Clozapine is the most effective agent for treatment-resistant patients with schizophrenia
(1) . However, treatment with clozapine has been associated with a number of metabolic disturbances. A 5-year naturalistic study with 82 patients confirmed that clozapine causes weight gain, a weight gain that continued approximately 46 months after initiation of treatment
(2) . A relationship between weight gain and improvement in psychosis during treatment with clozapine was first suggested by Leadbetter et al.
(3), who reported that improvements in Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) total score was significantly greater for eight patients with marked weight gain than for 13 other patients with less weight gain. Subsequently, Lamberti et al.
(4) reported a nearly significant correlation between decrease in BPRS total score and weight gain in 36 schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine for 6 months. Similar findings were reported by Czobor et al.
(5) for 38 patients receiving clozapine for 14 weeks. Meltzer et al.
(6) also found that increase in weight predicted improvement in psychosis after 6 weeks and after 6 months of clozapine treatment in 74 patients. On the other hand, no association between clinical response and weight gain with clozapine were reported by Umbricht et al. for 64, 45, and 19 schizophrenia patients treated for 4, 8, and 12 weeks, respectively
(7), by Bustillo et al.
(8) for 19 patients treated with clozapine for 1 year, or by Hummer et al. in 31 patients treated for 12 weeks
(9) . Meltzer et al. concluded that the relationship between weight gain and response was modest early in treatment but became significant in most long-term studies. Possible reasons for these inconsistent results may include failure to adjust for initial body weight and variability in outcome measures, reliability of assessment, concomitant medications, and clozapine dosage
(10) .
Patients receiving clozapine frequently continue with this medication for years
(11) . Previously, our team reported a significant correlation between weight gain and change in Clinical Global Impression (CGI) ratings in female but not male patients treated with clozapine for 14 months
