Thalamo-Cortical Activation and Connectivity During Response Preparation in Adults With Persistent and Remitted ADHD
Abstract
Objective
Method
Results
Conclusions
Method
Participants
| Characteristic | Comparison Subjects (N=32) | ADHD (N=35) | Remitted ADHD (N=19) | Persistent ADHD (N=16) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | |
| Age | 24.38 | 2.40 | 24.60 | 2.04 | 0.68 | 24.74 | 2.10 | 24.44 | 2.02 | 0.66 |
| Full-scale IQ | 102.81 | 15.78 | 96.94 | 16.15 | 0.13 | 98.53 | 16.68 | 95.06 | 15.83 | 0.51 |
| Socioeconomic status | 50.28 | 14.13 | 42.46 | 16.94 | 0.05 | 43.53 | 15.22 | 41.19 | 19.21 | 0.69 |
| Conners' Adult ADHD Diagnostic Interview for DSM-IV (number of symptoms) | ||||||||||
| Inattentive | 45.09 | 8.37 | 55.42 | 12.65 | <0.001 | 49.29 | 11.54 | 61.94 | 10.55 | <0.01 |
| Hyperactive/impulsive | 42.78 | 6.23 | 52.61 | 12.50 | <0.001 | 45.65 | 9.43 | 60.00 | 11.18 | <0.001 |
| ADHD symptom total | 43.41 | 7.86 | 55.36 | 14.38 | <0.001 | 47.76 | 11.91 | 63.44 | 12.43 | <0.001 |
| ADHD semistructured interview (number of symptoms) | 0.81 | 1.26 | 6.26 | 4.82 | <0.001 | 2.52 | 1.84 | 10.69 | 3.16 | <0.01 |
| N | % | N | % | p | N | % | N | % | p | |
| Male | 27 | 84.4 | 29 | 82.9 | 0.83 | 17 | 89.5 | 12 | 75.0 | 0.51 |
| Right-handed | 30 | 93.8 | 31 | 88.6 | 0.67 | 16 | 84.2 | 15 | 93.8 | 0.60 |
| Race | 0.26 | 0.50 | ||||||||
| Caucasian | 13 | 40.6 | 20 | 57.1 | 9 | 47.4 | 11 | 68.8 | ||
| African American | 11 | 34.4 | 7 | 20.0 | 4 | 21.1 | 3 | 18.8 | ||
| More than one race | 6 | 18.8 | 7 | 20.0 | 5 | 26.3 | 2 | 12.5 | ||
| Asian | 2 | 6.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Ethnicity | 0.24 | 0.88 | ||||||||
| Hispanic/Latino | 11 | 34.4 | 17 | 48.6 | 9 | 47.4 | 8 | 50.0 | ||
| Current mood disorder | 4 | 12.5 | 8 | 22.9 | 0.27 | 3 | 15.8 | 5 | 31.3 | 0.42 |
| Current anxiety disorder | 8 | 25.0 | 8 | 22.9 | 0.83 | 1 | 5.3 | 7 | 43.8 | 0.01 |
| Current substance disorder | 8 | 25.0 | 15 | 42.9 | 0.12 | 9 | 47.4 | 6 | 37.5 | 0.56 |
Procedures
Cued reaction time paradigm.
Image acquisition.
Statistical Analysis
Performance.
Neuroimaging.
Psychophysiological interaction.
