Substance Use Among College Students
Abstract
Abstract
Clinical Context
Substance Use on College Campuses
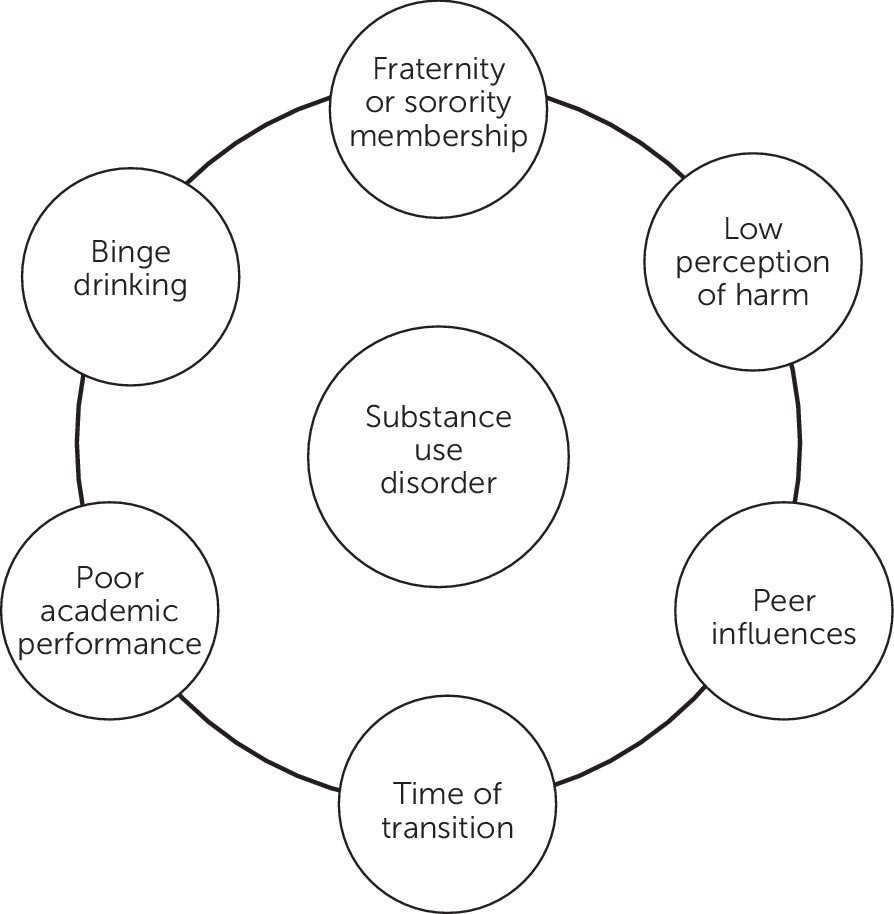
Risk Factors Specific for Substance Use on College Campuses
Substance Use and Sexual Assault
Treatment Strategies and Evidence
Overview
| Substance | High-risk population | Screening | Brief interventions | Treatment recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Fraternity and sorority membership, students who used heavily in high school | CRAFFT (for adolescents; car, relax, alone, forget, friends, trouble), CAGE Questionnaire (cut down, annoyed, guilty, eye opener), AUDIT (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test), TAPS Tool (tobacco, alcohol, prescription medication and other substance use), NM ASSIST (NIDA-Modified Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test) | BASICS Program; College Drinker's Check-up (CDCU); motivational interviewing to address discrepancy between problematic use and values and to assess readiness for change | Detoxification when withdrawal symptoms are present; referral for individual therapy, self-help groups, or pharmacotherapy (i.e., naltrexone or acamprosate) for alcohol use disorders; close monitoring around academic performance and necessary accommodations |
| Tobacco, nicotine | Fraternity and sorority membership, existing mental health difficulties | NM ASSIST | Motivational interviewing to address discrepancy between problematic use and values and to assess readiness for change | Nicotine replacement therapy; no evidence that vaporizing devices lead to reduced risk of relapse (may escalate use); behavioral therapy referral |
| Stimulants | Academic difficulties, preexisting ADHD, midterms | DAST (Drug Abuse Screening Test), TAPS Tool, NM ASSIST | Motivational interviewing to address discrepancy between problematic use and values and to assess readiness for change; warn of risk of using cocaine with alcohol. | No evidenced-based pharmacological intervention at this time; balance risk of prescribing stimulants with need, if indicated; cognitive-behavioral therapy and 12-step programming may be helpful; close monitoring of academic performance and necessary accommodations |
| Opioids | Withdrawal from social interactions, poor academic performance, existing mental health difficulties | DAST, TAPS Tool, NM ASSIST | Motivational interviewing not advised; thoroughly assess for signs of withdrawal and acute safety concerns | Significant risk of overdose; consider detoxification setting or residential treatment setting for regular use; buprenorphine-naloxone and long-acting injectable naltrexone are considered first-line treatment; close monitoring of academic performance and necessary accommodations |
| Marijuana, cannabis | Low perception of harm of marijuana use, peers who use, poor academic performance, existing mental health concerns | World Health Organization ASSIST (Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test), how many times have you used marijuana in the past 90 days, TAPS Tool, NM ASSIST | Motivational interviewing to address discrepancy between problematic use and values and to assess readiness for change; marijuana eCHECKUP TO GO | N-acetylcysteine 1,200 mg twice daily may reduce cravings and risk of relapse among motivated individuals up to age 21 in addition to contingency management; behavioral therapy referral; close monitoring of academic performance and necessary accommodations |
| Hallucinogens | Frequent attendance at “rave parties” or club settings | DAST, TAPS Tool, NM ASSIST | Motivational interviewing to address discrepancy between problematic use and values and to assess readiness for change; provide information about potential risks of “microdosing” (21) | Inform of risk of tolerance formation after only one use, as well as flashbacks; develop a plan for abstinence or reduction; referral for individual therapy |
| Benzodiazepines | Existing mental health difficulties, combining benzodiazepines and alcohol in party setting | DAST, TAPS Tool, NM ASSIST | Motivational interviewing to address discrepancy between problematic use and values and to assess readiness for change; provide psychoeducation about dangers of using benzodiazepines in combination with alcohol and other substances | Assess for withdrawal symptoms and consider detoxification if present, followed by residential treatment or long-term program; outpatient management is not recommended unless use is infrequent |
| Inhalants | Existing mental health difficulties, expressed need for escape and dissociation | DAST, NM ASSIST | Provide psychoeducation about the acute and long-term dangers of use | Significant health concerns and risk with acute intoxication; long-term use can lead to depression and brain damage; consider higher level of care, such as inpatient or partial program. |