(12) . The aim of this study was to determine whether initial antipsychotic response predicts subsequent weight change. Because these inpatients lived in the same hospital over the course of the study, the potentially confounding factors of diet, activity level, and drug compliance were optimally controlled. Furthermore, the patients had no exposure to other atypical antipsychotics because clozapine was the first and only atypical antipsychotic used at that time in the hospital. These conditions provided a favorable setting for investigating long-term weight change with clozapine.
Results
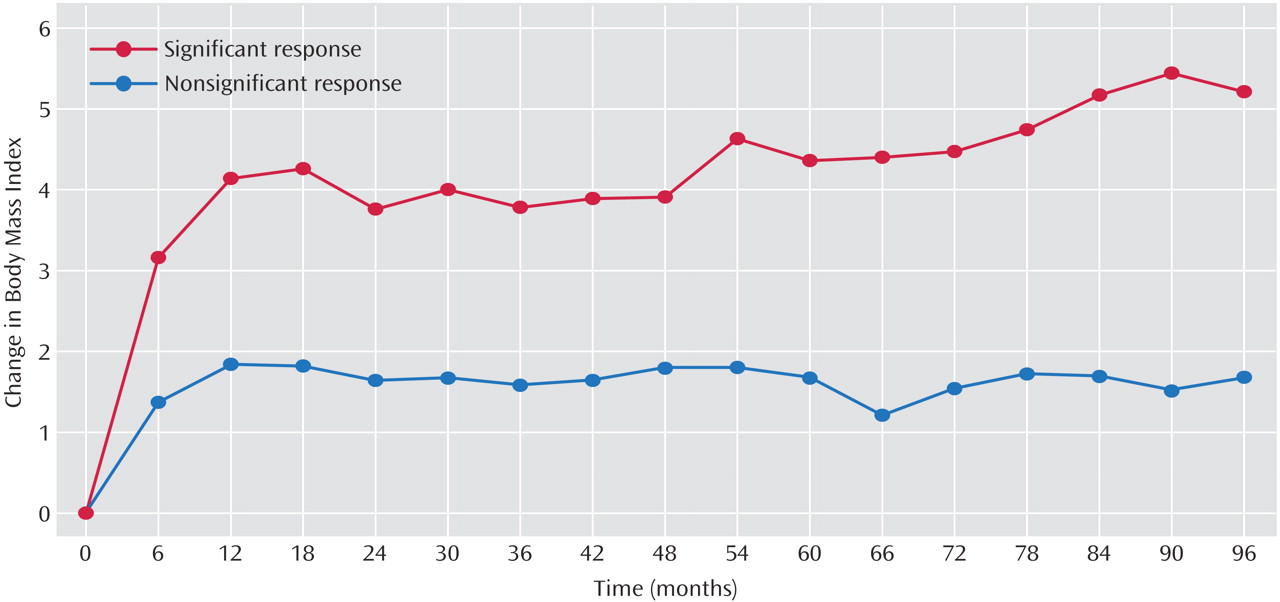
The 96 patients (46 women and 50 men) were 38.3 years old (SD=8) at clozapine initiation and had an average baseline BMI of 23.4 (SD=4.5). Fifty-five (57.3%) patients received clozapine for the entire 8-year study period. Forty-one patients were excluded because of incomplete weight records (N=10), unavailable medical records (N=4), discharge (N=4), death (N=4), or switch to other antipsychotics (N=19). Among the 19 patients switched to other antipsychotics, 17 had no response to clozapine and at the time of discontinuation, the average duration of clozapine treatment was 39.6 months (SD=29.3) and average weight gain was 4.5 kg (SD=15.1). The other two patients had responded, but one discontinued because of hypersalivation at the 48th month without weight change. The reason for the other patient’s discontinuation was unknown because the medical records were unavailable. There were no significant demographic differences or differences in initial 14-month weight change or clinical response between the 55 patients included in the analysis and the 41 who were excluded. For the 55 patients included in the study, the average weight gain was 11.7 kg (SD=1.6) over 8 years. Seventeen of these patients (30.9%) had a significant initial antipsychotic response (average CGI improvement rating: 2.0 [SD=0.6]). This group had an average 8-year weight gain of 13.8 kg (SD=8.4). The other 38 patients did not have a significant clinical response (average CGI improvement rating: 3.7 [SD=0.5]), and their average 8-year weight gain was 4.5 kg (SD=12.0). As seen in
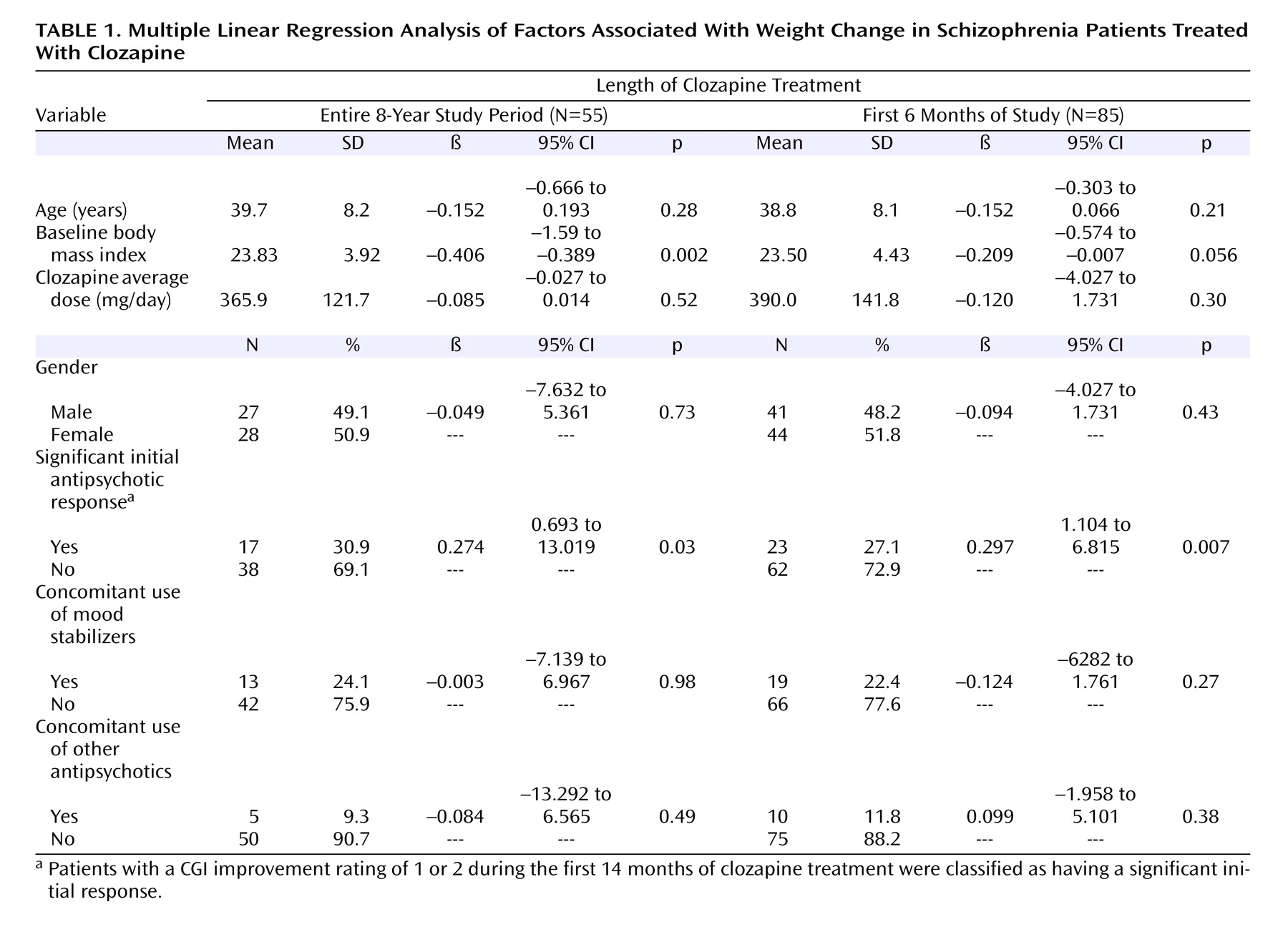
Figure 1, there was a significant difference in BMI change over the 8-year study period between those with and those without a significant initial antipsychotic response. Multiple linear regression showed that two factors, significant initial clinical response and lower baseline BMI, were associated with greater weight gain. When a supplementary regression analysis was performed that expanded the number of subjects to include those participating in the study at the 6-month mark (N=85), the results still showed that clinical response and baseline BMI were the two factors associated with weight gain (
