Although the ability of cocaine to increase dopamine in nucleus accumbens has been shown to be crucial for cocaine reinforcement (
1,
2), the role of dopamine in the loss of control and the compulsive self-administration of cocaine in the cocaine addict is much less clear. It has been postulated that the dopamine system's involvement in addiction is by means of its disruption of the brain regions that it modulates (
3). The expression of dopamine-mediated behaviors requires the activation of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) pathways (
4), which are therefore a particularly susceptible target for cocaine's effects. In fact, using positron emission tomography (PET), we have documented significant reductions in striatal dopamine D
2 receptors in cocaine abusers that persist after detoxification (
5,
6). Because dopamine D
2 receptors predominantly reflect postsynaptic elements on GABA cells (
7), these findings suggest an involvement of GABA in the dopamine abnormalities in cocaine abusers. In the present study we evaluated the GABA system indirectly by assessing the brain regional responsivity to GABA stimulation and compared the responses in cocaine-abusing subjects to those in comparison subjects.
Responsivity to GABA stimulation was quantified by measuring the regional brain metabolic response to lorazepam by using [
18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) and PET (
8). Benzodiazepines have been used to assess the response of the brain to GABA stimulation since they facilitate GABA neurotransmission (
9,
10). Benzodiazepines produce a pattern of changes in regional brain metabolism that parallels the regional concentration of benzodiazepine receptors in brain (
11) and that is reversed by the benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil (
12). Metabolic responses to benzodiazepines are highly reproducible in a given subject and are consistent across normal individuals (
13).
RESULTS
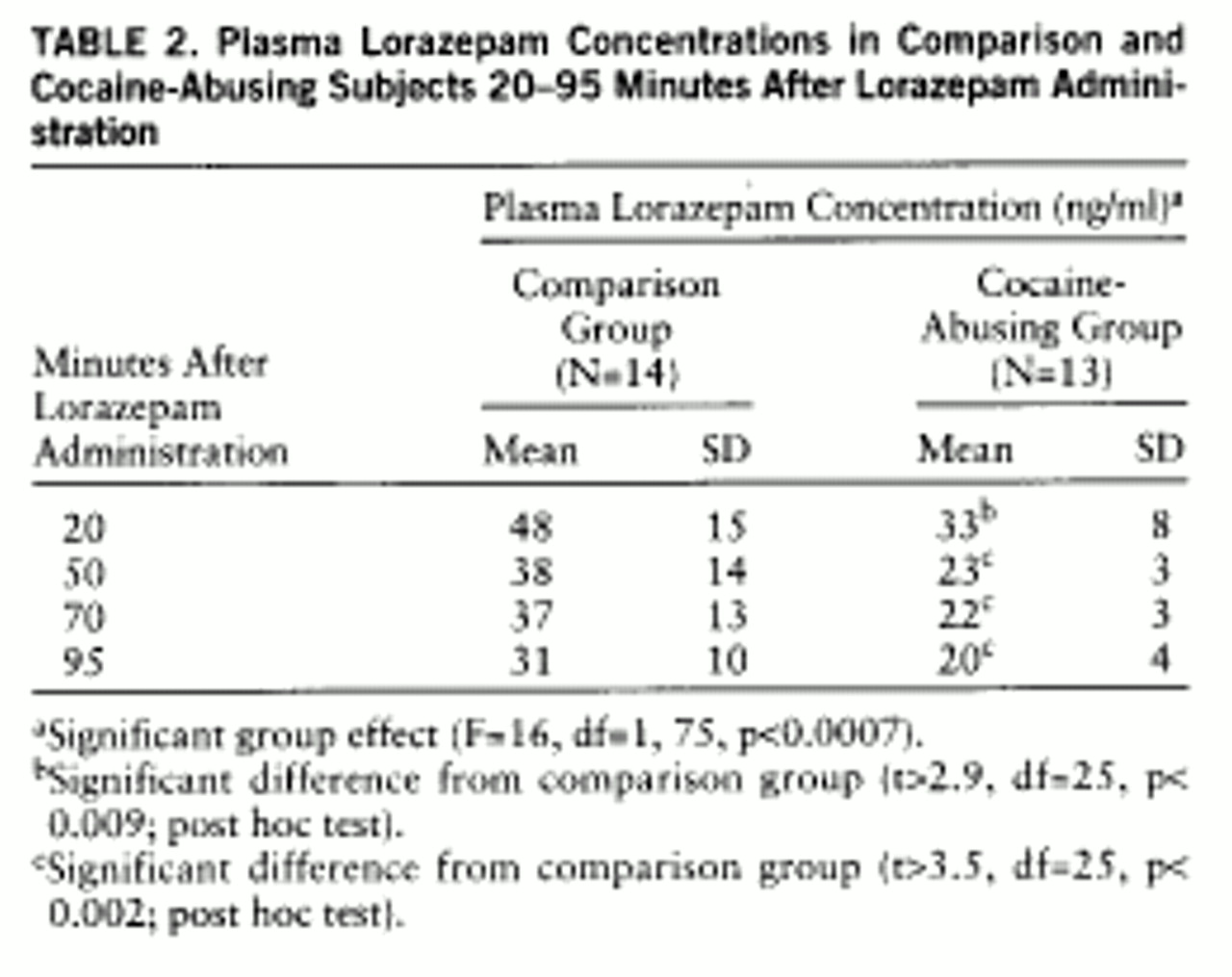
Plasma lorazepam concentrations were significantly higher in the comparison than in the cocaine-abusing group (group effect: F=16, df=1,75, p<0.0007) (
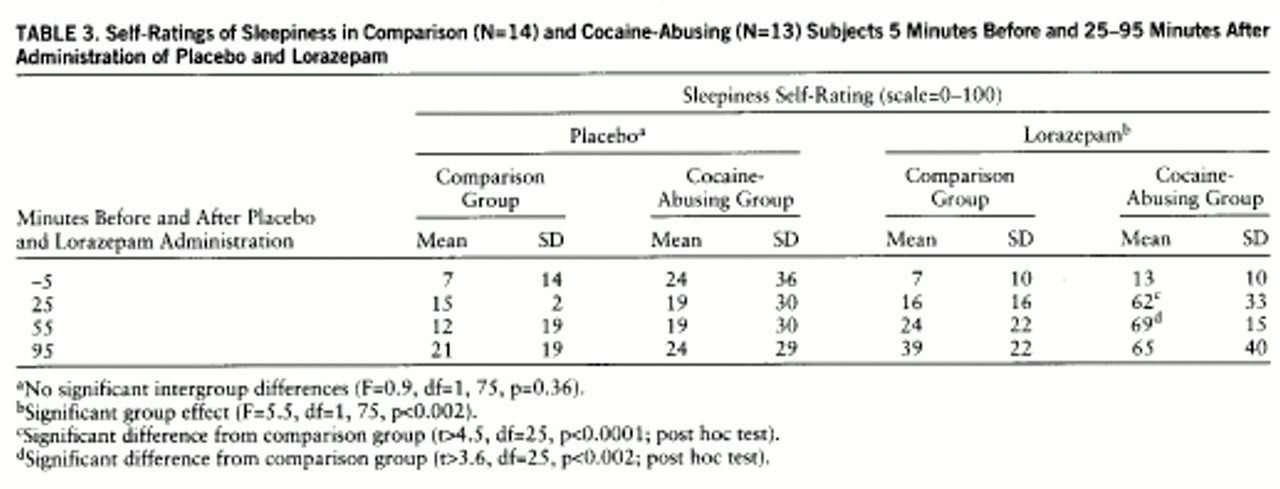
table 2). Despite higher plasma levels of lorazepam in the comparison group, reports of lorazepam-induced sleepiness were significantly higher in the cocaine-abusing group (interaction effect: F=5.5, df=1,75, p≤0.002) (
table 3). We do not report cognitive effects of lorazepam, since we were unable to assess them properly in the cocaine-abusing group because of the extreme and prolonged levels of sleepiness induced by lorazepam in some of these subjects. The ANOVA for the placebo condition showed no differences in self-reports of sleepiness between groups (F=0.9, df=1,25, p=0.36) (
table 3).
