Computerized Cognitive Training in Older Adults With Mild Cognitive Impairment or Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective:
Method:
Results:
Conclusions:
Method
Information Sources and Study Selection
Eligibility Criteria
Types of participants.
Types of interventions.
Types of controls.
Types of outcomes.
Data Collection and Coding
Risk of Bias in Individual Studies and Quality Appraisal
Data Analysis
Results
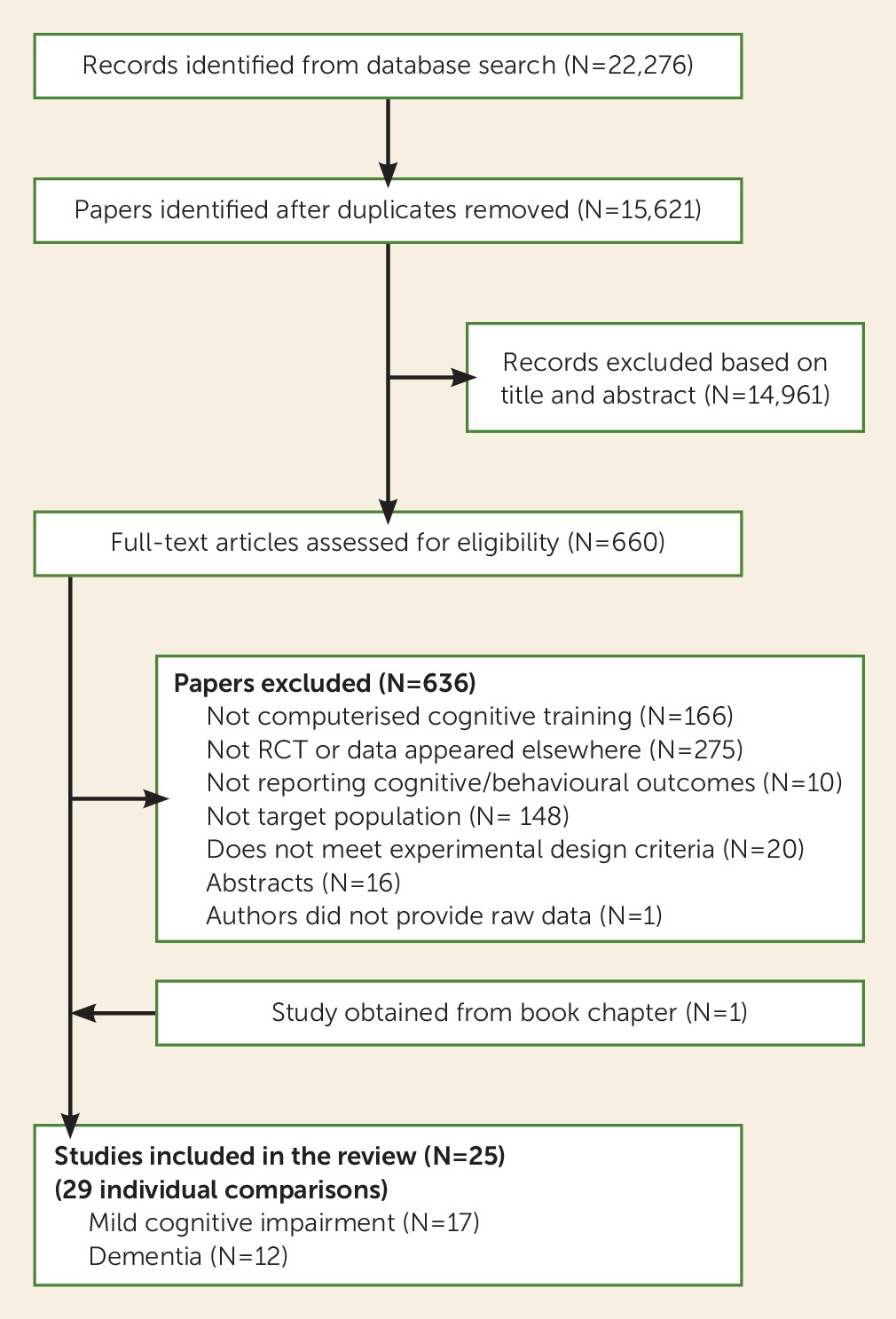
Study Selection
Characteristics of Included Studies
Mild cognitive impairment.
