The Role of the Major Histocompatibility Complex Region in Cognition and Brain Structure: A Schizophrenia GWAS Follow-Up
Abstract
Objective
Method
Results
Conclusions
Method
Cognition Sample Characteristics
German sample.
Irish replication sample.
Cognitive Assessment
Selection of SNPs.
Genotyping
Statistical Analysis
Structural Imaging Analysis
Results
Association With Cognition
German sample.
| General Cognitive Ability | Verbal Working Memory | Spatial Working Memory | Immediate Episodic Memory | Delayed Episodic Memory | Attention/Vigilance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | B | p | B | p | B | p | B | p | B | p | B | p |
| rs6904071 | 1.060 | 0.046 | 0.242 | 0.077 | 0.448 | 0.049 | 0.553 | 0.284 | 1.488 | 0.011 | 0.150 | 0.001 |
| rs13219354 | 0.968 | 0.138 | 0.033 | 0.847 | 0.200 | 0.474 | −0.275 | 0.663 | 0.525 | 0.465 | 0.102 | 0.063 |
| rs3131296 | −0.107 | 0.866 | −0.044 | 0.790 | −0.369 | 0.219 | 0.563 | 0.403 | 0.615 | 0.423 | 0.107 | 0.067 |
| rs6932590 | 0.909 | 0.056 | 0.131 | 0.284 | 0.362 | 0.081 | −0.335 | 0.473 | 0.002 | 0.997 | 0.077 | 0.053 |
| rs9960767b | 0.537 | 0.555 | 0.405 | 0.085 | −0.100 | 0.794 | −0.201 | 0.814 | 0.177 | 0.856 | −0.127 | 0.073 |
| rs12807809 | −1.03 | 0.060 | −0.104 | 0.460 | −0.064 | 0.791 | 0.309 | 0.570 | −0.276 | 0.656 | 0.003 | 0.950 |
| Cognitive Function | Test or Subscalea | Sample | N | AA | AG | GG | Regression Coefficientb | 95% CI | pc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||||
| General cognitive ability | Full-scale IQ | Patients | 342 | 106.5 | 17.8 | 100.8 | 17.7 | 99.3 | 18.5 | 1.060 | 0.020–2.101 | 0.046 |
| Comparison | 2,244 | 114.5 | 13.9 | 113.8 | 14.5 | 113.0 | 14.5 | |||||
| Verbal working memory | WAIS digit span | Patients | 342 | 16.4 | 4.6 | 14.0 | 3.5 | 13.3 | 3.7 | 0.242 | −0.026 to 0.511 | 0.077 |
| Comparison | 2,244 | 14.7 | 4.0 | 14.3 | 3.9 | 14.2 | 3.8 | |||||
| Spatial working memory | WMS-R spatial span | Patients | 239 | 18.5 | 3.73 | 15.3 | 2.98 | 14.91 | 3.40 | 0.448 | 0.002–0.895 | 0.049 |
| Comparison | 399 | 17.8 | 3.79 | 17.3 | 3.11 | 17.11 | 3.43 | |||||
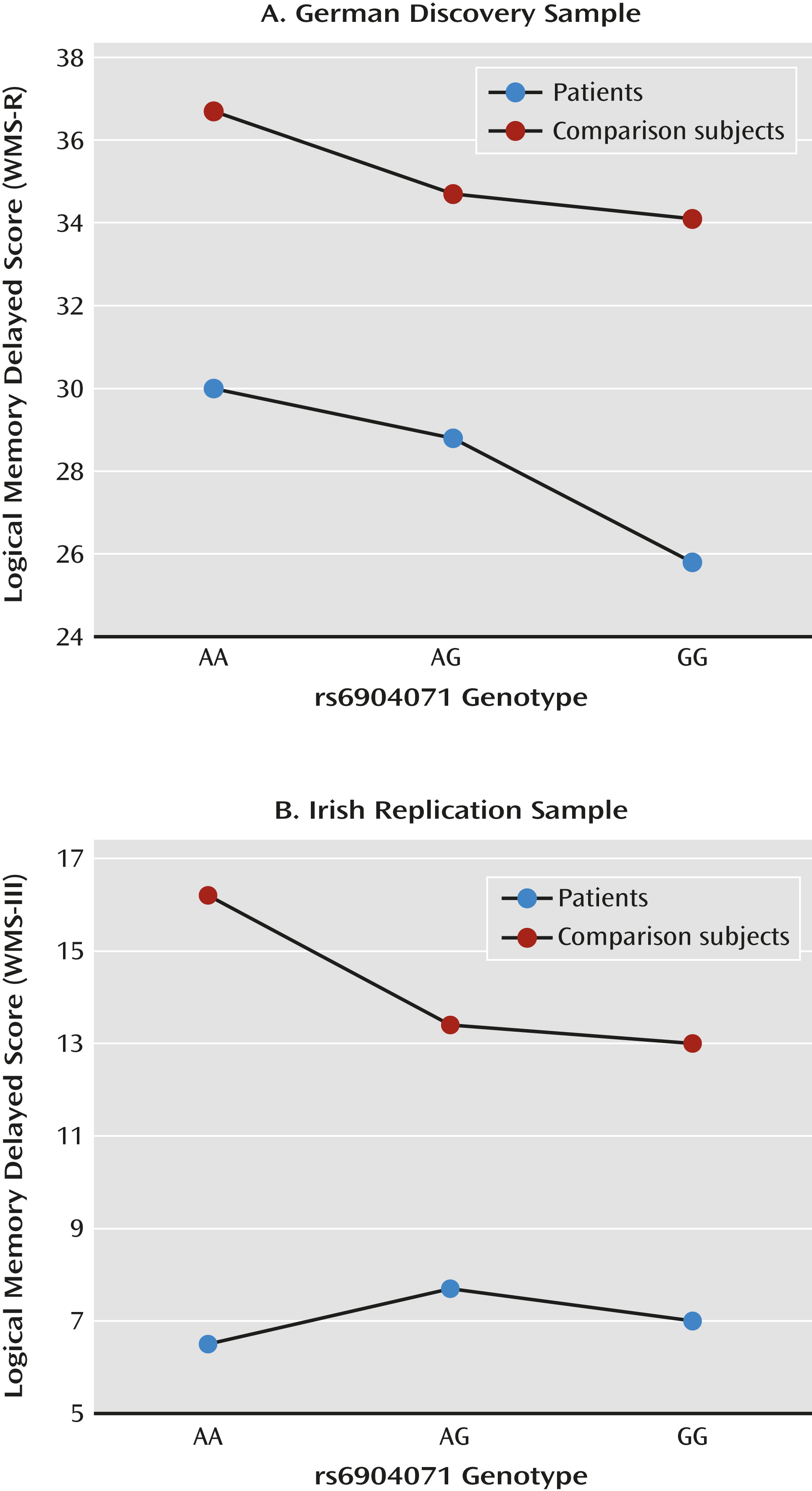
| Immediate episodic memory | WMS-R immediate logical memory | Patients | 240 | 29.2 | 8.6 | 24.8 | 8.2 | 23.9 | 9.0 | 0.553 | −0.461 to 1.566 | 0.284 |
| Comparison | 400 | 31.6 | 7.4 | 30.6 | 6.5 | 30.7 | 6.6 | |||||
| Delayed episodic memory | WMS-R delayed logical memory | Patients | 239 | 30.0 | 11.5 | 28.8 | 9.4 | 25.8 | 10.5 | 1.488 | 0.341–2.635 | 0.011 |
| Comparison | 400 | 36.7 | 9.1 | 34.7 | 6.6 | 34.1 | 7.4 | |||||