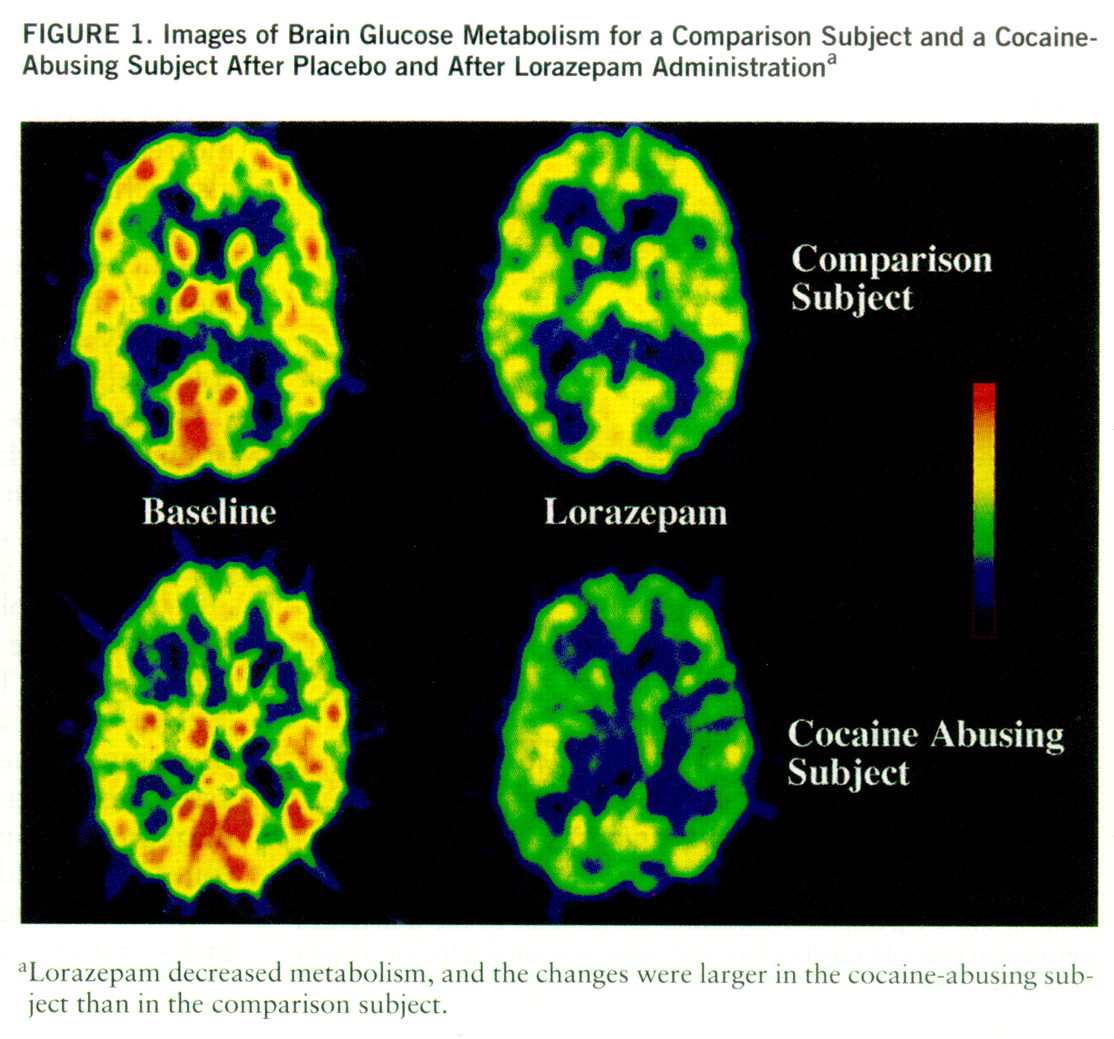
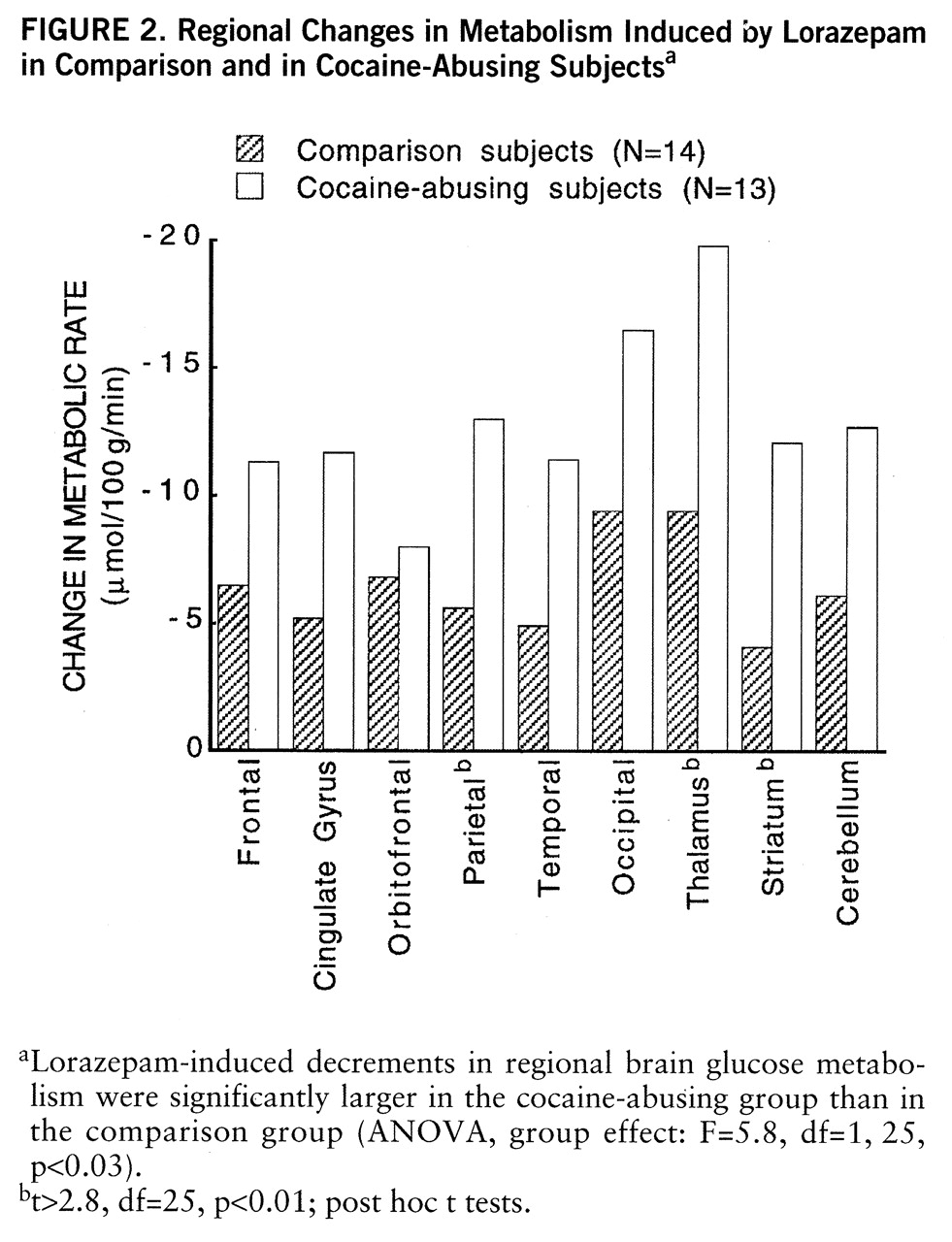
Lorazepam decreased global and regional brain glucose metabolism, and these decrements were significantly larger in the cocaine abuser than in the comparison group (
figure 1). Whereas in the comparison group whole brain metabolism decreased 13% (SD=7%), in the cocaine-abusing group it decreased 21% (SD=3%) (F=6.2, df=1,25, p<0.02). The results from the ANOVA obtained on the difference scores for the regional metabolic measures showed a significant overall difference between the abuser and the comparison groups (F=5.8, df=1,25, p<0.03), as well as a significant group-by-region interaction effect (F=2.8, df=1,200, p<0.006). The presence of a significant group-by-region interaction effect indicates that the lorazepam-induced differences in metabolic activity between the comparison and the abuser groups differed across brain regions. Post hoc t tests showed that these differences were significant in striatum (t=2.7, df=25, p<0.01), thalamus (t=2.8, df=25, p<0.01), and parietal cortex (t=2.8, df=25, p<0.01) (
