Measures
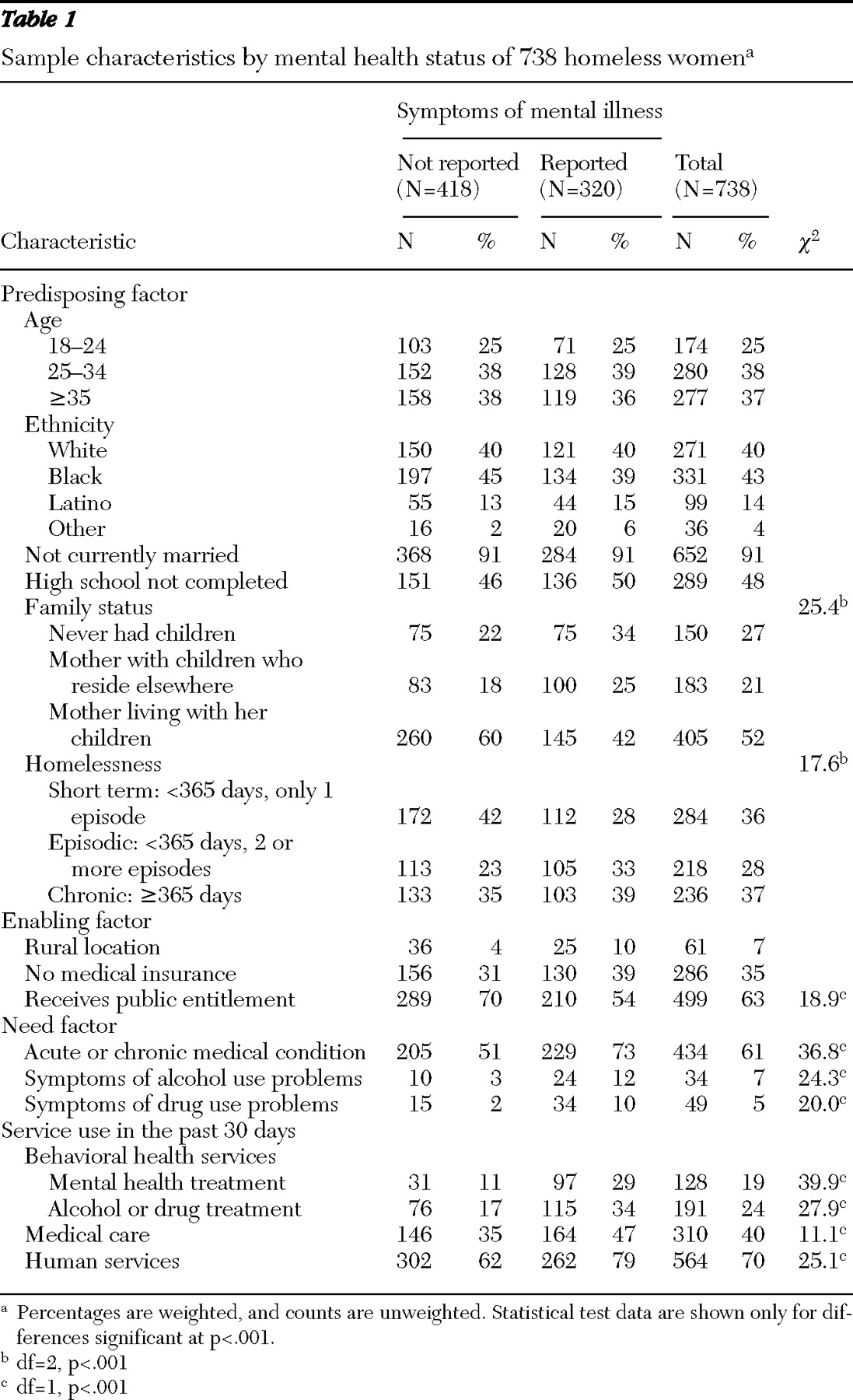
Symptoms of mental illness were measured by eight of the 11 items in the mental health component of the Addiction Severity Index (
17 ) regarding experiences of serious depression; serious anxiety or tension; hallucinations; trouble understanding, concentrating, or remembering; trouble controlling violent behavior; serious thoughts of suicide; attempted suicide; and having taken prescribed medications for any psychological or emotional problem. Respondents were classified as having symptoms of mental illness if they reported having any symptoms of mental illness in the past 30 days.
