Homeless persons who have both mental illness and a diagnosis of substance abuse are an especially difficult population to treat, because their problems are numerous and severe (
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6). Many studies have evaluated the treatment of homeless persons with serious mental illness (
7,
8,
9,
10), and at least six controlled studies have specifically examined intensive treatment approaches for those with comorbid substance abuse. Burnam and colleagues (
11), using an experimental design, found little benefit in intensive residential or outpatient treatment. However, Drake and colleagues (
12), using a quasi-experimental design, found better outcomes with integrated treatment. In a reanalysis of data from the sample in the study by Drake and colleagues, Trumbetta and associates (
13) found that frequent contact with members of Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) was associated with a reduction in alcohol use.
In a sample of homeless veterans with dual diagnoses, a fourth study (
14) compared outcomes between residential treatment programs for substance abuse and programs that specifically addressed both psychiatric and substance use disorders. Integrated treatment appeared to be associated with better outcomes, although differences were modest. That study, like the others, did not use random assignment, and the outcome assessments were based on global ratings completed by treating clinicians.
Nuttbrock and colleagues (
15) compared the outcomes of homeless persons with dual diagnoses who were treated in a highly demanding and structured therapeutic community and those who were treated in community residences and found that the demanding therapeutic community was more effective. However, Blankertz and colleagues (
16), who also compared a structured therapeutic community with a psychosocial rehabilitation residential program that promoted social integration, found significantly better outcomes for participants in the latter program. However, both these studies suffered from a high attrition rate (86 percent and 50 percent, respectively), making the validity of their findings uncertain.
Despite the methodological limitations of these studies, the results suggest that intensive treatment may improve outcomes for homeless persons who have both psychiatric and substance use problems. In addition, although most of the studies addressed the impact of various professional services, only one study (
13) assessed the benefit of self-help groups, such as AA and NA, which have been reported to be underused by and ineffective for persons with severe mental illness (
17).
Walsh and colleagues (
18) found that participation in AA without hospital treatment did not reduce the likelihood of an eventual hospitalization among employed persons who abused alcohol. However, Longabaugh and colleagues (
19) found that participation in AA was associated with superior outcomes, especially among clients who had strong social support for dealing with their drinking problems before they entered treatment. However, neither of these studies included homeless persons with comorbid mental illness.
In this study we used data from the Center for Mental Health Services' Access to Community Care and Effective Services and Supports (ACCESS) program (
20), a five-year, 18-site demonstration program to evaluate baseline characteristics and outcomes of homeless persons with both severe mental illness and substance abuse and to assess the association between substance abuse treatment and improvement in various domains.
Our study addressed four questions. First, how do clients who have dual diagnoses differ from those who do not in their overall community adjustment at baseline? Second, how do the outcomes of these two groups of clients differ at one-year follow-up when baseline differences are controlled for? Third, does self-perceived need for substance abuse treatment and receipt of treatment services improve outcomes among clients with dual diagnoses? And finally, is improvement in outcomes associated more strongly with participation in self-help groups such as AA and NA or with receipt of professional services?
Methods
The ACCESS program
In September 1993 nine states were awarded about $17 million through the ACCESS program to enable 18 communities to test strategies for fostering cooperation among agencies and reducing fragmentation of service systems. Each of the 18 sites enrolled 100 homeless persons with severe mental illness each year. The localities that received funds were Bridgeport and New Haven, Connecticut; the Edgewater-Uptown and Lincoln Park-Near North areas of Chicago; Sedgwick and Shawnee counties, Kansas; St. Louis and Kansas City, Missouri; Mecklenburg and Wake Counties, North Carolina; the West and Center City areas of Philadelphia; Fort Worth and Austin, Texas; Richmond and Hampton- Newport News, Virginia; and the uptown and downtown areas of Seattle. This study used the Case Managers Rating Scale (
21) and focused exclusively on clients who were accepted into the case management cohort of the program. All of these clients met specified criteria for both mental illness and homelessness.
Eligibility criteria and data sources
Participants were eligible for case management if they were homeless, had serious mental illness, and were not involved in ongoing community treatment. Clients who were identified as having severe mental illness that was due solely to the secondary effects of substance abuse were not eligible. The criteria for homelessness and mental illness have been described elsewhere, along with validating data (
22). A case management referral form was used to document the duration of homelessness at the time of referral to case management as well as the client's psychiatric and substance-related diagnoses.
Clients who met the program's eligibility criteria and who gave written informed consent were evaluated with a comprehensive baseline interview. These clients were reinterviewed three and 12 months after the initial baseline assessment. Participants were recruited between May 1994 and July 1997. The study protocol and the consent forms were approved by the institutional review board of each of the participating sites.
