Identification of Distinct Psychosis Biotypes Using Brain-Based Biomarkers
Abstract
Objective:
Method:
Results:
Conclusions:
Method
Subjects
| Clinical Characteristic | Biotype 1 (B1) | Biotype 2 (B2) | Biotype 3 (B3) | Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | % | χ2 | df | p | ||||
| Proband’s DSM psychosis diagnosis | |||||||||
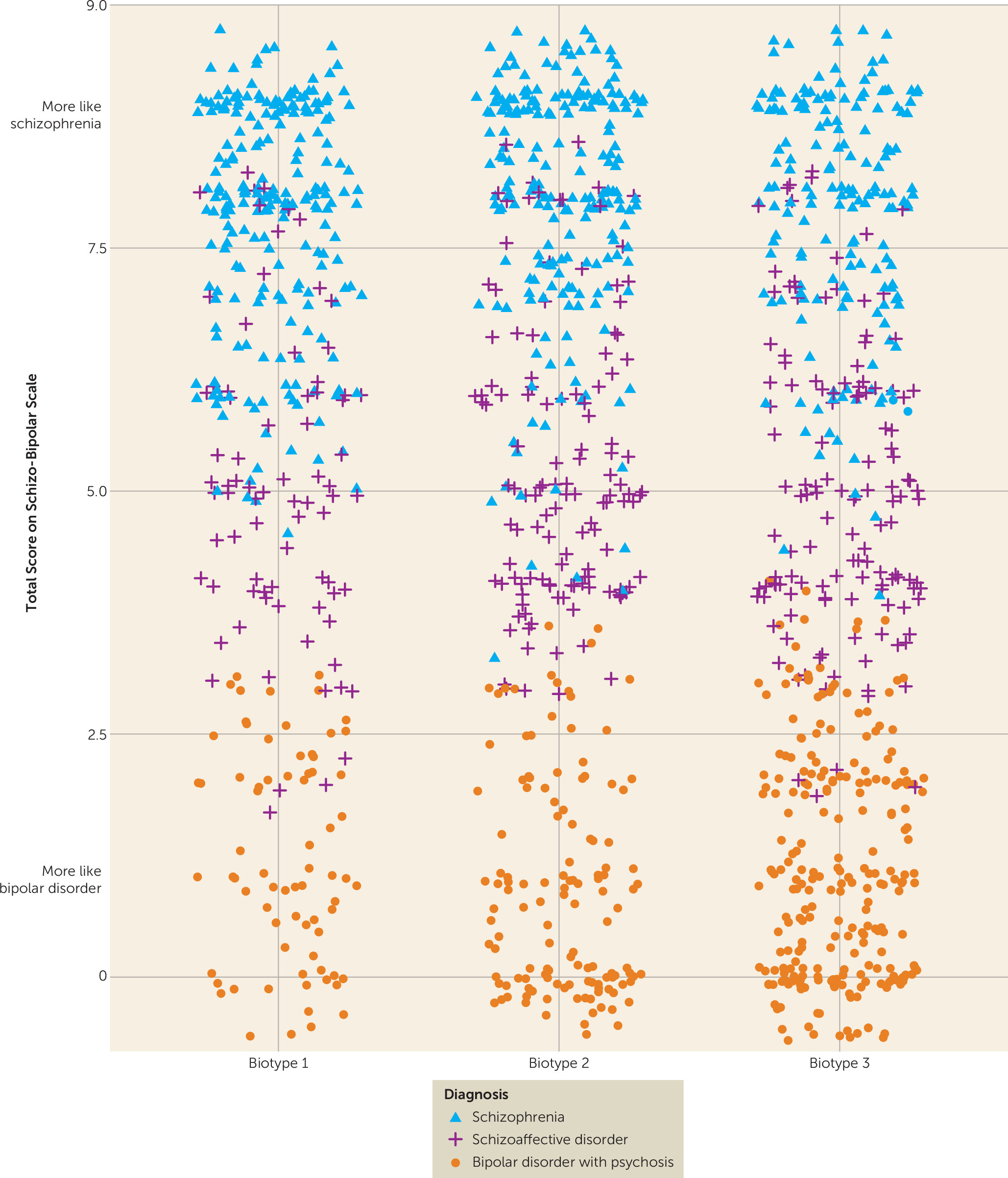
| Schizophrenia | 58.6 | 46.0 | 31.7 | 34.54 | 2 | <0.001a | |||
| Schizoaffective disorder | 21.2 | 26.8 | 24.5 | 1.80 | 2 | 0.41 | |||
| Bipolar disorder | 20.2 | 27.2 | 43.9 | 33.02 | 2 | <0.001b | |||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | F | df | p | |
| Schizo-Bipolar Scale score | 6.0 | 2.8 | 5.3 | 3.2 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 19.16 | 2, 687 | <0.001c |
| Proband’s clinical symptom scores | |||||||||
| PANSS positive subscale | 16.3 | 5.8 | 16.3 | 6.0 | 15.0 | 5.1 | 4.64 | 2, 692 | 0.01d |
| PANSS negative subscale | 16.2 | 5.9 | 15.5 | 5.3 | 13.7 | 5.2 | 13.84 | 2, 692 | <0.001e |
| Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale | 9.7 | 9.5 | 11.2 | 8.9 | 10.3 | 9.5 | 1.41 | 2, 687 | 0.24 |
| Young Mania Rating Scale | 5.5 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 1.99 | 2, 688 | 0.14 |
| Birchwood Social Functioning Scale score (healthy group: mean=154.8, SD=17.8) | |||||||||
| Probands | 116.8 | 23.4 | 123.0 | 24.1 | 131.3 | 25.0 | 142.41 | 3, 885 | <0.001f |
| Relatives | 144.2 | 22.9 | 145.2 | 22.4 | 149.3 | 21.4 | 13.88 | 3, 979 | <0.001g |
| % | % | % | χ2 | df | p | ||||
| Relative’s diagnosis | |||||||||
| Axis I psychosis | 14.0 | 12.3 | 9.2 | 3.53 | 2 | 0.17 | |||
| Axis II: clusters A and B personality disorders | 12.3 | 12.3 | 7.8 | 4.54 | 2 | 0.10 | |||
| Psychosis-related diagnosis (axis I psychosis + axis II clusters A and B)h | 25.9 | 23.8 | 16.7 | 8.39 | 2 | 0.02i | |||
Procedures
Laboratory Tasks
Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia (BACS).
Pro- and anti-saccade tasks.
Stop signal task.
Auditory paired stimuli and oddball evoked brain responses.
Magnetic resonance imaging acquisition and voxel-based morphometry.
Data Analyses for Biotypes
Data integration within paradigms.
