Review of Current Strategies for Delivering Alzheimer's Disease Drugs Across the Blood-Brain Barrier
Abstract
Introduction
Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease
Amyloid Hypothesis
Tau Protein
Others
Blood-Brain Barrier
BBB Permeation Mechanisms
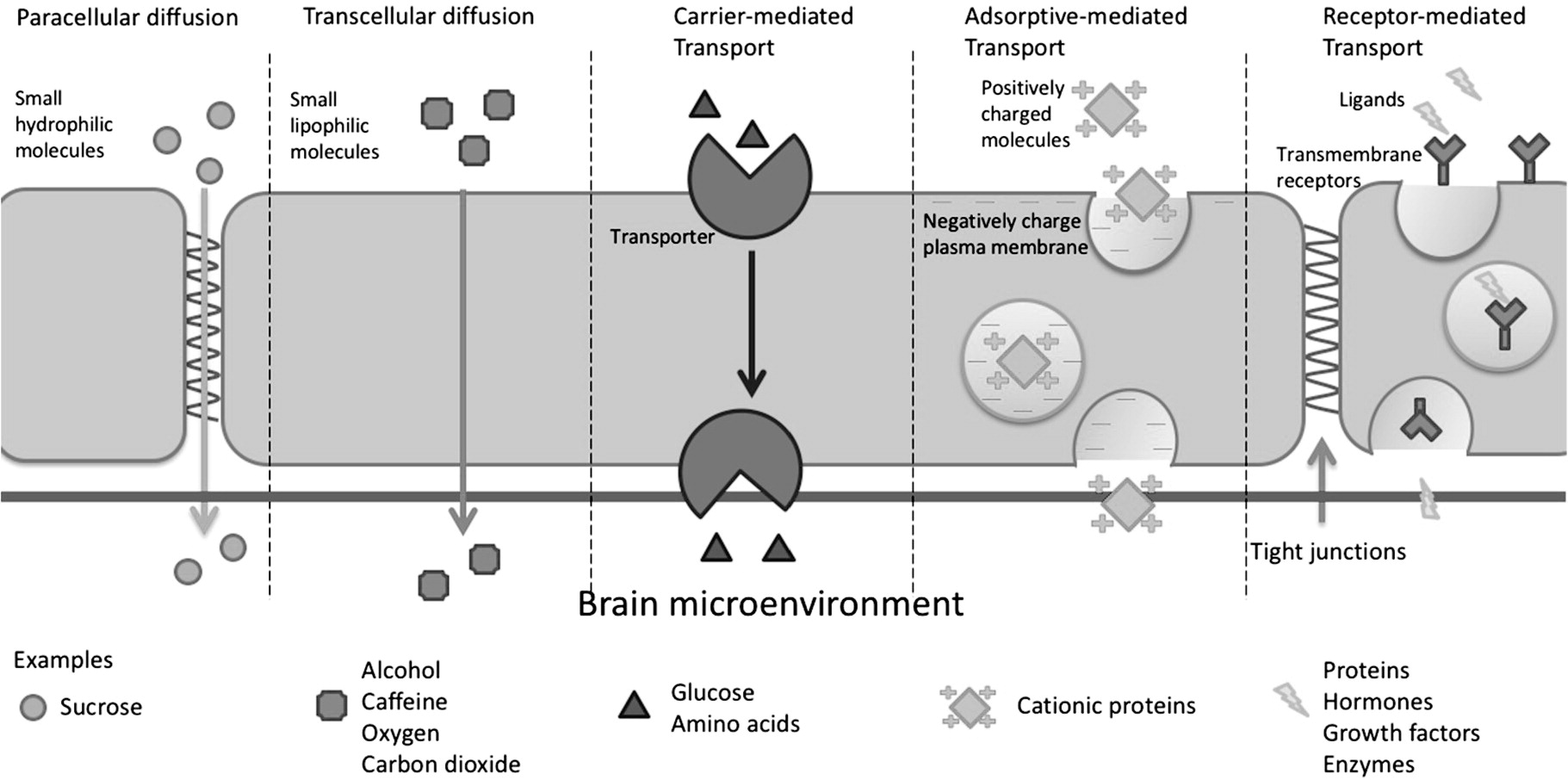
Paracellular and Transcellular Diffusion
Carrier-Mediated Transport
Adsorptive-Mediated Transcytosis
Syn-B Vectors
TAT-Derived Peptides
Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis
Transferrin Receptor
Insulin Receptor
Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor
Role of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Drug Delivery
| Component | Features in AD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Capillaries | Total length is shorter. | [36] |
| GLUT1 | Downregulate, result in reduction of Aβ clearance | [51] |
| Transferrin receptor | Number of receptors in hippocampus are less than normal. | [70] |
| Insulin receptor | Brain insulin receptor density decreases with aging. | [80] |
| Lactoferrin Melanotransferrin | Expression is upregulated. | [101] [102] |
| Targeting Vectors | Pathway | Features | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Syn-B vectors | Cross the BBB without compromising the BBB integrity | [55-57] | |
| TAT-derived peptides | Adsorptive-mediated transcytosis | Penetrating ability is related to the arginine residues in TAT. Non-specific transduction, induce Aβ deposition, tau phosphorylation and subsequent neuronal death in AD development | [60-65] |
| Polyarginines | Highly hydrophilic and cationic nature is responsible for charge repulsion which makes endocytosis possible. | [66] | |
| Transferrin | Receptor-mediated transcytosis (Transferrin receptor) | Compete with endogenous transferrin in the blood, affect cellular uptake of iron by the brain | [71,72] |
| OX 26 | Bind at extracellular domain without affecting transferrin binding, brain targeting effect is species-specific. | [73-76,78] | |
| MAb 8D3 | |||
| RI7217 | |||
| Insulin | Affect the clearance of Aβ and result in higher level of extracellular α short serum half-life, disturb insulin metabolism | [53,80-83] | |
| MAb83-14 | Receptor-mediated transcytosis (Insulin receptor) | Species-specific. Only transport across the BBB in Old-World primates | [84] |
| HIRMAb | Can be evaluated in animal model and humans | [85-87] | |
| IgG | Recognize both human transferrin and insulin receptors with ability to penetrate the BBB | [89] | |
| ApoE | APOE4 allele is a genetic risk factor for late-onset AD, ApoE can regulate the integrity of tight junctions | [31,32] | |
| Lactoferrin | Receptor-mediated trautcytosis (Low density lipoprotein receptor) | Expression is greatly upregulated in both neurons and glia in AD. | [98-101] |
