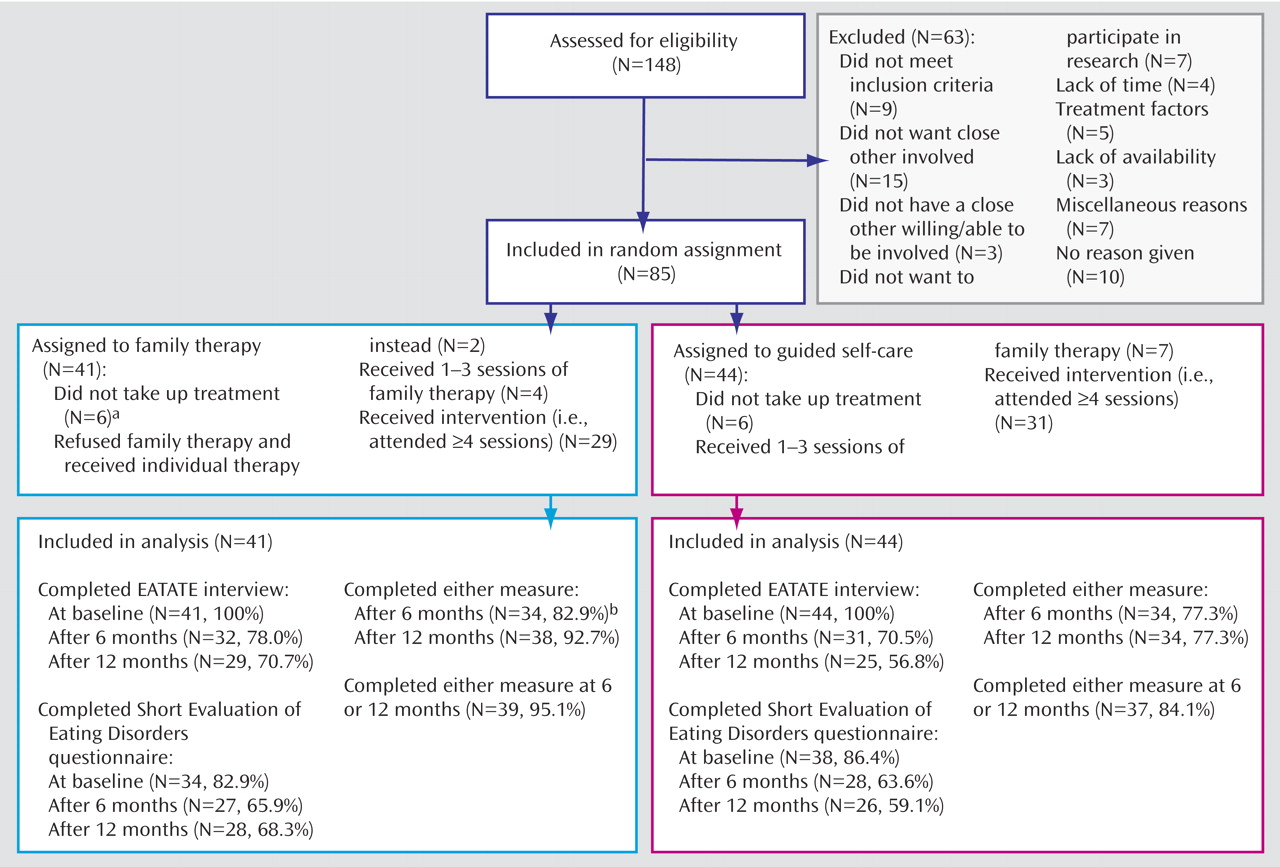
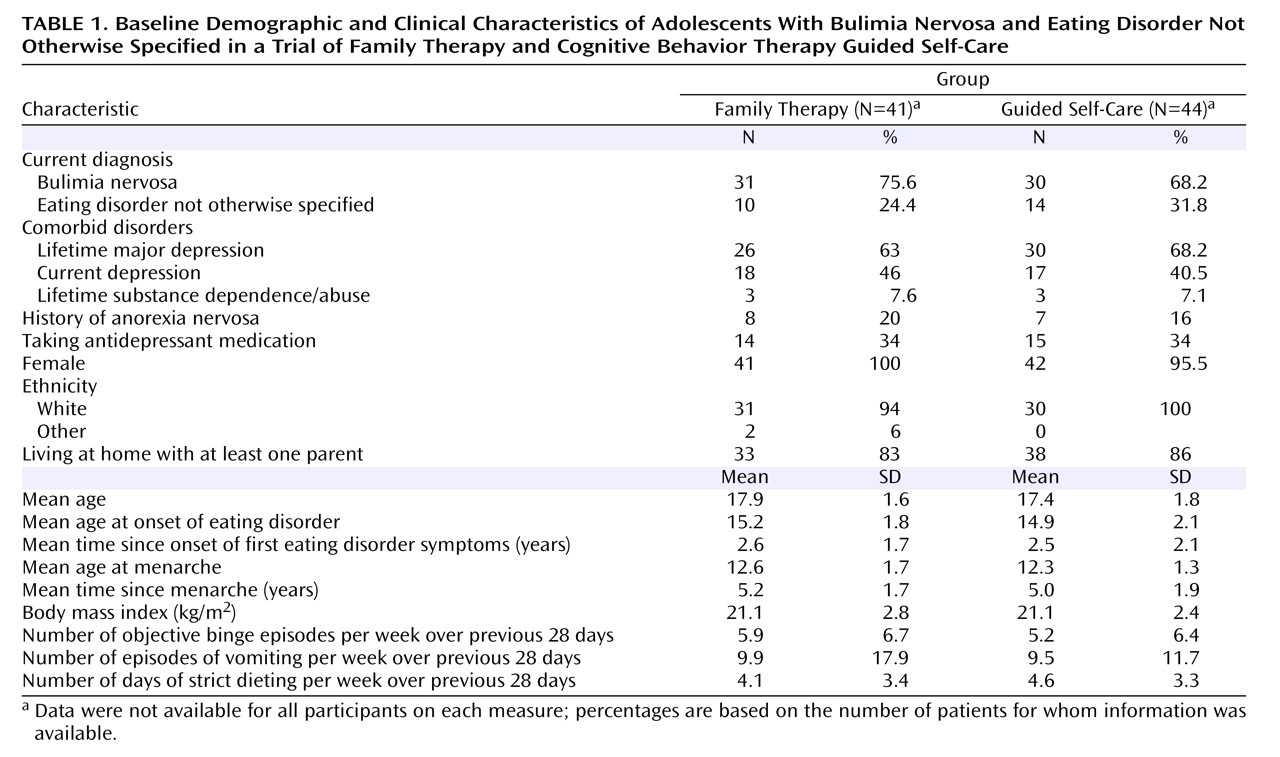
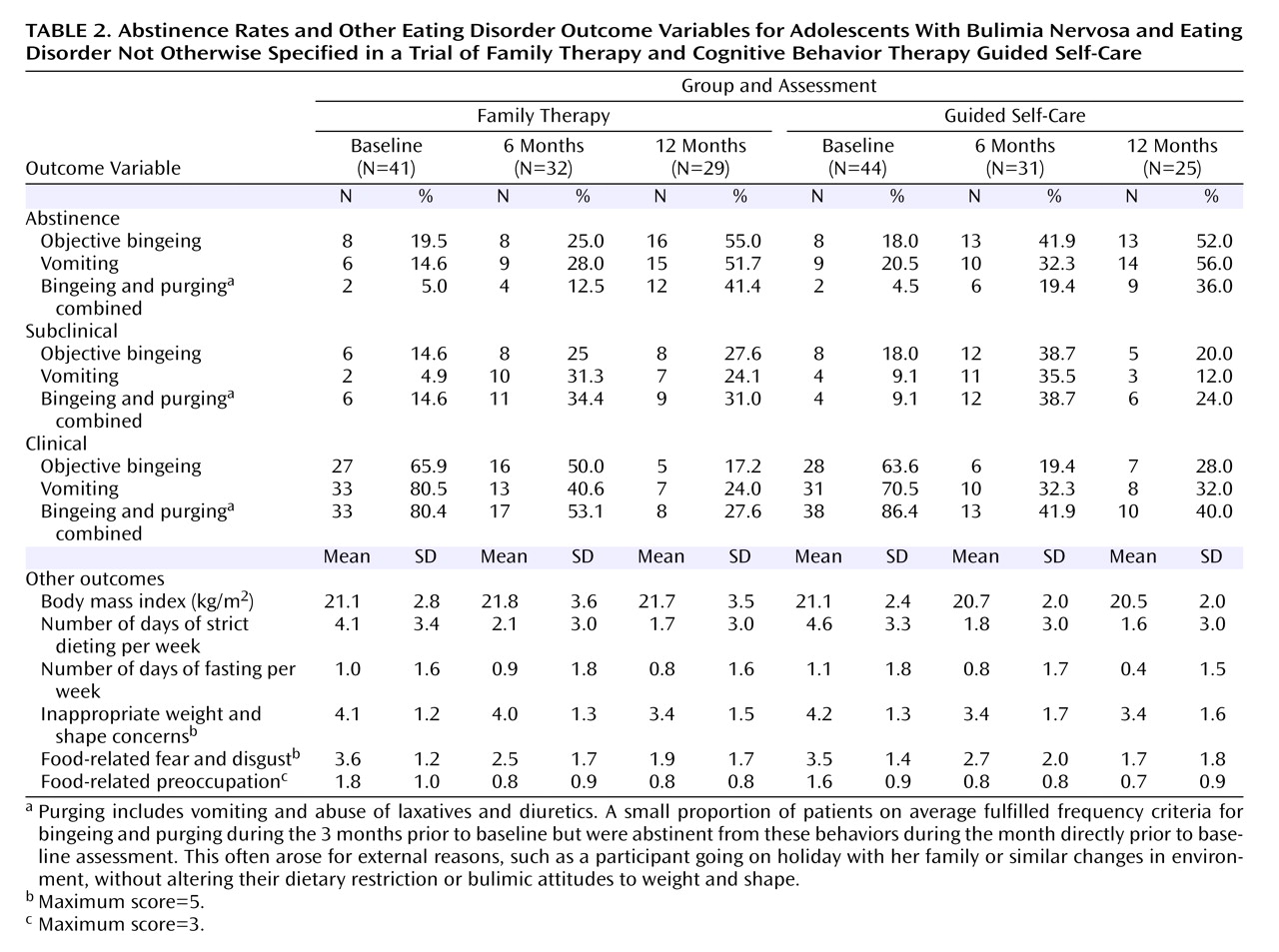
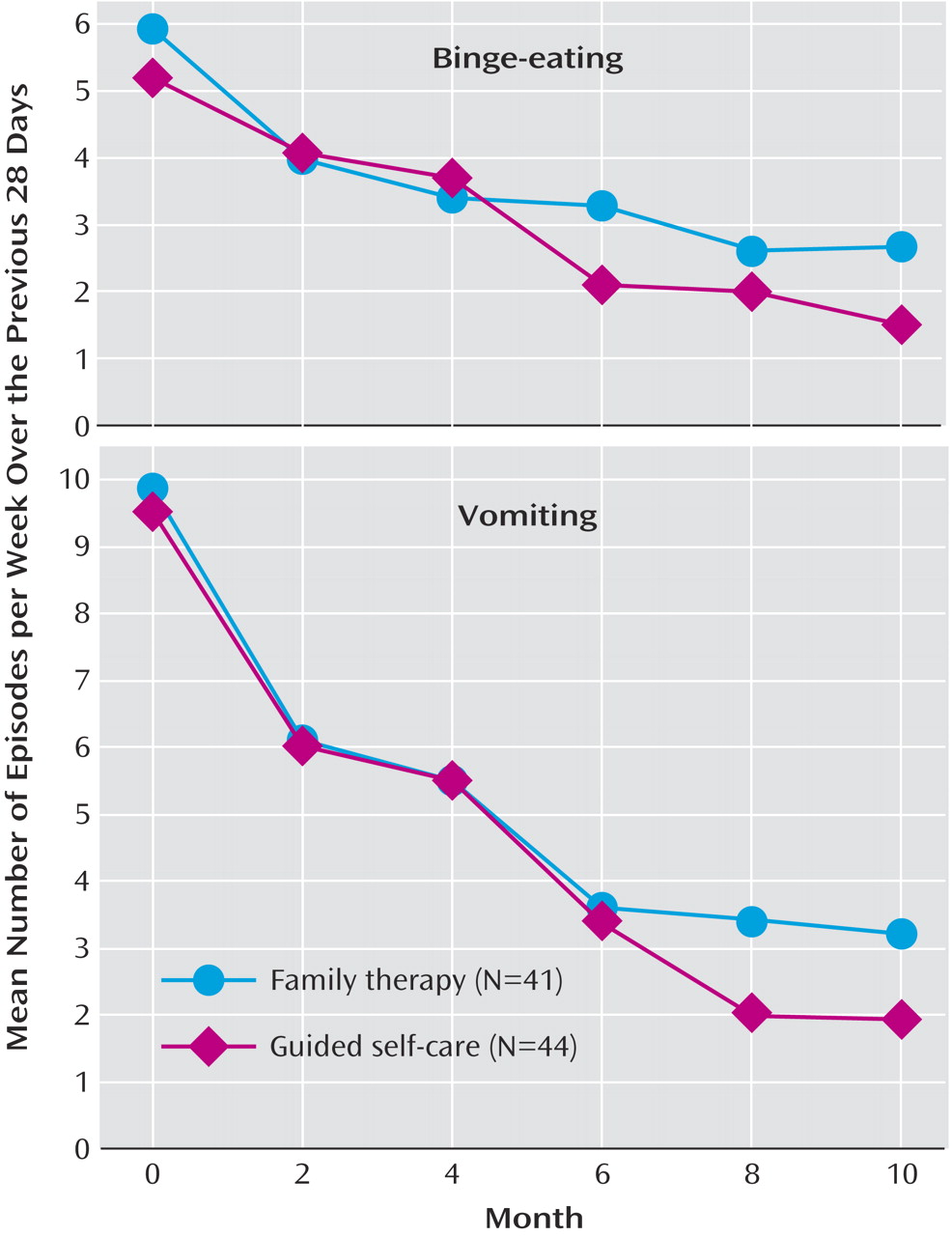
Some 4%–7% of young females in Western countries suffer from full or partial bulimia nervosa
(1) . Typically, bulimia develops in adolescence, and individuals with a partial syndrome are at risk of developing the full syndrome. Without treatment, bulimia nervosa tends to persist into adulthood. The disorder is associated with secondary physical and mental disorders and imposes a major burden on families
(1) .
Although numerous randomized controlled trials have been conducted with adults with bulimia nervosa
(2), none have been conducted with adolescents. U.K. guidelines on eating disorders
(2) have identified treatment of adolescent eating disorders as a research priority. The guidelines also noted that little is known about the health service utilization costs associated with these disorders.
