Neuropsychological Impairments in Schizophrenia and Psychotic Bipolar Disorder: Findings from the Bipolar-Schizophrenia Network on Intermediate Phenotypes (B-SNIP) Study
Abstract
Objective
Method
Results
Conclusions
Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder
Familial Patterns of Cognitive Deficits Across Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder
Method
Participants
Probands.
Family members.
Healthy comparison subjects.
| Variablea | Schizophrenia Group (N=293) | Schizoaffective Depressed Group (N=55) | Schizoaffective Manic Group (N=110) | Psychotic Bipolar Group (N=227) | Healthy Comparison Group (N=295) | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age (years) | 35.87 | 12.84 | 38.22 | 11.93 | 35.76 | 11.72 | 36.19 | 12.79 | 37.64 | 12.63 | n.s. |
| Education (years)b | 12.74 | 2.25 | 12.63 | 2.17 | 13.28 | 2.22 | 14.18 | 2.37 | 15.10 | 2.57 | ≤0.001 |
| WRAT-4, reading test, standard scorec | 93.96 | 15.52 | 93.49 | 15.29 | 98.28 | 14.29 | 101.35 | 13.76 | 103.09 | 13.80 | ≤0.001 |
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| Maled | 198 | 67.6 | 29 | 52.7 | 38 | 34.5 | 85 | 37.4 | 123 | 41.7 | ≤0.001 |
| Racee | ≤0.001 | ||||||||||
| Caucasian | 136 | 46.4 | 29 | 52.7 | 60 | 54.5 | 169 | 74.4 | 186 | 63.3 | |
| African American | 139 | 47.4 | 22 | 40.0 | 44 | 40.0 | 47 | 20.7 | 80 | 27.2 | |
| Other | 18 | 6.1 | 4 | 7.3 | 6 | 5.5 | 11 | 4.8 | 28 | 9.5 | |
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||||
| PANSSf | |||||||||||
| Total score | 65.2 | 16.9 | 66.2 | 17.0 | 68.5 | 14.4 | 53.4 | 14.1 | ≤0.001 | ||
| Positive score | 16.6 | 5.6 | 16.6 | 5.2 | 18.2 | 4.6 | 12.8 | 4.5 | ≤0.001 | ||
| Negative score | 16.7 | 5.9 | 16.4 | 5.3 | 15.4 | 4.7 | 12.1 | 4.0 | ≤0.001 | ||
| YMRSg | 5.3 | 5.8 | 5.1 | 5.9 | 7.9 | 6.8 | 5.9 | 6.6 | ≤0.01 | ||
| MADRSh | 8.6 | 7.8 | 15.4 | 9.5 | 14.7 | 10.5 | 10.4 | 9.2 | ≤0.001 | ||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||
| Medications | |||||||||||
| Antipsychotic | 264 | 90.1 | 51 | 92.7 | 92 | 83.6 | 164 | 72.2 | n.s. | ||
| Mood stabilizer | 44 | 15.0 | 20 | 36.4 | 57 | 51.8 | 119 | 52.4 | ≤0.001 | ||
| Lithium | 16 | 5.5 | 6 | 10.9 | 13 | 11.8 | 64 | 28.2 | ≤0.001 | ||
| Antidepressant | 115 | 39.2 | 34 | 61.8 | 61 | 55.5 | 102 | 44.9 | n.s. | ||
| Sedative/anxiolytic | 56 | 19.1 | 12 | 21.8 | 35 | 31.8 | 66 | 29.1 | n.s. | ||
| Stimulant | 10 | 3.4 | 1 | 1.8 | 6 | 5.5 | 23 | 10.1 | n.s. | ||
| Anticholinergic | 52 | 17.7 | 10 | 18.2 | 15 | 13.6 | 20 | 8.8 | n.s. | ||
| Variable | Relatives of Schizophrenia Probands (N=316) | Relatives of Schizoaffective Depressed Probands (N=64) | Relatives of Schizoaffective Manic Probands (N=133) | Relatives of Psychotic Bipolar Probands (N=259) | Healthy Comparison Subjects (N=295) | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age (years)a | 43.20 | 14.97 | 41.72 | 15.93 | 40.10 | 16.61 | 40.49 | 15.94 | 37.64 | 12.63 | ≤0.001 |
| Education (years)b | 13.99 | 2.41 | 14.41 | 2.82 | 13.77 | 2.93 | 14.61 | 2.73 | 15.10 | 2.57 | ≤0.001 |
| WRAT-4, reading test, standard scorec | 97.40 | 15.06 | 97.49 | 16.48 | 101.27 | 15.17 | 103.21 | 13.93 | 103.09 | 13.80 | ≤0.001 |
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| Maled | 95 | 30.1 | 19 | 29.7 | 42 | 31.6 | 85 | 32.8 | 123 | 41.7 | <0.05 |
| Racee | ≤0.001 | ||||||||||
| Caucasian | 170 | 53.8 | 40 | 62.5 | 83 | 62.4 | 208 | 80.3 | 186 | 63.3 | |
| African American | 128 | 40.5 | 23 | 35.9 | 40 | 30.1 | 43 | 16.6 | 80 | 27.2 | |
| Other | 18 | 5.7 | 1 | 1.6 | 10 | 7.5 | 8 | 3.1 | 28 | 9.5 | |
| History of psychosis | 39 | 12.3 | 12 | 18.8 | 15 | 11.3 | 23 | 8.9 | |||
| Relatives with no history of psychosis | |||||||||||
| Elevated cluster A traits | 44 | 13.9 | 10 | 15.6 | 21 | 15.8 | 31 | 12.0 | |||
| Elevated cluster B traits | 18 | 5.7 | 1 | 1.6 | 10 | 7.5 | 18 | 6.9 | |||
| Not elevated | 215 | 68.0 | 41 | 64.1 | 85 | 63.9 | 184 | 71.0 | |||
Procedures
Probands
Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Schizoaffective disorder.
