The pathological changes seen in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) consist of brain atrophy, particularly hippocampal and medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA), enlarged ventricles, and white matter hyperintensities (WMHs). Previous studies have shown that the WMH loci and burden were disproportional to gray matter atrophy in AD and that the occurrence of WMH may occur even earlier than does gray matter atrophy.
1,2 WMH has been shown to be an independent predictor of the severity of cognitive impairment in patients with AD,
3 as well as the conversion rate of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to AD.
4,5 Individuals with β-amyloid (Aβ) deposition were more likely to exhibit clinical manifestation of dementia if they had substantial WMH burden,
6 and the effects of Aβ and WMH burden on dementia were likely to be independent.
7 The mechanism of WMH initiation is largely unknown. Synergistic interactions between elevated levels of Aβ and comorbid vascular insufficiency are believed to result in WMH.
6,8Clinically, MCI is defined as a transitional clinical state from normal cognition to dementia
9 and can be separated into two subtypes according to the involved cognitive area. Whereas amnestic MCI (aMCI) predominantly involves memory, dysexecutive MCI (dMCI) involves nonmemory domains such as executive functions. Although dMCI was less explored in previous research, it accounted for more than 40% of MCIs in community-based studies.
3,10 Because white matter subserves rapid and efficient processing speed, the initial clinical manifestations of high WMH burdens involves the nonmemory domains. A longitudinal study
5 has shown that WMH burden and entorhinal cortex volume predict rapid cognitive decline among MCI individuals, but how WMH interact with MTA in terms of visual scores and how WMH loci predict clinical decline in patients with aMCI and dMCI is less well established. The present prospective study examined the interactive effects between the visual scores of MTA and WMH to determine whether visual rating of WMH can be an independent predictor of clinical cognitive decline in a clinical spectrum of the “normal,” dMCI, aMCI, and AD participants.
Methods
Subjects were recruited from the Dementia Clinic of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CGMH) and followed annually for 2 years. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed when the patient was enrolled, and the measurement of the visual scores was based on the baseline MRI. Yearly neuropsychological assessments were performed for 2 years. The inclusion criteria included the following: age between 50 and 85 years, modified Hachinski ischemic score of <4, and good general health with no additional diseases that could interfere with the study. Patients with a previous clinical history of neurological, psychiatric, somatic, stroke, or toxic causes of dementia were excluded. Exclusion criteria included cognitive impairment resulting from cerebral trauma, subdural hematoma, or hypoxic cerebral damage regardless of etiology; vitamin deficiency states, including folate, vitamin B12, and other B-complex deficiencies, such as thiamine deficiency in Korsakoff’s syndrome; central nervous system infection, brain neoplasm, and significant endocrine or metabolic disease, including thyroid or pituitary disease, Cushing’s syndrome, severe renal failure, or mental retardation; and meeting DSM-IV criteria for vascular dementia and the requirements of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Association Internationale pour la Recherche et l’Enseignement en Neurosciences criteria for probable vascular dementia.
A battery of neuropsychological assessments
11 was performed at baseline and each year for 2 years, which included the following: the Taiwanese version of the Wechsler Memory Scale (third edition) (mainly logical memory and visual reproduction subtests)
12 and Word Sequence Learning Test to assess memory;
13 the Semantic Association of Verbal Fluency;
14 the Three-Dimensional Block Construction Models to assess visuospatial function;
15 the digit span and digit symbol substitution subtests of the Taiwanese version of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (version 3) to assess attention;
16 and the Modified Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) and Trail-Making Test, Part B, to assess executive function.
17 The Mini-Mental State Examination, Cognitive Abilities Screening Instrument, Chinese Version,
18 and Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR)-sum of box were also used.
19 Significant clinical decline that may influence activities of daily living (ADL) was defined as a 0.5-point CDR increase above the baseline.