| Group Separation From Healthy Subjects (N=278), in Effect Size Units | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group and Composite Variablea | Proband DSM Diagnosisb | Proband Biotype Class | ||||
| A. Probands | BDP (N=226) | SzAff (N=173) | SZ (N=312) | Biotype 1 (N=198) | Biotype 2 (N=235) | Biotype 3 (N=278) |
| Cognitive control | ||||||
| BACS | –1.01 | –1.51 | –1.83 | –2.58 | –1.94 | –0.35 |
| Stop signal task | –0.41 | –0.61 | –0.55 | –0.99 | –0.78 | –0.05 |
| Antisaccade errors | 1.36 | 1.66 | 2.45 | 3.32 | 1.90 | 1.19 |
| Sensorimotor reactivity | ||||||
| EEG intrinsic activity | 0.07 | 0.09 | –0.01 | –0.55 | 0.68 | –0.05 |
| N100 ERP | –0.47 | –0.62 | –0.67 | –1.36 | –0.11 | –0.44 |
| Paired S2 ERP | –0.30 | –0.01 | 0.22 | 0.46 | –0.51 | 0.04 |
| P300 ERP | –0.35 | –0.49 | –0.73 | –1.27 | –0.15 | –0.34 |
| P200 ERP | –0.36 | –0.21 | –0.24 | –0.49 | 0.17 | –0.47 |
| Saccade latency | –0.17 | –0.06 | –0.29 | 0.19 | –0.24 | –0.38 |
| B. Relatives | BDP (N=289) | SzAff (N=231) | SZ (N=363) | Biotype 1 (N=227) | Biotype 2 (N=286) | Biotype 3 (N=370) |
| Cognitive control | ||||||
| BACS | –0.25 | –0.42 | –0.46 | –0.86 | –0.45 | –0.03 |
| Stop signal task | –0.02 | –0.29 | –0.18 | –0.38 | –0.11 | –0.05 |
| Antisaccade errors | 0.82 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 1.72 | 0.68 | 0.70 |
| Sensorimotor reactivity | ||||||
| EEG intrinsic activity | –0.07 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.32 | –0.06 |
| N100 ERP | –0.11 | –0.31 | –0.20 | –0.34 | –0.05 | –0.25 |
| Paired S2 ERP | –0.08 | –0.02 | 0.13 | 0.19 | –0.11 | 0.02 |
| P300 ERP | –0.13 | –0.30 | –0.32 | –0.48 | –0.13 | –0.22 |
| P200 ERP | –0.39 | –0.12 | –0.15 | –0.33 | –0.03 | –0.30 |
| Saccade latency | –0.17 | –0.17 | –0.10 | –0.04 | –0.14 | –0.17 |
| Variable Category | ||||||
| C. Familialityc | Biomarker Composites | Discriminant Functions | ||||
| Cognitive control | 0.51* | |||||
| BACS | 0.40** | |||||
| Stop signal task | 0.21† | |||||
| Antisaccade errors | 0.32*** | |||||
| Sensorimotor reactivity | 0.59* | |||||
| EEG intrinsic activity | 0.47*** | |||||
| N100 ERP | 0.62** | |||||
| Paired S2 ERP | 0.17† | |||||
| P300 ERP | 0.52** | |||||
Cluster determination.