First-Degree Relatives
Familiality.
Relatives of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder probands.
Personality traits.
Results
Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder Proband Comparisons
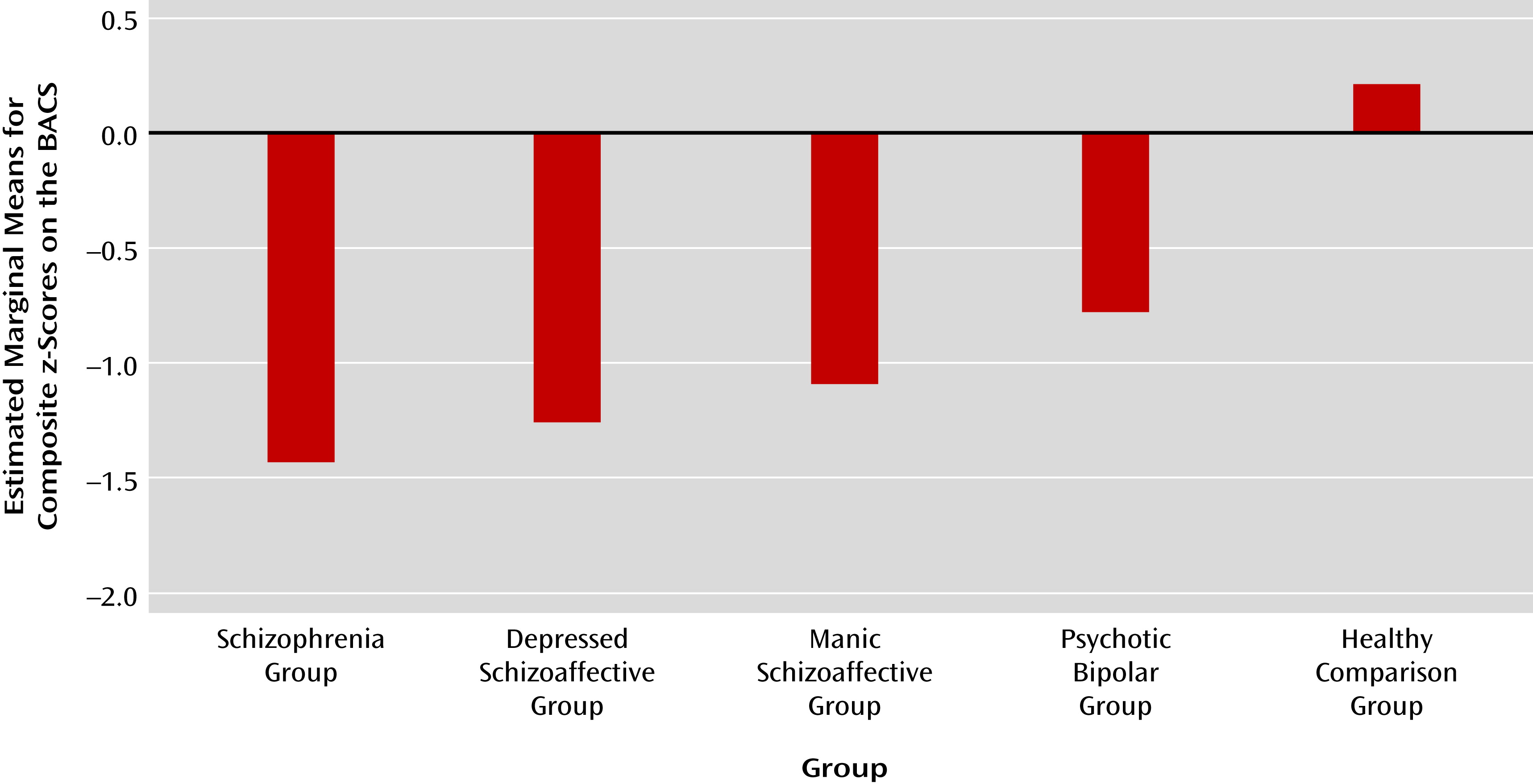
Profile comparisons.