The normal control subjects were defined when memory function was normal for age; CDR and memory box score were both zero; subjects were cognitively normal, on the basis of an absence of significant impairment in cognitive functions or ADL; an informant was available from people who had frequent contact with the subject (an average of 10 hours per week or more) and could be reached by the investigators in person or by phone. The aMCI group was defined by using the following criteria: memory complaints and memory difficulties that could be verified by an informant; abnormal memory function (≤1.5 standard deviations [SD] below the lower age-adjusted norms) on the Selective Reminding Test or comparable memory test for episodic memory; CDR score equal to .5 and memory box score of .5; cognitively normal, on the basis of an absence of significant impairment in cognitive functions or ADL; and general cognitive and functional performance sufficiently preserved such that a diagnosis of AD could be made by the physician at the time of the screening visit. The dMCI group was defined by using the following criteria: abnormal executive function ≤1.5 SDs below the lower age-adjusted norms on at least one of four executive function tests (WCST, Digit Span, Trail-Making Test, Part B, and the Semantic Association of Verbal Fluency); and preservation of memory and cognitive function. The AD group was defined by using the following criteria: CDR score equal to .5, 1.0, or 2.0; probable AD as defined by Alzheimer’s criteria from the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Diseases and Stroke/Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association;
20 and Cornell Scale for Depression in Dementia score of <8. For those with a CDR of .5, the diagnosis of incipient AD depended on the combined consensus of the investigators at a clinical level, ADL, and neuropsychological impairment.
21 This study was approved by the institutional review board of CGMH. All subjects gave written informed consent for the study.
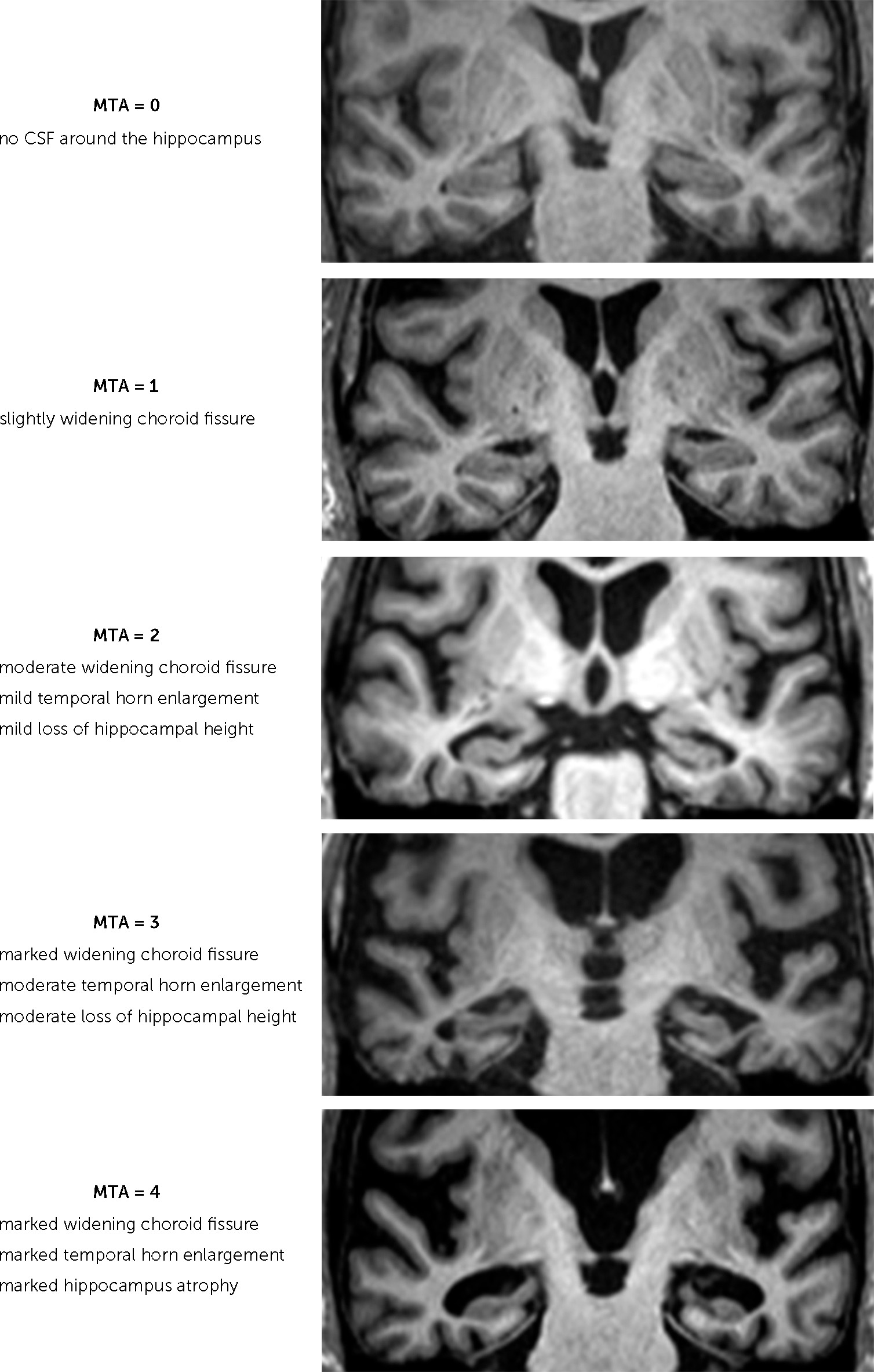
