Neural Correlates of the Dual-Pathway Model for ADHD in Adolescents
Abstract
Objective:
Methods:
Results:
Conclusions:
Methods
Participants
Population-based cohort.
| Characteristic or Measure | Baseline (N=1,963) | 2-Year Follow-Up (N=1,518) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | |
| Male | 952 | 48.5% | 728 | 48.0% |
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Age (years) | 14.43 | 0.40 | 16.47 | 0.57 |
| Hyperactivity-inattention subscale on parent SDQ | ||||
| Total score | 2.97 | 2.29 | 2.39 | 2.05 |
| Hyperactivity-impulsivity score | 0.70 | 1.05 | 0.47 | 0.87 |
| Inattention score | 2.27 | 1.65 | 1.92 | 1.57 |
| N | % | N | % | |
| ADHD categories by hyperactivity-inattention total scoreb | ||||
| Normal | 1,690 | 86.1 | 1,394 | 91.8 |
| Borderline | 107 | 5.5 | 64 | 4.1 |
| Abnormal | 166 | 8.5 | 62 | 4.1 |
| Mean | SD | |||
| Delay discounting | –1.98 | 0.61 | ||
| Working memory | 19.45 | 14.00 | ||
| Intrasubject variabilityc | 119.38 | 30.96 | ||
| Stop-signal reaction timec | 186.43 | 61.90 | ||
Clinical cohort.
Measurements
ADHD.
Delay discounting.
Working memory.
Intrasubject variability and stop-signal reaction time.
Structural MRI
Genetic Data
Statistical Analysis
Voxel-wise brain-wide association analysis.
Neuropsychological association analysis.
Prospective association analysis.
Polygenic analysis.
Validation.
Results
Descriptive Statistics
| ADHD Symptoms | Gray Matter Volume | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Score | Hyperactivity-Impulsivity | Inattention | Prefrontal Cluster | Posterior occipital Cluster | ||||||
