Advancing Recovery Science: Reliability and Validity Properties of the Recovery Assessment Scale
Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Methods
Results
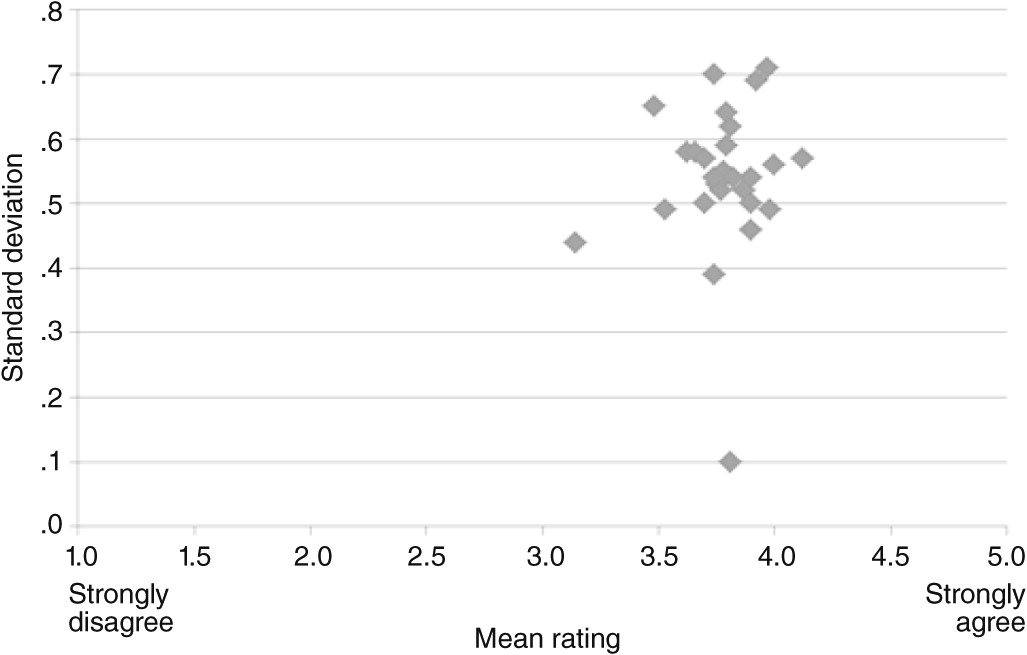
Means
Reliability
Factor structure
Validity
| Study | RAS basis of scoring | Version | Likert scalea | Scorea | N | Sample characteristics | RAS associationsb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrigan et al., 1999 (7) | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | NS | 35 | 35% female; mean±SD age=33.1±9.2; 57% black, 37% white, and 6% other, including Asian American; all with serious mental illness | Psychosocial well-being: +; symptoms, distress, poor health: –; social functioning and support: + |
| Corrigan et al., 2003 (61) | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Sum | 1,824 | 60% female; mean±SD age=41.8±10.4; 24% black, 75% white, 1% Asian, 18% Latino/Hispanic; 3% Native American; all with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or major depression and significant functional limitation | Religiosity and religious support: + |
| Ritsher et al., 2003 (15) | Total | RAS-41 | NS | NS | 127 | 6% female; mean±SD age=49.5±8.7; 62% white, 26% black, 9% Hispanic, 1% Asian/Pacific Islander, 5% Native American, 3% other race-ethnicity; 35% with schizophrenia, 21% paranoid psychosis, 27% affective psychosis, 82% depression, 39% PTSD, 34% anxiety disorder, 39% personality disorder, 76% substance use disorder, 68% alcohol abuse; all veterans | Stigma: – |
| Corrigan and Phelan, 2004 (53) | Subscales | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Sum | 176 | 62% female; mean±SD age=41.3±10.5; 84% white, 14% black, 5% Hispanic, 16% Native American, 1% Asian, 11% other race-ethnicity; all with serious mental illness and significant functional limitation | Social functioning and support: + |
| Flinn, 2004 (16)c | Total and subscales | RAS-24 | 0–4 | Sum | 355 | 38% female; 18% ages 18–39, 32% ages 40–49, 29% ages 50–59; 21% ages ≥60; 58% white, 40% black, 3% Hispanic; 61% with schizophrenia, 18% mood disorders, 3% anxiety disorders, 10% multiple diagnoses, 7% multiple diagnoses and substance abuse | Participation: +; other (stages of change): + |
| Andresen et al., 2006 (45) | Total | RAS-41 | NS | NS | 94 | 52% female; mean±SD age=44.1±12.6; Australia residents; 48% schizophrenia diagnosis, 43% self-reported schizophrenia, 2% schizoaffective disorder, 1% bipolar disorder, 5% other psychotic disorders | Other recovery measures: + |
| Deane and Andresen, 2006 (68) | Total | RAS-40 | 1–5 | Sum | 27 | 52% female; mean±SD age=46.2±10.4; Australia residents; 52% with schizophrenia, 22% with bipolar disorder, 22% with other diagnoses | Other (being partnered with community volunteers versus treatment as usual): no association |
| Lloyd et al., 2007 (58) | Total and subscales | RAS-24 | 1–5 | Sum | 44 | 32% female; mean age=33; Australia residents; all individuals with serious mental illness | Participation: + |
| McNaught et al., 2007 (33) | Subscales | RAS-24 | 1–5 | NS | 168 | 37% female; mean±SD age=39.0±12.1; all with psychotic disorder; Australia residents | Other recovery measures: +; symptoms, distress, poor health: – |
