Investigation of childhood precursors of adult psychosis will clarify our understanding of etiology and may aid strategies for early detection and treatment. Earlier investigations have shown that approximately one-third of schizophrenic patients exhibited obvious premorbid behavioral abnormalities (
1–
4). The premorbid adjustment of patients who develop affective psychosis has been studied less frequently. Studies directly comparing the premorbid functioning of schizophrenic patients and patients with affective psychosis have shown greater impairment in the schizophrenic subjects (
5–
8). Unfortunately, most studies of premorbid functioning in psychosis have lacked a healthy comparison group and have not been able to examine the distribution of childhood and adolescent social impairment among groups of patients compared with the normal population. In addition, few studies have controlled for possible confounding factors, such as sex, social class, ethnicity, and IQ, in the relation between premorbid social difficulties and schizophrenia. Prospective and retrospective cohort studies have found differences in childhood social and intellectual functioning between preschizophrenic children and the general population (
9–
12) but have not (with one exception [13]) found similar significant effects for children destined to develop affective psychosis. However, it has been suggested that poor premorbid functioning is a predictor of vulnerability to psychosis among patients with major depressive disorder (
14,
15).
We used data from a large treatment group of psychotic patients to answer the following questions. 1) Do patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder show poor social adjustment in childhood and adolescence, compared with healthy subjects, after control for confounding factors? 2) How large are these effects, and which domains of functioning are impaired? 3) Are there temporal changes? 4) Are risk factors for psychosis related to premorbid functioning?
METHOD
One hundred patients with schizophrenia and 49 patients with bipolar disorder were recruited during a survey of all admissions for functional psychotic illness to three psychiatric hospitals in South London between March 1987 and October 1989. That survey, the Camberwell Collaborative Psychosis Study, has been described in detail previously (
16). Inclusion criteria were age between 16 and 50 years and presence of psychotic symptoms in clear consciousness (
17). Subjects were interviewed within 3 days of admission and diagnosed according to DSM-III criteria. Severity of illness was not significantly different in the two diagnostic groups. The mean age at first admission was 23.4 years (SD=5.4) for the patients with schizophrenia and 23.3 years (SD=5.7) for those with bipolar disorder; the mean number of hospital admissions was 3.5 (SD=3.5) and 3.8 (SD=2.9), respectively.
The comparison subjects were chosen to represent the population aged 16–50 years who would be admitted to any of the three index psychiatric hospitals if they became psychotic. Persons with minor injuries who came to the casualty department of Kings College Hospital, a large general hospital in the same catchment area, were identified as a suitable population from which to draw our comparison group. Potential subjects were approached in the waiting area, the purpose of the study was explained, and they were asked whether they wished to participate. Of 330 persons approached during the study period, 202 individuals (104 male and 98 female) were not willing or eligible to participate: 74 were “just not interested,” 32 were called away by the doctor or were too ill to talk, 31 did not want to involve their mothers, 63 were ineligible because their mothers were dead, non-English-speaking, or living abroad, and two were excluded because they suffered from schizophrenia and had previously been interviewed as possible case subjects. Written informed consent, including permission to contact their mothers, was obtained from the remaining 128 persons after a complete description of the study had been given. A brief interview to obtain basic demographic details was carried out in an adjoining room, and subjects were asked to complete the New Adult Reading Test (
18) as an estimate of premorbid IQ. Social class was defined by parental occupation at the time of the subject's birth (
19). Of the 128 individuals who completed the proband interview, 28 could not be included in the study because their mothers subsequently refused to participate. The final comparison group thus comprised 100 individuals for whom complete maternal interviews were available.