| Study | N | Population Diagnosis | Mean Age (Years)b | Sex (% Female) | Mean Mini-Mental State Examination or Equivalent | Delivery | Program and Targeted Domains | Dosec | Number of Sessionsd | Session Lengthe | Session/Weekf | Control | Risk of Biasg | PEDro-P Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim et al. (66) | 30 (CCT, N=15; control, N=15) | Mild cognitive impairment | 78.7 | 70 | 26.7 | Supervised | Virtual reality simulating household tasks | 6 | 12 | 30 | 3 | Active | High | 7 |
| Rozzini et al. (51) | 37 (CCT, N=15; control, N=22) | Mild cognitive impairment | 26.2 | Supervised | Neuropsychological training: | 60 | 60 | 60 | 5 | Active | Low | 8 | ||
| Memory, attention, language, executive function, visuospatial processing | ||||||||||||||
| Barnes et al. (29) | 47 (CCT, N=22; control, N=25) | Mild cognitive impairment | 74 | 40 | Home-based | Posit science brain fitness | 50 | 30 | 100 | 5 | Active | High | 8 | |
| Speed, verbal memory, working memory | ||||||||||||||
| Finn et al. (48) | 16 (CCT, N=8; control, N=8) | Mild cognitive impairment | 72.69 | 50 | 27.76 | Home-based | Lumosity | 10 | 30 | 20 | 3–5 | Passive | High | 7 |
| Attention, speed, nonverbal memory, executive functions | ||||||||||||||
| Herrera et al. (56) | 22 (CCT, N=11; control, N=11) | Mild cognitive impairment | 76.63 | 50 | 27.27 | Supervised | In-house program | 24 | 24 | 60 | 2 | Active | High | 8 |
| Verbal memory, nonverbal memory, verbal learning, non- verbal learning, attention, speed | ||||||||||||||
| Tarnanas et al. (47) | 71 (CCT, N=32; control, N=39) | Mild cognitive impairment | 70.05 | 60.5 | 26.5 | Supervised | Virtual reality museum task | 60 | 40 | 90 | 2 | Active | High | 7 |
| Wittelsberger et al. (54) | 27 (CCT, N=17; control, N=10) | Mild cognitive impairment | 70.07 | 48.14 | 22.88 | Supervised | Nintendo Wii bowling | 12 | 12 | 60 | 2 | Passive | High | 5 |
| Finn et al. (49) | 24 (CCT, N=12; control, N=12) | Mild cognitive impairment | 73.95 | 29.16 | 27.79 | Supervised | Repetition lag training | 9 | 6 | 90 | 2 | Passive | High | 6 |
| Verbal learning, verbal memory | ||||||||||||||
| Hughes et al. (57) | 20 (CCT, N=10; control, N=10) | Mild cognitive impairment | 77.4 | 70 | 27.1 | Supervised | Nintendo Wii | 36 | 24 | 90 | 1 | Active | High | 7 |
| Fiatarone Singh et al. (43) (study 1 [CCT + exercise vs. sham CCT + exercise]) | 49 (CCT, N=27; control, N=22) | Mild cognitive impairment | 70.1 | 68 | 27 | Supervised | COGPACK | 78 | 52 | 90 | 2 | Active | Low | 9 |
| Verbal memory, nonverbal memory, executive functions, attention, speed | ||||||||||||||
| Fiatrone Singh et al. (43) (study 2 [CCT + sham exercise vs. sham CCT + sham exercise]) | 51 (CCT, N=24; control, N=27) | Mild cognitive impairment | 70.1 | 68 | 27 | Supervised | COGPACK | 78 | 52 | 90 | 2 | Active | Low | 9 |
| Verbal memory, nonverbal memory, executive functions, attention, speed | ||||||||||||||
| Barban et al. (44) (study 2, mild cognitive impairment) | 106 (CCT, N=46; control, N=60) | Mild cognitive impairment | 73.54 | 47.16 | 27.74 | Supervised | Sociable | 24 | 24 | 60 | 2 | Passive | High | 8 |
| Verbal memory, nonverbal memory, executive functions, language, attention, visuospatial processing | ||||||||||||||
| Hagovska et al. (45, 46) | 78 (CCT, N=40; control, N=38) | Mild cognitive impairment | 66.97 | 48.75 | 26.33 | Supervised | CogniPlus | 10 | 20 | 30 | 2 | Passive | High | 7 |
| Verbal memory, nonverbal memory, verbal learning, nonverbal learning, working memory, attention, executive functions, visuospatial processing | ||||||||||||||
| Barcelos et al. (53) | 17 (CCT, N=8; control, N=9) | Mild cognitive impairment | 80.6 | 56 | 20.8h | Supervised | In-house virtual reality enhanced recumbent stationary bike coin and dragon collection | 18 | 24 | 20–45 | 2 | Active | High | 6 |
| Visuospatial processing, executive functions, attention | ||||||||||||||