| Measure | r | 95% CI | r | 95% CI | r | 95% CI | r | 95% CI | r | 95% CI |
| Working memoryb | 0.19*** | 0.15, 0.24 | 0.09*** | 0.05, 0.14 | 0.21*** | 0.16, 0.25 | −0.04 | −0.08, 0.01 | −0.08*** | −0.12, −0.03 |
| Delay discountingb | 0.13*** | 0.08, 0.17 | 0.06** | 0.02, 0.11 | 0.14*** | 0.09.0.18 | −0.07** | −0.11, −0.02 | −0.06* | −0.10, −0.01 |
| Intrasubject variabilityc | 0.14*** | 0.10, 0.19 | 0.09*** | 0.04, 0.14 | 0.14*** | 0.10, 0.19 | −0.05* | −0.10, −0.01 | −0.06** | −0.11, −0.01 |
| Working memory corrected for delay discounting and intrasubject variability | 0.16*** | 0.12, 0.21 | 0.07** | 0.03, 0.12 | 0.18*** | 0.13, 0.22 | −0.04 | −0.09, 0.005 | −0.07** | −0.11, −0.02 |
| Delay discounting corrected for working memory and intrasubject variability | 0.10*** | 0.05, 0.15 | 0.05* | 0.001, 0.10 | 0.11*** | 0.06, 0.15 | −0.05* | −0.09, −0.002 | −0.05* | −0.09, −3.3e–4 |
| Intrasubject variability corrected for working memory and delay discounting | 0.12*** | 0.08, 0.17 | 0.08** | 0.03, 0.13 | 0.12*** | 0.07, 0.16 | −0.04 | −0.09, 0.005 | −0.05* | −0.10, −0.01 |
Neuroanatomical Correlates of Inattention in a Population-Based Cohort
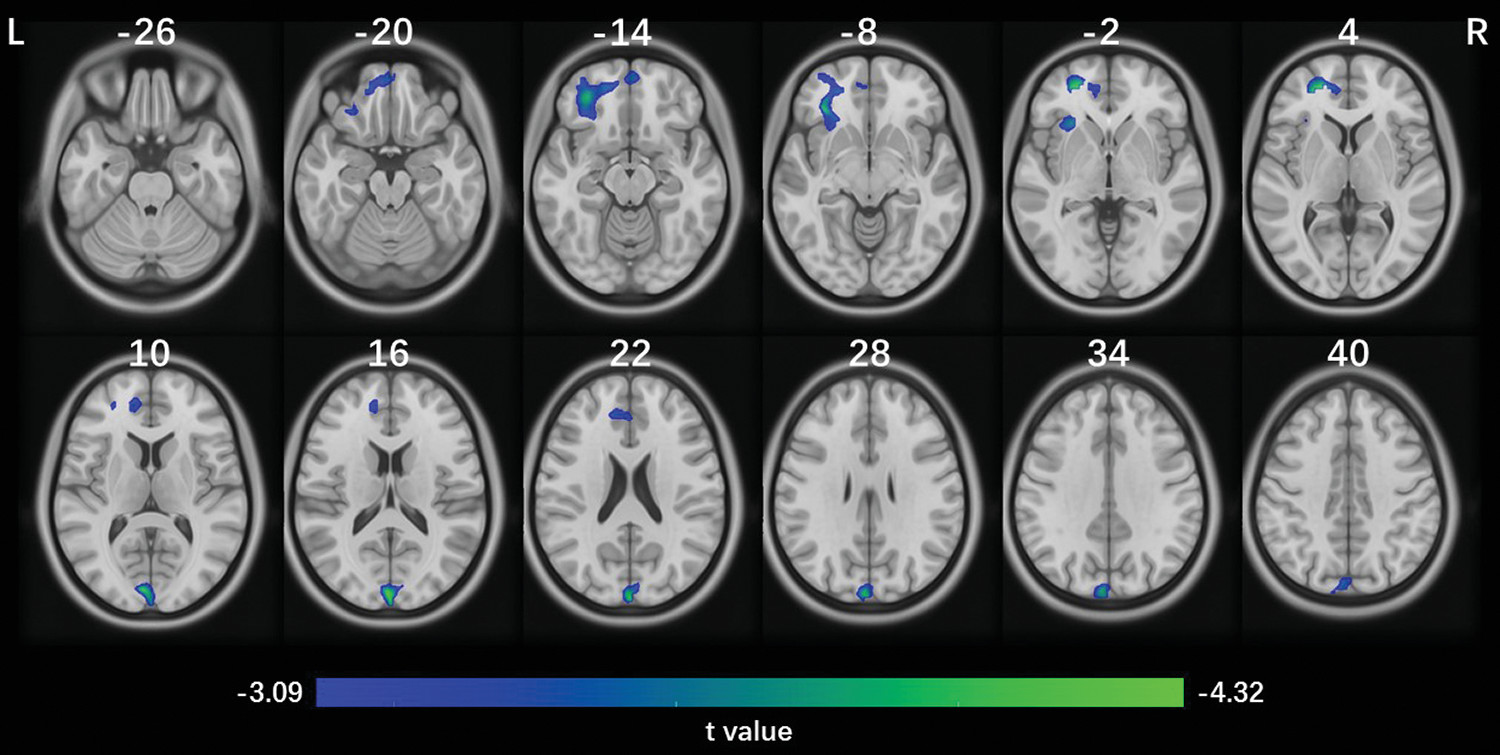
Neuroanatomical Correlates of Inattention Selectively Associated With Working Memory, Intrasubject Variability, or Delay Discounting
Prospective Associations With Inattention 2 Years Later
