Eleven subjects who met DSM-IV criteria for PTSD secondary to maltreatment and 11 healthy comparison subjects were recruited for single voxel proton MRS studies of the anterior cingulate region. Subjects were case matched within 6 months of age (mean age=10.23 years [SD=2.8] for the PTSD group and mean=10.15 years [SD=3.0] for the comparison group; age range=4.2–14.8 years) and by sex (six male pairs and five female pairs), race, Tanner stage, and Hollingshead four-factor index of socioeconomic status
(8) (mean=38.0 [SD=10.0] for the PTSD group and mean=38.4 [SD=7.5] for the comparison group). Subjects were case matched within 8 points of full-scale IQ (mean=114.9 [SD=12.5] for the PTSD group and mean=119.9 [SD=10.3] for the comparison group). Subjects were similar in weight (mean=85.5 lb [SD=31.9] for the PTSD group and mean=93.2 lb [SD=37.5] for the comparison group), height (mean=54.0 inches [SD=7.3] for the PTSD group and mean=55.7 inches [SD=8.0] for the comparison group), and intracranial volume (mean=1449.1 cm
3 [SD=142.1] for the PTSD group and mean=1487.1 cm
3 [SD=175.0] for the comparison group). Axis I mental disorders were assessed by using the Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-Age Children—Present and Lifetime Version, which includes a comprehensive PTSD interview
(9). Comorbidity in the PTSD group included: major depressive disorder (N=6), oppositional defiant disorder (N=5), and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (N=3). PTSD traumas included sexual abuse (N=7), physical abuse (N=2), and witnessing domestic violence (N=2). An estimate of subjects’ IQ was made on the basis of the vocabulary, digit span, block design, and object assembly subscales of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children
(10). An assessment of handedness was made by using the Revised Physical and Neurological Examination for Subtle Signs inventory
(11); subjects with a rating of right-handedness on eight of the inventory’s 12 handedness items were considered right-handed. All subjects except two in the PTSD group were right-handed. Exclusion criteria were 1) lifetime prior exposure to psychotropic drugs, 2) a significant medical or neurological illness or history of head injury, 3) gross obesity or growth failure, 4) full-scale IQ lower than 80, 5) presence of DSM-IV anorexia nervosa, autism, substance use disorder, or schizophrenia, and 6) a history of maltreatment or axis I disorder in comparison subjects. After a complete description of the study was given to subjects and their parents, written informed consent was obtained. Subjects received monetary compensation for participation.
For each subject, we obtained a single voxel
1H spectrum using a short TE stimulated echo acquisition sequence placed in the medial prefrontal cortex with the voxel centered on the anterior cingulate. We used a GE 1.5 Tesla scanner (Signa System, General Electric Medical Systems, Milwaukee) running version 5.4 software located at the Magnetic Resonance Research Center at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. The position of the voxel (2 ≥1.5 ≥1 cm, volume=3 cc) was determined from sagittal and coronal MR images at the anterior-most point of the genu of the corpus callosum, as previously described
(12). The short TE stimulated echo acquisition sequence is part of the GE spectroscopy package and utilizes the 90E-90E-90E stimulated echo sequence
(13). A TR of 1.5 seconds and 150 acquisitions was used. The MR spectrum was obtained with maximal receiver gain, 2000 Hz sweep width, and 2048 point spectral resolution. Spectral signal assignments were performed for
N-acetylaspartate, choline, and creatine by using estimations from an external standard, i.e., from spectra of phantoms containing known concentrations of these compounds using the LCModel software package (licensed by S.W. Provencher, Max-Planck-Institut, Gottingen, Germany). The LCModel is a user-independent fitting routine that employs a library of concentration-calibrated model spectra of all individual metabolites as an a priori database for assigning MRS signals to their appropriate frequencies. Thus, this program enables quantification of metabolites with overlapping signals. It has been demonstrated to be an accurate and reliable method for quantifying short TE
1H spectrum MRS data
(13,
14).
