Mega-Analysis of Gray Matter Volume in Substance Dependence: General and Substance-Specific Regional Effects
Abstract
Objective:
Method:
Results:
Conclusions:
Method
Behavioral Phenotyping
| Group or Dependence Subgroup | Total N | Female | Age (years) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | Mean | SD | ||
| All Groups | |||||
| Control | 1,100 | 449* | 40.8 | 28.5* | 9.9 |
| Case | 2,140 | 731 | 34.2 | 33.3 | 10.6 |
| Alcohol | |||||
| Control | 292 | 99 | 33.9 | 31.3* | 10.2 |
| Case | 898 | 291 | 32.4 | 34.7 | 10.7 |
| Nicotine | |||||
| Control | 290 | 155* | 53.4 | 26.1* | 8.0 |
| Case | 602 | 250 | 41.5 | 30.8 | 9.8 |
| Cocaine | |||||
| Control | 99 | 39* | 39.4 | 36.0* | 10.3 |
| Case | 227 | 54 | 23.8 | 40.2 | 7.7 |
| Methamphetamine | |||||
| Control | 173 | 71 | 41.0 | 31.7 | 9.3 |
| Case | 228 | 78 | 34.2 | 32.9 | 10.0 |
| Cannabis | |||||
| Control | 246 | 85 | 34.6 | 22.7* | 7.5 |
| Case | 185 | 58 | 31.4 | 26.5 | 10.0 |
Preparation of Structural MRI Data
Linear Mixed-Effects Models With Cross-Validation
General Versus Substance-Specific Dependence Effects
Past-30-Day Use
| Left | Right | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | Cohen’s d | p | Cohen’s d | |||
| Region and Comparison | 1st Half of Data | 2nd Half of Data | Both Halves of Data | 1st Half of Data | 2nd Half of Data | Both Halves of Data |
| Subcortical volume | ||||||
| Substance-dependent versus nondependent controls | ||||||