| Attention/vigilance | CPT-IP (3–7 version) | Patients | 346 | 4.59 | 0.67 | 4.28 | 0.83 | 4.10 | 0.95 | 0.150 | 0.063–0.236 | 0.001 |
| Comparison | 517 | 4.90 | 0.49 | 4.85 | 0.56 | 4.71 | 0.58 | |||||
Irish replication sample.
| Cognitive Function | Test or Subscalea | Sample | N | AA | AG | GG | Regression Coefficientb | 95% CI | pc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||||
| General cognitive ability | Abbreviated full-scale IQ | Patients | 300 | 92.5 | 19.3 | 91.5 | 18.0 | 90.5 | 18.1 | 1.389 | −1.592 to 4.369 | 0.180 |
| Comparison | 148 | 131.0 | 11.5 | 121.5 | 14.9 | 121.8 | 14.6 | |||||
| Spatial working memory | Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery spatial working memory task | Patients | 365 | −1.08 | 0.92 | −0.97 | 1.29 | −0.96 | 1.34 | 0.005 | −0.188 to 0.199 | 0.478 |
| Comparison | 140 | 0.26 | 0.83 | 0.26 | 0.75 | 0.17 | 0.84 | |||||
| Delayed episodic memory | WMS-III logical memory delayed | Patients | 377 | 6.5 | 3.3 | 7.7 | 3.2 | 7.0 | 3.3 | 0.575 | 0.083–1.067 | 0.011 |
| Comparison | 145 | 16.2 | 1.6 | 13.4 | 2.5 | 13.0 | 2.6 | |||||
| Attention/vigilance | CPT-IP (3 letters) | Patients | 257 | 2.27 | 1.5 | 1.97 | 0.87 | 1.95 | 1.04 | 0.031 | −0.209 to 0.271 | 0.399 |
| Comparison | n/a | |||||||||||
Combined sample.
| Cognitive Function | Participants | N | Comparison Subjects | Patients | Combined Samplea | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B (Regression Coefficient) | 95% CI | p | B | 95% CI | p | B | 95% CI | p | |||
| General cognitive abilityb | Patients | 642 | 0.072 | 0.006–0.139 | 0.034 | 0.113 | −0.040 to 0.265 | 0.149 | 0.08 | 0.018–0.141 | 0.011 |
| Comparison | 2,392 | ||||||||||
| Verbal working memoryc | Patients | 711 | 0.053 | −0.020 to 0.126 | 0.158 | 0.145 | 0.018–0.271 | 0.025 | 0.072 | 0.009–0.136 | 0.026 |
| Comparison | 2389 | ||||||||||
| Spatial working memoryd | Patients | 604 | 0.073 | −0.057 to 0.203 | 0.269 | 0.025 | −0.178 to 0.127 | 0.743 | 0.027 | −0.073 to 0.127 | 0.596 |
| Comparison | 539 | ||||||||||
| Immediate episodic memorye | Patients | 620 | 0.093 | −0.027 to 0.213 | 0.128 | 0.104 | −0.035 to 0.243 | 0.141 | 0.098 | 0.006–0.189 | 0.036 |
| Comparison | 545 | ||||||||||
| Delayed episodic memoryf | Patients | 616 | 0.156 | 0.042–0.270 | 0.007 | 0.180 | 0.042–0.317 | 0.01 | 0.166 | 0.077–0.255 | 2.66×10−4 |
| Comparison | 545 | ||||||||||
| Attention/vigilanceg | Patients | 603 | 0.148 | 0.040–0.257 | 0.007 | 0.180 | 0.010–0.349 | 0.038 | 0.164 | 0.063–0.265 | 0.001 |
| Comparison | 517 | ||||||||||
Structural Imaging
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 188.45 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

