Many if not most individuals with schizophrenia depend on Medicaid to fund mental health services, psychotropic medicines, or both (
1–
10). Unfortunately, Medicaid programs face substantial financial challenges (
11–
17) that may or may not be addressed by health care reform (
18).
Research in Florida around the year 2000 suggested that interruption of Medicaid was associated with a subsequent increase in inpatient care for beneficiaries with depression (
19). Work in Utah during the early 1990s (
5) indicated that interruption of Medicaid coverage led to increased psychiatric hospitalization for beneficiaries with schizophrenia. Studies in the early 1980s comparing Medicaid beneficiaries who had schizophrenia in New Hampshire (which limited Medicaid prescriptions) with those in New Jersey (which had unlimited Medicaid prescriptions) provided strong evidence that cutbacks led to substantial increases in psychiatric hospital admissions (
20,
21).
This project examined a “natural experiment” regarding health insurance for people with schizophrenia. In the early 1990s, Oregon expanded Medicaid eligibility (
22,
23). Under previous eligibility requirements, persons with chronic mental illness who received disability payments (such as Supplemental Security Income or Social Security Disability Insurance) were often considered “too wealthy” to qualify for Medicaid (
24), but after expansion of eligibility criteria, virtually anyone disabled by conditions such as schizophrenia could obtain Medicaid (
25).
Unfortunately, owing to revenue declines, in 2003 state policy makers instituted mechanisms, such as premiums, copayments, and stricter eligibility criteria, that forced many Medicaid beneficiaries out of the program (
12,
26–
31). Relatively speaking, there was little change in enrollment of traditional (federally mandated) Medicaid patients, such as those in the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program (
32). However, enrollment in Oregon’s expansion program dropped from about 102,000 patients in 2002 to around 51,000 in late 2003 (
30,
32). The state financial crisis worsened in February 2004, when voters defeated a proposed tax increase.
Large numbers of Medicaid beneficiaries with severe mental illnesses lost all coverage. Some 1,685 patients who had a psychiatric hospitalization during 2002 lost Medicaid coverage in 2003; between March and December 2003 some 2,373 Medicaid patients who had been dispensed at least one second-generation antipsychotic medication were dropped from Medicaid rolls. Loss of insurance coverage occurred in waves and was prolonged in that individuals seemed to be without Medicaid for months, if not years, after leaving the program (
12,
26,
28).
This tragic situation provided an opportunity to examine the impact of Medicaid cutbacks. Of particular interest to policy makers were involuntary (noncriminal) psychiatric hospitalizations (either to local general hospitals or to state psychiatric hospitals) because these admissions are paid for by the state if the patient is uninsured. In addition, the state mental health agency was especially concerned about individuals who had been prescribed second-generation antipsychotic medications because these persons might be at high risk of unfortunate consequences related to loss of health insurance (
20,
21). Given the considerable effort expended and the high hopes the state had for broadening Medicaid coverage (
22–
25), there was also interest in differential impact of policy changes on people in the “expansion” versus “traditional” Medicaid populations. Accordingly, analyses tested for possible interactions between type of Medicaid and coverage termination.
The purpose of this project was to compare involuntary psychiatric hospitalizations between individuals with schizophrenia who lost coverage versus those who continued Medicaid enrollment.