| Step | Category | Independent Variable | R2 | ΔR2 | pea | βfb | tfc | pfd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Covariates | Sex | 0.412 | 0.412 | <0.001 | 0.073 | 2.86 | 0.004 |
| Handedness | 0.016 | 0.79 | 0.430 | |||||
| Total intracranial volume | 0.010 | 0.375 | 0.708 | |||||
| Inattention at age 14 | 0.608 | 28.45 | <0.001 | |||||
| Site 1 | 0.018 | 0.66 | 0.508 | |||||
| Site 2 | 0.050 | 1.80 | 0.072 | |||||
| Site 3 | 0.068 | 2.57 | 0.010 | |||||
| Site 4 | 0.065 | 2.47 | 0.014 | |||||
| Site 5 | 0.010 | 0.36 | 0.721 | |||||
| Site 6 | 0.038 | 1.44 | 0.151 | |||||
| Site 7 | 0.036 | 1.37 | 0.170 | |||||
| Step 2 | Behavior | Working memory | 0.414 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.044 | 2.04 | 0.042 |
| Step 3 | Delay discounting | 0.414 | 0.000 | 0.593 | 0.007 | 0.35 | 0.724 | |
| Step 4 | Intrasubject variability | 0.415 | 0.001 | 0.164 | 0.028 | 1.31 | 0.190 | |
| Step 5 | Brain structure | Gray matter volume in prefrontal cluster | 0.415 | 0.000 | 0.685 | 0.047 | 1.88 | 0.060 |
| Step 6 | Gray matter volume in posterior occipital cluster | 0.42 | 0.005 | <0.001 | –0.083 | –3.55 | <0.001 |
Associations of Neuropsychological and Neuroanatomical Intermediate Phenotypes With Polygenic Risk for ADHD
Validation Using an ADHD Clinical Cohort
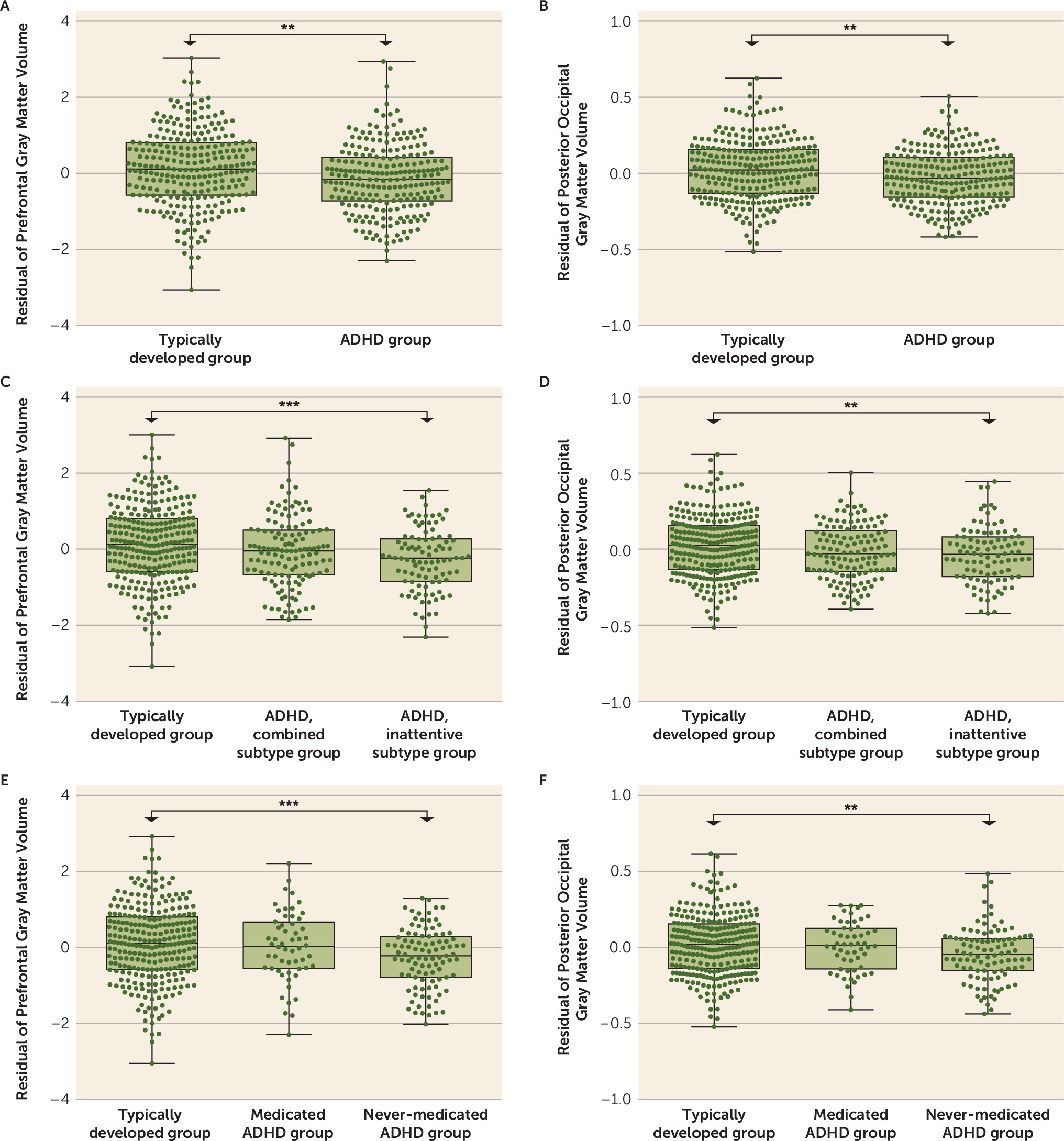
Medication Effects
Discussion
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Footnote
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 422.88 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Author Contributions
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