Results
Performance
| Variablea | Comparison Subjects (N=32) | ADHD (N=35) | Remitted ADHD (N=19) | Persistent ADHD (N=16) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Reaction time cued target | 311.67 | 52.51 | 346.87 | 82.37 | 341.82 | 60.38 | 352.86 | 104.59 |
| Reaction time noncued target | 491.19 | 61.26 | 509.24 | 89.18 | 514.07 | 86.33 | 503.50 | 94.97 |
| Reaction time standard deviation cued target | 79.54 | 26.25 | 100.23 | 36.51 | 98.33 | 27.29 | 102.50 | 45.58 |
| Reaction time standard deviation noncued target | 93.19 | 23.94 | 100.26 | 24.45 | 100.17 | 23.29 | 100.37 | 26.53 |
| Commission errors | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.49 | 0.24 | 0.51 | 0.30 | 0.49 |
| Omission errors | 4.30 | 5.64 | 6.39 | 6.93 | 4.82 | 4.93 | 8.66 | 8.92 |
Neuroimaging
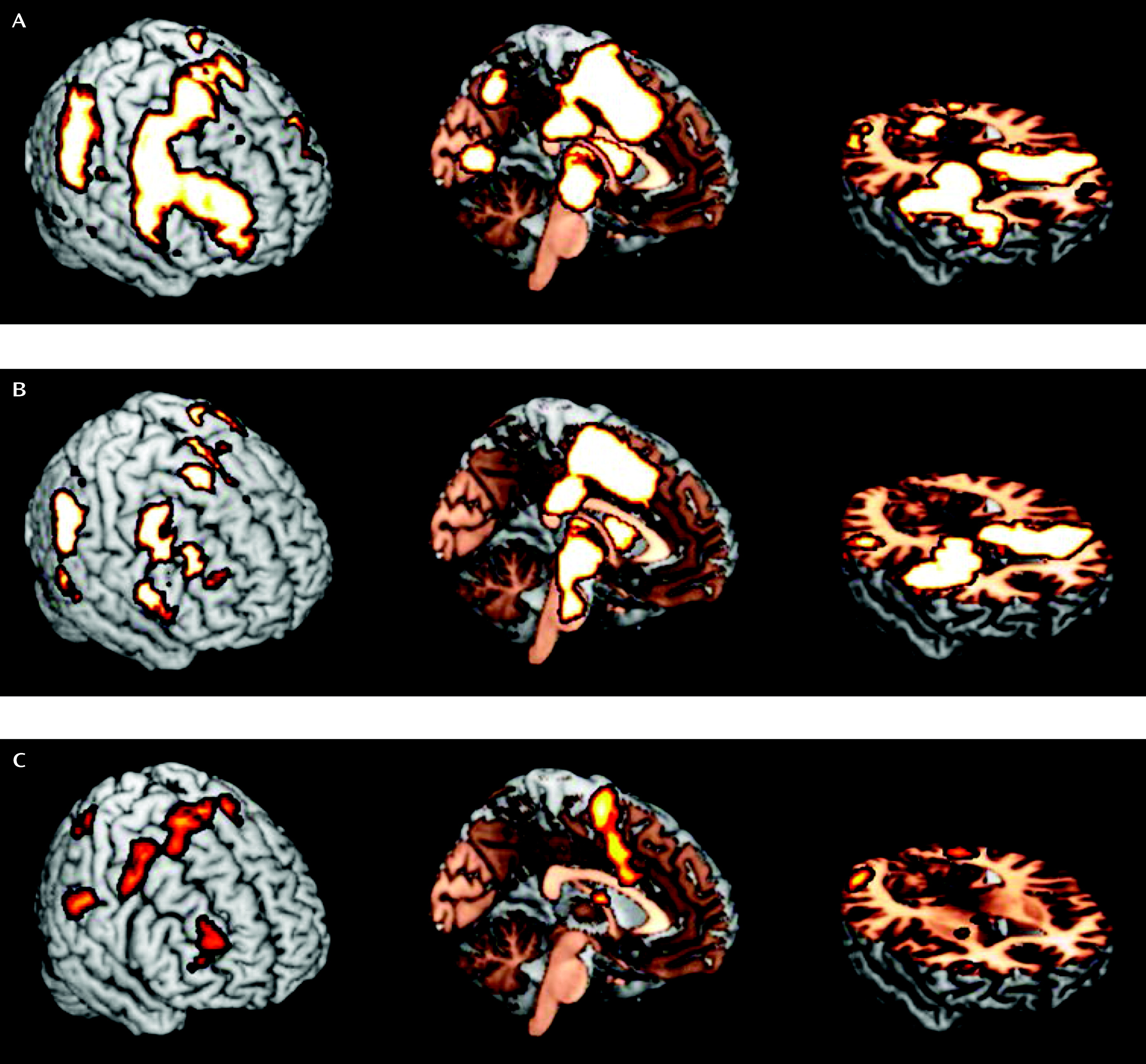
| MNI Coordinates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast and Region | BA | Cluster Size | x | y | z | t |
| Comparison subjects > probands | ||||||