Table 1 ).
Discussion
The results show that in this patient group, the initial antipsychotic response to clozapine was associated with subsequent weight gain over an 8-year period. Previous studies have also shown evidence for an association between weight gain and clinical response with other atypical antipsychotic drugs
(13) and typical antipsychotics
(14,
15) . These results suggest that the relationship found in our study between weight gain and antipsychotic response may be a more generalized phenomenon. The patients in our study who showed significant initial antipsychotic response gained up to 14 kg (30.8 lb), suggesting a morbidity concern for which a weight control program for these patients may be recommended from the start. Our results are consistent with previous reports that patients with a lower baseline BMI demonstrate greater weight gain associated with clozapine treatment
(16) as well as with olanzapine treatment
(17 –
19) . Our previous study noted the association between weight gain and clinical response in female but not male patients
(11) . However, after baseline BMI was controlled, the gender difference no longer existed at 14 months and at 8 years, which indicated that future weight gain studies should control for baseline BMI.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to report that initial antipsychotic response predicts long-term weight gain. However, the study was retrospective in nature and therefore selection bias may exist. But this concern might be alleviated by the similar characteristics between patients included in the study group and those who were excluded. Another concern is that the initial clinical response was determined only by the CGI. However, the ratings were all performed by one experienced psychiatrist-in-charge, who cared for these patients for years, which avoids the concern about interrater reliability. Moreover, the clinical response rate to clozapine was 30.9%, similar to the 30% that Kane et al. reported
(20) . Considering the long-term health risks associated with excess weight gain, for patients with lower baseline BMI and a good initial clinical response, weight change and associated metabolic syndrome symptoms should be closely monitored.