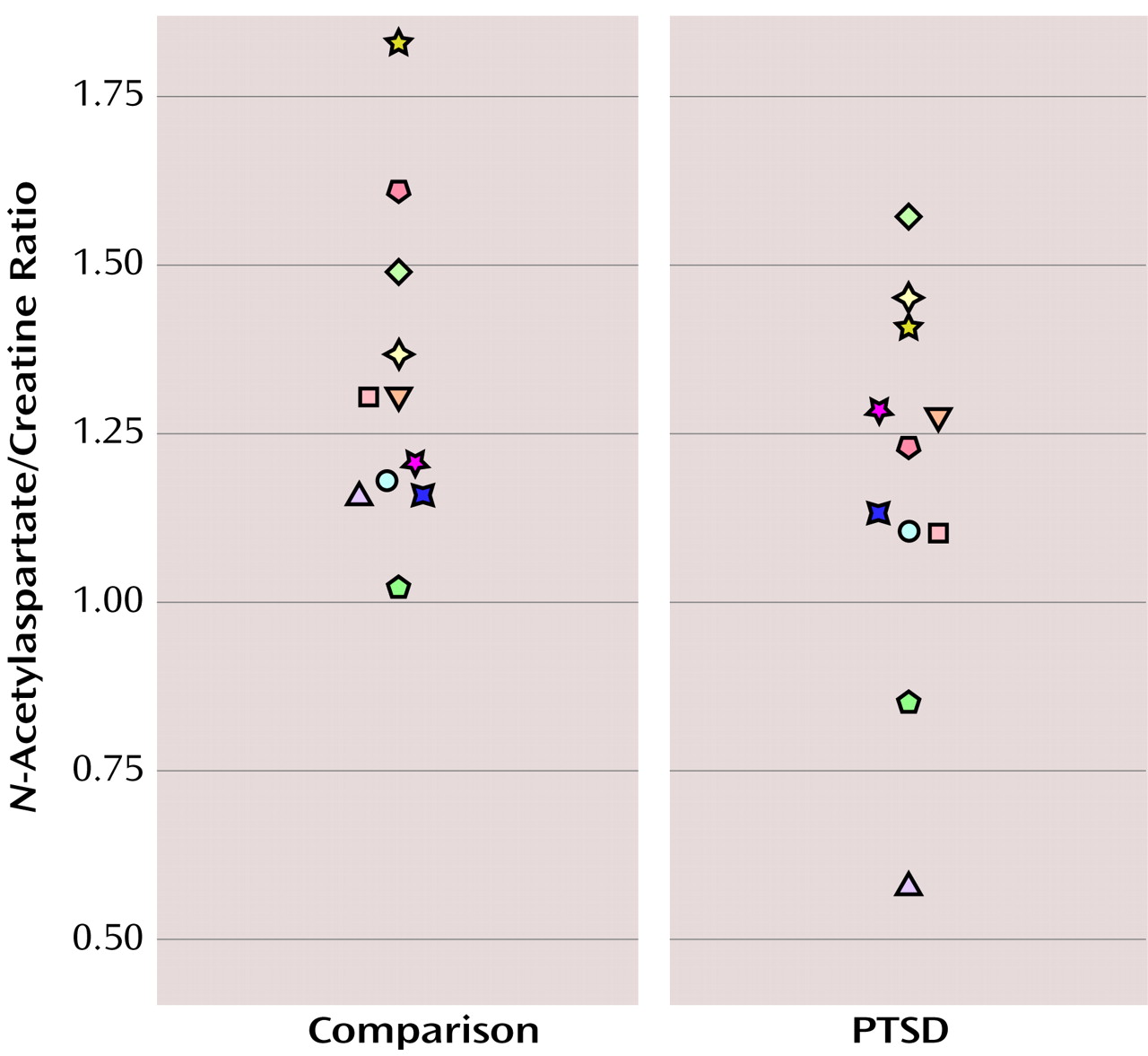
Because creatine is thought to be a measure of overall brain metabolism and is generally stable (for review, see reference
15), total
N-acetylaspartate was quantified in relationship to creatine. In view of the very close matching of the PTSD and comparison subjects, we used two-tailed paired t tests for group comparisons
(16).