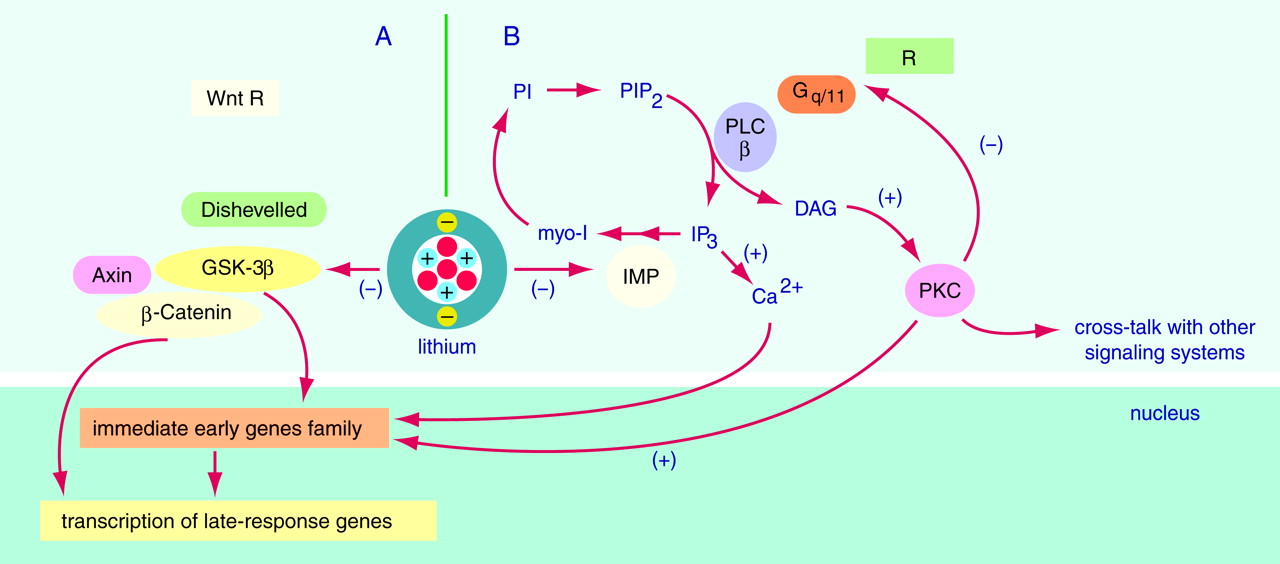
Rhythmicity is a fundamental characteristic of living matter. When a variable is longitudinally monitored and the data series assessed by inferential statistics, the results are approximated with a sum of several rhythmic components with different periods and amplitudes. The most prominent rhythmic component under normal conditions has a period of 24 hours. Such a rhythm usually reflects a complex interaction between endogenous rhythmic and other (homeostatic, adaptive, pathological, etc.) mechanisms. The 24-hour rhythms with a proven endogenous component are called circadian, a term reflecting the observation that under constant external conditions the rhythms free-run with an endogenous period that is close to but significantly different from 24 hours
(62). The circadian period of mammalian locomotor activity is controlled by a circadian clock located in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus
(63). Under synchronized conditions, all circadian rhythms appear with identical periods but have very different amplitudes and/or peak times (acrophases). Chronic (but not acute) lithium treatment prolongs the free-running period in almost all studied biological systems, including humans
(16,
64). Lithium’s effects under synchronized conditions are variable specific, with some variables showing significant acrophase delays and others exhibiting advances
(65). The effects also depend on the timing of application, with evening application of lithium hydroxybutyrate for 10 days destabilizing circadian rhythms in the rat, in contrast to morning administration
(66). The mechanism of lithium’s action on the diverse circadian rhythms probably involves combined effects at the level of the circadian clock and at the level of integration of circadian rhythmicity with other regulatory systems. Experiments in a simple circadian model (
Neurospora crassa) do not support the potential role of inositol depletion in lithium’s effects on the circadian clock and its light synchronization
(67).
