | Both | Yes | NS gray matter volume; emotional neglect: decreased white matter volume on L in females, L and R in males |
| Thomaes (157) | Physical or sexual | Complex PTSD, controls | 33 | 30 | 35.5 | 11.0 | Female | Yes | R decreased (p<0.04); R inverse correlation with abuse severity (p<0.02) |
| Landré (158) | Sexual | PTSD, unexposed controls | 17 | 17 | 24.8 | 4.7 | Female | No | NS |
| Sala (159) | Physical or sexual | BPD, matched controls | 15 BPD (6 physical or sexual abuse) | 15 | 33.5 | 7.9 | Both | Yes | R decreased 12.7% for BPD versus control; R, L decreased for BPD with versus without physical or sexual abuse |
| Everaerd (160) | List of Threatening Life Events | No psychopathology; 5HTTLPR genotyping | 357 | Used ratings, not groups | 23.7 | 5.6 | Both | No | Gene-by-abuse-by-gender; decreased R, L for males with S′-allele and severe adversity (p<0.002) |
| Teicher (42) | CTQ and ACE scores | No diagnosis required; 46% exposed history major depression | 104 | 89 | 21.9 | 2.1 | Both | No | Decreased 6% in L subfields dentate gyrus and CA3; not related to major depression or PTSD |
| Dannlowski (43) | CTQ score | No psychopathology | 148 | Used ratings, not groups | 33.8 | 10.4 | Both | No | R decreased (p<0.05) |
| Carballedo (161) | CTQ score | No psychopathology, with versus without family of history major depression | 20 positive, 20 negative family history | Used median split ratings | 36.5 | 13.1 | Both | No | Decreased L, R hippocampal heads in subjects with emotional abuse and positive family history |
| Children and adolescents | |||||||||
| De Bellis (91) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 44 | 61 | 12.1 | 2.3 | Both | No | NS 2.2% increase |
| Carrion (148) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms versus controls | 24 | 24 | 11.0 | 2.2 | Both | Yes | NS 7.6% decrease |
| De Bellis (162) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 9 | 9 | 10.6 | 1.6 | Both | Yes | NS at baseline or while followed longitudinally for >2 years |
| Chugani (163) | Early deprivation, mean 38 months | Romanian orphans versus epilepsy control | 10 | 7 | 10.3 | 3.9 | Both | No | Decreased PET glucose metabolism in L temporal region, including hippocampus |
| De Bellis (92) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus SES-matched controls | 28 | 66 | 11.5 | 2.9 | Both | No | NS 1.8% decrease |
| Tupler (107) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus SES-matched or typical controls | 61 | 122 | 11.7 | 2.6 | Both | No | NS gray matter volume; increased white matter volume; reanalysis |
| Carrion (106) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms | 15 | 0 | 10.4 | 8–14 | Both | Yes | Inverse correlation (r=–0.48) between volume and cortisol level over 12–18 months |
| Mehta (120) | Early deprivation, 24 months | Romanian orphans versus controls | 14 | 11 | 16.1 | 0.8 | Both | No | L, R decreased 16% absolute, NS after adjusted for brain volume |
| Rao (44) | Early life adversity | Major depression, high risk, and controls | 30 major depression 22 high risk, 35 controls | Ratings of exposure within each group | 14.9 | 1.8 | Both | No | Decreased R, L with early life adversity in high risk and controls; hippocampal volume partially mediated risk for major depression with early life adversity |
| Carrion (164) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms versus controls | 16 | 11 | 13.9 | 2.0 | Both | Yes | Abnormal (decreased) R BOLD response on verbal memory task |