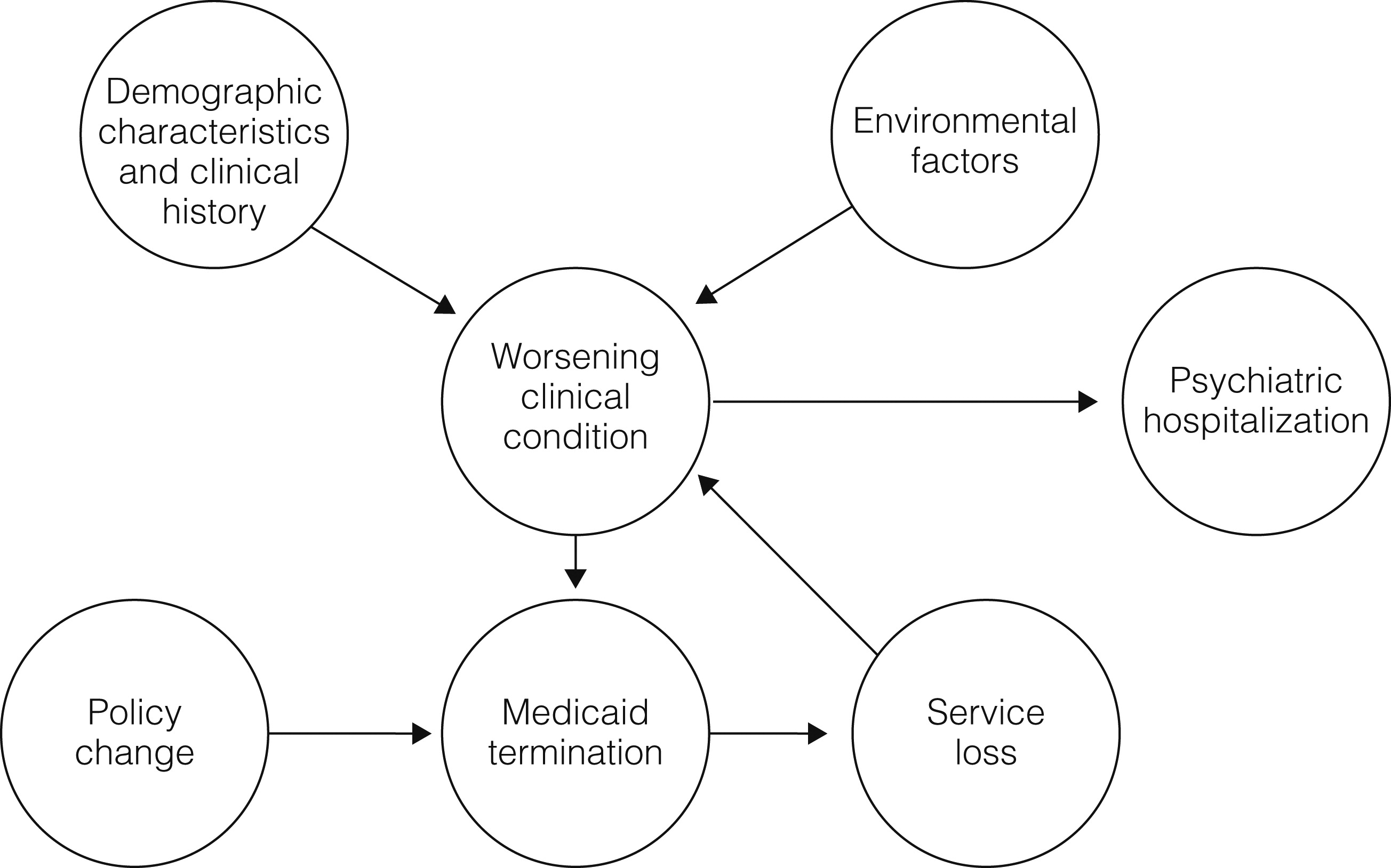
Figure 1 shows the conceptual framework. In one pathway, policy change results in Medicaid termination, which in turn leads to loss of services and psychiatric hospitalization, presumably because of worsening clinical condition. However, the situation is more complicated than just described because other influences on clinical condition (such as demographic characteristics, clinical history, or environmental factors) might also drive hospitalization. Moreover, a worsening clinical condition could itself lead to loss of Medicaid coverage. For example, people whose psychotic symptoms increase may be unable to comply with the numerous administrative tasks (such as reenrollment) required to maintain Medicaid coverage. Accordingly, analyses included approaches in which persons served as their own control group.
We hypothesized that Medicaid recipients who lost their benefits would be more likely than those who retained coverage to be involuntarily hospitalized in a psychiatric hospital. Here, too, analysis was complicated because in Oregon civil state psychiatric hospital admissions (for nongeriatric adults) are almost entirely via court commitment (
33,
34). Moreover, involuntary admission to a local general hospital is (in virtually all cases) a prerequisite for civil court commitment to a state psychiatric hospital (
34,
35). Admission to a state psychiatric hospital requires a civil commitment hearing in which a judge finds the person to be dangerous to self or others or gravely disabled (
35). Such hearings almost always take place after at least a few days in a general hospital psychiatric unit. Roughly 10% to 20% of involuntary general hospital admissions lead to civil commitment (
34). Therefore, analyses distinguished between general hospital versus state psychiatric hospital involuntary admissions.