Two recent breakthroughs are relevant to future approaches to the study of molecular and cellular mechanisms of lithium action. First, single dissociated suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons contain a circadian clock and express circadian rhythm in impulse activity
(68). Second, a powerful combination of mutagenesis, isolation of behaviorally arrhythmic mutants, and molecular genetics was used to identify a set of four genes representing the molecular cogwheels of the cellular circadian clock in
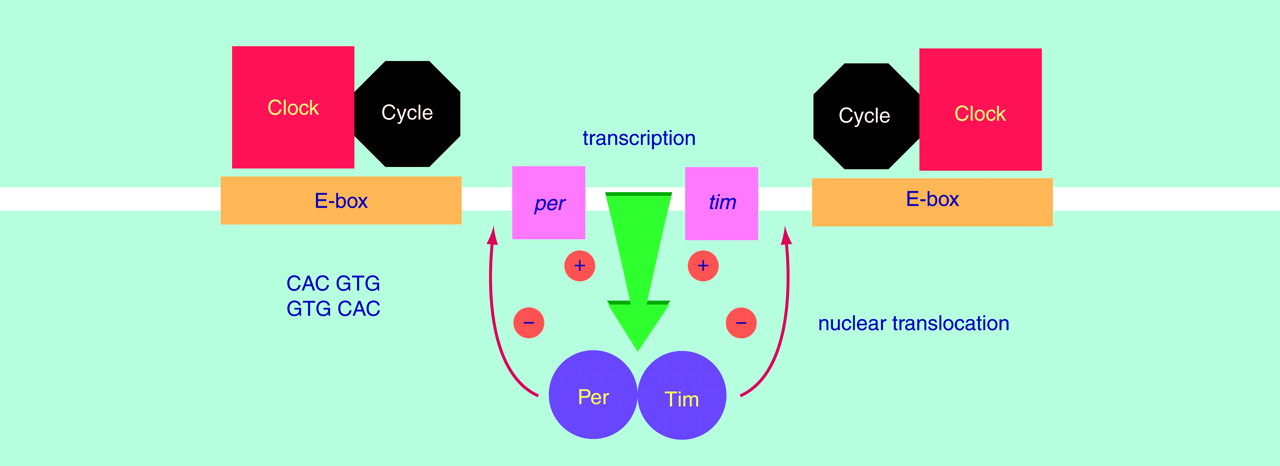
Drosophila (69) (
Figure 2). Two of the genes—
period (
per) and
timeless (
tim)—oscillate in a circadian fashion at both the mRNA and protein levels. It is important that the Per and Tim proteins form a cytosolic dimer, which translocates into the cell nucleus and suppresses their own transcription. The other two proteins—Clock and Cycle—also form a dimer in the nucleus. This dimer induces the transcription of
per and
tim mRNA by binding to E-boxes (5′-CACGTG-3′ sequence) located in the regulatory region of each gene. The activation of
per and
tim transcription may be suppressed by their own protein dimers, thus creating a molecular circadian clock based on a negative feedback loop
(69). It is noteworthy that a mouse arrhythmic mutant has a single base mutation in the mammalian
clock gene, which is highly homologous to the
clock gene in
Drosophila. The same holds true for the hamster BMAL1 gene—a partner of mammalian
clock and homologous to the
Drosophila cycle gene
(69). Finally, mammals have three
Drosophila per homologues with conservative E-boxes in their promoters
(70). Overall, these observations imply that intracellular circadian clocks are based on evolutionary conserved molecular mechanisms. Together with the evolutionary conserved effects of chronic lithium treatment, this evidence suggests that the genes implicated in circadian clock function may also be targets for chronic lithium action. The potential consequences of chronic lithium treatment for circadian rhythms are illustrated by the following example. If we assume that lithium treatment results solely in a selective 6-hour acrophase delay, then a single-time-point study will be insufficient for properly characterizing the effect and possibly misleading; i.e., is the expression of the gene truly up or down, or simply phase-shifted? This cautionary note suggests that chronobiological studies are needed for many of lithium’s putative molecular targets in order to determine whether the observed effects reflect changes in the spatiotemporal patterns of gene expression in critical neuronal circuits, effects that are likely to underlie the complex behavioral effects of lithium. Indeed, the importance of circadian factors and the sleep-wake cycle in bipolar disorder has been recognized for many years (discussed in reference
1).