Study Design
We conducted an epidemiological register-based cohort study on women from the Danish population. The main exposure variable was defined as any first psychiatric inpatient or outpatient contact within the first 90 days postpartum.
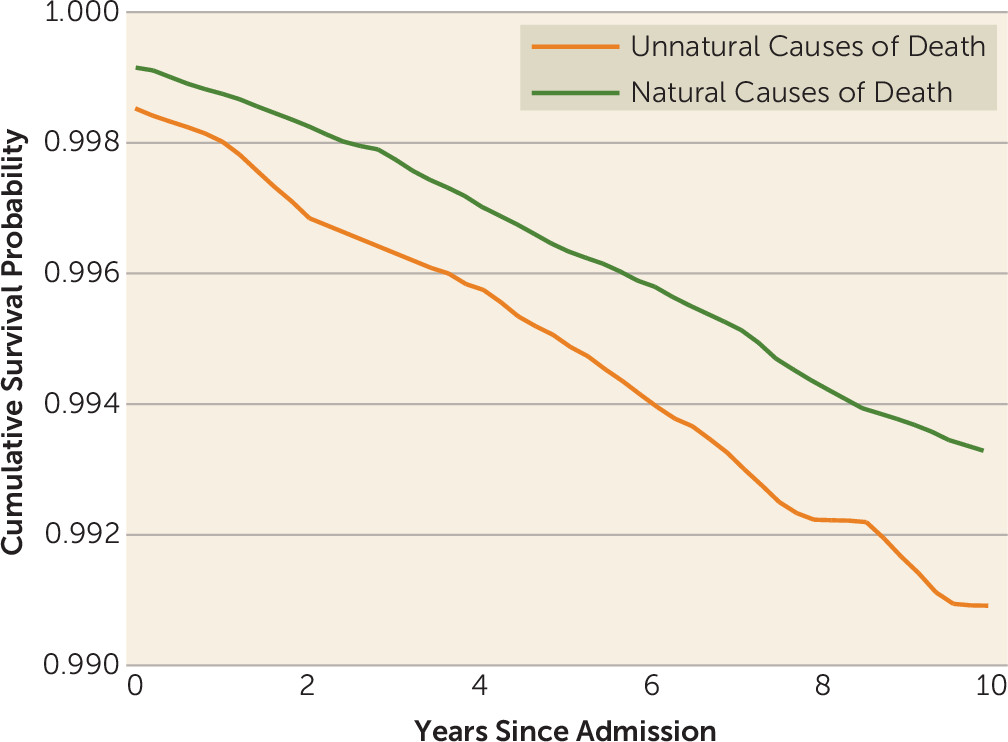
The outcome variable was defined as death by any natural cause (mortality from internal causes, such as diseases and medical conditions) or unnatural cause (mortality from external causes, such as suicide, accidents, and homicide) within the follow-up period.
Data were collected on all women born in Denmark on Jan. 1, 1950, or later. A total of 1,545,857 women were included in the study cohort after excluding women who emigrated from Denmark or died before age 15.
The follow-up period started on the women’s 15th birthday or on Jan. 1, 1970, whichever came later, to ensure as much as possible that there was complete information on cohort members. Follow-up ended at the date of emigration from Denmark, at the date of death, or on Dec. 31, 2011, whichever came first. This time frame provided a maximum follow-up period of 42 years and a maximum age of 62 for the women in the cohort.
Data Sources
Data on the women in our cohort were collected through the linkage of four Danish population registers, described below. Every individual in Denmark has a unique identification number registered through the Danish Civil Registration System (CRS) (
17) that is used in every Danish national register. This personal identifier allows for accurate linkage of information between and within the registers used in this study.
The CRS was established in 1968 and contains information on CRS number, gender, date of birth, updated vital status, data on all legal children, and CRS numbers of parents. We used the CRS registry in the present study to identify members of the cohort.
The Danish Psychiatric Central Register (
18) was computerized in 1969 and contains data on all admissions to Danish psychiatric inpatient facilities. Data covering outpatient contacts were added to the register in 1995. For the present study, the Danish Psychiatric Central Register provided information on all psychiatric inpatient and outpatient history for all cohort members as well as for their parents, thereby offering additional information on psychiatric family history. For the evaluation of psychiatric treatments in relation to childbirth, we observed women who gave birth on Jan. 1, 1970, or later to ensure as complete follow-up information as possible. As there are no private psychiatric inpatient facilities in Denmark, all admissions are represented in this register.
