Cognitive Impairments and Dysexecutive Behavioral Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Methods
Design and Setting
Patients
Assessments at Baseline
Clinical variables.
Neuropsychological assessment.
MRI.
Laboratory tests.
Data Analyses
Results
| Characteristic | N | % | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and clinical data | ||||
| Age (years) | — | — | 62.58 | 11.01 |
| Male gender | 22 | 55.0 | — | — |
| Educational level (years) | — | — | 10.7 | 3.2 |
| Right-handedness | 39 | 97.5 | — | — |
| Chronic kidney disease stage: 2, 3, 4, 5a | 7, 19, 8, 6 | 17.5, 47.5, 20.0, 15.0 | — | — |
| Hypertension | 33 | 84.6 | — | — |
| Weight (kg) | — | — | 76.3 | 14.84 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | — | — | 27.5 | 5.92 |
| Diabetes | 16 | 41.0 | — | — |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 25 | 64.1 | — | — |
| Smoker | 14 | 43.8 | — | — |
| Pulse-wave velocity (m/s) | — | — | 9.9 | 3.37 |
| MRI features | ||||
| Normalized brain tissue volume (cm3) | — | — | 1,414.2 | 66.5 |
| Stroke volume (mm3) | — | — | 3,678.9 | 2,0265 |
| Total hippocampal atrophy | — | — | 2b | 1–4b |
| White matter hyperintensities burdenc | 12, 19, 4, 5 | 30, 47.5, 10, 12.5 | — | — |
| Presence of microbleeds | 6 | 15 | — | — |
| Infarct and hemorrhage | 9 | 22.5 | — | — |
| Metabolic data | ||||
Estimated glomerular filtration rate (mL/min/1.73 m2)d | — | — | 42.48 | 17.71 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | — | — | 219.29 | 168.01 |
| Anion gap (mmol/L) | — | — | 12.34 | 3.1 |
| Prothrombin time | — | — | 93.3 | 16.64 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | — | — | 4.22 | 2.96 |
| Albuminemia (g/L) | — | — | 42.4 | 3.88 |
| Leukocyte count (103/mm) | — | — | 7.13 | 1.9 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | — | — | 12.92 | 1.64 |
| Hematocrit (%) | — | — | 38.98 | 4.5 |
| Erythrocyte count (103/mm) | — | — | 4.28 | 0.61 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | — | — | 4.44 | 1.22 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | — | — | 2.31 | 0.93 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | — | — | 1.72 | 1.43 |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | — | — | 1.38 | 0.39 |
| Parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | — | — | 145.18 | 162.6 |
| Calcitriol 1.25(OH)vitamin D3 (pg/mL) | — | — | 36.70 | 21.14 |
| Calcidiol 25(OH)vitamin D3 (pg/mL) | — | — | 26.276 | 10.818 |
| Glycemia (mmol/L) | — | — | 6.065 | 2.306 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | — | — | 2.34 | 0.156 |
| Uric acid (µmol/L) | — | — | 475.33 | 131.395 |
| Indole–3-acetic acid (µmol/L) | — | — | 1.52 | 0.81 |
| P-cresyl sulfate (µmol/L) | — | — | 81.34 | 84.47 |
| Indoxyl sulfate (µmol/L) | — | — | 25.08 | 32.9 |