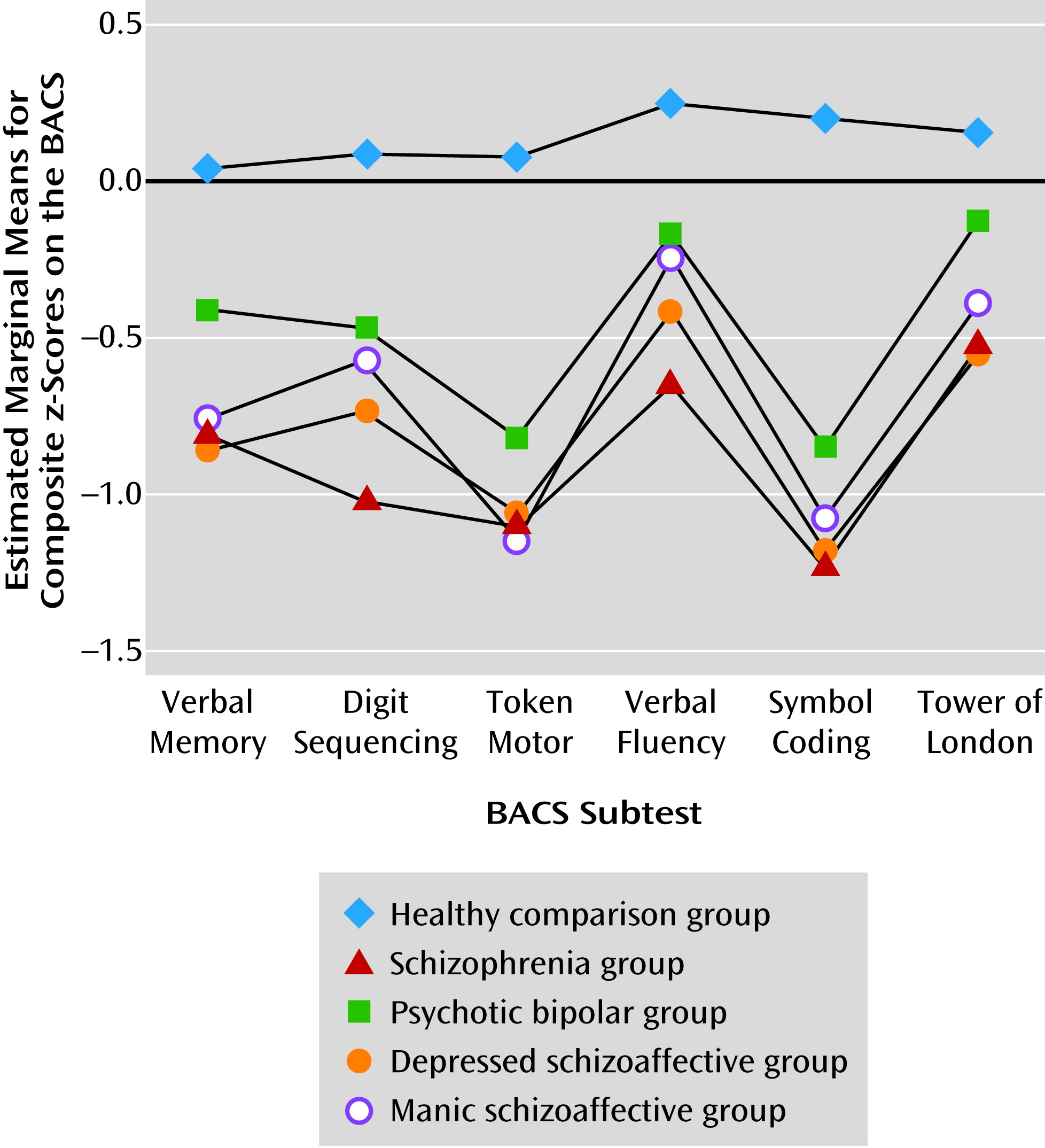
Schizoaffective disorder.