| Maheu (165) | Caregiver deprivation—emotional neglect | Orphans or foster care versus controls | 11 | 19 | 13.5 | 2.6 | Both | No | Abnormal (increased) L BOLD response to fearful and angry versus neutral faces |
| Tottenham (121) | Early deprivation, 63 months | Orphans versus healthy controls | 34 | 28 | 8.9 | 2.1 | Both | ? | NS 2.5% decrease on L in late adoptees (after 15 months) |
| Edmiston (166) | CTQ score | No psychopathology | 42 | Used ratings, not groups | 15.33 | 1.37 | Both | No | Decreased with total scores on R, L in females; decreased with emotional neglect on R, L in males and females |
| Lupien (122) | Mothers with chronic major depression | Exposed versus controls | 17 | 21 | 10 | Both | No | NS | |
| Number of Subjects | Age (Years) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Author (Reference) | Types of Maltreatment | Diagnostic Requirement | Exposed | Comparison | Mean | SD | Gender | Medication | Main Cortical Findingsb |
| De Bellis (91) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 44 | 61 | 12.1 | 2.3 | Both | No | Increased prefrontal cerebrospinal fluid (volume loss) |
| De Bellis (109) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 11 | 11 | 10.2 | 29 | Both | No | Decreased N-acetyl aspartate/creatine ratio in anterior cingulate |
| Carrion (108) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms versus controls | 24 | 24 | 11.0 | 2.2 | Both | Yes | Decreased frontal asymmetry |
| Chugani (163) | Early deprivation, mean=38 months | Romanian orphans versus epilepsy control | 10 | 7 | 10.3 | 3.9 | Both | No | Decreased PET glucose metabolism in R, L orbital frontal gyrus, infralimbic prefrontal cortex |
| De Bellis (92) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus SES-matched controls | 28 | 66 | 11.5 | 2.9 | Both | No | Increased prefrontal cerebrospinal fluid (volume loss) |
| De Bellis (167) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus typical controls | 43 | 61 | 12.1 | 2.3 | Both | No | Increased R, L superior temporal gyrus gray matter volume; reanalysis |
| De Bellis (144) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD versus SES-matched or typical controls | 61 | 122 | 11.7 | 2.6 | Both | No | Increased prefrontal cerebrospinal fluid (volume loss); reanalysis |
| Brambilla (102) | Physical or sexual | BPD versus healthy controls | 10 | 20 | 33.0 | 8.9 | Both | No | NS in temporal lobes and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex |
| Richert (168) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms versus controls | 23 | 24 | 11.0 | 2.2 | Both | Yes | Increased middle inferior ventral prefrontal gray matter volume; reanalysis (108) |
| Cohen (114) | ELSQ high versus low, 0–12 years | No psychopathology | 122 | 84 | 39.9 | 17.2 | Both | No | Decreased anterior cingulate total volume |
| Kitayama (169) | Physical, sexual | PTSD versus healthy controls | 8 | 13 | 39.3 | 8.2 | Both | ? | Decreased R anterior cingulate volume |
| Andersen (93) | Sexual versus healthy controls | No diagnosis required; 27% with history of PTSD | 26 | 17 | 19.8 | 1.4 | Female | No | Decreased total frontal gray matter volume; sensitive period, ages 14–16 |
| Tomoda (111) | Sexual versus healthy controls | No diagnosis required; most without axis I, II disorders | 23 | 14 | 19.7 | 1.4 | Female | No | Decreased occipital gray matter volume in BA 17–18; sensitive period, before age 12; partial reanalysis (93) |