Brain MRI was conducted with a 3-Tesla MR scanner (Magnetom Trio with TIM; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). The MTA was rated on coronal T1-weighted images on a slice through the corpus of the hippocampus at the level of the anterior pons (Scheltens’ score) (
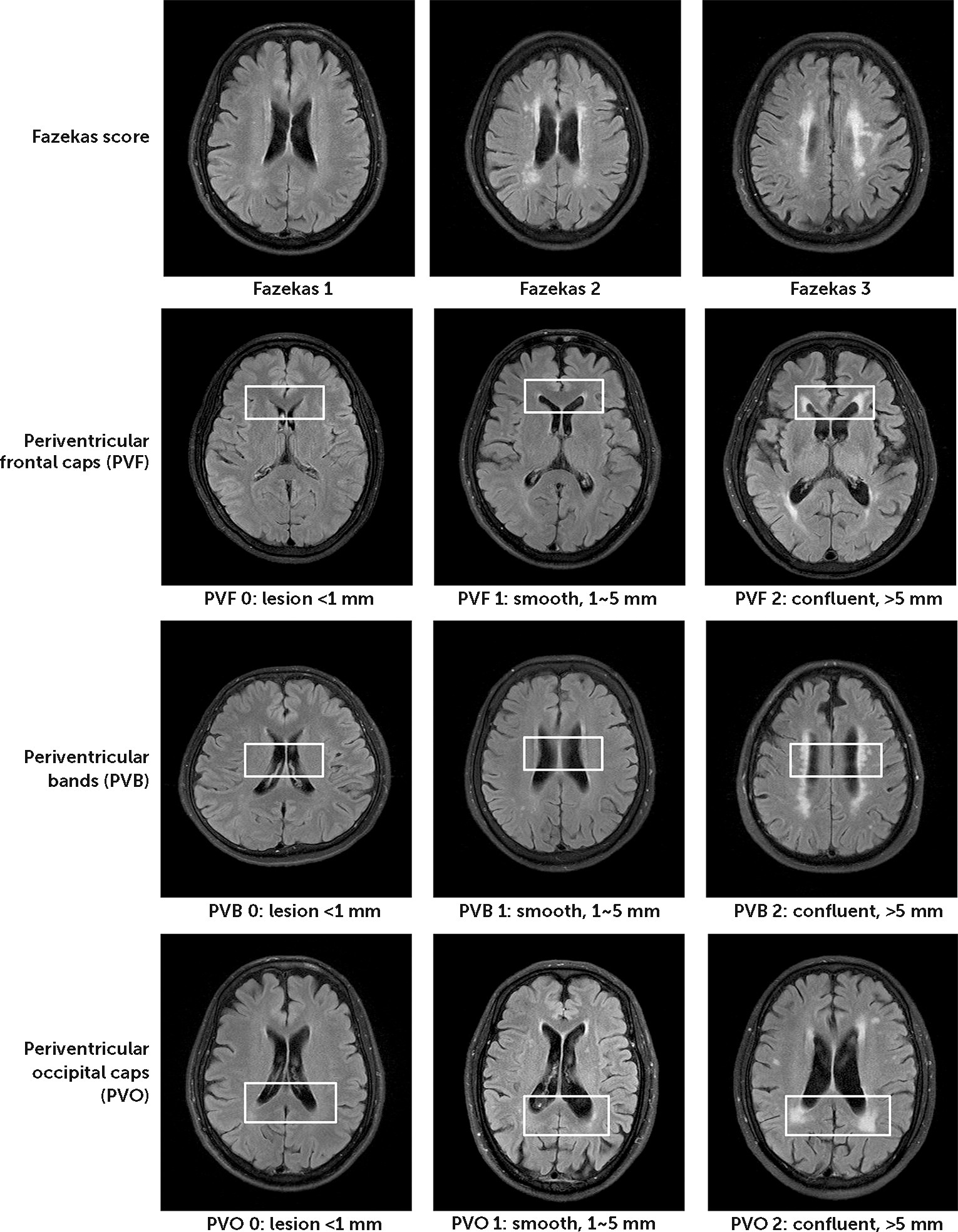
Figure 1). Visual rating of WMHs was based on the criteria of Fazekas scale
22 and Scheltens’ Scale
23 to grade the severity of WMH on T2-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery scans (see
Figure 2). The investigators for visual rating were blinded to the clinical information of the participants. Fazekas grade 1 was defined by WMH <9 mm for a single lesion and <20 mm for grouped lesions. Fazekas 2 was early confluent lesions of 10–20 mm for a single lesion and >20 mm for grouped lesions without connecting bridges between lesions. Fazekas grade 3 was a single lesion or confluent lesion ≥20 mm. Scheltens’ Scale was evaluated and summed by visual rating with 0- to 6-point severity ratings in the periventricular (frontal caps, PVBs, and occipital bands), deep (frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital), basal ganglia (caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, thalamus, internal/external capsule), and infratentorial (cerebellum, mesencephalon, pons, medulla) areas.
23,24 As is classified using the recommendations of STRIVE [standards for reporting vascular changes on neuroimaging],
25 WMH included periventricular and deep WMHs. When hyperintensities in the subcortical gray matter (basal ganglia as defined by Scheltens’ Scale) or brainstem were included, the collective term was subcortical hyperintensities. Silent lacune was defined when lacune lesion was discovered on MRI with no clinical history of stroke.
The chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, or t test was utilized to compare demographic data and the distributions of risks between groups, where appropriate. Two-tailed p values were derived from the tests. Association analyses were examined by general linear models (GLM) and logistic regression, where appropriate. Under the assumption that the effect of increase on each point of the score was the same, GLM was used for comparisons of visual rating scales between participants. Confounding factors included age, sex, education, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking, and the presence of the APOE4 allele. Survival analysis was performed with the Kaplan-Meier estimate, and the Cox proportional hazards model was used to test the WMH effect on the time of clinical functional decline (arbitrarily defined as a .5 point of CDR increase), adjusting for MTA and confounding factors.
Results
We enrolled 200 subjects in this study, including 57 people with normal cognitive function, 93 people with MCI (dMCI, N=40; and aMCI, N=53), and 50 patients with AD. The demographic data for the enrolled population is shown in
Table 1. The sex proportions were similar between the groups. Normal control subjects were younger and had more years of education than did the other three groups. The proportion of hypertension and diabetes mellitus was borderline higher in the MCI and the AD groups than in the normal group. There were more carriers of the
APOE4 allele in the aMCI and AD groups than in the control group (p=.003 and .018, respectively). The distribution of body mass index and smoking frequency was not different between the groups. As was expected, neuropsychological examinations showed that global cognitive function and all of the domains examined were significantly different between the controls and each of the other three groups (
Table 1), including the domains of memory, language, attention, executive, and visual spatial function. In contrast to the aMCI group, patients with dMCI had relatively preserved global and memory function but impaired executive function (
Table 1) (WCST, p=.003). The yearly follow-up rate was 85% and 68% for 2 years (
Table 1). There was no difference in the mean survival time to clinical decline between the dMCI and the aMCI groups.