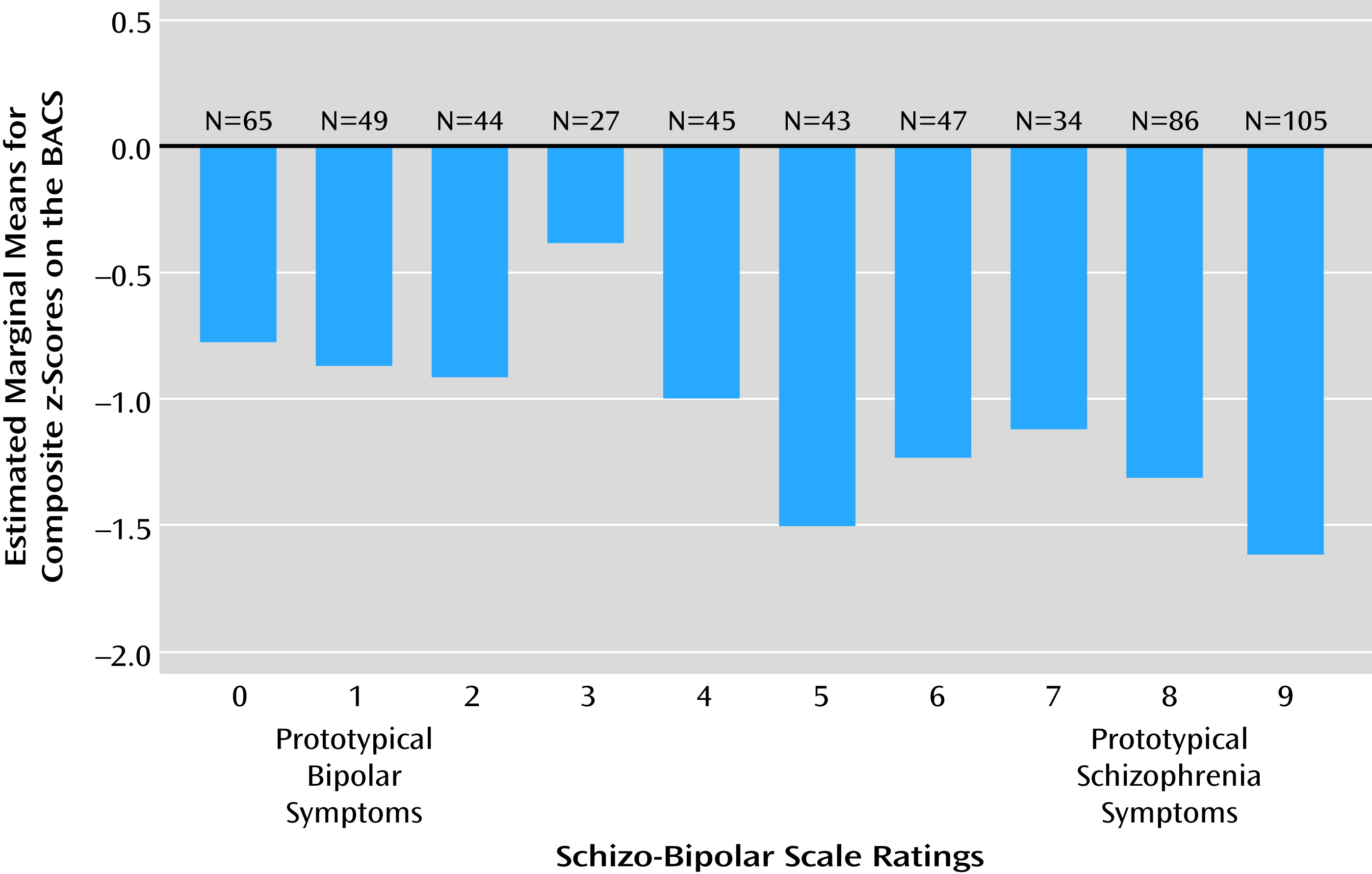
Bipolar-schizophrenia dimension.