| Salyers et al., 2007 (30) | Total | NS | NS | Mean | 59 | 34% female; mean±SD age=43.5±10; 41% white, 51% black, 2% Native American, 7% Hispanic/Latino; all with psychiatric disabilities | Other recovery measures: +; symptoms, distress, poor health: – |
| Walby, 2007 (42)c | Subscales | RAS-41 | NS | Mean | 350 | 69% female; mean±SD age=41.1±11.3; 50% with serious mental illness, 50% with mild to borderline severe mental illness being treated in an outpatient setting | Psychosocial well-being: +; stigma: –; social functioning and support: + |
| Potokar, 2008 (18)c,d | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Mean | 65 | 17% female; mean±SD age=51±9.8; 86% white; 52% with schizophrenia, 34% schizoaffective disorder, 14% bipolar disorder | Psychosocial well-being: +; other (loss due to mental illness): – |
| Clarke et al., 2009 (65) | Subscales | RAS-41 | 0–4 | Sum | 71 | 56% female; mean±SD age=40.7±11.3; Australia residents; 69% with schizophrenia, 14% major depressive disorder with psychotic features, 10% schizoaffective disorder, 7% bipolar disorder | Other (goal attainment): + |
| Hedden, 2009 (19)c,d | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Mean | 81 | 51% female, 4% unknown; mean±SD age=44±13.1; 6% with schizophrenia, 10% schizoaffective disorder, 16% bipolar disorder, 40% major depression, 28% with multiple diagnoses | Religiosity and religious support: – |
| Hendryx et al., 2009 (59)d | Total | NS | NS | Sum | 153 | 49% female; mean±SD age=48.8±14.8; 94% white; 40% with schizophrenia | Participation: + |
| Pernice-Duca and Onaga, 2009 (13) | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Mean | 221 | 53% female; mean±SD age=43.5±9.9; 10% black, 82% white, 5% multiracial, 3% Latino, Native American, Arab American, or other race-ethnicity; 53% with schizophrenia and related disorders, 33% major affective disorders, 14% other axis 1 diagnoses | Social functioning and support: + |
| Townley et al., 2009 (14) | Total | RAS-20 | 1–5 | NS | 40 | 55% female; mean age=46; 53% white, 45% black, 2% biracial; >50% with schizophrenia, all others with major depression or bipolar disorder | Participation: +; community inclusion: + |
| Andresen et al., 2010 (46) | Total and subscales | RAS-41 | 0–4 | Sum | 281 | 42% female; mean±SD age=39.71±11.84; Australia residents; 72% with schizophrenia, 8% schizoaffective disorder, 11% bipolar disorder, 9% depressive psychosis | Other recovery measures: + |
| Buckley-Walker et al., 2010 (47) | Total | RAS-24 | 0–4 | NS | 40 | 40% female; mean±SD age=40.9±10.5; Australia residents; all with serious mental illness | Other recovery measures: + |
| Chiba et al., 2010 (21) | Total | RAS-24 | NS | Sum | 209 | 41% female; mean±SD age=48.3±15.7; Japan residents; 61% with schizophrenia, 13% bipolar disorder, 10% depression, 16% other or unknown diagnoses; 45% living in community, 55% inpatients | Psychosocial well-being: +; symptoms, distress, poor health: – |
| Chiba et al., 2010 (48) | Total | RAS-24 | 1–5 | Sum | 223 | 41% female; mean±SD age=47.6±15.5; Japan residents; 60% with schizophrenia, 14% bipolar disorder, 11% depression, 16% other or unknown | Other recovery measures: + |