Methods
Data and eligibility criteria
Information was obtained from state Medicaid, mental health, and vital statistics data systems. The Medicaid Management Information System provided eligibility and pharmacy data plus diagnostic information. The state mental health information system captured all involuntary admissions to local general and state psychiatric hospitals. Dates of death were obtained from state vital statistics. A state project called the Integrated Client Data Base facilitated data linkage via name, date of birth, Social Security Number, and a Medicaid alphanumeric identifier known as the “prime number.”
Inclusion criteria were enrollment in the Oregon Medicaid program for at least 90% of calendar year 2002, diagnosis of schizophrenia, and use of outpatient mental health services or receipt of at least one second-generation antipsychotic medication dispensed during 2002. Exclusion criteria were Oregon Medicaid coverage for <90% of the calendar year 2002 or residence in a nursing home during calendar year 2002. Diagnosis of schizophrenia was established by either a hospital discharge diagnosis of schizophrenia or two outpatient diagnoses of schizophrenia in 2002 or earlier (
36,
37). Analyses were restricted to persons between ages 18 and 65 during calendar year 2002 (which excluded 5% of the potential study population) and to persons whose state psychiatric hospitalization days during 2002 were fewer than 90 (which excluded .3% of the potential study population).
Medicaid enrollee cohorts
Persons included in the study were placed in one of three mutually exclusive cohorts. To be considered covered during a given year, an individual was required to have been enrolled in Oregon Medicaid for >90% of the 12-month period. Conversely, noncoverage was defined to be enrollment for <50% of the 12-month period. Cohort A (N=435) was covered in 2002 but not covered in 2003 and 2004 (that is, individuals had just one year of coverage). Cohort B (N=187) was covered in 2002 and 2003 but not in 2004 (that is, individuals had two years of coverage). Cohort C (N=3,427) was covered in 2002, 2003, and 2004 (continuous coverage).
Mortality differences among cohorts were expected, given the selection procedures. Specifically, there were likely to be few if any deaths in the continuous Medicaid coverage group, whereas deaths during the study period were more likely among those who lost coverage. Accordingly, times at risk of hospitalization during the study period were calculated for all persons between January 1, 2002, and December 31, 2004 (or ending with date of death).
There were 52 deaths during the study period (January 1, 2002, through December 31, 2004) in cohort A (12%), 45 in cohort B (24%), and 14 in cohort C (.4%). Mean±SD times at risk of hospitalization among cohorts were 1,025±201 days for cohort A, 1,022±135 days for cohort B, and 1,095±7 days for cohort C.
Outcome measure and analyses
The outcome measure was involuntary psychiatric hospitalization. By definition, all state psychiatric hospital admissions were involuntary and were almost always preceded by involuntary general hospital psychiatric admissions.
Predictors included cohort, year, race-ethnicity, gender, age, Medicare (yes or no), and type of Medicaid (traditional versus expansion). Year was one-dimensional. There were also two-way interaction terms (year by type of Medicaid, cohort by year, and cohort by type of Medicaid) as well as the three-way interaction term (year by cohort by type of Medicaid).
All analyses were repeated with the first study year (2002) as baseline so individuals were their own controls for analysis. Outcomes were hospitalizations during 2003, 2004, or both years. Predictors included cohort, year, race-ethnicity, gender, age, Medicare, type of Medicaid, and hospitalization during 2002 plus two-way and three-way interaction terms.
Binary logistic regression models were used in analyses of admissions (yes versus no). For studies of hospitalization days, the data were markedly skewed (many persons had no hospitalization days). Therefore, models included Poisson regression, negative binomial regression (
19), and two-part models in which admission (yes versus no) was predicted by a binary logistic regression equation and then hospitalization days (given admission) were predicted by a linear model. To account for repeated measures, generalized estimating equations were used (with an unstructured variance-covariance matrix).
Stratification via propensity score subclassification (
38–
41) was used to adjust for differences among cohorts. With the use of logistic regression, the dependent variable was Medicaid coverage status (lost versus retained). Potential predictors included age, gender, race-ethnicity, and type of Medicaid (expansion or traditional). Statistically significant regression coefficients were used to generate the propensity score for each person. Typically, persons were grouped into percentiles of the propensity score (
42).