Definition of dual diagnosis
Clients were considered to have dual diagnoses if, in addition to meeting the study's inclusion criteria, they were given a diagnosis of alcohol or drug dependence by the referring clinician and also received from a second clinician a rating of 3, 4, or 5—indicating abuse, dependence, or severe dependence, respectively—on the Clinical Rating Scale (
23) for alcohol use and for drug use. A total of 2,175 clients (43 percent) met both diagnostic criteria; 607 (12 percent) had only alcohol abuse or dependence, 455 (9 percent) had only drug abuse or dependence, and 1,113 (22 percent) had both alcohol and drug abuse or dependence. Of the clients with dual diagnoses who had only drug abuse or dependence, 297 (73 percent) reported using cocaine, 266 (65 percent) reported using marijuana, 62 (15 percent) reported taking opiates, and 61 (15 percent) reported using other substances during the previous month.
Measures
Personal characteristics that were measured included age, sex, race, income, degree of social support, duration of the current episode of homelessness, and housing status during the 60 days before each interview. Psychiatric status was assessed with self-reported symptoms of depression (
24) and psychosis (
25) as well as interviewer ratings of psychotic behavior on standardized scales. Psychiatric, alcohol, and drug problems were assessed with composite scores from the Addiction Severity Index (ASI) (
26). Diagnoses were based on the working clinical diagnoses of the admitting clinicians on the case management teams.
Service use was assessed with a series of 23 questions about the use of various types of health and social services during the 60 days before the interview. A second series of questions addressed receipt of public support payments and services from public housing agencies. At baseline, clients were asked to indicate their need for a variety of services, one of which was their need for substance abuse services.
Analyses
The analyses proceeded in several stages. First, we compared the sociodemographic and baseline clinical characteristics of the two groups of clients by using chi square tests and t tests. Measures for which significant differences were found between the groups were included as covariates in subsequent multiple regression analyses. Next, repeated-measures analysis was used to assess the significance of improvement between baseline and the 12-month follow-up on multiple measures in seven domains: psychiatric problems, alcohol and drug problems, service use, community adjustment, income, illegal activities, and housing status.
We then used a series of analyses of covariance (ANCOVAs) that controlled for baseline characteristics to examine differences in improvement between clients with dual diagnoses and those without. A final series of analyses was designed to identify factors that might be associated with greater improvement among persons with dual diagnoses. In the first, we considered whether clients with dual diagnoses who perceived that they needed substance abuse services at baseline fared better than the less-motivated clients with dual diagnoses or whether they had outcomes similar to those of clients who did not have dual diagnoses.
Next, to evaluate the impact of substance abuse services, a nominal variable was developed through the following two-stage process. First, we constructed a continuous variable that represented use of substance abuse services throughout the year by summing participation in self-help groups, counseling, and sobering programs reported by each individual at baseline, at three months, and at 12 months. Counseling sessions are individual interventions that focus on reducing or stopping substance use, whereas sobering programs are more intensive interventions, usually delivered by a multidisciplinary team, that promote abstinence and address related areas of impaired community functioning.
We then divided the sample into four mutually exclusive groups: persons without dual diagnoses (2,370 clients, or 57 percent), persons with dual diagnoses and no use of substance abuse services (528 patients, or 13 percent), persons with dual diagnoses and substance abuse service use below the median of 32 visits among service users (low use; 626 patients, or 15 percent), and persons with dual diagnoses and substance abuse service use above the median of 32 visits (high use; 612 patients, or 15 percent). Using a modified form of this classification, we developed two similar variables to address participation in self-help groups and use of professional services. The medians used to develop these variables were 21 visits for self-help groups and 16 visits for professional services.
To determine whether there was an association between improvement in outcomes and greater use of services and whether clients with dual diagnoses and high service use had outcomes comparable to those of clients without dual diagnoses, a series of ANCOVAs was conducted in which the dependent variables were the outcomes described above, and the independent classification variables were those described in the previous paragraph. Finally, an ANCOVA was also used to determine the differential impact within the dual diagnosis group of the receipt of professional services and participation in self-help groups.
Results
Sample characteristics
Of 5,432 enrollees for whom baseline data were complete, follow-up data were available on one or more measures at 12 months for 4,415 (81 percent). Clients for whom follow-up data were available differed significantly (p<.05) on several baseline sociodemographic, clinical, and community-adjustment measures from clients who were lost to follow-up. Clients who were not included in the final analysis were more likely to be younger, to be white, to be male, to have a diagnosis of major depressive or anxiety disorder, and to have a poorer subjective quality of life, and they were less likely to have been contacted through outreach efforts and to have reported strong social support. No significant differences in psychiatric symptoms, substance use, housing, income, or employment were observed.