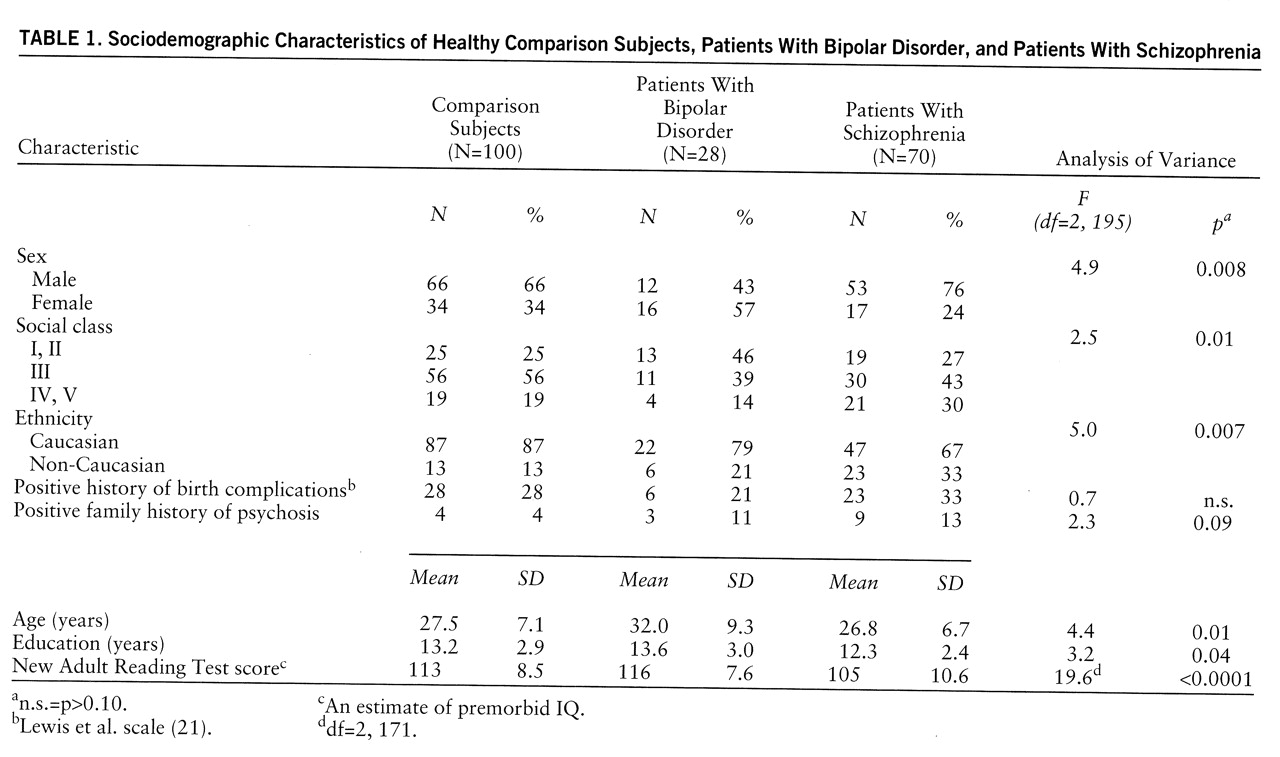
There were significant differences between the three subject groups in sex, social class, ethnicity, age, years of education, and premorbid IQ (
table 1). The patients with bipolar disorder were more likely to be female and from social classes I and II than the schizophrenic patients or the comparison subjects and were older at the time of recruitment. The patients with bipolar disorder also had a significantly higher premorbid IQ than the schizophrenic patients but not the comparison subjects. The patients with schizophrenia had a lower premorbid IQ and fewer years of education than the patients with bipolar disorder or the comparison subjects and were less likely to be of Caucasian origin. These group differences were taken into account in the statistical analysis.
The mothers of all subjects who had completed the proband interview were asked to take part in the study. One hundred mothers of healthy comparison subjects, 70 mothers of schizophrenic patients, and 28 mothers of patients with bipolar disorder gave their consent to be interviewed. Interviews took place over the telephone or in the mother's home and were carried out by one of two interviewers (M.C. and A.F) who were blind to case diagnosis and to the results of the proband interview. Interrater reliability was assessed by means of a set of 10 audiotaped interviews; an interrater correlation coefficient of 0.71 was obtained.
The semistructured maternal interview consisted of three parts.
1. The Premorbid Social Adjustment scale (
5), an adapted version of the Cannon-Spoor scale (
20), was used to assess five areas of adjustment (referred to as items): sociability, peer relations, scholastic performance, adaptation to school, and interests. Each subject received a score for each item, rated on a 7-point Likert scale that ranged from 1 (excellent adaptation) to 7 (extremely poor adaptation) (appendix 1). Each item was rated separately for childhood (5–11 years) and adolescence (12–16 years).
2. The obstetric complications scale of Lewis et al. (
21) was used to collect information on pregnancy and birth history. This scale was constructed for scoring a limited range of birth complications uncovered through retrospective parental reporting.
3. Information on family history of psychiatric illness in first-degree relatives was obtained with the Family History Research Diagnostic Criteria (FH-RDC) schedule (
22), which involves obtaining information from one relative about all other family members.