Because there were three cohorts, two propensity scores were generated. One score (p1) was generated by a logistic regression model that predicted loss of Medicaid coverage versus continuous coverage. Statistically significant (p<.005) predictors were gender, Medicare, and type of Medicaid coverage. Scores computed with or without inclusion of deceased persons were highly correlated (Pearson R=.999). There were only eight unique p1 values, and scores for 93% of persons fell within five values. The other score (p2) predicted whether loss of coverage would occur earlier or later. Statistically significant (p<.008) predictors of p2 were gender and Medicare. Scores calculated with or without inclusion of deceased persons were highly correlated (Pearson R=1.000). There were only four unique p2 values among members of cohorts A and B. Subclassification of persons was determined by a two-dimensional grid (percentiles of p1 crossed with percentiles of p2).
Because propensity score matching accounted for demographic characteristics, Medicare, and type of Medicaid, the predictors in the stratified models were cohort, study year, and the interaction of cohort and study year (the group-by-time interaction term). Coefficients pertaining to the group-by-time interaction term (from each stratum) were summed. Estimated standard errors for those coefficients were combined to generate an estimated standard error for the overall group-by-time interaction term coefficient.
SPSS, version 17, statistical software was used for the analyses. The project was approved by the Oregon Health and Science University Institutional Review Board.
Results
Women were overrepresented in the group with continuous coverage, but there were no statistically significant differences among cohorts in age or race-ethnicity (
Table 1). As expected, persons with expansion Medicaid were markedly overrepresented among the cohorts who lost coverage. Similarly, people dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid coverage were overrepresented in the early loss-of-Medicaid cohort.
The anticipated differences among cohorts in mortality and in times at risk of hospitalization were also found (
Table 1).
Some 749 persons were involuntarily hospitalized, of whom 731 (98%) had at least one general hospital admission. As expected, only a minority of persons with an involuntary admission to a general hospital (124 or 17%) also had state psychiatric hospitalization days during the study period.
General hospital admissions
Roughly 20% of each cohort had at least one involuntary admission to a general hospital. In bivariate analyses, there were no statistically significant differences among cohorts in general hospital psychiatric admissions. In multivariate analyses, the only statistically significant predictors were age and gender. Analyses stratified by propensity score showed that the group-by-time interaction coefficient was not significant for either cohort A or cohort B with study year. Using the first study year as baseline, we found that the only statistically significant predictors were age, gender, and admission (yes or no) in 2002. For all analyses, results were unchanged when deceased persons were included in the calculations.
Table 2 summarizes these results.
There were roughly two to three involuntary general hospital psychiatric days per cohort member per year. There were few changes over time in general hospitalization days for cohort C (continuous coverage). Conversely, the group with only two years of coverage showed an increase in general hospitalization days initially and then a decline. The group with the shortest Medicaid coverage showed a continuous decline in general hospitalization days (see summary of results in
Table 2).
Analyses were conducted with general hospital psychiatric days as the dependent variable. The coefficient pertaining to the three-way interaction term for cohort A was positive and statistically significant (p<.005) for all models. The other three-way interaction term coefficient (pertaining to cohort B) was not statistically significant in any model. The implication of this finding is that among individuals with only one year of Medicaid, there was a greater decline in general psychiatric hospitalization days over time for those in the expansion population compared with traditional Medicaid. Similarly, with the first study year as the baseline, the only statistically significant predictors of general hospitalization days were age and number of general hospitalization days in 2002. Results were unchanged whether or not deceased persons were included. Results were also unchanged when the dependent variable was the percentage of days at risk of hospitalization (that is, days prior to death or the end of the study period) spent in a general hospital psychiatric unit.