Baseline differences
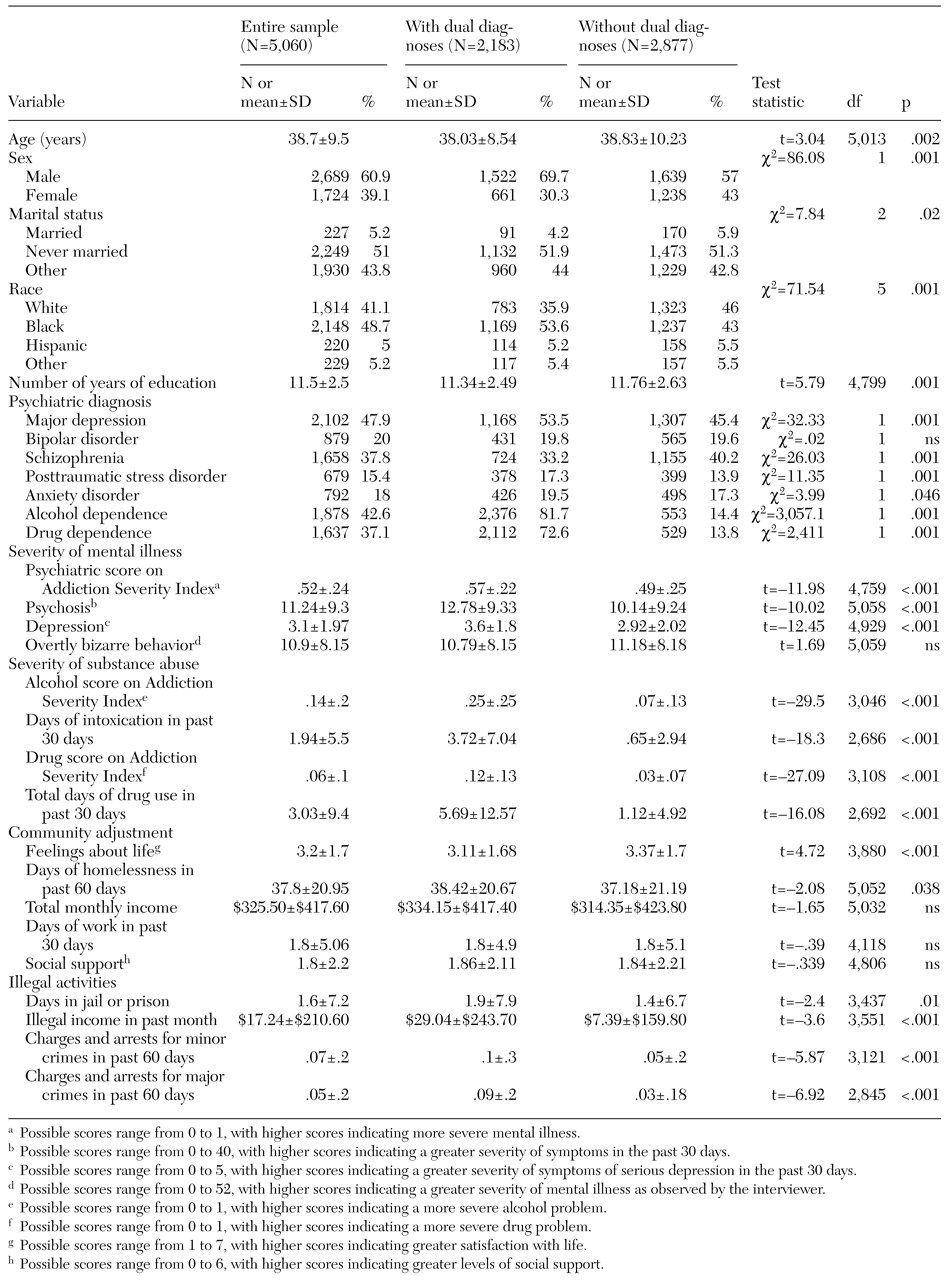
Baseline sociodemographic and clinical data for the entire sample and for the subgroups of clients with and without dual diagnoses are summarized in
Table 1. Enrollees with dual diagnoses were slightly younger and had slightly less education on average, were more likely to be African American or male, and were less frequently married than those who did not have dual diagnoses. Initial clinical assessment showed that those who had dual diagnoses were more likely to have a diagnosis of major depressive disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, or anxiety disorder and less likely to have a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
As expected, clients with dual diagnoses were far more likely to have a diagnosis of alcohol or drug abuse or dependence than clients without dual diagnoses, although some of the clients without dual diagnoses also received substance abuse diagnoses as a result of the strict definition of dual diagnosis that we used. At baseline, clients with dual diagnoses showed significantly poorer clinical status and community adjustment than clients without dual diagnoses. The clients with dual diagnoses had significantly higher scores on the psychiatric composite index of the ASI and on measures of symptoms of both psychosis and depression. They also had higher scores on all substance abuse measures, although the clients without dual diagnoses showed some problems on these measures as well. The clients with dual diagnoses had spent significantly more days homeless and reported more involvement with the criminal justice system and a lower subjective quality of life.