| Melanotransferrin | Stronger BBB-penetrating ability than lactotransferrin in bovine, not change integrity of the brain capillary endothelial cell monolayer | [102,103] |
Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Penetrating the BBB to Treat AD
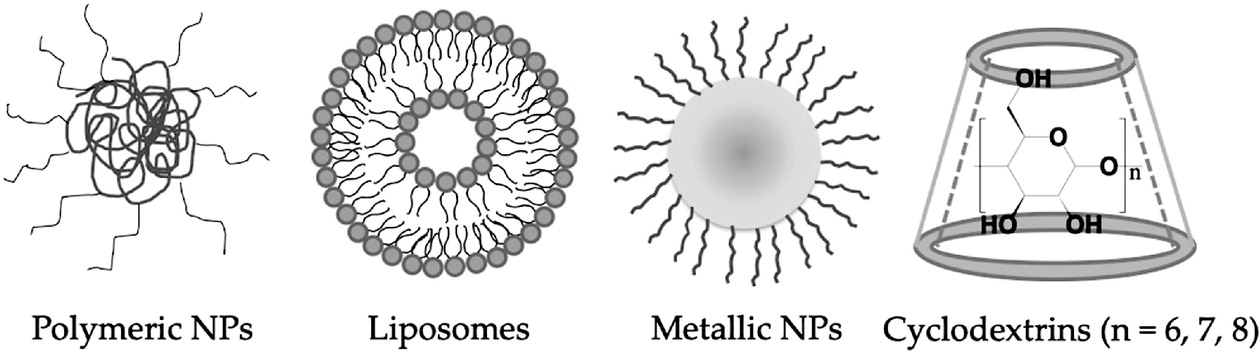
Polymeric Nanoparticles
| Encapsulated Agents | Carrier Composition | Targeting Vectors | Elevated Model | Therapeutic Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phytol | PLGA, PVA | - | Neuro2a cells, without in vivo data | Sustained Release, show anti-amyloid activity, show neuron protective effect | [115] |
| Galantamine | Polysorbate 80, PLGA | - | HeLa cells, SH-SY5Y cells, without in vivo data | Sustained release, show AchE inhibition ability | [116] |
| Curcumin | PLGA, PVA | Tet-1 peptide | GI-1 glioma cells | Show anti-amyloid activity, show neuronal targeting effect | [117] |
| Curcumin | PLGA-PEG-5000 | - | Mice | Increase drug serum level, longer half-life | [118] |
| Curcumin | PLGA, PVA | - | Neural stem cells, neurospheres, rats | Internalized by cells in vitro, cross the BBB in vivo, improve memory and cognitive ability, inhibit Aβ-induced neurodegeneration | [119] |
| Curcumin | PLGA-PEG-3400 | CRT peptide and S1 inhibitor | bEnd3 cells, SH-SY5Y cells, BV2 cells, mice | Nontoxic to neuron cells, decrease Aβ burden, gliosis and inflammation in vivo, improve spatial memory and recognition | [120] |
| Dexibuprofen | PLGA-PEG, PVA | - | PC12 cells, bEnd3 cells, glial cells, APPswe/PS1dE9 mice | Nontoxic to cells in vitro, increase the BBB permeation coefficient, reduce memory impairment | [121] |
| - | P(HDCA-co-RCA- co-MePEGCA), MePEGCA-co-Bio- PEGCA-co-HDCA | Anti-Aβ1-42 MAb | Tg2576 mice | Reduce triton-soluble Aβ peptides and oligomers levels in the brain | [122] |
Lipid-Based Nanocarriers—Liposome
| Encapsulated Agents | Carrier Composition | Targeting Vectors | Elevated Model | Therapeutic Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rivastigmine | Cholesterol, DPPC, Methyl cellulose, dimethyl-β-CD, sodium taurocholate | - | Balb-C type mice | Increase amount of drug delivered into the brain | [125] |
| H102 peptide | EPC, DSPE-PEG2000 and cholesterol | - | SD rat | Enhance peptide stability, increase amount of peptide delivered into the brain, improve spatial memory impairment, increase activities of ChAT and IDE | [126] |
| α-Mangostin | DSPC, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG2000, DSPE-PEG2000-COOH | Transferrin | bEnd3 cells, astrocytes, SD rat | Penetrate in vitro BBB model without destroying the structure of liposomes, improve bioavailability of drug and increase amount of drug in brain | [127] |
| - | CHETA, DDAB, DOPE, PC | Lactoferrin | BCE cells, astrocytes, Kunming Mice | Enhance the uptake of Lf-procationic liposomes | [99] |