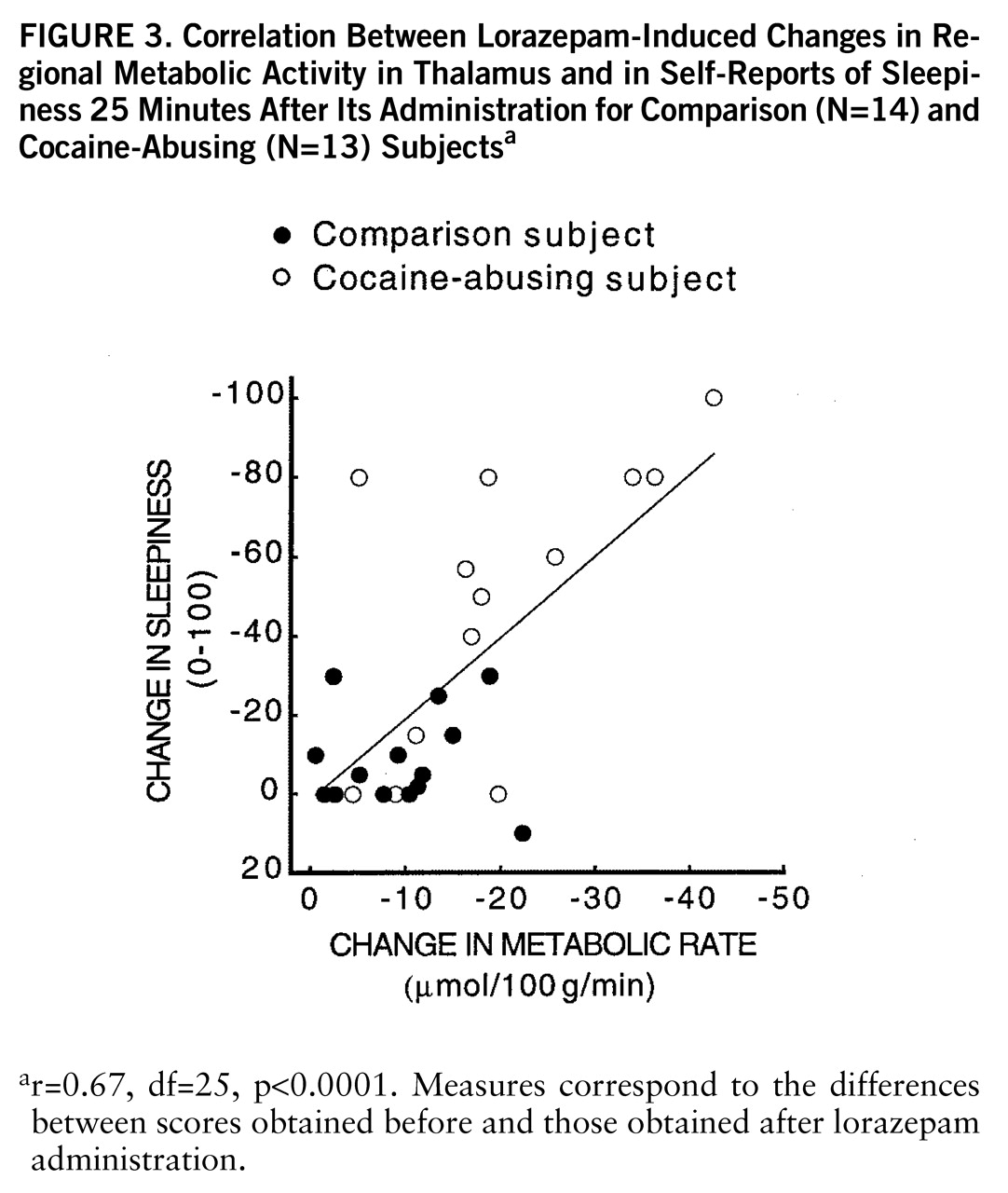
figure 2). Lorazepam-induced increases in self-ratings of sleepiness obtained 25 and 55 minutes after lorazepam administration were significantly correlated with the decreases in thalamic metabolism (r=0.67, df=25, p<0.0001, and r=0.65, df=25, p<0.0002) (
figure 3). There were no significant correlations between plasma lorazepam concentration and lorazepam-induced metabolic changes.
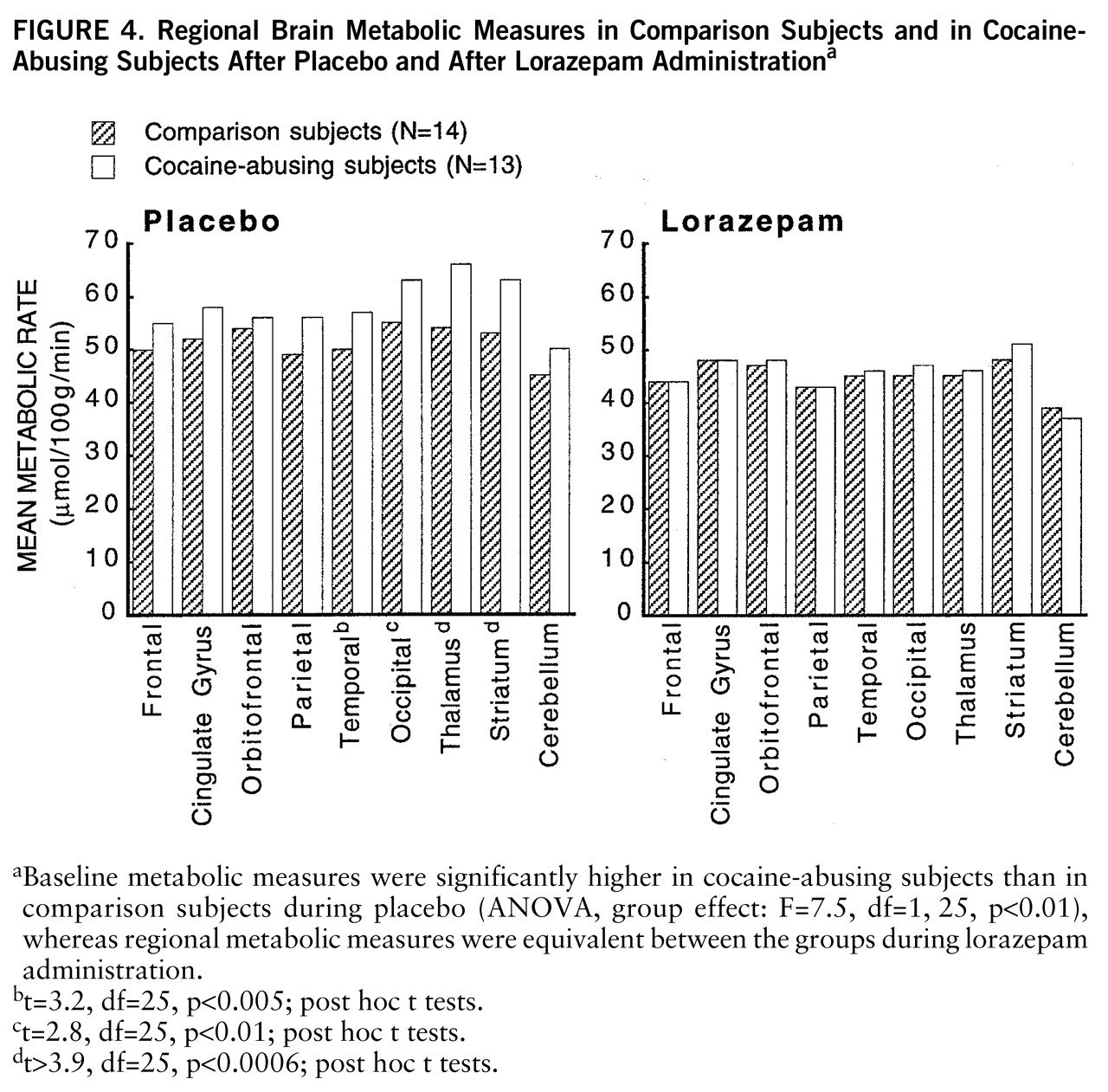
At baseline, whole brain metabolism was significantly higher in the cocaine-abusing group than in the comparison group (ANOVA, group effect: F=7.5, df=1,25, p<0.01), whereas after lorazepam administration, regional metabolic measures were equivalent for the abuser and the comparison groups (
figure 4). Post hoc t tests showed that differences in baseline metabolic measures were significantly higher in cocaine-abusing subjects in the occipital cortex (t=2.8, df=25, p<0.01), temporal cortex (t=3.2, df=25, p<0.005), thalamus (t=3.9, df=25, p<0.0006), and striatum (t=4, df=25, p<0.0004).