In the statistical analysis, between-group differences in childhood, adolescent, and total Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores were examined by one-way analysis of variance followed by post hoc t tests with Bonferroni corrections for multiple tests. Log transformations of Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores were used to fulfill the assumption of equal variances. Change scores were computed by subtracting the childhood score from the adolescent score to examine premorbid deterioration with age (
23). A principal-components analysis, with varimax rotation, was performed on the Premorbid Social Adjustment item scores from both age periods and for all three groups of subjects and revealed two factors with eigenvalues greater than 1, which explained 67.8% of the variance. Items relating to socialization, peer relations, and interests loaded onto one factor, sociability (eigenvalue=4.8). Items relating to school performance and school adjustment loaded onto a second factor, schooling (eigenvalue=1.9). Items from both periods that related to social adjustment (items 1, 2, and 5) (appendix 1) and to school adjustment (items 3 and 4) were then summed and examined as separate subscores, as they appeared to represent distinct domains of adjustment.
Since there were differences between groups in sex, social class, ethnicity, and premorbid IQ (
table 1) and since these factors can influence social and school adjustment, these variables were treated as confounders. Logistic regression techniques were used to examine the association between Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores and adult psychiatric outcome adjusted for confounding factors. Using the epidemiological methods of Jones et al. (
24), we found that the distribution of Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores in the comparison group was divided into four equal categories, and the scores of the patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder were examined in terms of where they lay within this distribution, with use of the lowest scores (i.e., best adjustment) as baseline. Results were expressed as adjusted odds ratios, tested with –2 log likelihood chi-square tests. Dummy variables were used to obtain odds ratios for each quartile, and a linear trend was tested by entering the quartile term into the model as a continuous variable. Analyses were performed with the statistical package Stata (
25). Genetic and obstetric risk factors for schizophrenia were categorized as dichotomous variables, present or absent, and mean Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores were compared between categories by means of t tests. Birth weight was divided into quartiles based on the distribution in the comparison group, and mean Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores were calculated for each quartile. Standard linear regression techniques were used to examine linear trends of mean Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores across quartiles of birth weight.
RESULTS
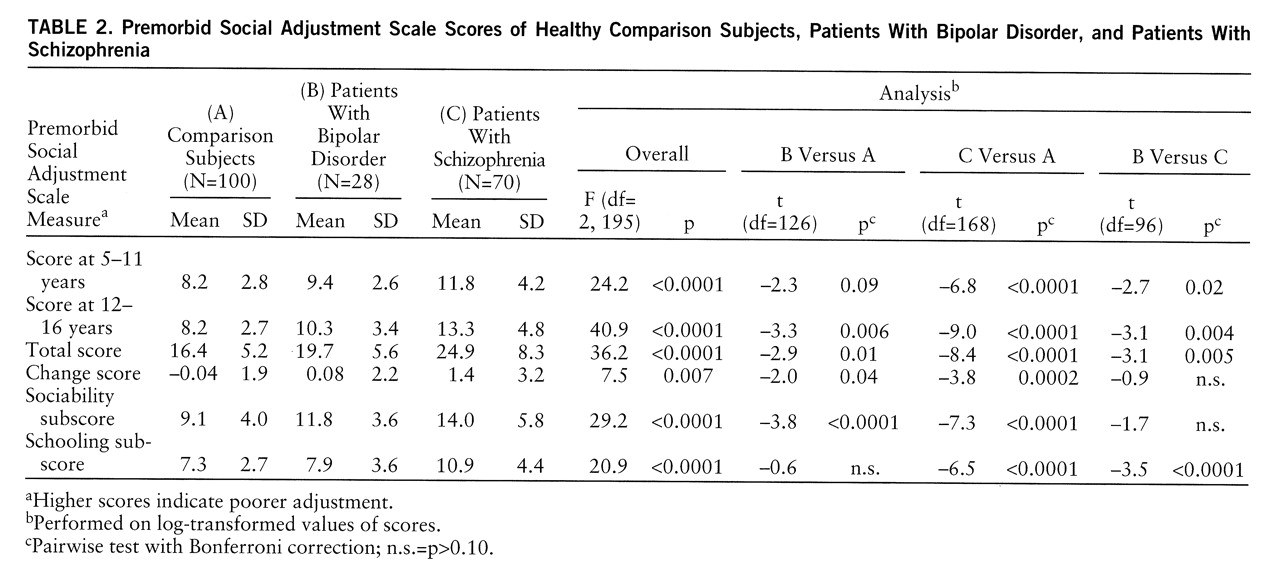
The schizophrenic patients scored significantly worse than both the comparison subjects and the patients with bipolar disorder on childhood, adolescent, and overall adjustment (
table 2). The patients with bipolar disorder scored significantly worse than the comparison group only on adolescent and overall adjustment (
table 2). The comparison subjects showed a negative mean change score, indicating that social adjustment improved in adolescence. In contrast, both patient groups exhibited positive mean change scores, indicating functional deterioration in adolescence. The schizophrenic subjects exhibited a greater deterioration in functioning than the bipolar subjects. There was no significant relation between Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores and number of hospital admissions.