Twelve-month outcome measures
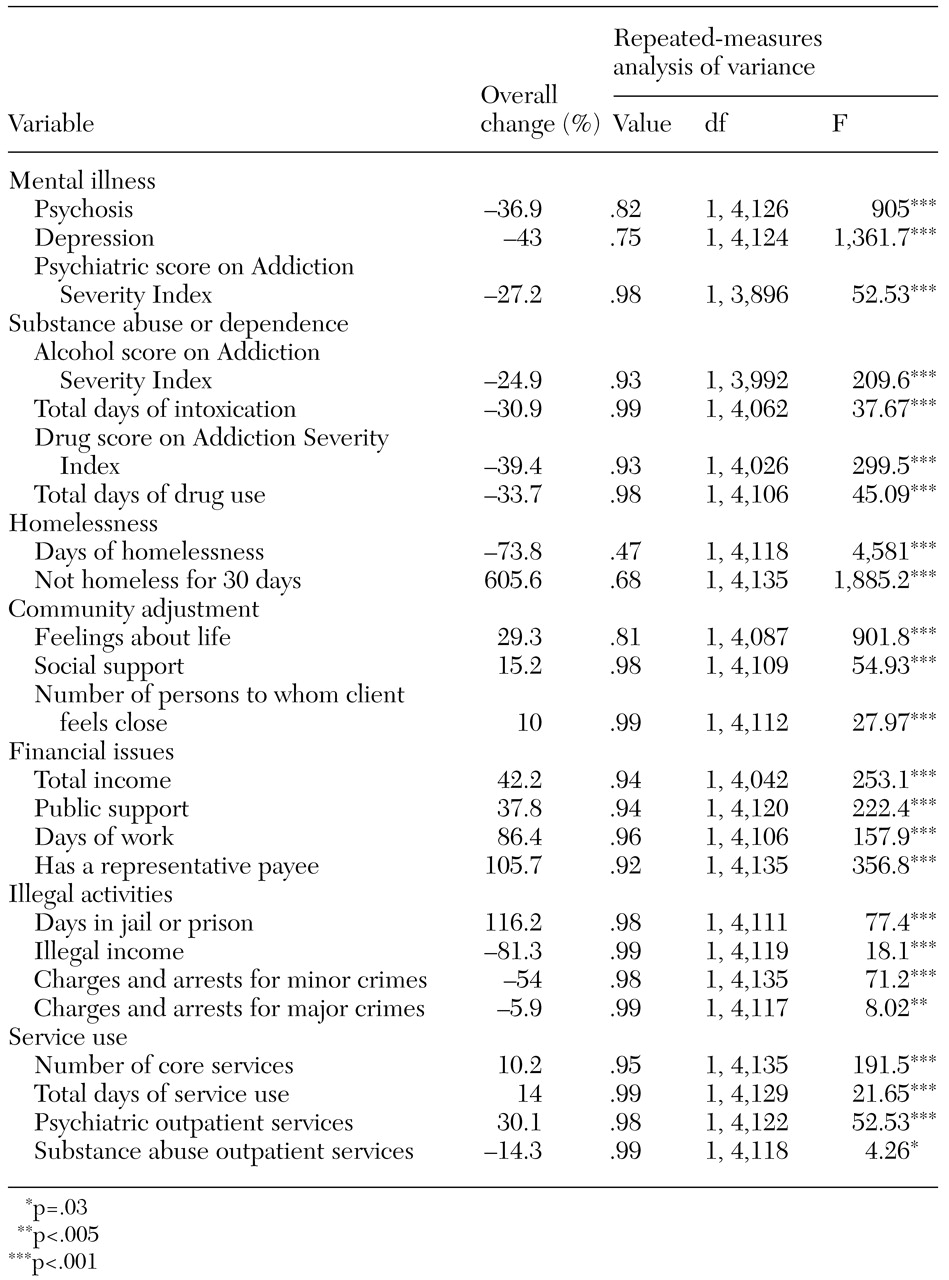
Table 2 presents the results of a repeated-measures analysis of variance of the variables in seven domains between baseline and 12-month follow-up for the sample, along with the average percentage change for each variable. The repeated-measures analysis of variance showed that, overall, both groups improved significantly on all measures of clinical status and community adjustment, with one exception: for both groups, there was a significant increase in the number of days spent in jail or prison at 12 months. This may reflect incarceration for crimes that occurred before the participants enrolled in the study.