Differences in visual WMH scores utilizing Scheltens’ Scale corresponding to the MTA score are shown in
Table 2. Visual score of MTA significantly correlated with that of periventricular WMH (pvWMH, beta=0.1, 95% CI=0.06–0.2, p=0.0004), following adjustment for confounding factors. The magnitude of this significance was notably decreasing when adjusting for subgroups (p=.03), suggesting that the correlation between MTA and pvWMH within each subgroup is weak. The associations between MTA and total score of subcortical hyperintensities fell short of statistical significance (p=0.046). There was no association between MTA and hyperintensities in deep white matter, basal ganglia, or brainstem areas.
In all the participants, the associations between cognitive assessment and total subcortical hyperintensities were analyzed in detail (
Table 3). As was expected, MTA was significantly associated with global cognition and all cognitive domains (p<0.0001), except for a borderline significance with the WCST (p=0.02). In contrast, overall subcortical hyperintensity was specifically associated with the domain of semantic fluency (beta=−0.4, 95% confidence interval [CI]=–0.7 to –0.2, p=0.002), which remained borderline significant after further adjusting for MTA (beta=−0.3, 95% CI=–0.5 to –0.1, p=0.017). Specifically, both pvWMH (beta=−2.2, 95% CI=–3.5 to –0.9, p=0.001) and deep WMH (beta=−0.5, 95% CI= –0.8 to –0.15, p=0.004) were related to the performance of semantic fluency. When further adjusting for MTA, pvWMH was no longer associated with semantic fluency (p=0.055), while deep WMH and semantic fluency remained associated (beta=−0.3, 95% CI= –0.6 to –0.04, p=0.027).
Differences in visual rating scores on the MRI scans between the subgroups are shown in
Table 4. When adjusting for confounding factors, the MTA score was significantly higher in the AD group than in the control group (p<0.0001). There was no remarkable difference in the MTA score between the control group and the two MCI groups. Silent lacunar lesions discovered in the MRI scans were slightly higher in the aMCI group than in the control group (p=0.04). With regard to WMH, we found that the distribution of the Fazekas score was different between the control group and the AD group (p=0.016). When further estimated using Scheltens’ scoring for WMH, the association between the Fazekas score and AD was mainly contributed to by the lesions at pvWMH (beta=0.3, 95% CI=0.1–0.4, p=0.001), especially the periventricular occipital caps (beta=0.2, 95% CI=0.1–0.3, p=0.0003). The periventricular occipital caps score was found to be slightly higher in the aMCI group than that in the control and dMCI groups (p=0.036 and 0.049, respectively). There was no significant difference between subgroups regarding the hyperintensities of whole subcortical areas. Diabetes mellitus was the only risk factor for pvWMH (beta=0.61, 95% CI=0.23–0.64, p=0.002).