| Supplementary motor area | 6 | 1,279 | 8 | –2 | 68 | 4.56 |
| Anterior cingulate gyrus | 24 | 6 | 6 | 42 | 4.02 | |
| Middle frontal gyrus | 6 | 163 | 46 | 2 | 50 | 3.45 |
| Middle frontal gyrus | 10 | 217 | 34 | 48 | 18 | 3.90 |
| Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex | 9 | 32 | 42 | 30 | 2.73 | |
| Inferior parietal lobule | 40 | 356 | 62 | –30 | 24 | 3.92 |
| Inferior parietal lobule | 40 | 392 | –64 | –30 | 24 | 3.73 |
| Fusiform gyrus | 19 | 112 | 26 | –56 | 12 | 3.24 |
| Thalamus | 208 | 4 | –4 | 14 | 3.15 | |
| Putamen | 24 | 4 | –2 | 2.97 | ||
| Caudate | 14 | –2 | 14 | 3.07 | ||
| Precuneus | 7 | 318 | –6 | –74 | 38 | 2.99 |
| Middle occipital gyrus | 19 | 353 | 50 | –64 | –10 | 3.80 |
| Cerebellum | 408 | –34 | –56 | –24 | 3.79 | |
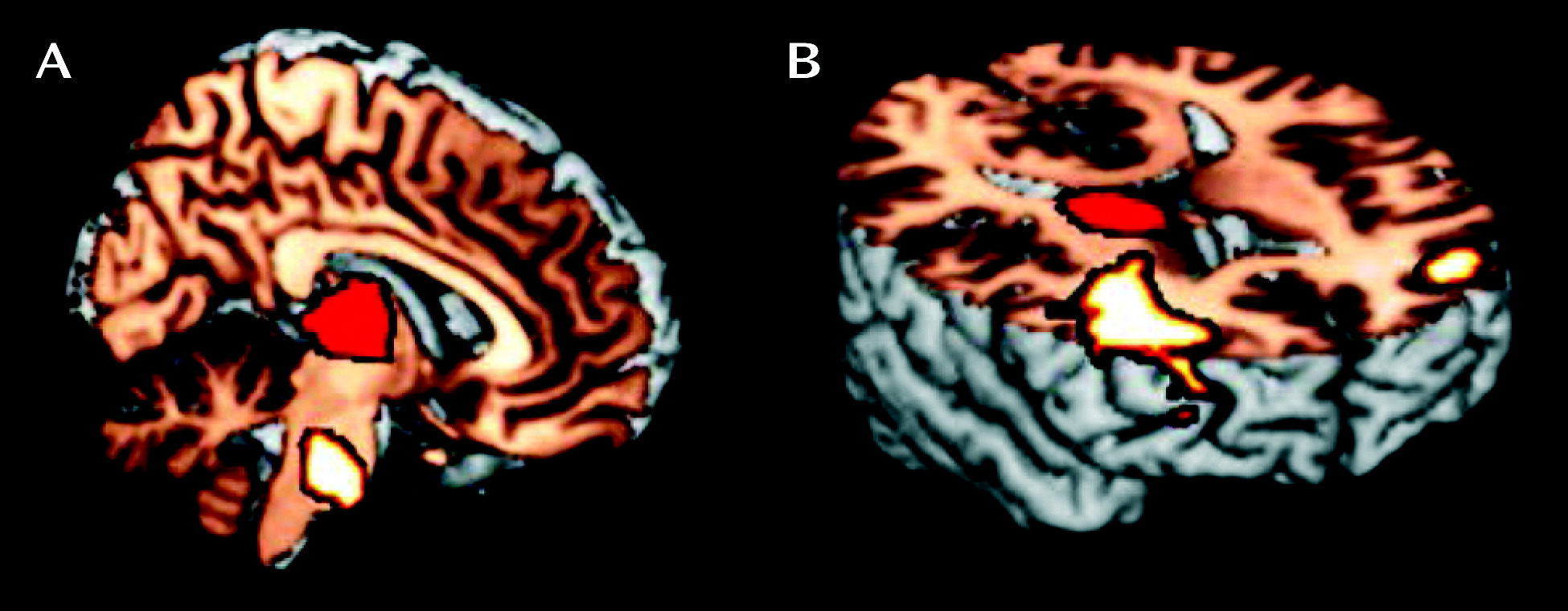
| Remitted ADHD > persistent ADHD | ||||||
| Posterior insula | 13 | 125 | 44 | –12 | 2 | 3.34 |
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 156.04 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