Cognitive Impairments and Behavioral Disorders
| Measure | Cohen’s d | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mini-Mental State examination | 0.792 | 0.468–1.116 | 0.0001 |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment | 0.597 | 0.279–0.915 | 0.0100 |
| Boston Naming Test | 0.729 | 0.359–1.099 | 0.0001 |
| Complex figure (copying) | 0.523 | 0.206–0.840 | 0.0012 |
| Free and Cued Selective Recall Test | |||
| Free recall sum | 0.446 | 0.123–0.770 | 0.0068 |
| Total recall sum | 0.188 | –0.139–0.516 | 0.2588 |
| Recognition | 0.033 | –0.287–0.353 | 0.8391 |
| Delayed free recall | 0.169 | –0.153–0.492 | 0.3022 |
| Delayed total recall | –0.098 | –0.420–0.224 | 0.5513 |
| Baddeley Doors test | 0.158 | –0.163–0.479 | 0.3339 |
| Complex figure (recall) | 0.136 | –0.186–0.459 | 0.4071 |
| Trail-Making Test | |||
| Part A completion time | 0.682 | 0.361–1.002 | 0.0001 |
| Part B completion time | 1.147 | 0.820–1.474 | 0.0001 |
| Test errors B–A | 0.786 | 0.453–1.118 | 0.0062 |
| Digit Symbol Substitution Test | 0.939 | 0.620–1.258 | 0.0001 |
| Letter fluency | 0.809 | 0.495–1.123 | 0.0001 |
| Category fluency | 0.631 | 0.320–0.942 | 0.0001 |
| Behavioral Dysexecutive Syndrome Inventory | 0.825 | 0.610–1.041 | 0.0002 |
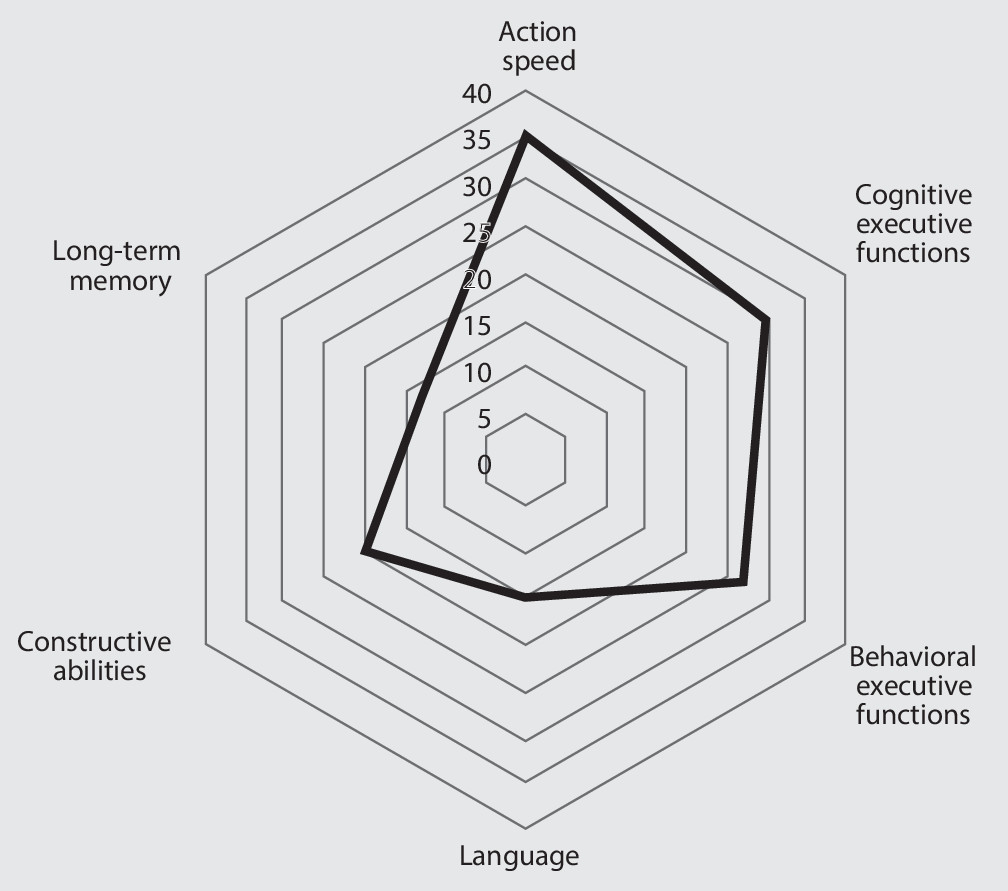
Risk Factors of Cognitive Impairment
| Features | Cognitive Impairment Present (N=13) | Cognitive Impairment Absent (N=27) | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | Mean | SD | N | % | Mean | SD | ||
| Demographic and clinical data | |||||||||
| Age (years) | — | — | 62.08 | 14.14 | — | — | 62.81 | 9.45 | 0.84 |
| Male gender | 7 | 53.9 | — | — | 15 | 55.6 | — | — | 1 |
| Education level (years) | — | — | 10.54 | 2.2 | — | — | 10.74 | 3.59 | 0.85 |
| Right handedness | 13 | 100 | — | — | 26 | 96.3 | — | — | 1 |
| Hypertension | 12 | 92 | — | — | 21 | 77.8 | — | — | 0.20 |
| Weight (kg) | — | — | 70.46 | 10.97 | — | — | 79.92 | 13.17 | 0.06 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | — | — | 25.39 | 3.41 | — | — | 28.46 | 6.61 | 0.16 |
| Diabetes | 4 | 33.3 | — | — | 12 | 44.4 | — | — | 0.77 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 8 | 66.7 | — | — | 17 | 63.0 | — | — | 1 |
| Smoker | 4 | 40.0 | — | — | 10 | 45.4 | — | — | 1 |
| Pulse wave velocity (m/s) | — | — | 9.23 | 1.31 | 10.24 | 4.01 | 0.42 | ||
| MRI features | |||||||||
| Normalized brain tissue volume (cm3) | — | — | 1,364.4 | 68.2 | — | — | 14,379.4 | 51.6 | 0.0005 |
| Stroke volume (mm3) | — | — | 11,302.7 | 35233.3 | — | — | 8.16 | 24.34 | 0.0048 |
| Total hippocampal atrophy | — | — | 2a | 0–5a | — | — | 2a | 1–3a | 0.83 |
| White matter hyperintensities burdenb | — | — | 1a | 1–1a | — | — | 1a | 0–1a | 0.93 |
| Presence of microbleeds | 2 | 15.4 | — | — | 4 | 14.8 | — | — | 1 |