Family-based treatment produces excellent outcomes in adolescents with anorexia nervosa
(2), and it has been adapted for adolescents with bulimia nervosa
(3) . Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) is the treatment of choice for adults with bulimia nervosa
(2) . Self-care formats of CBT for bulimia nervosa can be as effective as therapist-delivered CBT if guided by a therapist
(4) . Guided self-care was recommended as a first-line intervention for adults with bulimia nervosa in the U.K. guidelines
(2), and it may be a useful early intervention for bulimia in adolescents.
The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of family therapy and CBT guided self-care in adolescents with bulimia nervosa or eating disorder not otherwise specified. Our primary hypothesis was that in adolescents with bulimia nervosa or eating disorder not otherwise specified, family therapy would produce higher rates of abstinence from binge-eating and vomiting, both at completion of treatment and at follow-up. Our secondary hypothesis was that guided self-care would be less costly than family therapy.
Method
Participants
The study was carried out in four eating disorder services in the National Health Service in the United Kingdom, which are the main service providers for the populations in their respective areas. Patients were referred by general practitioners.
Recruitment took place between September 2000 and May 2003. Written informed consent was sought from participants and a “close other” at assessment. For patients age 16 and under, consent from a parent was sought. The research ethics committees of the participating centers approved the study.
Consecutively referred patients were invited to participate if they were 13–20 years of age, met DSM-IV criteria for bulimia nervosa or eating disorder not otherwise specified, and had at least one “close other” to accompany them for “family treatment.” Eating disorder not otherwise specified was defined as binge eating and/or purging (vomiting and abuse of laxatives or diuretics) less than twice a week or for less than 3 months or use of inappropriate compensatory behaviors without bingeing in patients with normal body weight. “Close others” included parents, other relatives, and partners.
We excluded patients with a body mass index below the 10th percentile for age and sex
(5), patients whose knowledge of English was insufficient to understand the treatment, and patients with learning disability, severe mental illness, or substance dependence. We did not exclude patients taking antidepressants provided they had been on a stable dose for at least 4 weeks.
Interventions
Family Therapy
The family therapy used in this study was adapted from the Maudsley model of family therapy for anorexia nervosa
(6,
7) and detailed in a manual (Eisler et al., unpublished). In this model, the family is seen as a key resource in the young person’s recovery. An attempt is made to engage family members and show them that they are in the best position to help the adolescent. Treatment is problem oriented, emphasizing the role of the family in promoting restoration of normal eating and providing education about the effects of bulimia. Families are encouraged to find a way to help the patient reduce bulimic behaviors. Finally, control over eating is handed back to the patient, and discussions of autonomy and independence take place. Patients were offered up to 13 sessions with close others and two individual sessions over a 6-month period.
CBT Guided Self-Care
We used a manual
(8) that was previously tested with adults with bulimia nervosa
(4) . The Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level test suggests that the manual can be read by eighth graders (ages 13–14 years). Accompanying workbooks are available for patients and close others, as well as a guide for clinicians
(9) . Patients had 10 weekly sessions, three monthly follow-up sessions, and two optional sessions with a close other. The therapist’s role is to motivate patients and guide them through the workbook to fit their needs.
Initially treatment focuses on the function of bulimia in the person’s life and builds motivation to change. Information about how bulimic symptoms are maintained is introduced, using self-monitoring of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Problem solving with behavioral experiments and goal setting is used to help patients alter vicious cycles of behavior. A case formulation is developed collaboratively. After 10 sessions the therapist writes a good-bye letter. The follow-up sessions focus on relapse prevention. Regular homework accompanies the treatment. The sessions with the close other address how the other could help the patient.
Therapists
Treatments were delivered by 23 experienced therapists from diverse backgrounds with training in family therapy and guided self-care. Therapists participated in training workshops for both therapies prior to the study and received weekly supervision. Most therapists had equal numbers of family therapy and guided self-care patients, under separate supervision. Seven therapists saw only one patient because of the timing of their transfer into or out of the service.