State psychiatric hospital admissions
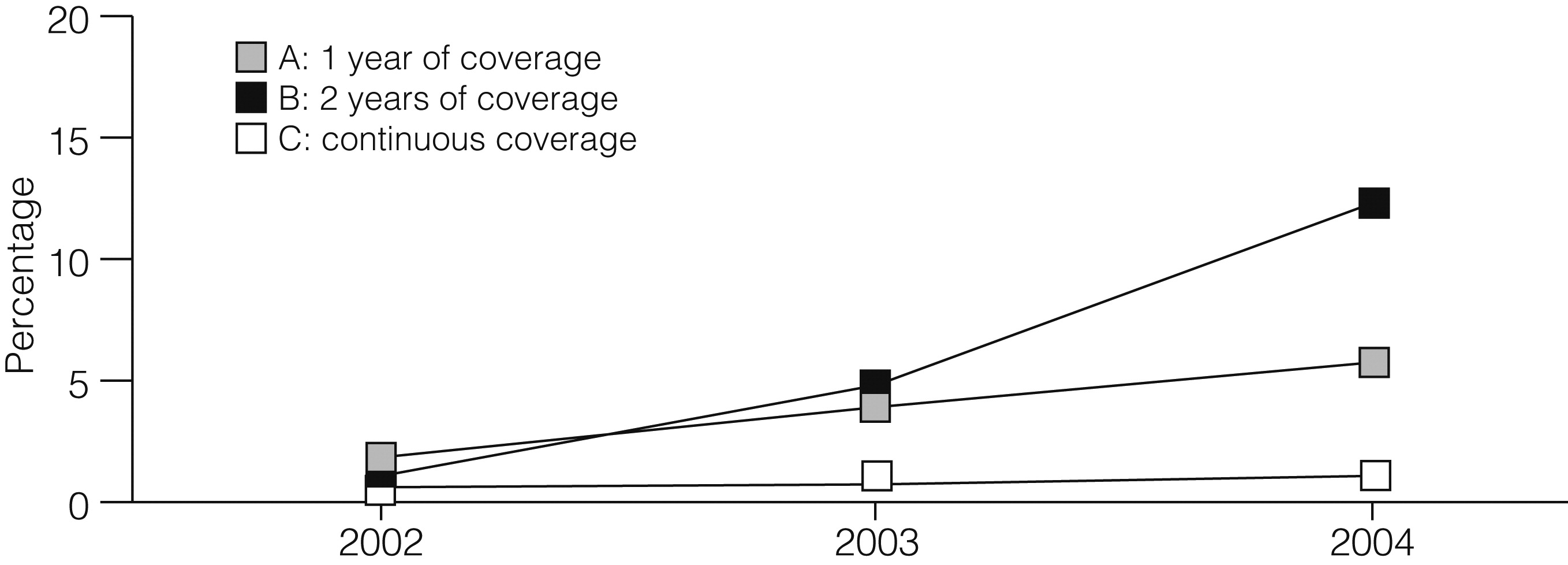
The situation was much different for utilization of the state psychiatric hospitals. About .5% of persons had a state psychiatric hospital admission in the first study year (2002) with no differences among cohorts (by chi square test). However,
Figure 2 shows that the percentage of persons admitted to a state psychiatric hospital rose over time for members of cohort A and cohort B and that there was little or no change over time for cohort C (continuous coverage) members. As shown in
Table 1, over the three study years only 2% of members in the continuous coverage group (cohort C) had a state psychiatric hospital admission, compared with 6% and 16% of cohorts A and B, respectively, who lost Medicaid coverage.
In binary logistic generalized estimating equation models, the coefficient pertaining to the three-way interaction term for cohort A (early Medicaid loss) was negative and statistically significant (p=.03). The other three-way interaction term coefficient (pertaining to cohort B) was not statistically significant in any model. The implication is that among individuals with only one year of Medicaid, there was a greater increase in chances of state psychiatric hospital admission over time for those with expansion (versus traditional) Medicaid. Medicare status was not a statistically significant predictor.
Owing to small numbers of state psychiatric hospital admissions in some cells of the statistical analysis, it was not possible to repeat the analyses with propensity score matching. Presumably for similar reasons, there were convergence problems when attempting an analysis in which the first study year was used as baseline.