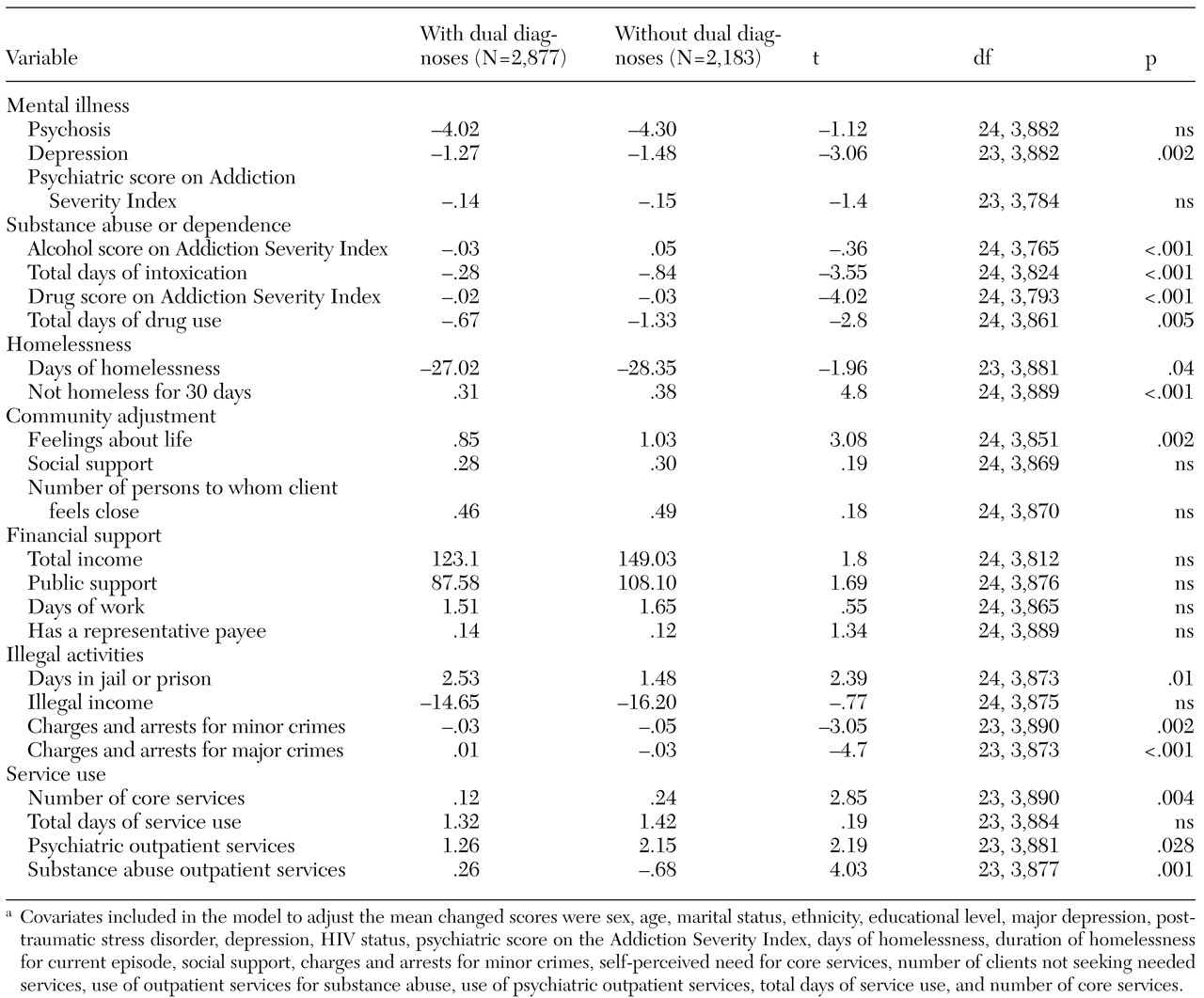
Table 3 presents the results of comparisons of changes between the two groups over 12 months, with baseline differences controlled for. Clients without dual diagnoses improved significantly more than clients with dual diagnoses on 15 (62 percent) of 24 outcome measures, and clients with dual diagnoses did not show greater improvement on any measure. The dual diagnosis group had significantly less reduction in self-reported symptoms of depression. In addition, even though substance use problems were more severe in the dual diagnosis group at baseline, these clients had a smaller reduction after 12 months on all substance abuse measures. At the 12-month follow-up, the clients with dual diagnoses also had a smaller reduction in the number of days of homelessness and had spent fewer days housed. In the domain of community adjustment, clients with dual diagnoses reported less improvement in subjective quality of life, spent more days in jail or prison, and had a smaller reduction in the number of charges and arrests for criminal activity. Finally, clients with dual diagnoses had a smaller increase in total use of health services and use of psychiatric services, although they showed a greater increase in the use of substance abuse services.
Perceived need for substance abuse services
Outcomes for the subgroup of dual diagnosis clients who perceived a need for substance abuse treatment when they entered the program showed that improvement in this group was comparable to that among clients without dual diagnoses on the alcohol composite index of the ASI and on symptoms of depression. In addition, improvement on these two measures was greater than that for clients with dual diagnoses who did not perceive a need for substance abuse treatment at baseline (t=2.05, df=25, 3,746, p=.03; t=1.95, df=24, 3,863, p=.05, respectively). The differences for other measures were not significant.