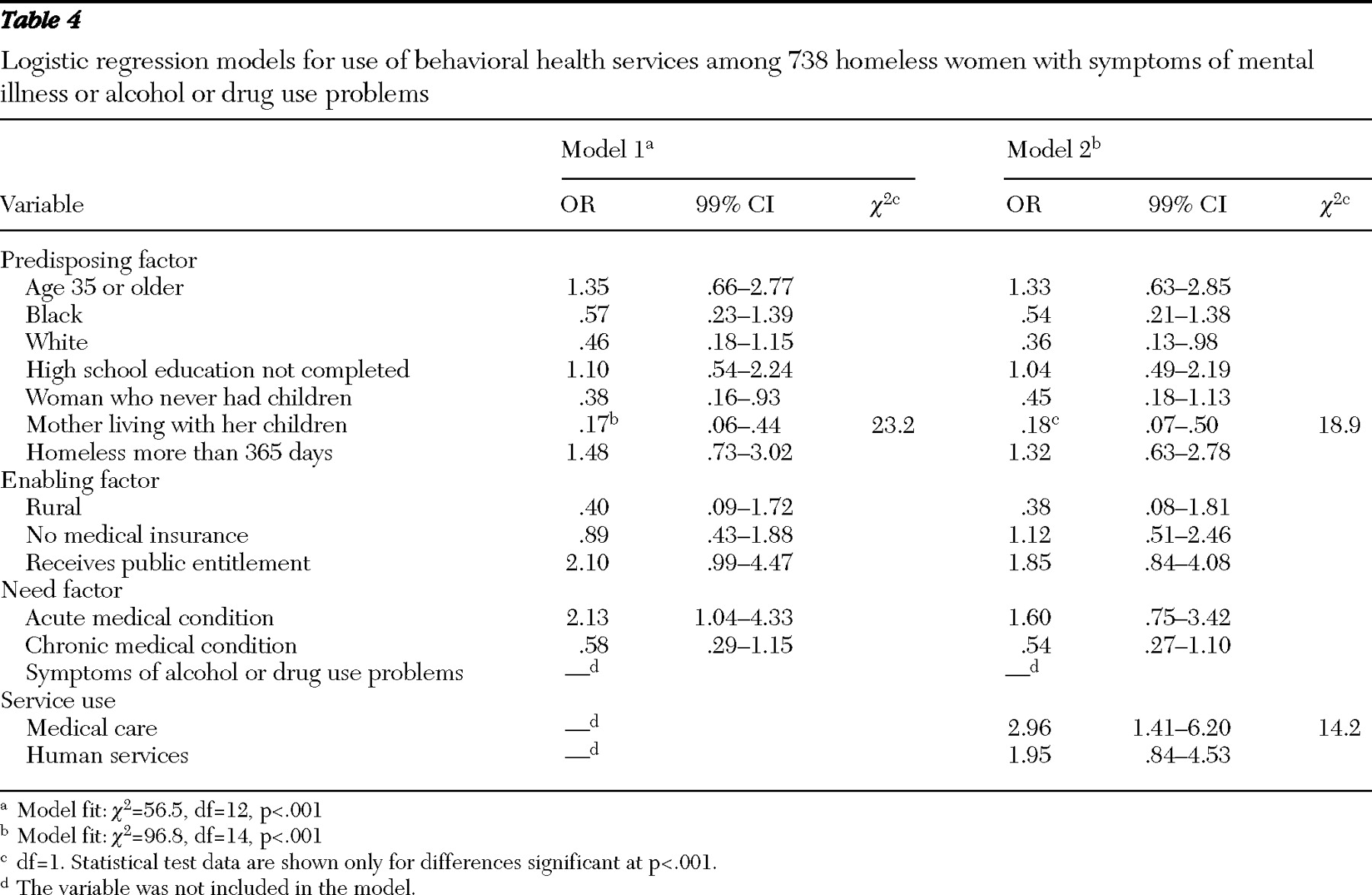
Service use within the past 30 days served as our outcome variable and was measured by three dichotomous variables. Human service use included getting any assistance with basic needs (clothing and transportation), finance (managing money and obtaining public benefits), housing (finding affordable housing or assistance with rent, mortgage, or utilities), job seeking or training, parenting, legal advice, or help with domestic violence problems. Health care service use included treatment or examination by a doctor or nurse. Behavioral health service use included inpatient or outpatient treatment or counseling for emotional or mental problems and alcohol or drug problems.
Guided by Aday-Andersen's health services utilization model, we considered independent variables from three domains (predisposing, enabling, and need). The predisposing factors included age, ethnicity (white, black, Latino, or others), marital status (married or single), education (high school education completed or not), family status (mothers with minor-age children living with them, mothers with minor-age children not living with them, and women who never had children), and homeless status (short term, homeless for less than 365 days and only one episode; episodic, homeless for less than 365 days and two or more episodes; and chronic, homeless for more than 365 days).
The enabling factors included current health insurance (insured or not), receipt of public entitlement (including Aid to Families With Dependent Children, general assistance, Supplemental Security Income, food stamps, or a housing subsidy or housing assistance) in the past 30 days and geographic locale (rural or urban).
Need factors were measured by four dichotomous variables indicating the presence of any acute or chronic medical conditions and alcohol or drug dependence symptoms in the past 30 days. Respondents were asked if they had any infectious acute conditions, including chest infection, cough, cold, bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, chlamydia, other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) but not AIDS (other types of STIs are not specified in survey), or any noninfectious acute conditions such as skin disease, skin infection, skin sores, skin ulcers, lice, scabies, or other similar infestations. Chronic medical conditions included reports of diabetes, anemia, high blood pressure, heart disease or stroke, problems with the liver, arthritis, rheumatism, joint problems, cancer, problems walking, lost limb, other handicap, HIV positive, or AIDS.
Symptoms of alcohol problems included craving alcohol; adverse effects from alcohol; withdrawal symptoms from alcohol, such as seizures, shaking, or hallucinations; and desire to stop drinking but inability to do so. The same set of items was asked in regard to symptoms of drug problems.