| Tomoda (115) | Harsh corporal punishment versus healthy controls | No diagnosis required; most without axis I, II disorders | 23 | 22 | 21.7 | 2.0 | Both | No | Decreased gray matter volume in dorsolateral, anterior cingulate, and medial prefrontal |
| Carrion (148) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms versus controls | 24 | 24 | 11.0 | 2.2 | Both | Yes | Increased R, L inferior and superior prefrontal gray matter volume; reanalysis (108) |
| Carrion (170) | Sexual, physical, or witnessing domestic violence | PTSD symptoms versus controls | 30 | 15 | 13.2 | 2.1 | Both | No | Decreased L ventral and inferior prefrontal gray matter volume; inverse correlation between prebedtime cortisol level and L ventral gray matter volume |
| van Harmelen (171) | Emotional abuse or neglect | Major depression or anxiety disorders versus controls | 84 | 97 | 37.5 | 10.4 | Both | Yes | Decreased L dorsomedial prefrontal gray matter volume, independent of psychopathology |
| Sheu (88) | Harsh corporal punishment versus controls | No diagnosis required; 63% no lifetime history | 19 | 23 | 21.9 | 2.1 | Both | No | Increased T2 relaxation time (decreased regional cerebral blood volume) in R, L dorsolateral prefrontal |
| Hanson (89) | Physical versus health controls | No diagnosis required | 31 | 41 | 11.8 | 1.1 | Both | Yes | Decreased R orbital frontal, dorsolateral, temporal, and left and right parietal lobes |
| Frodl (98) | CTQ score | Major depression and healthy controls | 43 | 42 | 44.1 | 12.4 | Both | Yes | Physical neglect: decreased prefrontal gray matter volume |
| Thomaes (157) | Physical or sexual | Complex PTSD and controls | 33 | 30 | 35.5 | 11.0 | Female | Yes | Decreased R dorsal anterior cingulate, R orbitofrontal |
| Landré (158) | Sexual | PTSD and unexposed controls | 17 | 17 | 24.8 | 4.7 | Female | No | NS regional measures of cortical thickness |
| Tomoda (112) | Parental verbal abuse versus healthy controls | No diagnosis required, 48% with history of mood disorder | 21 | 19 | 21.2 | 2.2 | Both | No | Increased L superior temporal gyrus gray matter volume |
| Edmiston (166) | CTQ score | No psychopathology | 42 | Used ratings not groups | 15.33 | 1.37 | Both | No | Decreased dorsolateral, orbitofrontal, subgenual prefrontal gray matter volume |
| Gerritsen (172) | List of Threatening Life Events | No psychopathology; BDNF polymorphism | 568 | Used ratings not groups | 23.4 | 5.4 | Both | No | Decreased anterior cingulate and medial orbitofrontal at 1.5-T but not 3-T; G×E BDNF versus events for subgenual anterior cingulate |
| Carballedo (161) | CTQ score | No psychopathology, with versus without family history of major depression | 20 positive 20 negative family history | Used median split ratings | 36.5 | 13.1 | Both | No | Decreased L dorsolateral and medial prefrontal, R anterior cingulate with emotional abuse and positive family history |
| Tomoda (128) | Witnessed domestic violence versus healthy controls | No diagnosis required, 59% past psychiatric history | 22 | 30 | 21.7 | 2.2 | Both | No | Decreased gray matter volume and thickness in R lingual gyrus (BA 18), decreased thickness R, L V2 and L occipital pole; sensitive period, ages 11–13 |
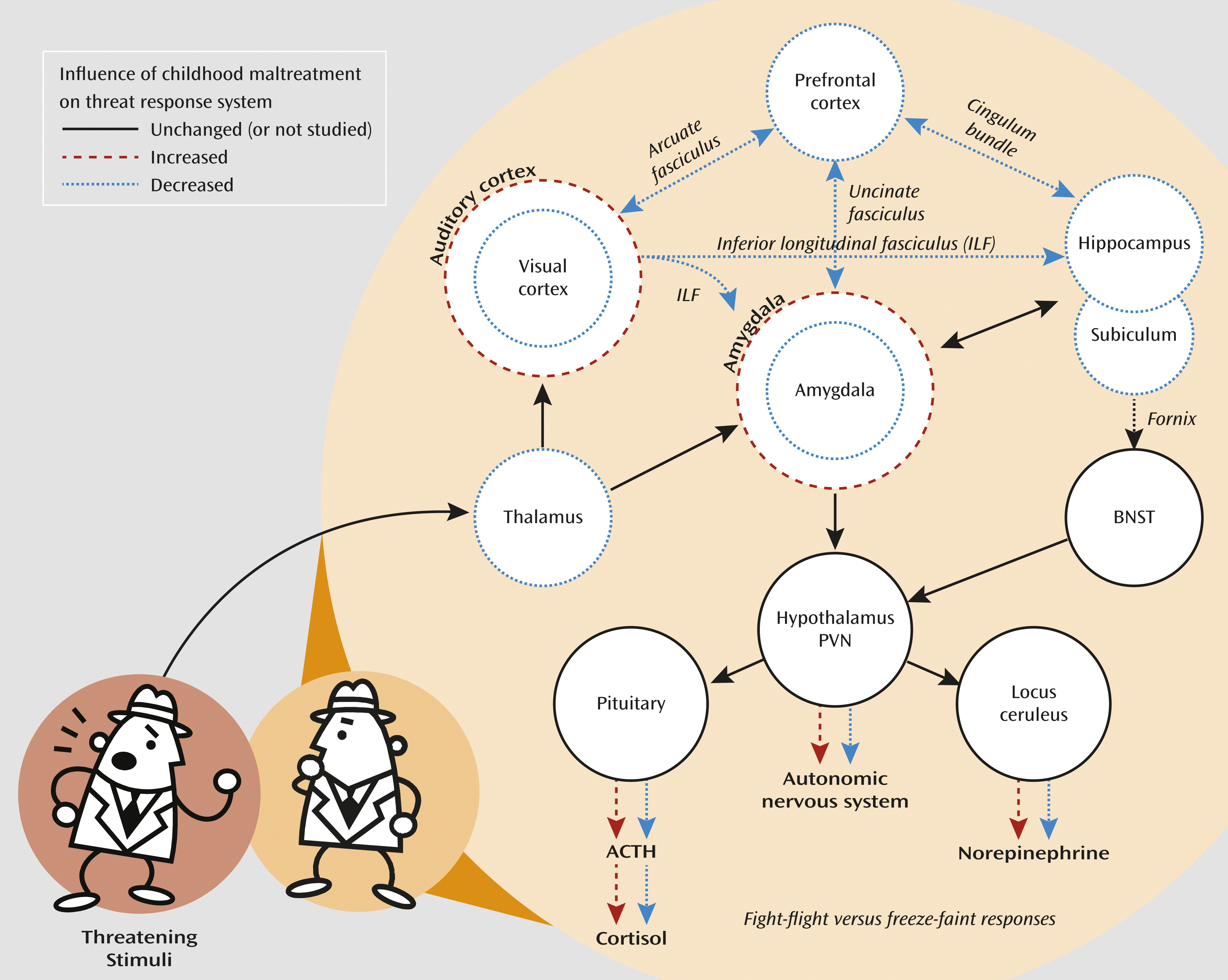
Psychosocial Correlates of Exposure
Treatment Implications
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 171.70 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