Familiality
| Schizophrenia Pedigrees | Bipolar Pedigrees | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instrument | h2 | 90% CI | h2 | 90% CI |
| WRAT-4, reading test | 0.75 | 0.60–0.90 | 0.70 | 0.54–0.86 |
| BACS composite | 0.50 | 0.37–0.63 | 0.61 | 0.42–0.79 |
| BACS subtests | ||||
| Verbal memory | 0.51 | 0.35–0.67 | 0.42 | 0.26–0.58 |
| Digit sequencing | 0.49 | 0.34–0.64 | 0.51 | 0.35–0.67 |
| Token motor | 0.32 | 0.16–0.48 | 0.39 | 0.21–0.57 |
| Verbal fluency | 0.33 | 0.17–0.49 | 0.52 | 0.34–0.70 |
| Symbol coding | 0.40 | 0.22–0.58 | 0.47 | 0.29–0.65 |
| Tower | 0.29 | 0.16–0.42 | 0.45 | 0.27–0.63 |
Relatives of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder probands.
Personality traits in relatives.
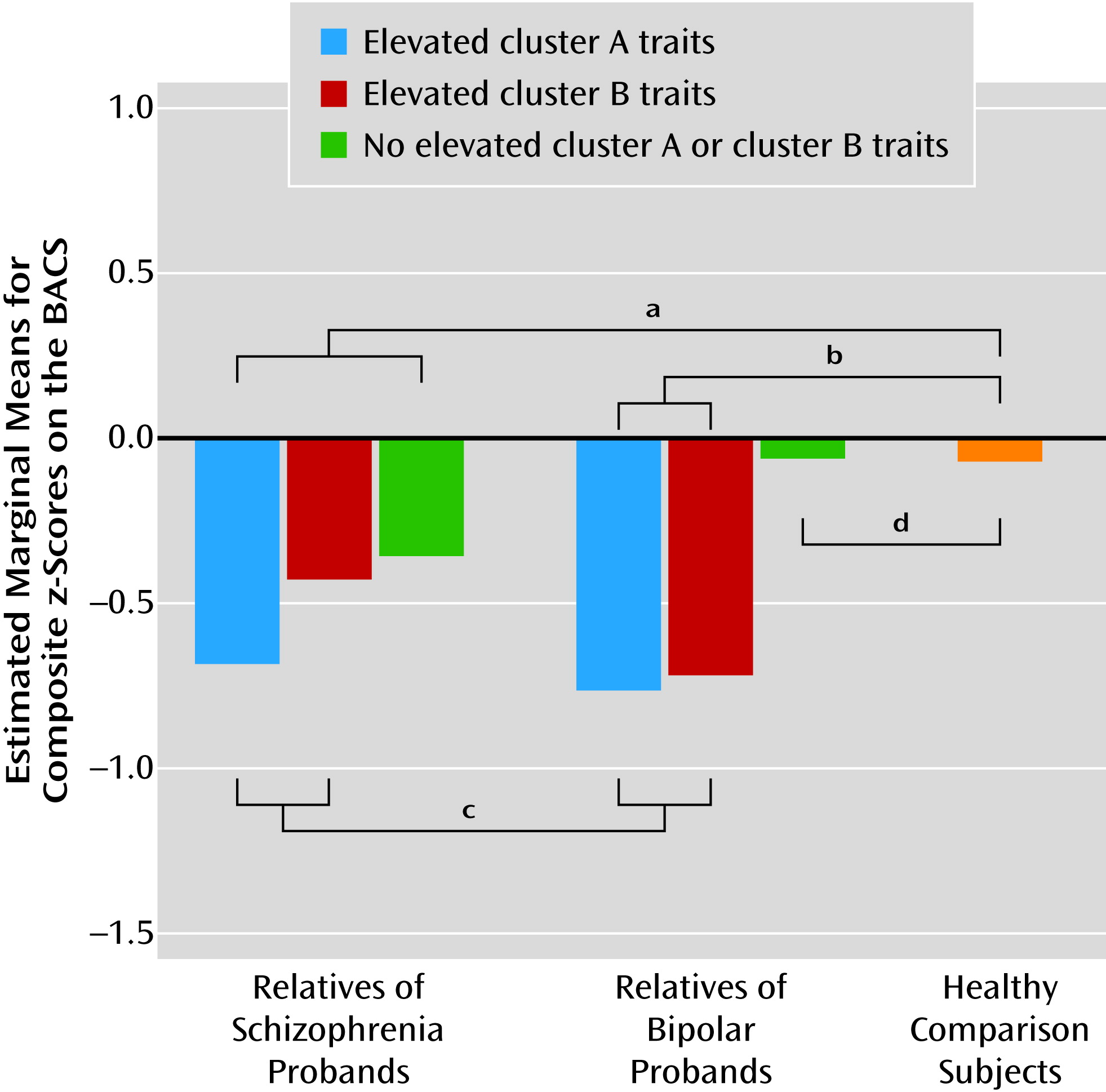
Discussion
Familiality
Personality features.
General and specific measures.
Limitations
Acknowledgments
Footnote
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 72.94 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