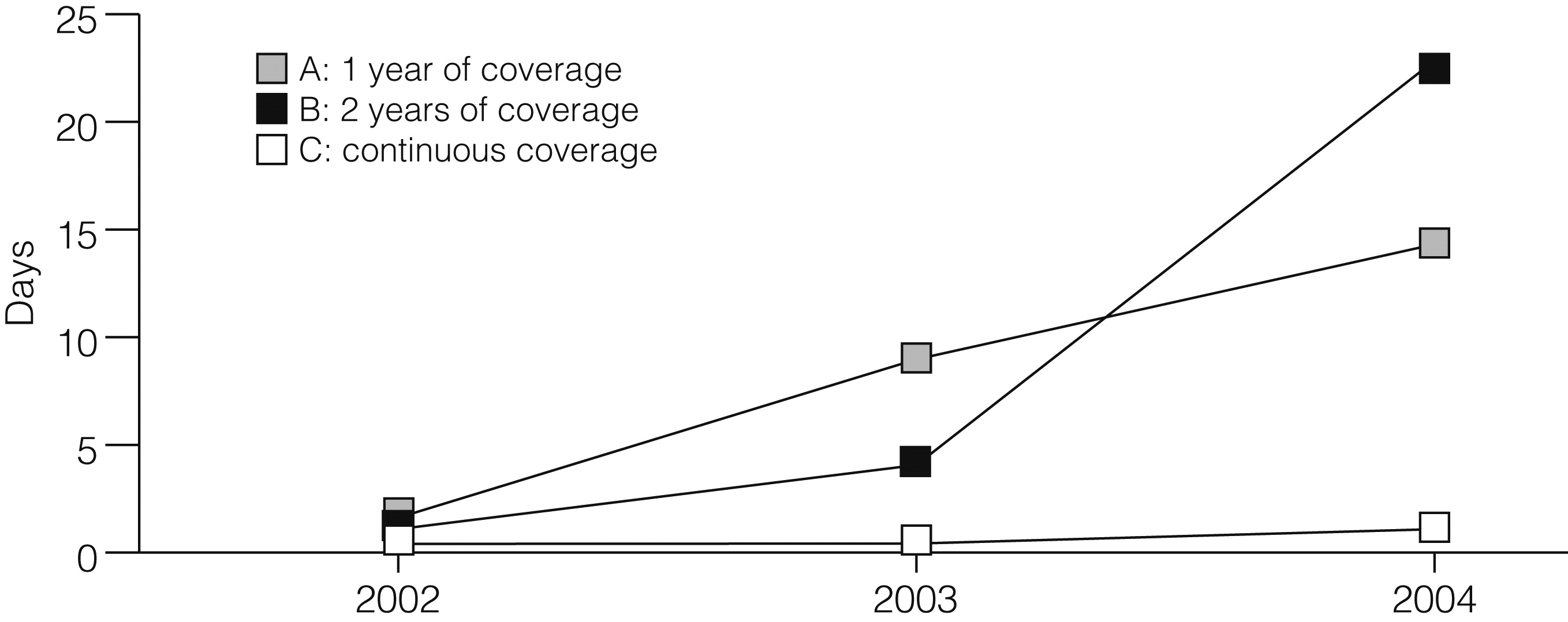
Figure 3 shows average state psychiatric hospitalization days per person per year for each cohort. The continuous coverage group (cohort C) had very low levels of state psychiatric hospital use throughout the study period, whereas state psychiatric hospitalization days increased over time for the persons who lost Medicaid coverage. The picture was the same whether or not deceased persons were included.
Analyses were conducted with state psychiatric hospitalization days as the dependent variable. The coefficient pertaining to the three-way interaction term for cohort A was negative and statistically significant (p<.003) for all models. The other three-way interaction term coefficient (pertaining to cohort B) was not statistically significant in any model. The implication is that among individuals with only one year of Medicaid, there was a greater increase in state psychiatric hospitalization days over time for those with expansion (versus traditional) Medicaid. Medicare status was not a statistically significant predictor. In general, the various models gave very similar results, except that the negative binomial model could not be estimated owing to singularity of the Hessian matrix. Results were similar whether or not deceased persons were included. Results were also similar when the dependent variable was percentage of days at risk of state hospitalization (that is, days to death or end of the study period) that were spent in a state psychiatric hospital.
There were convergence problems related to matrix singularity in some models that used the first study year as the baseline from which to predict state psychiatric hospitalization days during 2003 or 2004. Indeed, the negative binomial model could not be estimated.
However, for the other types of models, the coefficient pertaining to the three-way interaction term for cohort A (early Medicaid loss) was negative and statistically significant (p<.03 for all models). Again, the implication is state hospitalization days increased for expansion (versus traditional) Medicaid recipients who lost coverage early during follow-up. Results were unchanged whether or not deceased persons were included.
Conceivably, individuals might have been hospitalized (especially in a state psychiatric hospital) and subsequently have lost Medicaid coverage. However, only a minority (26%) of the sample who lost their Medic- aid coverage did so within 30 days of hospitalization.
Discussion
The findings partially supported the hypothesis. Loss of Medicaid coverage seemed to have little impact on involuntary admission to local general hospitals. Conversely, there was a strong connection between Medicaid termination and increased state psychiatric hospitalization.