Biotype construction.
Results
Distinct Psychosis Biotypes Identified by Multivariate Biomarkers
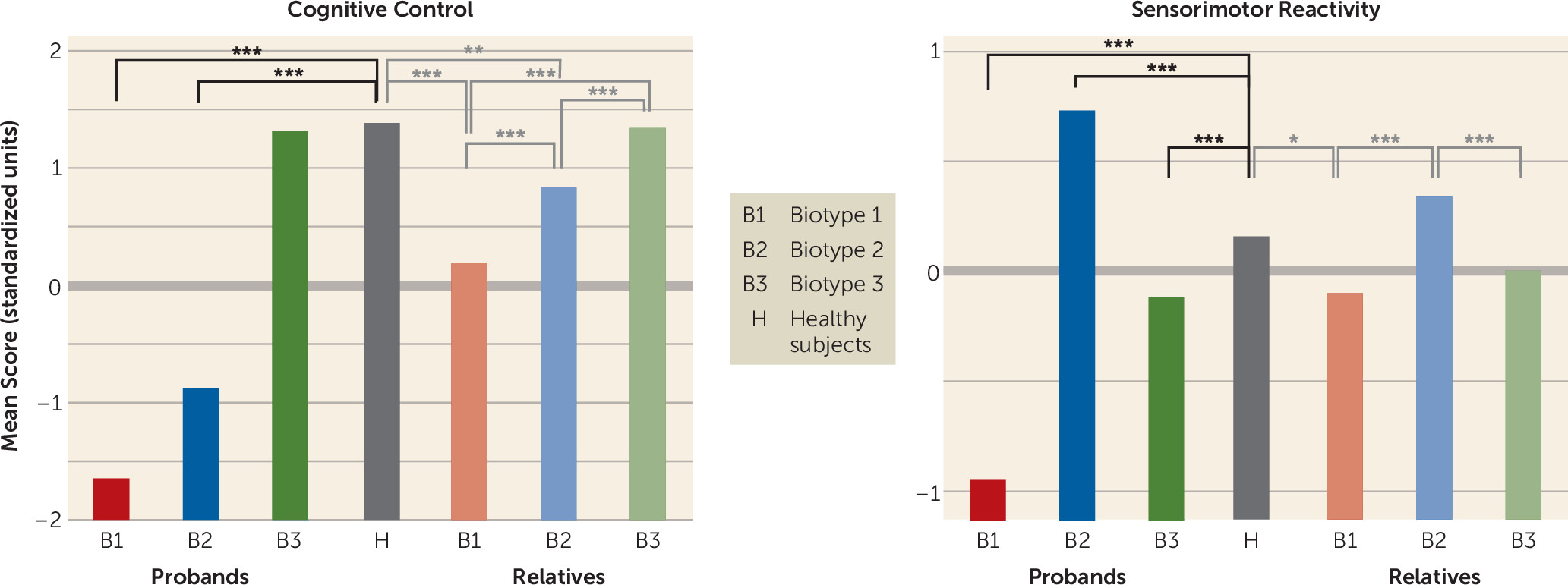
Clinical Characteristics of Biotypes and Relation to DSM Diagnoses
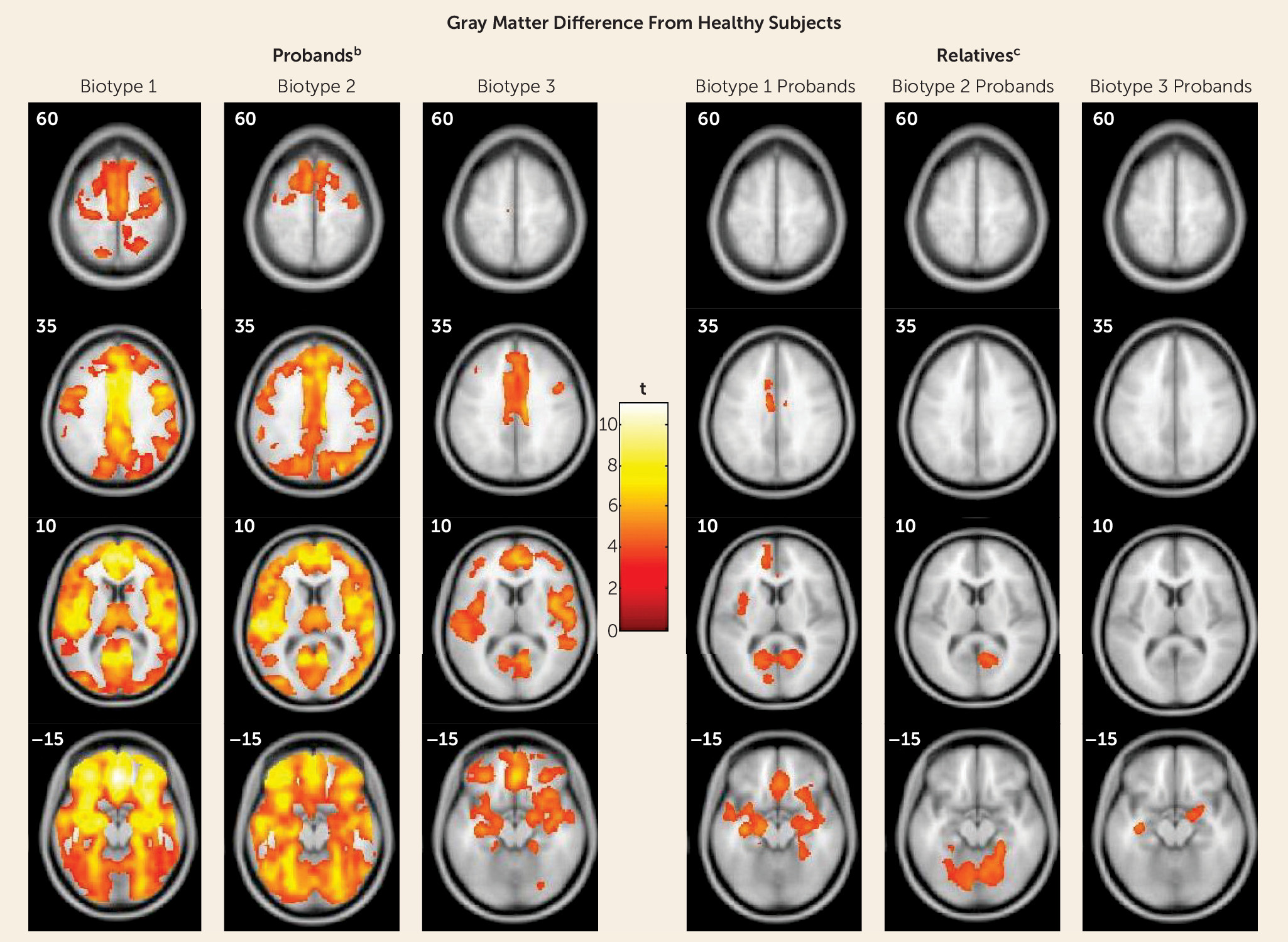
Structural Neuroanatomical Features of Biotypes
| Group Separation From Healthy Subjects, in Effect Size Units | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proband DSM Diagnosisb | Proband Biotype Class | |||||
| Group and Brain Region | BDP | SzAff | SZ | Biotype 1 | Biotype 2 | Biotype 3 |
| Probands | ||||||
| Frontal/inferior frontal gyrus | 0.54 | 0.70 | 0.84 | 1.0 | 0.82 | 0.52 |
| Cingulate gyrus | 0.43 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 0.66 | 0.52 |
| Temporal/superior temporal gyrus | 0.55 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.53 |
| Occipital/lingual gyrus | 0.16 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.65 | 0.38 |
| Cerebellum | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.34 |
| Overall | 0.34 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.46 |
| Relatives | ||||||
| Frontal/inferior frontal gyrus | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.43 | 0.00 | 0.16 |
| Cingulate gyrus | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Temporal/superior temporal gyrus | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.34 |
| Occipital/lingual gyrus | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.00 |
| Cerebellum | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.00 |
| Overall | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
Neurobiological and Clinical Characteristics of Biological Relatives by Biotype
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 13.92 KB
- View/Download
- 3.55 MB
- View/Download
- 3.55 MB
- View/Download
- 27.36 KB
- View/Download
- 27.36 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