| Fuller, 2010 (66)d | Total and subscales | RAS-41 | 1–5 | NS | 100 | 50% female; mean±SD age=40.6±12.4; 93% white, 6% black, 1% Asian; 35% with schizophrenia, 37% with bipolar disorder, 32% with major depression, 29% with anxiety disorder, 20% with substance dependence | Other (disorder: substance use versus serious mental illness or co–occurring disorders): +; other (peer support): no association |
| Green et al., 2010 (63) | Total and subscales | NS | NS | Sum | 170 | 52% female; mean±SD age=49.2±14.5; 94% white, 6% black, 3% Native American/Alaska Native, 2% Asian/Pacific Islander, 5% mixed heritage, 1% Hispanic; 43% with schizophrenia spectrum disorder, 47% bipolar disorder, 11% affective psychosis | Other (behavior activation): + |
| Leung, 2010 (57)c | Total | NS | 1–5 | Sum | 50 | 50% female, 2% no gender information; ages ≥18; 90% white, 2% Hispanic, 2% Native American, 6% non-Hispanic or other; 42% with schizophrenia, 58% bipolar disorder or affective psychosis | Positive outlook: +; symptoms, distress, poor health: – |
| Lloyd et al., 2010 (41) | Total | RAS-24 | 1–5 | Sum | 161 | 49% female; mean±SD age=41.0±12.8; Australia residents; 34% with schizophrenia, 30% depression, 24% bipolar disorder, 8% anxiety disorder, 3% schizoaffective disorder, 1% personality disorder | Psychosocial well-being: +; community inclusion: +; other (unmet needs): –; other (paid employment): +; other (diagnosis: bipolar disorder versus schizophrenia or depression): + |
| Pernice-Duca, 2010 (54)d | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Mean | 169 | Slightly fewer men than women; ages 30–45; mostly white; 41% with schizophrenia or a related disorder, 58% major affective disorder | Social functioning and support: + |
| Rogers et al., 2010 (44) | Total | RAS-41 | NS | NS | 1,827 | 60% female; mean±SD age=43.0±10.2; 57% white, 17% black, 26% Hispanic, other race-ethnicity, or multiracial; 50% with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, or other psychotic disorders, 22% major depression or affective disorder, 18% bipolar disorder, 10% other disorders | Psychosocial well-being: + |
| Wolstencroft et al., 2010 (50) | Total | RAS-23 | NS | NS | 18 | 67% female; mean±SD age=46.50±11.07; Australia residents; 17% bipolar disorder, 11% schizophrenia, 72% depression, 17% PTSD, 6% obsessive-compulsive disorder, 6% anxiety, 11% schizoaffective disorder, 6% dissociative disorder | Other recovery measures: + |
| Chiba et al., 2011 (60) | Total | RAS-24 | 1–5 | Sum | 120 | 36% female; mean±SD age=41.2±12.2; Japan residents; 53% with schizophrenia, 18% bipolar disorder, 12% depression, 18% other or unknown disorder | Positive outlook: + |
| Connell et al., 2011 (12) | Total | RAS-41 | 0–4 | Sum | 234 | 35% female, 21% no gender information; mean±SD age=39.7±11.8; Australia residents; 65% schizophrenia, 11% bipolar disorder, 9% schizoaffective disorder, 9% depressive psychosis, 4% both schizophrenia and depression, 3% schizophrenia and comorbid conditions | Other (employment): no association |
| Conrad-Garrisi, 2011 (34)c | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Sum for total; means for subscales | 143 | 46% female; mean age=47.1; 76% white, 17% black, 4% Arabic, 1% Latino, 1% Asian, 1% Native American; all clubhouse members with schizophrenia, mood disorders, anxiety disorder, and other mental illnesses | Psychosocial well-being: +; symptoms, distress, poor health: –; community inclusion: +; other (stages of change): +; other (financial deprivation): – |