Financial considerations may be pertinent when interpreting the results because Medicaid usually pays for general hospital care but does not cover state psychiatric hospital services. Perhaps general hospital providers were more likely to facilitate civil commitment court hearings (the gateway to the state psychiatric hospital) for individuals who lost Medicaid than for those who retained coverage.
Medicare coverage did not appear to attenuate impact of Medicaid loss. In fact, individuals with dual Medicare-Medicaid coverage were overrepresented among persons who lost Medicaid early in the study period, presumably because their incomes (thanks to disability payments) exceeded Oregon’s newly reduced threshold. Persons who lost Medicaid were then at increased risk of state psychiatric hospitalization regardless of Medicare coverage. Explanations for this finding include the possibility that Medicare might be a marker for especially severe disability as well as scenarios in which community mental health agencies did not serve beneficiaries covered only by Medicare.
Type of Medicaid (via traditional or expanded coverage) was related to involuntary psychiatric hospitalization but in complex ways. Membership in the Medicaid expansion group was, if anything, related to decreased utilization of general hospital services. Conversely, being in the Medicaid expansion group was a powerful predictor of admission to the state psychiatric hospitals and of the number of days spent in a state psychiatric hospital (even after adjustment for loss of Medicaid coverage, among other factors).
Although these seemingly contradictory findings regarding hospitalization might have arisen by chance, there is at least one plausible explanation. In particular, use of the state psychiatric hospitals may well reflect clinical severity. As noted, virtually all admissions to a state psychiatric hospital were preceded by general hospital psychiatric admissions. Conversely, only a small fraction of individuals admitted to a general hospital were subsequently admitted to a state psychiatric hospital. The implication here is that individuals admitted to a state psychiatric hospital were much more disabled than persons who had only a general hospital admission.
A plausible scenario is that an individual who maintained Medicaid coverage also maintained contact with outpatient care providers who facilitated general hospital admission if the client showed signs of deterioration. Conversely, an individual who lost Medicaid coverage would most likely have also lost contact with outpatient services. In the case of Medicaid loss, general hospital admission might have been delayed until the person had experienced substantial decline. Such a person might require both general hospital and state psychiatric hospital care. It would be expected, then, that an individual who lost Medicaid coverage would have both reduced general hospital usage plus increased state psychiatric hospital usage compared with people who had continuous Medicaid coverage.
In this scenario, the change in Medicaid policy influenced Medicaid coverage with subsequent impact on hospitalization. Indeed, for an overwhelming majority of persons, loss of Medicaid preceded hospital admission.
Because the project was observational, there were limitations. People who lost Medicaid coverage could have left Oregon and become lost to follow-up. However, differential loss to follow-up would bias the results against the hypothesis because people who left did not generate hospitalizations in Oregon. Persons were not assigned at random to lose or keep Medicaid coverage, and there were numerous differences between the comparison groups. Clinical data pertaining to illness severity were not available. However, in several analyses each person was his or her own control. Moreover, the pre-post comparisons and the generous sample sizes should have obviated problems with “difference in differences” methodology (
43). In addition, propensity score matching was used to compensate for lack of randomization. Also, loss of coverage was largely due to policy decisions external to the client in contrast to earlier studies of Medicaid interruptions (
5,
19). Nonetheless, results need to be interpreted cautiously and with recognition that association is not necessarily causation.
A significant limitation is that (by design) the project focused on involuntary hospitalizations. Inability to link follow-up voluntary admissions means that impacts (if any) of Medicaid cutbacks on voluntary hospitalization remain unknown. Conceivably, providers could have been more likely to invoke involuntary (rather than voluntary) admission of persons who lost Medicaid versus people who retained coverage. However, this bias would apply only to general hospitals because all state hospital admissions are involuntary. In fact, most Oregon psychiatric admissions are involuntary (
34). For example, 60% of general hospital psychiatric admissions of Medicaid clients in 2004 were involuntary, as were 78% of non-Medicaid admissions.
Conclusions
These limitations notwithstanding, it appears that state Medicaid policies designed to reduce coverage may have resulted in increased use of state psychiatric hospitals by people with schizophrenia. In addition to unfortunate consequences for persons who lost their Medicaid coverage, from the state’s perspective there might well have been a trade-off between savings on Medicaid versus growth in state psychiatric hospital expenditures. Decision makers need to weigh benefits against risks when considering Medicaid policy changes.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grant R03 MH 074471-01 from the National Institute of Mental Health and by an unrestricted investigator-initiated research grant from Eli Lilly and Company.