| Over-the-counter medications (dextromethorphan, antihistamines) | Existing mental health difficulties, expressed need for escape and dissociation | DAST | Motivational interviewing to address discrepancy between problematic use and values and to assess readiness for change | Risk of significant impairment from acute intoxication; inpatient hospitalization for any accompanying suicidality, paranoia, or persistent hallucinations. |
Prevention and Brief intervention
| Program | Medium | Format | Goal | How to access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlcoholEdu for College (60–63) | Online | A 1- to 3-hour interactive multimedia online course that consists of a baseline survey and four modules | Reduce alcohol use and alcohol-related negative consequences | Contact the program supplier for pricing information (everfi.com) |
| Alcohol Literacy Challenge (64, 65) | Classroom based | A 50-minute group-delivered classroom session that incorporates slides and videos | Reduce alcohol use by correcting erroneous beliefs about its positive and negative effects | $5,000 onsite training and $1 per student per year licensing fee (64) |
| Brief Alcohol Screening and Intervention for College Students (BASICS) (55, 57, 58, 66, 67) | In person | Two 1-hour one-on-one interviews with a BASICS facilitator and one online survey | Motivate high-risk students to reduce alcohol consumption; prompt students to change their drinking patterns; teach coping skills | $4,500 onsite training and $1,000 licensing fee; annual licensing fee for online assessment varies (67) |
| Challenging College Alcohol Abuse (68) | Campaign | Social media campaign that places advertisements in the school newspaper and other media and provides minigrants to support nonalcohol social activities | Reduce binge drinking by challenging misconceptions about peer use; reduce the negative impact of heavy alcohol use on campus | Free |
| College Drinker’s Check-up (59, 69, 70) | Computer-based software and online version | A 45-minute Web-based brief motivational interview that includes screening, assessment, feedback, and setting a plan; optional follow-up sessions are also available | Reduce alcohol consumption among heavy, episodic drinkers; give at risk students personalized feedback and invite them to participate in the intervention module | One-time fee $2,500 for colleges with fewer than 15,000 students and $4,500 for colleges with more than 15,000 students (71) |
| InShape Prevention Plus Wellness (72) | In person | A 30-minute session, including a baseline screen, a one-on-one consultation, and a behavioral goal plan | Reduce alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drug use; promote healthy eating, exercise, and other positive changes | $499 teacher’s manual; optional online and in-person webinars and workshops (73) |
| Kognito At-Risk for College Students (74, 75) | Online | A 30-minute interactive training simulation with virtual avatars | Increase knowledge and awareness about mental health; identify warning signs of psychological distress; promote help-seeking | Starting at $2,000 per year; price depends on size of the institution (76) |
| PRIME for Life (77, 78) | In person | A motivational risk reduction program delivered by instructors and group leaders | Change drinking and drug use behaviors of high-risk individuals; typically used by agencies serving individuals who have violated some type of substance use policy | Contact the program supplier for pricing information |
| Safer California Universities Study (SAFER) (79, 80) | Online | An alcohol risk management prevention strategy that includes action plans for enforcing alcohol control measures on and around college campuses | Reduce heavy drinking on and around campus; reduce alcohol-related risky behaviors, such as driving while intoxicated | Free ( http://www.prev.org/Safer-Toolkit) |
| Say It Straight (SIS) (81–83) | Classroom-based | Five to ten 45- to 50-minute sessions led by one or two trainers; sessions are action oriented and involve components such as role-plays | Prevent risky or destructive behaviors (i.e., substance use, violence, and dropout) and promote positive changes through drug refusal skill practices and communication training | $750 per participant in training workshop; $750 certification; $250 trainer manual in addition to workbooks and posters (84) |
Treatment Considerations
Campus Recovery Programs
Special Circumstances
Questions and Controversy
Recommendations
Recommendation 1: Be Clear About Confidentiality Limitations
Recommendation 2: Screen for Past Sexual Assault and Violence
Recommendation 3: Consider the Student’s Time Constraints in Treatment Planning
Recommendation 4: Formalize the Procedure for Planning a Medical Leave of Absence
Recommendation 5: Specify Treatment Site for International Students Taking Medical Leave
Recommendation 6: Plan Ahead for Treatment Occurring Outside the Academic Year
Recommendation 7: Discuss Tuition Insurance With Families
Future Directions
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