| NGF | DPPC, DSPE-PEG2000, DSPE-PEG2000-CA | Lactoferrin | HBME cells, human astrocytes, SK-N-MC cells, without in vivo data | Accelerate drug delivery across the BBB model, prevent Aβ-induced neurotoxicity | [128] |
| Quercetin | DPPC, cardiolipin, DSPE-PEG2000-CA, SPC, stearylamine, cholesterol | Lactoferrin, RMP-7 | HBME cells, SK-N-MC cells, human astrocytes, without in vivo data | Slightly enhance paracellular drug delivery, protect neurodegeneration caused by Aβ-induced neurotoxicity | [129] |
| - | DSPC, DSPE-PEG2000, DSPE-PEG-Mal, DSPE-PEG2000-biotin | OX 26/RI7217/ApoE3/ OX26 + ApoE3/RI7217 + ApoE3 | hCMEC/D3 cells, FVB Mice | Cellular uptake of dual functionalized-liposomes was nearly twice as compared to mono-functionalized liposomes. In vivo results did not comply with in vitro results as ApoE peptide was inactivated by serum proteins. | [130] |
| - | Sphingomyelin and cholesterol | Phosphatidic acid, mApoE | APP/presenilin 1 mice | Decrease total Aβ fibrils and oligomers in brain, slow neurodegeneration | [131] |
| - | DSPC, DSPE-PEG2000 and cholesterol | Lipid-PEG-curcumin derivative, OX26, RI1227 | Brain from AD patient | Able to bind amyloid deposits | [132] |
Metal-Based Nanoparticles
| Encapsulated Agents | Carrier Composition | Targeting Vectors | Elevated Model | Therapeutic Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | AuNPs | - | - | Large AuNPs induce amorphous aggregates on the brain lipid bilayer. Smaller AuNPs induce protofibrillar Aβ structures. | [134] |
| - | Amine-modified AuNPs, Citrate-modified AuNPs | - | - | Positively charged AuNPs attached to Aβ more tightly. | [134] |
| - | AuNRs, AuNCs | - | - | Aβ was preferentially bound to the long axis of AuNRs and fewer fibrils were formed. All the facets of AuNCs interacted with Aβ to produce the fibril networks. | [134] |
| - | AuNPs, AuNRs | Transferrin | CD34+-derived ECs with bovine pericytes, C57BL/6 inbred strain mice | Cross the BBB both in vitro and vivo. With the use of NIR, irradiation, formulations could preferentially accumulate in the neurogenic niches. | [135] |
| - | AuNPs | POMD, LPFFD peptide | PC12 cells, S4880202 normal mice | Synergistic effects in inhibiting Aβ activity and Aβ-induced cytotoxicity in vitro, penetrate the BBB in vivo | [136] |
| HP-β-CD | HP-β-CD | - | SwN2a cells, Tg19959 mice | Reduce the levels of Aβ42 and membrane cholesterol in vitro, improve spatial learning and memory, reduce Aβ plaque deposition and tau immunoreactive dystrophic neurites in vivo | [139] |
| Doxorubicin | Rame-β-CD or crysme-β-CD | - | BCE cells | Increase the transport of doxorubicin, modulate P-gp activity | [141] |
| Doxorubicin | β-CD, poly(p-amino ester) | - | BME cells | High permeability across the in vitro BBB models | [142] |
Others—Cyclodextrins
Discussion and Future Perspective
Conclusions
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBGet Access
Login options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