DISCUSSION
This study documents an increased sensitivity to lorazepam in active cocaine-abusing subjects as assessed by the enhanced responses to its sedative effects and to its reduction of brain glucose metabolism. Although the accentuated brain metabolic responses were global, there were some brain regions where these effects were more pronounced than others, as shown by the significant group-by-region interaction effect. More specifically, the differences in responses between the abuser and the comparison groups were largest in thalamus, striatum, occipital cortex, and parietal cortex. Because metabolism reflects activity in terminal regions (
18), the metabolic changes induced by lorazepam in a given area predominantly reflect the responses in the projecting GABA cells. Thus, one could speculate that the increased metabolic response to lorazepam in thalamus in the cocaine abusers could reflect increased GABA sensitivity in pallidum and in substantia nigra reticulata (
4). However, it could also reflect changes in other GABA-ergic populations (i.e., GABA interneurons). We interpret these findings as reflecting adaptation changes in the GABA system secondary to intermittent cocaine intoxication.
The regional specificity for the enhanced responses in the cocaine abusers is likely to reflect the sequential as well as the parallel organization of GABA output systems (
19). Thus, adaptive processes in response to dopamine stimulation are likely to depend on the brain regions and the balance between them (
20), as well as the subtype of GABA and/or dopamine receptors that prevail in a given region (
19). In addition, regional metabolic responses to benzodiazepines probably reflect not only direct interactions with benzodiazepine receptors but also secondary effects. The extent to which the enhanced response to lorazepam reflects differences in receptors or secondary effects cannot be determined by this study. Future imaging studies using benzodiazepine receptor ligands coupled to metabolic studies with a benzodiazepine challenge are required to clarify this issue.