Treatment Fidelity
In family therapy, to ensure competent and uniform treatment delivery, three experienced supervisors who had previously been involved in developing or testing the Maudsley model of family therapy for anorexia nervosa used a one-way screen to provide regular “live” supervision. In guided self-care, therapists received weekly supervision by supervisors trained in motivational interviewing and CBT for bulimia nervosa. Family sessions were videotaped, and guided self-care sessions were audiotaped to allow analysis of the therapeutic process (to be reported separately).
Assessments
An initial clinical interview determined patients’ eligibility for the study. Those who consented to participate were assessed by a research assistant who remained blind to the treatment assignment throughout the study. Assessments were made at 6 and 12 months for patients and close others.
Patient Assessments
Body mass index (BMI; kg/m
2 ) was measured. A lifetime eating disorder history was obtained with the EATATE interview (unpublished 2000 manuscript of M.B. Anderluh et al.), a semistructured weight and eating disorder history based on the Longitudinal Interval Follow-Up Evaluation
(10) that includes variables from the Eating Disorder Examination
(11) . Although full validation of this instrument has not yet been published, preliminary analyses indicate excellent interrater reliability, with kappa values between 0.88 and 1.0 for first and second eating disorder diagnosis and 0.82 for the number of lifetime diagnoses. Spearman’s coefficients for longitudinal assessment of symptoms are high: objective bingeing, 0.84; vomiting, 0.97; laxative or diuretic abuse, 0.89; and strict dieting, 0.85. We used this interview at baseline to make DSM-IV diagnoses and at baseline, 6 months, and 12 months to assess eating disorder symptoms over the previous month. We also used it at multiple time points to assess the time course of recovery (at baseline and at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 months).
We also used the Short Evaluation of Eating Disorders
(12), a brief, valid, and reliable self-report measure assessing eating disorder symptoms over the previous 4 weeks. We included this measure to obtain information by mail or telephone on the outcome of patients who failed to attend the follow-up assessment.
To assess psychiatric comorbidity at baseline, we used an adapted version of the Oxford, England, Risk Factor Interview
(13) and the EATATE. Other instruments were used to assess other factors, such as general psychopathology and family relationships, as well as parental outcomes, including mental health and burden of caring, that will be reported separately.
Health Economic Assessment
The economic component used well-established methods of data collection, cost estimation, and analysis
(14,
15) . The Client Service Receipt Inventory
(14,
15) documents each adolescent’s use of education, health, and social care services, as well as additional expenses for them or their family that are a consequence of bulimia nervosa. Unit costs for each service were taken from nationally applicable data
(16) or estimated using an equivalent methodology. Costs per case were calculated as the unit costs multiplied by the use made of service over the 3 months preceding each assessment.
Randomization
The randomization sequence to family therapy or guided self-care was generated by an independent statistician, using permutated blocks of random sizes between 4 and 10. Treatment assignment codes were contained in a computerized randomization database that concealed the sequence until interventions were assigned. Names were entered into the database by an independent administrator, and the treatment assignment was conveyed to the assessing clinician, who then informed the patient.
Statistical Analysis
The power calculation underpinning the study was based on the estimate that 30% of patients receiving guided self-care and 60% in family therapy (extrapolated from studies of anorexia and bulimia nervosa)
(17,
18) would be abstinent from bingeing and vomiting at 6 months. A two-group chi-square test with a two-sided significance level set at 0.05 has 80% power to detect the difference between a guided self-care group proportion of 0.3 and a family therapy group proportion of 0.6 when each group has a sample size of 42.
All analyses were based on the intention-to-treat principle and were conducted in SAS, version 9.1 (SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.), or Stata, release 9 (Stata Corp, College Station, Tex.).
Primary outcome variables were abstinence rates from bingeing and vomiting over the previous month, assessed at 6 and 12 months on the EATATE interview. The four secondary outcome variables were abstinence rates from bingeing and vomiting over the previous month, assessed at 6 and 12 months on the Short Evaluation of Eating Disorders; longitudinal assessment of bingeing and vomiting by interview; other eating disorder symptoms; and cost of care.