| Amygdala | 0.0002 | 0.0039 | –0.055 | 0.0011 | 0.0037 | –0.041 |
| Hippocampus | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | –0.087 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | –0.081 |
| Nucleus accumbens | 0.0068 | 0.0214 | –0.025 | |||
| Cortical thickness | ||||||
| Substance-dependent versus nondependent controls | ||||||
| Caudal middle frontal gyrus | <0.0001 | 0.0370 | –0.038 | |||
| Fusiform gyrus | <0.0001 | 0.0231 | –0.036 | |||
| Inferior parietal cortex | <0.0001 | 0.0298 | –0.026 | |||
| Insula | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | –0.056 | 0.0007 | 0.0003 | –0.042 |
| Isthmus of cingulate gyrus | <0.0001 | 0.0447 | -0.035 | |||
| Medial orbitofrontal cortex | 0.0095 | 0.0491 | –0.029 | |||
| Middle temporal gyrus | 0.0910 | 0.0065 | –0.030 | 0.0040 | 0.0474 | –0.026 |
| Paracentral lobule | 0.0019 | 0.0015 | –0.031 | 0.0421 | 0.0056 | –0.024 |
| Precentral gyrus | <0.0001 | 0.0025 | –0.039 | <0.0001 | 0.0042 | –0.042 |
| Precuneus | <0.0016 | 0.0425 | –0.023 | |||
| Superior parietal cortex | 0.0082 | 0.0472 | –0.022 | |||
| Supramarginal gyrus | 0.0049 | 0.0131 | –0.027 | 0.0046 | 0.0319 | –0.026 |
| Left | Right | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | Cohen’s d | p | Cohen’s d | |||
| Region and Comparison | 1st Half of Data | 2nd Half of Data | Both Halves of Data | 1st Half of Data | 2nd Half of Data | Both Halves of Data |
| Subcortical volume | ||||||
| Alcohol-dependent versus nondependent controls | ||||||