Studies in laboratory animals have shown that chronic cocaine affects the GABA system, and this includes changes in GABA receptors (function, concentration, composition, and transduction elements) (
21–
23) and in enzymes that regulate GABA synthesis (
24). In general, most studies document enhancement of GABA-ergic responses with chronic cocaine administration, including an enhanced sensitivity to the sedative effects of benzodiazepines (
25). However, results are not always consistent. For example, while most binding studies have reported increases in striatal concentration of GABA receptors (
26,
27), others have reported decreases (
28). Similarly, while some studies of chronically treated animals have reported an enhanced sensitivity to iontophoretically applied GABA (
29,
30), others have reported decreases (
31). These inconsistencies could reflect the different adaptation responses in GABA cells depending on whether they receive direct or indirect dopamine projections. Inconsistencies could also reflect differences in the regimens of cocaine administration used as well as the time after withdrawal at which measurements were made (
25,
27). Although most of these studies have linked the changes in the GABA system to the process of sensitization (
32), their role in cocaine addiction per se has not been evaluated.
Studies of cocaine abusers have also shown evidence of changes in the GABA system. However, as with the laboratory animal literature, there are few studies, and the pattern of abnormalities has not been consistent. For example, while some studies have reported increases in peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in platelets of cocaine abusers (
33), others have shown decreases (
34). The phenomenology associated with cocaine intoxication and withdrawal is also suggestive of an involvement of GABA. For example, convulsions associated with cocaine intoxication respond to benzodiazepine agonists but not to the anticonvulsant phenytoin (
35). In addition, cocaine intoxication is associated with anxiety, agitation, and, not infrequently, panic attacks, which are symptoms that respond to benzodiazepines (
36,
37). Furthermore, the frequent combined use of alcohol and cocaine by cocaine-abusing subjects (
38) could reflect in part a means to compensate for cocaine-induced decreases in GABA activity, since alcohol potentiates GABA-induced chloride flux at the GABA receptor (
39,
40). In this respect, it was interesting to note that the increased metabolic activity at baseline observed in the cocaine abusers, which we had previously reported to be related to days since last cocaine use (
41), returned to values similar to those in the comparison group after lorazepam administration. Thus, one could postulate that this metabolic hyperactivity observed during early detoxification may reflect decreased GABA-ergic activity shortly after cocaine discontinuation. Although in laboratory animals discontinuation of chronic low doses of alcohol can produce global increases in glucose metabolism (
42), alcohol consumption in the abusers is unlikely to account for the baseline metabolic differences between groups, since the amount of alcohol they reported they used was comparable to that reported by the comparison subjects (
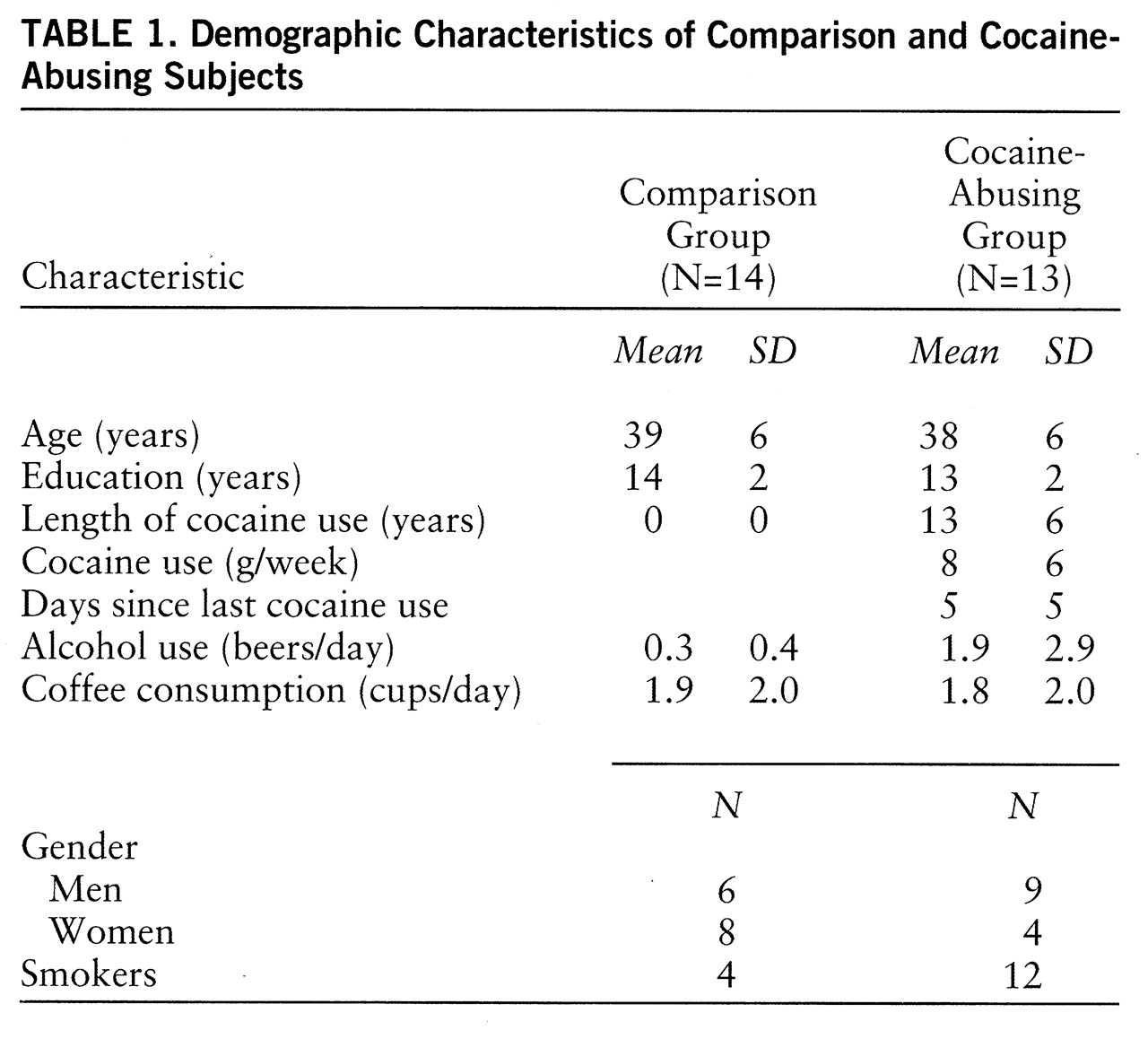