| Copic et al., 2011 (36) | Subscales | RAS-24 | 0–4 | Mean | 77 | 41% female; mean age=43; Australia residents; 61% with schizophrenia, 18% schizoaffective disorder, 11% bipolar disorder, 8% depressive psychosis, 3% no available diagnosis information | Other recovery measures: +; psychosocial well-being: +; positive outlook: +; other (treatment involvement): + |
| de Pina Gonçalves de Sousa, 2011 (39)c | Subscales | RAS-24 | 1–5 | Mean | 17 | 12% female; mean±SD age=38.1±8.7; Portugal residents; all with schizophrenia | Stigma: – |
| Depp et al., 2011 (62)d | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Sum | 73 | 47% female; mean±SD age=50.3±6.3; 45% white, non-Hispanic, 26% black non-Hispanic, 15% Hispanic, 8% Asian or Native American; all with schizophrenia | Other (behavior activation): + |
| Färdig et al., 2011 (51) | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Sum | 107 | 38% female; mean±SD age=43±13.7; Sweden residents, 65% born in Sweden, 35% immigrants; 71% with schizophrenia, 29% with schizoaffective disorder | Other recovery measures: + |
| Liu, 2011 (55)e | Total and subscales | NS | NS | NS | 310 | All mental health consumers who were members of rehabilitation centers or half-way houses; Taiwan residents | Social functioning and support: + |
| Mukolo, 2011 (37)f | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Sum for total; means for subscales | 110 | 61% female; mean±SD age=44.1±12.2; 72% white, 16% black, 12% other races; 16% with schizophrenia, 15% bipolar disorder, 9% comorbid bipolar and schizophrenia, 14% depression, 43% other or unspecified, 5% undisclosed diagnoses | Psychosocial well-being: + |
| Muñoz et al., 2011 (23) | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | NS | 108 | 26% female in low–self-stigma group, 50% female in high–self-stigma group; mean±SD age=36.8±8.5; Spain residents; 74% with schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders, 11% personality disorder, 4% schizophrenia and personality disorder, 5% bipolar disorder, 3% obsessive-compulsive disorder, 2% organic mental disorder | Stigma: –; social functioning and support: + |
| Roe et al., 2011 (40)d | Total | RAS-20 (analysis of 12 items) | NS | NS | 159 | 33% female; mean±SD age=43.2±10.7; Israel residents fluent in Hebrew; all with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder | Symptoms, distress, poor health: – |
| Siqueira, 2011 (64)c | Subscales | RAS-24 | 0–4 | NS | 41 | 63% female; mean±SD age=42.3±12.8; Australia residents; all with a chronic mental illness for past ≥12 months | Other (psychological acceptance): + |
| Webb et al., 2011 (25)d | Total | RAS-41 | 1–5 | Sum | 81 | 53% female, 3% gender not reported; mean±SD age=43±12; 84% white, 1% black, 12% Hispanic (12%), 1% Asian; 15% with schizoaffective disorder or schizophrenia, 41% depression, 19% bipolar disorder, 22% multiple diagnoses, 4% did not provide diagnosis information | Social functioning and support: +; religiosity and religious support: + |