| Gooding et al. (30) (study 1 [CCT and ACG]) | 41 (CCT, N=31; control, N=10) | Mild cognitive impairment | 75.59j | 61.9j | 50.62i | Supervised | BrainFitness by Posit Science | 30 | 32 | 60 | 2 | Active | High | 5 |
| Memory, attention, executive functions | ||||||||||||||
| Gooding (30) (study 2 [CVT and ACG]) | 33 (CCT, N=23; CTL, N=10) | Mild cognitive impairment | 75.59j | 61.9j | 50.84i | Supervised | BrainFitness by Posit Science | 30 | 32 | 60 | 2 | Active | High | 5 |
| Memory, attention, executive functions | ||||||||||||||
| Lin et al. (67) | 21 (CCT, N=10; control, N=11) | Mild cognitive impairment | 73.0 | 47.62 | 25.02h | Home-based | Posit Science InSight. | 24 | 24 | 60 | 4 | Active | High | 7 |
| Processing speed, visuospatial, attention, executive functions | ||||||||||||||
| Optale et al. (31) | 31 (CCT, N=15; control, N=16) | Mixedk | 80.96 | 67.74 | 21.91 | Supervised | Virtual reality Virtools platform | 18 | 36 | 30 | 3 | Active | High | 8 |
| Nonverbal learning, nonverbal memory, attention, visuospatial processing | ||||||||||||||
| Galante et al. (32) | 11 (CCT, N=7; control, N=4) | Mixedk | 75.51 | Not reported | 22.9 | Supervised | Neuropsychological training | 12 | 12 | 60 | 3 | Active | High | 9 |
| Memory (domain unspecified), working memory, language, attention, executive functions, visuospatial processing | ||||||||||||||
| Zhuang et al. (33) | 33 (CCT, N=19; control, N=14) | Mixedk | 78.07 | 75.75 | 10.16 | Supervised | In-house program | 108 | 72 | 90 | 3 | Not Specified | High | 8 |
| Nonverbal learning, Nonverbal memory, executive functions, visuospatial, processing | ||||||||||||||
| Heiss et al. (58) | 35 (CCT, N=18; control, N=17) | Dementia | 66.29 | 45.71 | 21.1 | Supervised | Rigling Reha-Service | 48 | 48 | 60 | 2 | Active | High | 6 |
| Memory, executive functions, visuospatial | ||||||||||||||
| Lowenstein et al. (52) | 44 (CCT, N=19, control, N=25) | Dementia | 76.43 | 34.09 | 23.96 | Supervised + home-based | Commercial games | 18 | 24 | 45 | 2 | Active | High | 7 |
| Language, executive functions, nonverbal learning, nonverbal memory, verbal memory, nonverbal memory, attention | ||||||||||||||
| Tarraga et al. (59) | 31 (CCT, N=15; control, N=16) | Dementia | 76.54 | 87.09 | 21.55 | Supervised | Smart Brain | 24 | 72 | 20 | 3 | Active | High | 7 |
| Memory, attention, language, visuospatial processing, working memory, executive functions | ||||||||||||||
| Fernandez-Calvo et al. (55) | 30 (CCT, N=15; control, N=15) | Dementia | 75.7 | 43.33 | 19.66 | Supervised | Nintendo Wii Big Brain Academy | 36 | 36 | 60 | 3 | Passive | Low | 8 |
| Nonverbal memory, working memory, executive functions, visuospatial processing | ||||||||||||||
| Boller et al. (42) (study 1 [recollection + control]) | 18 (CCT, N=12; control, N=6) | Dementia | 80.82 | 55.5 | 24.59 | Supervised + home-based | Repetition lag training | 6 | 30 | 20 | 15 | Passive | High | 9 |
| Verbal learning, verbal memory | ||||||||||||||
| Boller et al. (42) (study 2 [recognition + control]) | 18 (CCT, N=12; control, N=6) | Dementia | 81.5 | 55.5 | 25.51 | Supervised + home-based | Repetition lag training | 6 | 30 | 20 | 15 | Passive | High | 9 |
| Verbal learning, verbal memory | ||||||||||||||
| Lee et al. (60) | 13 (CCT, N=7; control, N=6) | Dementia | 77.7 | 69.23 | 16.07 | Supervised | In-house computerized errorless learning program | 6 | 12 | 60 | 2 | Active | High | 6 |
| Verbal memory, nonverbal memory, working memory, verbal learning, nonverbal learning, attention, executive functions, global cognition | ||||||||||||||
| Man et al. (50) | 44 (CCT, N=20; control, N=24) | Dementia | 80.29 | 85 | 22.03 | Supervised | Virtual reality home and shop simulation | 5 | 10 | 30 | 2–3 | Active | Low | 7 |
| Barban et al. (44) (study 1) | 81 (CTT, N=42; control, N=39) | Dementia | 76.79 | 70.37 | 23.4 | Supervised | Sociable | 24 | 24 | 60 | 2 | Passive | High | 8 |
| Verbal memory, nonverbal memory, executive functions, language, attention, visuospatial processing |
Dementia.