| Amygdala | <0.0001 | 0.0021 | –0.107 | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | –0.111 |
| Globus pallidus | 0.0274 | 0.0005 | –0.075 | |||
| Hippocampus | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | –0.196 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | –0.180 |
| Nucleus accumbens | 0.0159 | 0.0013 | –0.048 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | –0.088 |
| Putamen | 0.0006 | <0.0001 | –0.098 | 0.0001 | 0.0014 | –0.080 |
| Thalamus | 0.0149 | 0.0002 | –0.098 | |||
| Cortical thickness | ||||||
| Alcohol-dependent versus nondependent controls | ||||||
| Caudal middle frontal gyrus | 0.0006 | 0.0219 | –0.062 | 0.0264 | 0.0298 | –0.054 |
| Fusiform gyrus | 0.0017 | 0.0002 | –0.072 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | –0.094 |
| Inferior temporal gyrus | 0.0021 | 0.0146 | –0.056 | 0.0148 | 0.0214 | –0.047 |
| Insula | 0.0023 | <0.0001 | –0.087 | |||
| Isthmus of cingulate gyrus | 0.0009 | 0.0005 | –0.078 | |||
| Lateral occipital cortex | 0.0013 | 0.0211 | –0.042 | |||
| Lateral orbitofrontal cortex | 0.0322 | 0.0021 | –0.061 | |||
| Medial orbitofrontal cortex | 0.0432 | 0.0197 | –0.060 | |||
| Parahippocampal gyrus | 0.0281 | 0.0265 | –0.076 | |||
| Paracentral lobule | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | –0.074 | 0.0053 | 0.0003 | –0.062 |
| Posterior cingulate gyrus | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | –0.091 | 0.0004 | <0.0001 | –0.085 |