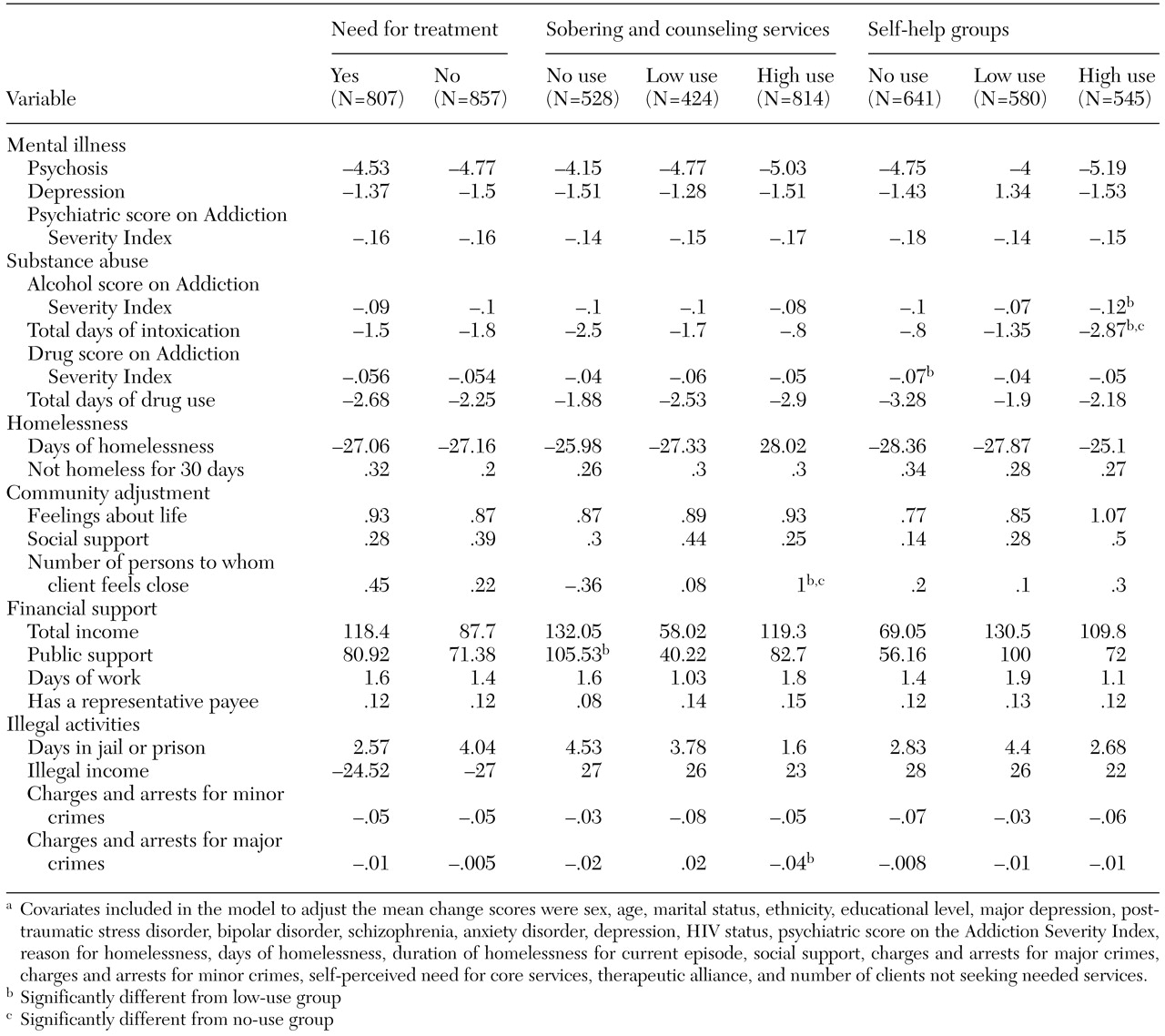
Use of substance abuse services
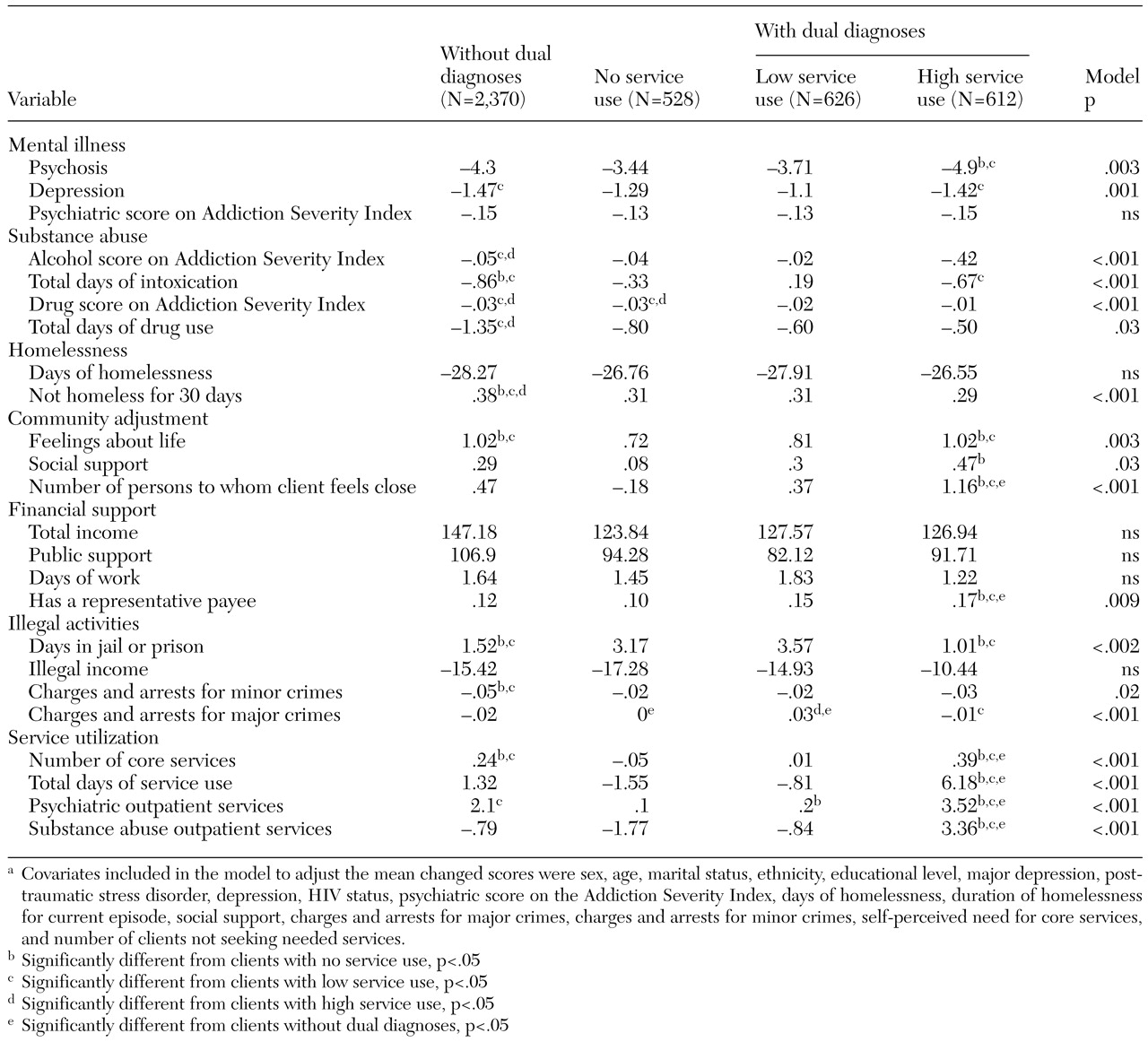
As
Table 4 shows, clients with dual diagnoses who were rated as having a high use of substance abuse services showed greater improvement on measures of psychosis, social support, and the number of people to whom they felt close than clients in each of the other two dual diagnosis subgroups and clients without dual diagnoses. These high service users showed greater clinical improvement than the other clients with dual diagnoses and showed improvement equal to that of clients without dual diagnoses on symptoms of depression, number of days of alcohol intoxication, subjective quality of life, number of days spent in jail or prison, and number of charges and arrests for major crimes. Thus high service use appeared to close the outcome gap between the two groups of clients on several measures. Participation in self-help groups was highly correlated with use of professional services (r=.51, p<.001), suggesting that these interventions are complements to rather than substitutes for each other.
Perceived need, self-help groups, and professional services
In the final model, we simultaneously examined the relationship between outcomes and perceived need for substance abuse services, use of professional services, and participation in self-help groups among clients with dual diagnoses. The results are summarized in
Table 5. High use of professional services was associated with a significantly greater reduction in the number of arrests and charges for major crimes and with an increase in the number of persons to whom clients felt close. A high level of participation in self-help groups was associated with greater improvement on the alcohol composite index of the ASI and the number of days of alcohol intoxication. When measures of service use were included in the model, perceived need for treatment was not associated with greater improvement on any measure, which suggests that the effect of perceived need for treatment is mediated by level of service use.
Discussion
In this study we found that homeless persons with severe mental illness and a diagnosis of substance use disorder were at a greater disadvantage at baseline than other homeless clients and showed less improvement over 12 months of treatment. However, intensive use of substance abuse services appeared to be associated with a significant reduction in the improvement gap between clients who had dual diagnoses and those who did not. When use of services provided by substance abuse professionals was compared with use of services obtained through self-help groups, the former was associated with fewer legal problems and more social support, and the latter was associated with greater improvement in alcohol abuse.