The schizophrenic patients scored significantly worse than the comparison subjects on both sociability and schooling (
table 2). When the results were adjusted for the confounding factors by means of linear regression, the differences remained significant for both sociability (t=7.2, df=139, p<0.0001) and schooling (t=6.5, df=139, p<0.0001). The bipolar patients differed significantly from the comparison group only on the sociability subscore, not schooling (
table 2). After adjustment for the confounding factors, the difference between the bipolar patients and the comparison group remained significant for sociability (t=3.8, df=105, p<0.0001) and just achieved significance for schooling (t=2, df=105, p<0.04). The bipolar patients did not differ from the schizophrenic patients on the sociability subscore, but their performance in school was significantly better.
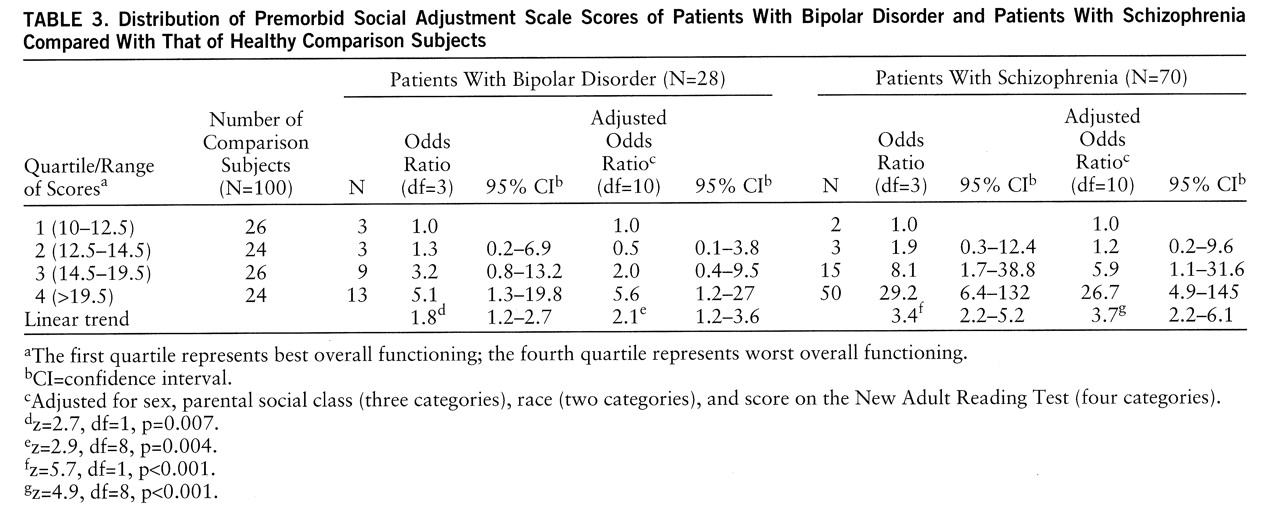
There were significant linear trends for the schizophrenic patients and, to a lesser extent, for the patients with bipolar disorder to have scores that fell into the quartile indicating the most impaired social adjustment, and these linear trends persisted after adjustment for the confounding factors (
table 3). The schizophrenic patients were almost 27 times more likely than the comparison subjects to have scores in the quartile for the worst social adjustment, and the patients with bipolar disorder were 5.6 times more likely than the comparison subjects to have scores in that quartile. The strong evidence for a linear trend in both groups means that this effect operates throughout the entire range of Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores. There was no evidence of a bimodal distribution of these scores in any of the groups, and including a quadratic term did not improve the fit of the model.