Primary outcomes from the EATATE interview were analyzed using a logistic regression for ordinal variables based on the assumption of proportional odds
(19) . Three outcome categories were examined for bingeing and vomiting: “abstinence” (behavior absent during the previous 28 days), “subclinical” (behavior present during previous 28 days less than twice per week), and “clinical” (behavior present during previous 28 days two or more times per week). Abstinence rates on the Short Evaluation of Eating Disorders and other categorical data were analyzed in a similar fashion.
The longitudinal course of patients’ bingeing and vomiting was explored using monthly symptom frequencies from the EATATE interview over the 12-month period from baseline to follow-up. Patients’ mean numbers of bingeing and vomiting episodes at six time points (at baseline and at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 months) were used to assess the time course of recovery in models for repeated measurements
(20) .
Other continuous outcomes, such as BMI and EATATE variables (e.g., days of strict dieting), were also analyzed using models for repeated measurements.
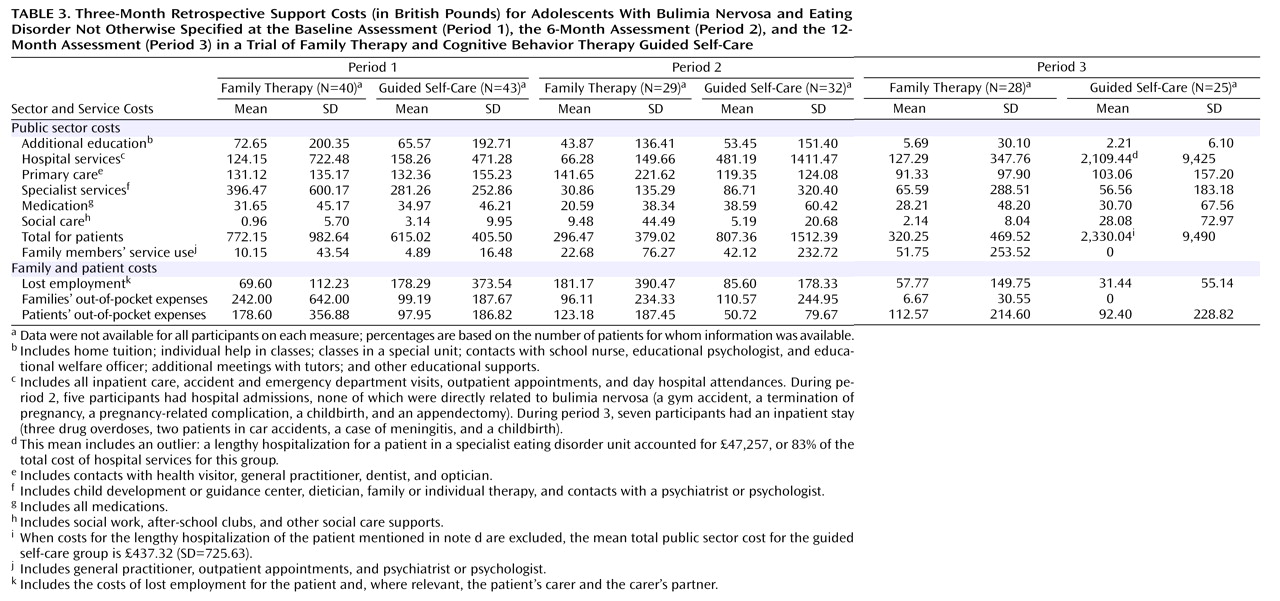
Independent-samples t tests with two-sided significance levels were used to make cost comparisons between the two groups for three 3-month periods: period 1 was the 3 months preceding the baseline assessment, period 2 the 3 months preceding the 6-month assessment, and period 3 the 3 months preceding the 12 month assessment. Where a significant difference was indicated, the data were retested using bootstrap techniques in Stata
(21) . Cost differences between period 1 and period 3 were calculated using paired t tests.