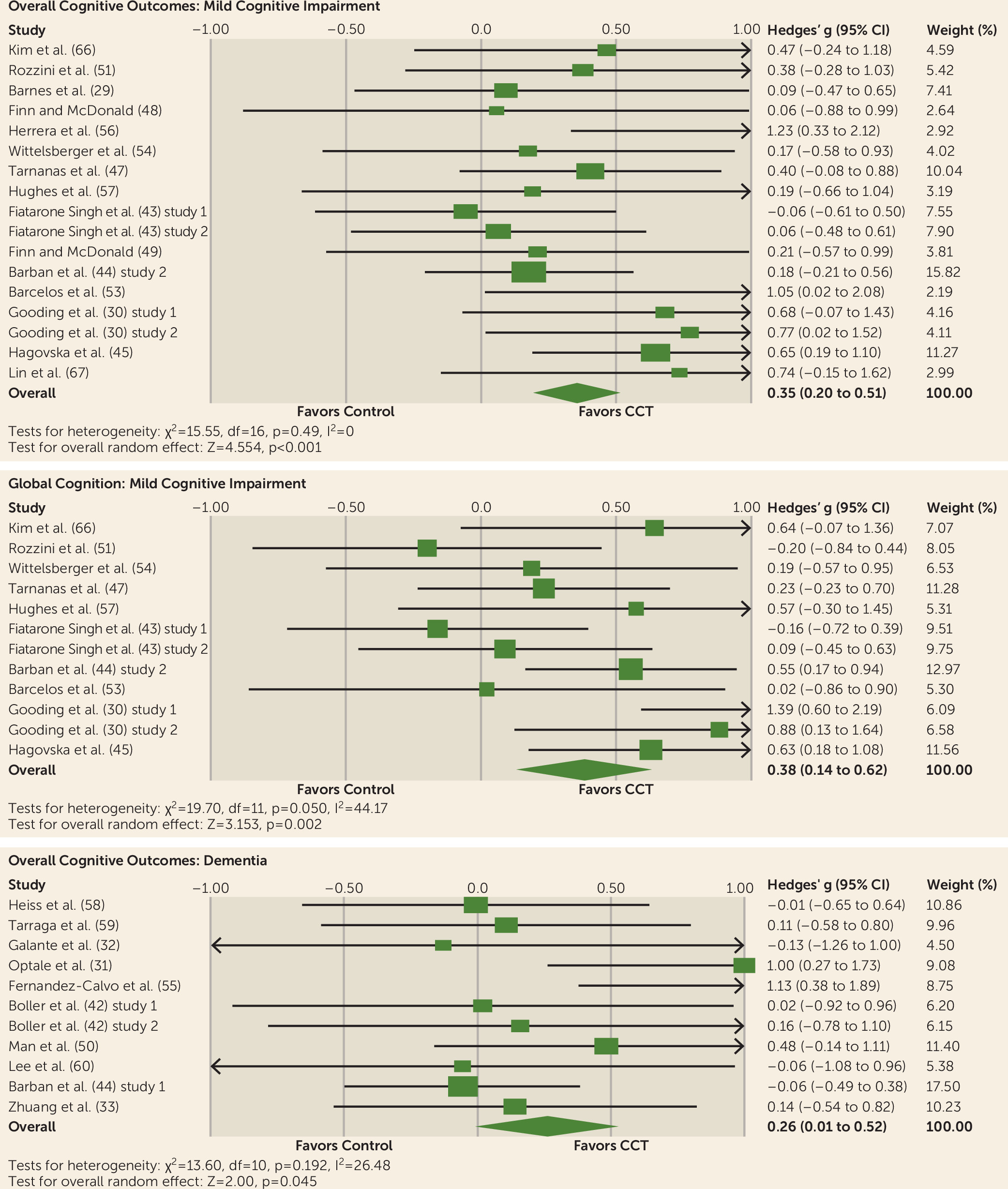
Meta-Analysis of Mild Cognitive Impairment Outcomes
Overall efficacy on cognitive outcomes.