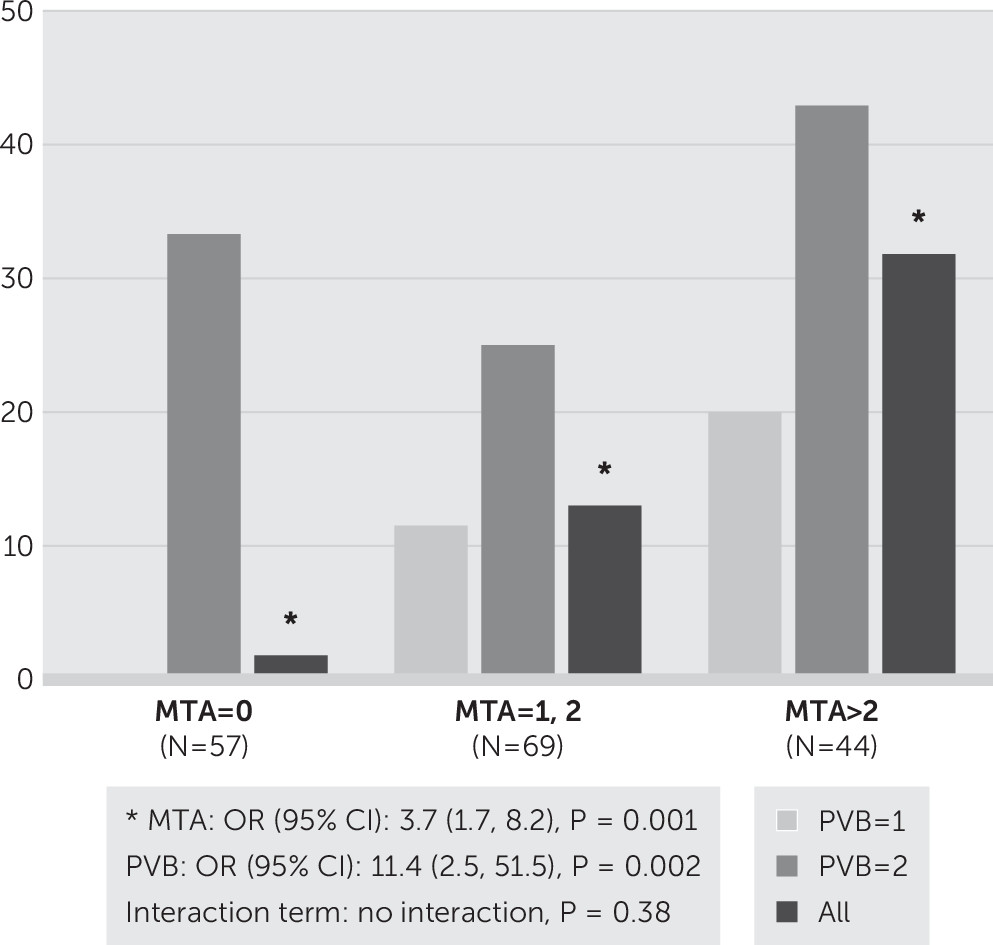
In all the participants, we found that the pvWMH at the PVBs (
Figure 2) was a significant predictor for 1-year and 2-year cognitive decline. To explore the effects of PVB on 2-year cognitive decline, we performed a Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and showed that the mean survival period to clinical decline was 1.9 years (95% CI=1.8–1.9) for subjects with a score of 1 for PVB, in comparison with 1.6 years (95% CI=1.4–1.8) for the group with a score of 2 (log-rank test, p=0.005). In those whose MTA score was zero, equal to 1 or 2, and >2, the mean survival was 1.98 years (95% CI=1.95–2.02), 1.85 years (95% CI=1.76–1.93), and 1.73 years (95% CI=1.59–1.86), respectively (p<0.0001). The significant drop rate prohibited us from exploring the exact prediction effect beyond 1 year; the survival analyses were therefore performed utilizing only the data of the first year. Still, in the 1-year follow-up, a Cox proportional hazards model adjusting for confounding factors for evaluating the PVB effect on 1-year cognition showed that the visual PVB score predicted clinical decline in all of the participants (hazard ratio [HR]=5.3, 95% CI=1.8–15.7, p=0.002). This significance remained when further adjusting for MTA (HR=4.0, 95% CI=1.3–12.1, p=0.013). The MTA score was also an independent predictor for 1-year clinical decline (HR=2.2, 95% CI=1.2–4.3, p=0.015). There was no interactive effect between MTA and PVB in predicting clinical decline (p=0.31). Specifically, PVB significantly predicted the 1-year clinical decline (odds ratio [OR]=11.4, 95% CI=2.5–51.5, p=0.002), which was independent of the effects of MTA and the other covariables (
Figure 3). When the MTA score was equal to 1 or 2, the rate of 1-year clinical decline was higher in the group with a score of 2 (25%) than it was in the group with a score of 1 (11.5%). Following a similar pattern, when the MTA score was >2, the rate of 1-year clinical decline was higher in the PVB group with a score of 2 (42.9%) than in the group with a score of 1 (20%). Nonetheless, MTA is also an independent risk factor for 1-year clinical decline (OR=3.7, 95% CI=1.7–8.2, p=0.001). Still, there was no interactive effect between MTA and PVB in predicting 1-year clinical decline. When stratified by the clinical subgroups, we found that neither visual rating PVB score nor visual rating MTA score could be a strong predictor for 1-year decline in each of the subgroups, suggesting a ceiling effect of utilizing a visual score to predict 1-year clinical outcome in each subgroup.