Discussion
Our main hypothesis, that family therapy would be superior to guided self-care, was not confirmed. Our primary analysis found that guided self-care resulted in earlier reduction of binge-eating than family therapy, even after adjusting for baseline antidepressant use. The self-report data and the analysis of the time course of recovery confirmed this finding. This difference between groups at 6 months in bingeing only is puzzling. The suppression of binges in guided self-care was not offset by increased dieting, which was reduced in both groups. It also was not explained by group differences in antidepressant use. In both groups, similar proportions of patients were on antidepressants throughout treatment, with a reduction in the proportion on antidepressants over time (from 34% at baseline to 20.8% at 12 months). The earlier reduction of bingeing in the guided self-care group may be due to this treatment’s specifically addressing bingeing as a key symptom.
In both groups substantial improvement occurred between 6 months (end of the treatment) and 12 months, with no group differences in outcome. Thus, in the absence of a waiting-list or attention placebo control group, we cannot rule out the possibility that improvement was simply due to passage of time or to nonspecific effects, although previous trials of adults with bulimia nervosa have found little or no change in people on waiting lists
(22) .
Our second hypothesis was partially supported. While the cost of treatment was lower for guided self-care than for family therapy, there was little differential impact on support costs. There were no other differences between groups on other cost categories. Notably, public sector costs and some of the family and patient costs decreased over time. Together, the cost and outcome findings suggest a cost-effectiveness advantage to guided self-care.
Family involvement in treatment was not always acceptable to young people: 28% of eligible adolescents who chose not to enter the study cited this as the reason for their refusal. This proportion may not reflect clinical practice, where initial reluctance to involve the family can often be resolved over time. Our design allowed adolescents to involve “close others” other than parents in treatment, and one-quarter of the participants did so
(23) . These patients were older, were less likely to live at home, had more chronic symptoms and more comorbidity, and had poorer relationships with their parents. This suggests the need to offer at least some individual therapy to these young people.
Our study has several strengths. First, it is the first randomized controlled trial of adolescents with bulimia nervosa and thus addresses a gap in our knowledge. Second, it was conducted in a catchment-area-based setting, where all comers were taken, which makes the findings highly generalizable. Third, the longitudinal outcome assessment, which enabled us to examine the course of change over time, suggests that different mechanisms of change may underpin the two treatments. Finally, the inclusion of a health economic component in bulimia research is rare. Indeed, a recent systematic review
(2) found only two cost studies and one economic evaluation that compared antidepressants, CBT, and a combination of the two for bulimia nervosa.
One important limitation of the study lies in its sample size, which may have been too small to allow the detection of differences on some outcomes. A second major limitation is the absence of a waiting list or attention placebo control group.
A number of broader points are worth noting here. First, the outcomes in this study compare well with those from randomized controlled trials of CBT or guided self-care of adults with bulimia nervosa, even though the number of sessions offered was lower than recommended for adults
(2) . This suggests that these young patients’ symptoms may be less entrenched than those in adults, where a typical illness duration is about 10 years
(2) . Second, our treatment costs compare well with those estimated for adults, where the average cost of 16 to 20 sessions of bulimia-specific CBT was £967 in 2000–2001
(2), which is more than three times the cost of guided self-care and twice that of family therapy in this study. Third, while the costs themselves may be specific to the United Kingdom, the cost differences between the treatments are likely to generalize to other countries.
Our findings suggest that in adolescents with bulimia nervosa or eating disorder not otherwise specified, guided self-care has a slight advantage over family therapy in terms of acceptability, outcome, and treatment cost. The clinical implication is that guided self-care for adolescents with bulimia nervosa is of value as an early intervention that can be delivered in nonspecialist settings. Future research should address the mechanisms of change, whether different subgroups of adolescents respond differently to these treatments, and whether different ways of involving the family in treatment might be more beneficial.