| Weeks et al., 2011 (49) | Total | RAS-50 | 1–5 | Sum | 50 | 34% female; mean±SD age=32.4±12.1; U.K. residents; 58% white, 30% black, 6% Asian, 6% other race-ethnicity; 42% with schizophrenia, 22% other psychotic disorders, 12% mental or substance use disorder, 10% bipolar disorder, 6% depression, 4% obsessional disorder, 2% schizoaffective disorder, 2% emotionally unstable personality disorder | Other recovery measures: + |
| Bottonari et al., 2012 (67)g | Total | RAS-42 | 1–5 | Sum | 192 | 8% female; mean±SD age=52±10; 72% white, 29% black, 1% Asian, 3% American Indian, 10% Hispanic/Latino; 64% with mood disorder, 51% PTSD or other anxiety disorder, 28% psychotic disorder, 64% substance use disorder; all veterans | Other (peer support): no association |
| Brusilovskiy and Salzer, 2012 (69)e | Total | RAS-20 | 1–5 | Sum | 378 | 59% female; mean±SD age=48.4±9.8; 63% black, 37% white; 61% with schizophrenia spectrum disorder, 39% major depression | Other (community crime): +; other (community socioeconomic status): + |
| Clarke et al., 2012 (52) | Total and subscales | RAS-24 | 0–4 | NS | 144 | 48% female; mean±SD age=39.3±11.7; Australia residents; 69% with schizophrenia, 13% bipolar disorder, 12% schizoaffective disorder, 6% major depressive disorder with psychotic features | Other recovery measures: + |
| Cook et al., 2012 (28) | Total | RAS-41 | NS | Sum | 428 | 56% female; mean±SD age=42.8±10.9; 54% white, 34% black, 4% Hispanic/Latino, <1% Asian/Pacific Islander, 6% American Indian/Alaska Native, 2% other race-ethnicity; 15% with schizophrenia, 5% schizoaffective disorder, 40% bipolar disorder, 18% depression, 9% other | Psychosocial well-being: + |
| Hicks et al., 2012 (38) | Total | RAS-24 | 0–4 | Mean | 61 | 38% female; mean±SD age=45.6±10.9; Australia residents; 80% with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, 20% bipolar disorder or major depression | Psychosocial well-being: +; other (provider relationship): + |
| Kaplan et al., 2012 (43)d | Total | RAS-20 | 1–5 | Sum | 1,827 | 60% female; 233 ages 17–30, 1,594 age ≥31; 54% white only, 16% black only, 29% all other race-ethnicities; 47% with schizophrenia, 40% bipolar disorder or depression, 14% all other mental illnesses | Psychosocial well-being: + |
| Norman et al., 2013 (56)d | Subscales | RAS-24 | NS | NS | 84 | 31% female; mean±SD age=28.0±7.4; Canada residents; 63% with schizophrenia, 13% schizoaffective disorder, 6% schizophreniform disorder, 6% substance-induced disorder, 8% psychosis NOS, 2% delusional disorder, 1% affective psychosis | Symptoms, distress, poor health: –; social functioning and support: + |
Characteristics examined
Psychological well-being (12 studies).
Other recovery measures (11 studies).
Social functioning and support (nine studies).
Psychiatric symptoms, distress, and poor health (eight studies).
Stigma (four studies).
Community participation (four studies).
Perceived community inclusion (three studies).
Positive coping (three studies).
Religiosity and religious support (three studies).
RAS and other constructs (15 studies).
RAS and change over time
Other quantitative analyses
Discussion
Conclusions
Acknowledgments and disclosures
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