| Precentral gyrus | 0.0091 | 0.0007 | –0.063 | 0.0008 | 0.0003 | –0.079 |
| Precuneus | 0.0008 | 0.0003 | –0.062 | 0.0039 | 0.0002 | –0.061 |
| Rostral anterior cingulate cortex | 0.0381 | 0.0090 | –0.082 | |||
| Superior frontal gyrus | <0.0001 | 0.0030 | –0.071 | 0.0003 | 0.0060 | –0.071 |
| Superior parietal cortex | 0.0198 | 0.0272 | –0.040 | |||
| Superior temporal gyrus | 0.0239 | 0.0353 | –0.062 | |||
| Supramarginal gyrus | 0.0493 | 0.0168 | –0.044 | |||
| Temporal pole | 0.0518 | 0.0464 | –0.063 | |||
| Cocaine-dependent versus nondependent controls | ||||||
| Supramarginal gyrus | 0.0177 | 0.0491 | –0.047 | |||
| Nicotine-, cocaine-, methamphetamine-, and cannabis-dependent versus nondependent controls | ||||||
| Inferior parietal cortex | 0.0011 | 0.4630 | –0.029 | |||
| Insula | 0.0057 | 0.0300 | –0.041 | 0.0303 | 0.0274 | –0.033 |
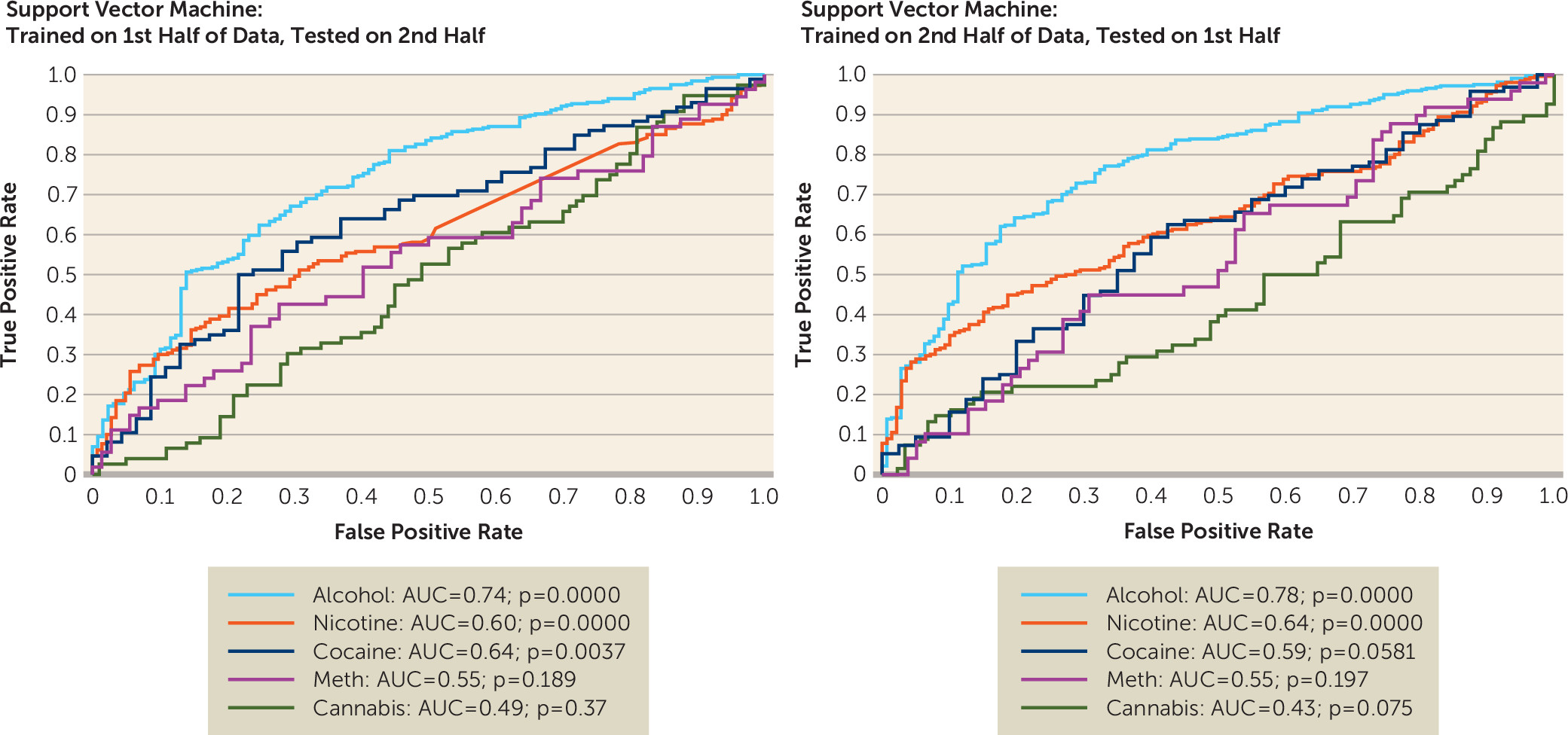
Support Vector Machine Classification
Results
Model 1: Dependent Versus Nondependent Subjects
Model 2: Substance Dependence Groups Compared Separately to Nondependent Control Subjects
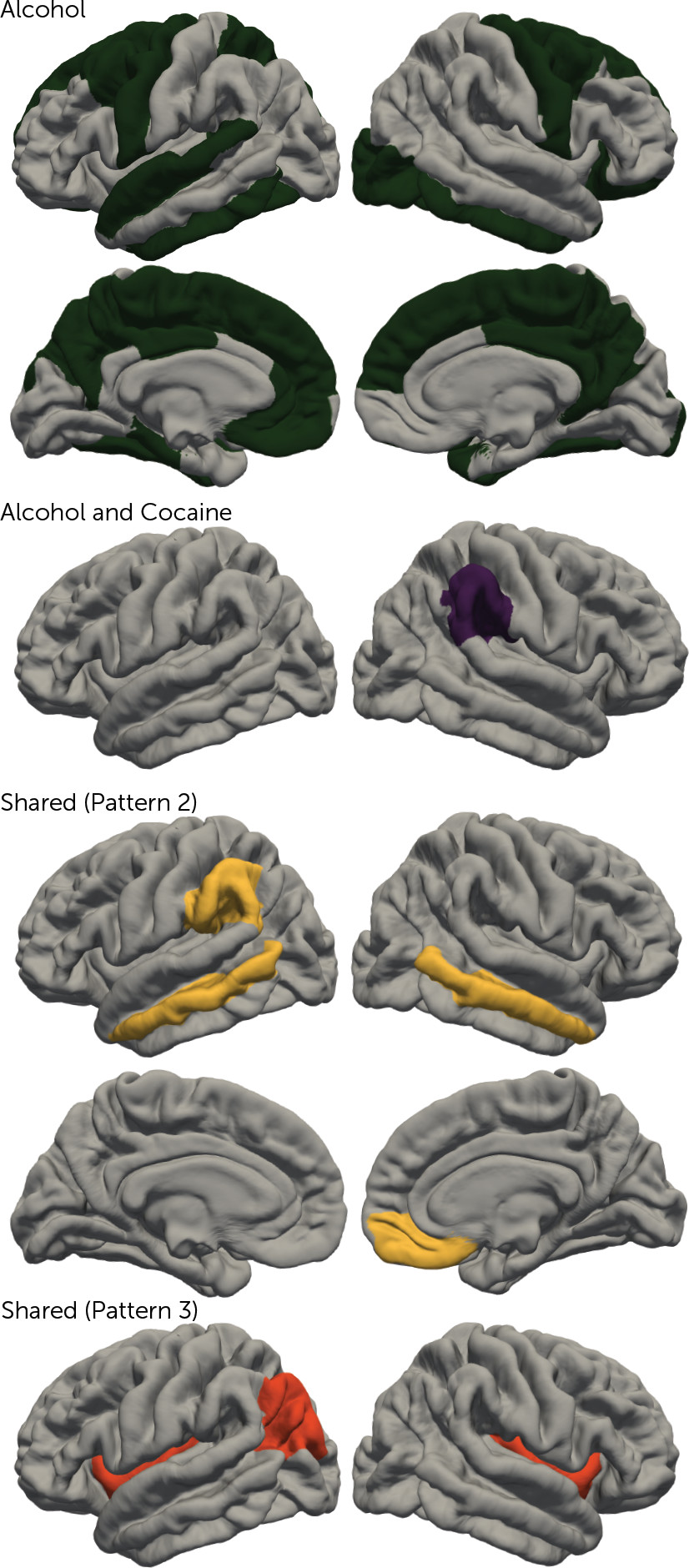
Substance-Specific Versus Shared Substance-General Effects
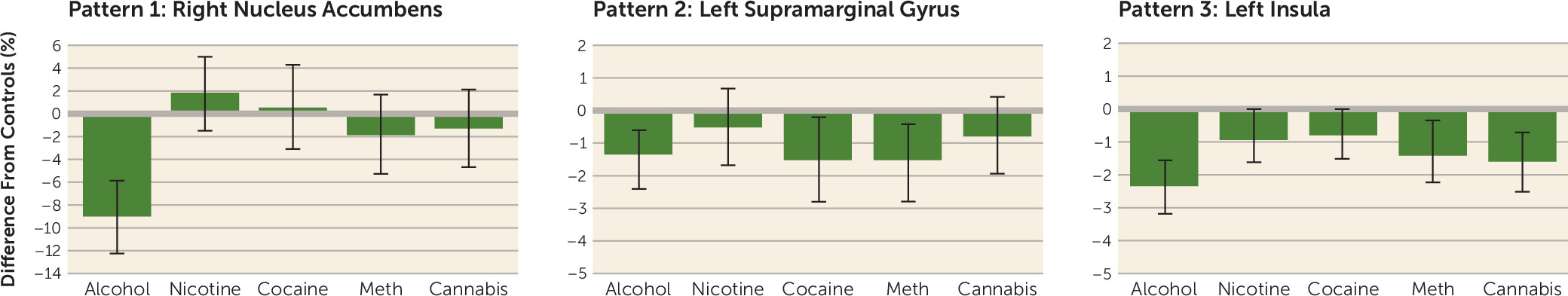
Pattern 1 (substance specific).
Pattern 2 (substance general).
Pattern 3 (substance general).
Past-30-Day Use
Support Vector Machine
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 82.46 KB
- View/Download
- 358.73 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