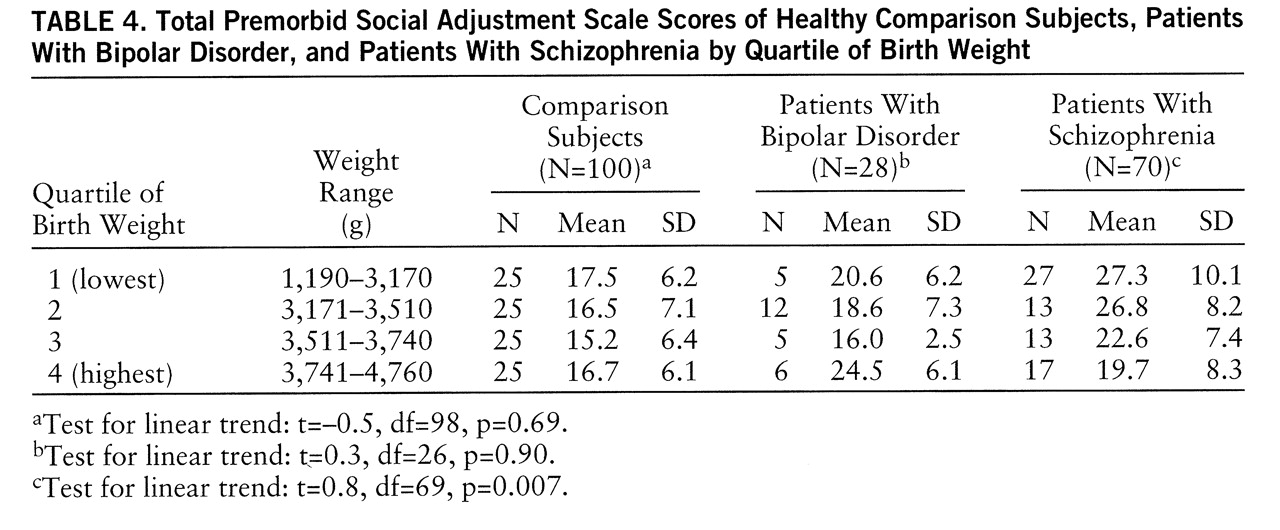
Mean Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores did not differ significantly between the subjects with a positive family history of psychosis and those with no family history of psychosis in any of the three groups separately or overall. Mean total Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores did not differ between those with a history of one or more obstetric complications, as measured by the Lewis et al. scale, and those with no history of obstetric complications in any of the three groups separately or overall. However, a post hoc analysis, based on previous work (
26,
27), found a significant linear relation between Premorbid Social Adjustment scale score and birth weight among the schizophrenic patients. Patients with schizophrenia in the lowest quartile of birth weight had the highest mean Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores, and these scores decreased linearly over each quartile, indicating better premorbid adjustment with increasing birth weight (
table 4). This linear relationship held for both the sociability and schooling domains of functioning. No such relationship was observed among the patients with bipolar disorder or the healthy comparison subjects (
table 4).
DISCUSSION
The results of this study confirm a clear association between poor social functioning in childhood and adult psychosis. Significant differences in premorbid social ability and school functioning between the schizophrenic patients and the normal comparison subjects were demonstrated. A lesser, but still significant, difference was observed between the patients with bipolar disorder and the normal subjects in childhood social ability but not in school functioning. The risk of psychosis was spread throughout the study group such that the poorer one's social adjustment, the greater the risk of developing schizophrenia or, to a lesser extent, bipolar disorder.
The main strengths of our study design were the inclusion of a large group of normal comparison subjects assessed with the same instruments used for the patients and the use of mothers as the source of information on premorbid adjustment. Other studies have used chart reviews (
28–
30) or interviews with patients (
3,
31,
32), but we considered that mothers are best placed to give accurate retrospective information about a child's early development. However, there may be a problem of recall bias when such a source of retrospective data is used, namely, that the mother's knowledge of her child's adult outcome may influence her memory of childhood behavior.
We have considered this methodological problem from several viewpoints. 1) The patients with bipolar disorder and those with schizophrenia did not differ from each other in severity of adult illness, as measured by mean age at onset and mean number of hospital admissions. If mothers' replies were influenced by the current adult status of the offspring or the current perceived burden of care, then both groups of patients should have been rated more or less the same on childhood adjustment. In fact, the bipolar patients were consistently rated by their mothers as
less severely impaired in childhood. 2) The public perception of schizophrenia as a more long-term and chronic illness than bipolar disorder may have influenced the mothers' expectations of a poorer prognosis in schizophrenia. If so, this factor is likely to be most important for a mother whose child has been admitted to the hospital for the first time and should become progressively less important with subsequent admissions. In our study, however, the mean Premorbid Social Adjustment scale scores of the first-admission patients did not differ significantly from the scores of the patients who had had more than one admission, indicating that maternal ratings of childhood adjustment are independent of length of time since diagnosis. 3) There is also the contrasting possibility of “idealization” of the childhood behavior of ill offspring among some mothers, which would tend to underestimate the differences found between subject groups and which may “neutralize” the possible sources of bias we have mentioned. 4) Finally, studies of premorbid functioning in schizophrenia that are free from recall bias, such as school record studies (
3,
11) and studies of national birth cohorts (
10,
12), show results similar to ours and support the validity of our findings.