| Metabolic data | |||||||||
| Estimated glomerular filtration ratec (mL/min/1.73cm2) | — | — | 41.3 | 21.71 | — | — | 43 | 16.21 | 0.81 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | — | — | 229.36 | 144.82 | — | — | 215.19 | 179 | 0.82 |
| Anion gap (mmol/L) | — | — | 12.36 | 2.34 | — | — | 12.33 | 3.43 | 0.97 |
| Albuminemia (g/L) | — | — | 44.18 | 3.58 | — | — | 41.64 | 3.79 | 0.07 |
| Prothrombin time | — | — | 88.92 | 22.92 | — | — | 95.4 | 12.66 | 0.27 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | — | — | 3.59 | 1.04 | — | — | 4.48 | 3.44 | 0.41 |
| Parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | — | — | 222.33 | 249.01 | — | — | 109.58 | 87.59 | 0.04 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | — | — | 2.25 | 0.22 | — | — | 2.38 | 0.1 | 0.015 |
| Calcitriol 1.25(OH)vitamin D3 (pg/mL) | — | — | 35.18 | 20.23 | — | — | 37.43 | 21.97 | 0.78 |
| Calcidiol 25(OH) vitamin D3 (pg/mL) | — | — | 23.63 | 9.5 | — | — | 27.45 | 11.33 | 0.32 |
| Leukocytes (103/mm) | — | — | 6.44 | 1.26 | — | — | 7.44 | 2.07 | 0.13 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | — | — | 12.64 | 1.73 | — | — | 13.26 | 1.69 | 0.07 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | — | — | 1.93 | 0.58 | — | — | 2.14 | 0.99 | 0.13 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | — | — | 2.0 | 2.3 | — | — | 1.58 | 0.77 | 0.42 |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | — | — | 1.34 | 0.38 | — | — | 1.4 | 0.4 | 0.68 |
| Glycemia (mmol/L) | — | — | 4.55 | 0.4 | — | — | 6.77 | 2.49 | 0.004 |
| Uric acid (µmol/L) | — | — | 521.36 | 126.83 | — | — | 439.48 | 98.88 | 0.03 |
| Indole–3-acetic acid (µmol/L) | — | — | 1.69 | 1.03 | — | — | 1.44 | 0.69 | 0.38 |
| P-cresyl sulfate (µmol/L) | — | — | 75.43 | 59.19 | — | — | 84.30 | 95.58 | 0.76 |
| Indoxyl sulfate (µmol/L) | — | — | 21.68 | 17.59 | — | — | 26.79 | 38.56 | 0.65 |
| Potential Predictor | Regression Coefficient (Estimated) | Standard Error of the Regression Coefficient | p | Bootstrap (%) (N=1,000 Permutations) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 7.251×10–3 | 7.514×10–3 | 0.34 | 45 |
| Stroke volume (mm3) | –7.221×10–2 | 3.074×10–2 | 0.026 | 87 |
| Brain tissue volume (mm3) | 1.485×10–6 | 1.619×10–6 | 0.367 | 41 |
| Parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | –1.655×10–3 | 5.673×10–4 | 0.007 | 86 |
| Glycaemia (mmol/L) | 1.059×10–1 | 4.780×10–2 | 0.035 | 90 |
| Uric acid (µmol/L) | –1.815×10–3 | 7.230×10–4 | 0.018 | 88 |
Discussion
Cognitive Impairments and Behavioral Disorders
Risk Factors of Cognitive Impairment
Vascular hypothesis of cognitive impairment.
Metabolic hypothesis of cognitive impairment: hyperparathyroidism, neuronal toxicity of the uremic state, and hypoglycemia.
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