Global cognition.
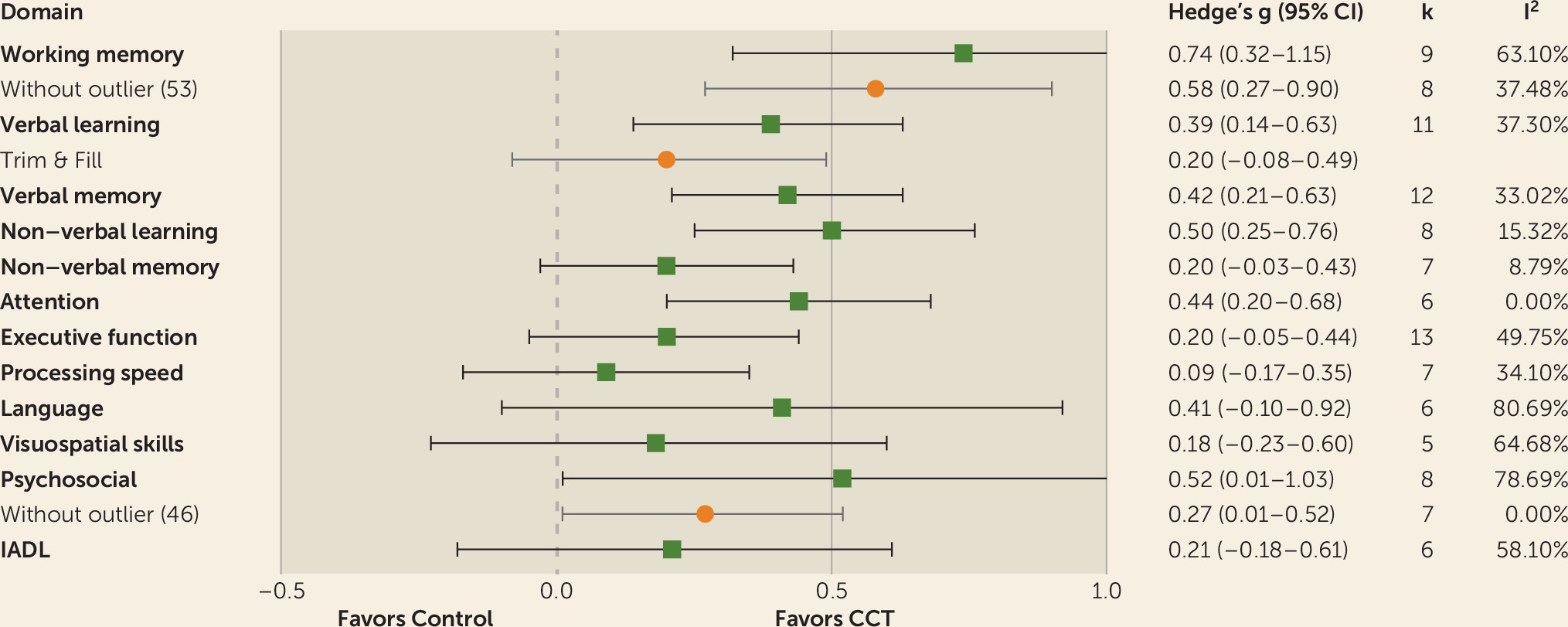
Verbal learning.
Verbal memory.
Nonverbal learning.
Working memory.
Attention.
Psychosocial functioning.
Other domains.
Meta-Analysis of Dementia Outcomes
Overall efficacy on cognitive outcomes.
Efficacy on individual cognitive domains.
Long-Term Outcomes
Discussion
Limitations
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 843.98 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