ICD-8 was the diagnostic system used in Denmark until Dec. 31, 1993 (
19), and on Jan. 1, 1994, ICD-10 was introduced (
20). We identified all diagnostic codes included in the chapter on mental and behavioral disorders in ICD-10 and the corresponding diagnostic codes in ICD-8 (
21).
To characterize the variation of specific diagnoses in the postpartum period, the frequency of the following diagnostic groups was calculated: mental and behavioral disorders associated with the puerperium (ICD-10: F53.1, F53.9; ICD-8: 294.49); neurotic, stress-related, and somatoform disorders (ICD-10: F40.9, F43.02, F43.2, F43.22, F43.9; ICD-8: 300.09, 300.19, 307.99); mood (affective) disorders (ICD-10: F31.2, F32.1, F32.9; ICD-8: 296.29, 296.99, 298.09, 298.19, 300.49); schizophrenia, schizotypal, and delusional disorders (ICD-10: F23.01; ICD-8: 298.29, 298.39, 298.89, 298.99, 299.05, 299.09, 301.83); and remaining diagnoses (ICD-10: F06.0, F10.0, F10.2, F11.2, F13.24, F99.9; ICD-8: 301.80, 301.81, 304.09, 304.49, 304.99, 310.99, 793.09, Y119).
The Danish Register of Causes of Death (
22) was computerized in 1970 and provides data on all causes of death for Danish citizens who die in Denmark. This register contained the data necessary to differentiate between natural and unnatural causes of death as well as information on the specific cause of death. Natural causes of death were defined as death from diseases and medical conditions. Specific subgroups of natural causes of death were defined as malignant neoplasm (ICD-10: C00–D09; ICD-8: 140–209), cardiovascular disease (ICD-10: I00–I25, I27, I30–I52; ICD-8: 390–429), and other natural causes of death (ICD-10: A15–A19, B90, A00–A09, A20–A99, B00–B89, B91–B99, F03.9, I60–I72, R54, J00–J99, K00–K93, N00–N99, Q00–Q99, P00–P96; ICD-8: 000–019, 020–136, 430–438, 794, 290–315, 440–448, 460–577, 580–629, 740–779). Unnatural causes of death were suicides, homicides, and accidents (ICD-10: V01–Y98; ICD-8: E9500–9590, E9600–9790, E8100–8239, E8000–8079, E8250–9499). Information on natural and unnatural causes of death was missing in 713 of the 33,395 deaths in the cohort, but the information was available for all cases of fatality among women with postpartum psychiatric disorders. To calculate mortality rate ratios (MRRs) for suicide, we used the ICD-10 codes X60–X84 and the ICD-8 codes E950–E959. Note that these specific diagnostic codes in ICD-10 are named “intentional self-harm” and were defined as suicides for the present study. Accidental deaths were defined by the ICD-10 codes V01–X59, Y10–Y86, Y87.2, and Y88–Y89 and the ICD-8 codes E810–823, E800–807, and E825–949.
The Danish National Patient Register (
23) contains information on medical inpatient contacts for all hospitals in Denmark from 1977 onward. Outpatient data were added to the register after 1995. This register offered the information necessary to calculate a Charlson comorbidity index for each of the women in the cohort. The Charlson index, an indicator of disease burden, consists of 19 severe chronic diseases, each assigned a weight from 1 to 6 corresponding to the severity of the disease. The score is then calculated by the sum of the weights (
24).
To assess the interaction of comorbid alcohol and substance abuse among the women in the cohort, we combined information from the Danish National Patient Register (
23) and the Danish Psychiatric Central Register (
18) using the following codes: alcohol: ICD-8: 291, 303, 570, 57100, 57110, 57300, 57301, 57710, 979, 980; ICD-10: F10, T510, Z721, R780, K70, K711, K712, K86; substance abuse: ICD-8: 304, 2944; ICD-10: F11, F12, F13, F14, F15, F16, F18, F19.