Discussion
The prospective study herein demonstrates that pvWMH, especially the occipital caps, is independently associated with AD. Although the visual score of MTA is the strongest predictor for clinical outcome in the overall participants, the pvWMH at the PVBs is another independent predictor for clinical decline. We did not find an interactive effect between visual scores of MTA and WMH on the clinical outcome. When considering the confounders, the association between the visual scores of MTA and the total subcortical WMH is weak. For the neuropsychological examinations, in contrast to the involvement of the global function and multiple domains of MTA, semantic fluency was the only independent domain correlated to subcortical hyperintensities and therefore may be useful for clinical evaluation of total hyperintensities burden. Although WMH alone might not be a major risk for MCIs and AD, both MTA and pvWMH at the PVBs were independent predictors for 1-year clinical decline, suggesting that treatment targeting WMH may play an important role in the prevention of AD. Moreover, this study also suggests that diabetes mellitus is an important target for the prevention of pvWMH.
The semantic fluency test is frequently used to test a circumscribed aspect of executive function. During examination, participants have to generate as many items of a certain category as possible in a given time.
26 Anatomical mapping of semantic fluency in stroke patients suggested the functional loci in the left inferior frontal gyrus and insula, left medial temporal regions, and the right inferior frontal gyrus, which related to application of a visuospatial mental imagery strategy in semantic fluency.
26 There was no report addressing the correlation between subcortical hyperintensities and semantic fluency to date. Our study suggests that despite the strong effect of MTA in semantic fluency, subcortical hyperintensities, especially deep WMH, play an independent role in functioning semantic fluency. Further replication of this study, especially functional mapping, is important.
The associations between hippocampal volume reduction
27 and clinical decline
28 with pvWMH but not deep WMH have been reported. It was discovered that pvWMH shows an almost 30% loss of axons and multiple biochemical marker changes in histological tests.
29 Diffusion tensor imaging displays disturbances in track integrity in the bilateral corona radiata, superior longitudinal fasciculus, cingulum, and corpus callosum in patients with AD, and all of these contain fibers that pass through the periventricular region.
30 Although having MCIs or AD per se is a risk of 1-year clinical decline in this study, the burden of PVB is similar between the clinical subgroups, suggesting that visual rating of PVB could be an independent predictor for 1-year clinical decline. This study shows that pvWMH at PVBs is an independent predictor for 1-year clinical decline that may support the aforementioned neuropathological findings.
It is worth mentioning, however, that there are limitations to our study. First, the proportion of participant follow-up dropped significantly after 1 year, which prohibited us from exploring the exact prediction effect beyond 1 year. The survival results that are derived from an overall 2-year follow-up in this study should be interpreted with caution until a robust replication is available. Second, the biological relevance of brain integrity and WMH is not clear and remains to be investigated. Thus, further cohort studies with adequate sample sizes are needed to confirm our results before the pvWMH score can be viewed as an independent marker of clinical decline. Nevertheless, this study provides evidence for significant associations of visual WMH scores with semantic fluency and AD risks. Because both MTA and PVB are independent predictors for clinical decline, future treatments targeting WMH may provide an additional prevention role for AD.