Known risk factors for psychosis did not appear to influence premorbid social functioning in the patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. We found no relation between premorbid social adjustment and genetic risk of psychosis in this study, thus replicating previous work (33 and manuscript by M. Taylor et al. submitted for publication). However, it is possible that use of the FH-RDC method to assess genetic risk may have led to underdetection of illness among relatives and reduced power to find an effect. Previous studies comparing the family history method with the family study method—a method that involves direct interview of all available relatives—have shown that up to 60% of relatives with major affective illness and 40% of cases of psychosis may be missed by using the FH-RDC (
34–
36). We also did not find a relation between overall number of birth complications and premorbid adjustment, which again agrees with previous work (
33). However, we did find a linear relation between low birth weight and poor premorbid functioning that was specific to schizophrenia. This finding adds to the evidence suggesting a continuum of abnormality extending from prenatal development through childhood social difficulties to adult schizophrenia (
12,
26,
27,
37–
40).
In conclusion, our study shows that both schizophrenic patients and patients with bipolar disorder exhibit premorbid social maladjustment in comparison with a group of normal subjects, but there are some differences between the groups. The degree of functional deterioration among patients with bipolar disorder is not as severe as that seen in schizophrenic patients. In addition, bipolar patients show relative preservation of school functioning despite deterioration of social functioning in adolescence. Patients with schizophrenia, on the other hand, are impaired socially from a young age, with a marked deterioration during adolescence, and they show poor school adjustment, even when differences between groups in premorbid IQ are taken into account. We propose that poor social adjustment in adolescence is an early manifestation of vulnerability to adult psychotic illness. One possible explanation is that pathogenic processes, possibly of neurodevelopmental origin (
41), leading to psychosis in adulthood, can also predispose a person to attentional difficulties, distorted perceptions, unusual thought processes, and decreased empathic ability, thus compromising social functioning. The reasons for the earlier onset and more global nature of the premorbid impairment in schizophrenia compared with bipolar disorder are not yet understood and would repay further study.
APPENDIX 1. Premorbid Social Adjustment Scale (Foerster et al. [5], adapted from Cannon-Spoor et al. [20])
Standardized entry questions are used for each item. Scoring is on a scale from 1 to 7 for each of the five items. Examples of the descriptive anchor points to aid scoring are shown, with corresponding scores given in parentheses. Each item is scored separately for childhood (5–11 years) and adolescence (12–16 years).
1. Sociability and isolation
Would you describe X between ages 5 and 11 as outgoing and liking the company of others or as shy and withdrawn?(1) Not withdrawn, active social interaction(3) Mild withdrawal, enjoyed socialization when involved—occasionally sought opportunities to socialize(5) Moderately withdrawn, given to daydreaming and excessive fantasy, did not seek contact(7) Unrelated to others, isolated, avoided contacts
2. Peer relations
Did X make friends easily during childhood? How many friends did X have? Were there any really close friends?(1) Many friends, close relationships(3) Casual friends only(5) Deviant friendship patterns: only friendly with children older or younger(7) Socially isolated, not even superficial relationships
3. Scholastic performance
What sort of student was X between ages 5 and 11? Did X come at the top or bottom of his/her class?(1) Excellent student, top of class(3) Average student(5) Failing all classes(7) Required special education
4. Adaptation to school
Did X get into trouble at school during childhood? How much and what kind of trouble?(1) Good adaptation, enjoyed school, no discipline problems(3) Fair adaptation, occasional discipline problems, not very interested in school(5) Poor adaptation, disliked school, frequent truancy and discipline problems(7) Refused to have anything to do with school—delinquency or vandalism directed against school
5. Interests
During childhood did X have many interests and hobbies? Did his/her interests involve others?(1) Active, involved in a range of school, sporting, and social activities and hobbies(3) Involved in one school, sporting, or social activity with other young people(5) Introverted interests—one or a few hobbies which required no contacts with others(7) No interests—withdrawn and indifferent toward interests of the average youngster