Baseline characteristics and outcomes
Many studies have identified the sociodemographic characteristics and numerous problems of homeless persons with severe mental illness who also have a diagnosis of a substance use disorder (
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
27,
28). However, most of these studies did not make baseline statistical comparisons or evaluate outcome data of clients with and without dual diagnoses, and nearly all the study samples were limited to one sex. Our results show that homeless persons with severe mental illness who have co-occurring substance abuse or dependence appear to have significantly worse psychiatric problems and poorer community adjustment than clients who do not have dual diagnoses and that they show less improvement in these areas during one year of treatment. Thus our study demonstrated the severe problems of these clients and their poorer prognosis with greater breadth and depth than was the case with previous studies. Furthermore, our sample was probably more representative of homeless persons with dual diagnoses than those used in other studies, because it was drawn from 18 communities in different parts of the United States.
Perceived need for substance abuse services
We also found that clinical improvement and the perceived need for services among the clients who had dual diagnoses were significantly associated and that this relationship was mediated by greater service use. This finding suggests that interventions that strengthen clients' motivation or readiness for change (
29) may be especially helpful for this population.
Intensive substance abuse treatment
Because clients in this study were participants in the ACCESS program, each client received services from an assertive community treatment team (
30) and was actively linked to other needed services. The observation that clients with dual diagnoses who had extensive involvement in sobering programs, counseling sessions, and self-help groups had outcomes that were as good as or significantly better than those of clients without dual diagnoses on eight (30 percent) of 24 measures suggests that these treatments yield substantial benefit for clients with dual diagnoses.
These results are similar to those of other studies that demonstrated better outcomes for persons with substance use disorders when a combination of outpatient mental health treatment and participation in a 12-step group was used than when either approach was used alone (
31,
32). Moggi and colleagues (
33) also observed improvement when combined treatment was used with patients who had dual diagnoses.
In our study, a substantial number of clients with dual diagnoses participated in self-help groups, and those who participated in such groups made extensive use of professional services. Some previous reports have suggested that patients with serious mental illness are reluctant to participate in self-help groups such as AA because they feel alienated or think they will be criticized for taking medications and that they thus may prefer professional services (
17,
34,
35). We showed that persons who have severe mental illness and comorbid substance use disorders not only may be interested in attending such self-help groups but also can benefit from them.
Professional services and participation in self-help groups
We showed that high use of professional substance abuse services—sobering programs and counseling sessions—was specifically associated with a reduction in the number of charges and arrests for major criminal activities and that intensive participation in self-help groups was associated with a reduction in alcohol abuse.
Our findings are consistent with those of previous studies that showed an association between participation in self-help groups and reduced alcohol abuse among homeless persons with severe mental illness and substance abuse (
11,
13) and among persons with alcohol dependence without mental illness (
18). Further studies are needed to replicate these findings.
Limitations
The primary methodological limitation of this observational study was that clients received different levels of services on the basis of their perceived needs or preferences and on the basis of their clinicians' judgment. As a result, the patients who received more extensive services may have differed from the other clients in ways that could have led to better outcomes regardless of participation in treatment. The ideal way to address this problem is to randomly assign patients to different levels of service in an experimental design. We addressed the problem by including as covariates measures that were significantly different across groups at baseline, but it is possible that there were still selection biases.
Second, although participation in self-help groups refers predominantly to participation in AA or NA, other types of self-help groups may be of benefit. Finally, because clients who participated in the follow-up differed on some measures from those who did not, the generalizability of our results is uncertain. However, follow-up data were successfully obtained for 80 percent of the sample, suggesting that any selection biases were likely to have been of limited importance.
Conclusions
Homeless persons with dual diagnoses showed poorer adjustment on most baseline measures and showed significantly less clinical improvement at 12-month follow-up than clients who did not have dual diagnoses. However, the clients with dual diagnoses who received extensive substance abuse treatment showed improvement at 12 months that was similar to that of the clients who did not have dual diagnoses. The positive results of intensive treatment for this vulnerable population are of special interest in view of recent reductions in funding for intensive community services in many programs. Adequate treatment of this population seems to demand the availability of both intensive clinical services and the facilitation of referrals to self-help groups.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded in part by the Van Ameringen Foundation/American Psychiatric Association Health Services Research Scholar award and under interagency agreement AM-98C1200A between the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Center for Mental Health Services and the Department of Veterans Affairs Northeast Program Evaluation Center. The authors thank Brett Kloos, M.A., Suzanne Golub, M.A., Simeon Goodwin, Ph.D., Jacob Tebes, Ph.D., Mardi Solomon, M.A., Sue Pickett, Ph.D., Greg Meissen, Ph.D., Robert Calsyn, Ph.D., Phyllis White, M.A., Janine Johnson, Cheryl Roberts, M.A., Coleman Poses, M.S.W., Laverne Knezek, Ph.D., Deborah Webb, Ph.D., Marilyn Biggerstaff, D.S.W., Peter Brissing, M.S.W., and Jennifer Cahill.