table 1). However, because histories of alcohol and drug use are not always reliable and we had no laboratory corroboration, we cannot exclude the contribution of variables other than cocaine in the hypermetabolic baseline measures observed in the abusers.
In cocaine-abusing subjects brain glucose metabolism decreases after protracted withdrawal (
43), and thus further studies are required to determine if the enhanced responsivity to lorazepam in the abusers also decreases as a function of withdrawal or whether it represents a more lasting adaptation (or predisposing factor), as seen for the changes in dopamine D
2 receptors that persist after detoxification (
6).
The finding of an enhanced sensitivity to lorazepam in cocaine-abusing subjects differs markedly from the findings reported in alcoholic subjects, in whom a blunted response to lorazepam-induced changes in regional brain metabolism has been reported (
14). Because subjects at risk for alcoholism do not show the blunted brain metabolic response to lorazepam (
8), the response in the alcoholics was interpreted as reflecting the effects of alcohol administration and/or alcohol withdrawal. In this study we excluded subjects who abused alcohol, and thus future studies comparing response to lorazepam between cocaine-abusing subjects who abuse alcohol and those who do not are required to determine the generalizability of our findings in cocaine-abusing subjects.
The lower plasma lorazepam concentration in the cocaine-abusing group than in the comparison group is most likely due to enhanced metabolism of lorazepam and may reflect hepatic enzymatic induction in cocaine-abusing subjects, since lorazepam is metabolized by glucuronide conjugation in the liver (
44). The mechanisms accounting for the enzyme induction are unclear and could reflect the use of other substances (i.e., alcohol, cigarettes, other sedative/hypnotic drugs) in the cocaine-abusing subjects. In addition, because cocaine can be metabolized by glucuroconjugation (
45), the possibility of a direct effect of cocaine on glucuronyl transferase should be further investigated. Because the enhanced sensitivity to lorazepam in cocaine-abusing subjects was observed even in the presence of much lower plasma lorazepam concentrations, the potential toxicity of sedative hypnotic drugs for which there is no enhanced metabolism and/or for which the safety is not as good as for benzodiazepines should be further evaluated. This increased sensitivity, for example, could contribute to the enhanced toxicity and mortality observed with the combined use of alcohol and cocaine (
46).
In addition, the extreme sedative effects observed for some of the cocaine-abusing subjects after lorazepam administration should alert the clinician of potential untoward reactions with the use of these drugs by active cocaine-abusing subjects in situations where alertness is required.In summary, these data document an accentuated sensitivity to benzodiazepines in cocaine-abusing subjects, which appears as an enhanced response to the sedative effects of lorazepam and an enhanced decrease in regional brain metabolism relative to that in nonabusing subjects. These results support the notion of disruption of GABA activity in the brain of cocaine-abusing subjects. Further studies are required to determine the extent to which these changes are due to cocaine withdrawal and/or prolonged sleep deprivation and whether they will decrease and/or disappear with protracted detoxification.