Factor analytic studies of schizophrenia reliably group psychopathological features into two basic symptom categories, with the most common distinction being between negative or “deficit” symptoms and positive or “psychotic” symptoms. Classic positive symptoms include primarily delusions and hallucinations. Characteristic negative symptoms include flattened affect, alogia, avolition, anhedonia, and inattention, although there is debate regarding the defining symptoms of this construct
(1).
Previous research to characterize the neurobiological significance of the distinction between these symptom complexes has indicated that negative but not positive symptoms in schizophrenia are consistently associated with cognitive impairment. Deficits include poorer performance on measures of verbal memory
(2), visual-spatial and visual-motor processing
(2–
5), and mental processing speed
(5,
6). Although cognitive impairments associated with negative symptoms cut across multiple cognitive domains, deficits on measures of executive or frontal lobe functioning are quite common and may underlie poor performance on other neuropsychological tasks. Negative symptoms in schizophrenia have also been associated with lower prefrontal white matter volume
(7), lower metabolism in the prefrontal region
(8), and left hemisphere hypofrontality
(9).
Additional research on negative symptoms in schizophrenia has focused on the distinction between negative symptoms and major depression, given the similarities in the presentations of these syndromes. Inconsistent findings regarding the ability of instruments assessing negative symptoms to distinguish schizophrenic patients with negative symptoms from nonpsychotic subjects with major depression have generated debate about the existence of negative symptoms as a syndrome distinct from depression
(10–
12). This concern suggests that concurrent assessment of depression is important in identifying the unique clinical, cognitive, and neuroradiological concomitants of negative symptoms.
Recently, interest in the concept of negative symptoms has broadened to other clinical groups besides patients with schizophrenia. For instance, negative but not positive symptoms are predictive of length of hospital stay in stroke patients
(13). Negative symptoms have also been found to be more severe in patients with Alzheimer’s disease than in healthy elderly comparison subjects
(14), and negative symptoms have been associated with hypoperfusion in the frontal cortex
(15). Thus, negative symptoms do not appear to be specific to schizophrenia, and research on negative symptoms may contribute to the understanding of neuropsychiatric features and neurobehavioral functioning in patients with neurological disorders.
Temporal lobe epilepsy is a common neurological disorder. Researchers have a long history of interest in the interictal psychiatric features that may be evident over the course of the disorder
(16). It is generally acknowledged that behavioral and psychiatric features in temporal lobe epilepsy are varied, but particular interest has focused on the schizophrenia-like psychoses sometimes associated with epilepsy
(17). This research has been concerned with the presence and nature of hallucinations, delusions, and other positive symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy. To our knowledge, there has not been a systematic investigation of the rate and correlates of both negative and positive symptoms in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy with concomitant psychoses or, more important, in nonpsychotic patients during the interictal state.
The purpose of this investigation was to determine the frequency of interictal negative and positive symptoms in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Further, matched groups of epilepsy patients with and without negative symptoms and healthy comparison subjects were contrasted on a broad battery of neuropsychological measures and quantitative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) volumes. Finally, current levels of depressive symptoms and lifetime history of major depression and other depressive disorders were measured to rule out the possibility that negative symptoms were merely secondary to mood disorders, which are known to be more frequent in epilepsy patients
(18).
Method
Subjects
A total of 84 patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and 74 healthy comparison subjects served as the study subjects. The initial selection criteria for epilepsy patients included 1) chronological age from 18 to 60 years, 2) presence of complex partial seizures of definite or probable temporal lobe origin, 3) absence of MRI abnormalities other than atrophy on clinical reading, and 4) absence of any other neurological disorder. The patients’ medical records were reviewed by a board-certified neurologist with expertise in epilepsy who was blinded to all quantitative imaging, cognitive testing, and psychiatric history data. This review included seizure semiology, previous EEGs, clinical neuroimaging reports, and all available medical records. On the basis of this review, each patient was classified as having simple or complex seizures of definite, probable, or possible temporal lobe origin, with or without secondary generalization. Definite temporal lobe epilepsy was defined by continuous video/EEG monitoring of spontaneous seizures demonstrating temporal lobe seizure onset. Probable temporal lobe epilepsy was determined by a review of clinical semiology with features consistent with complex partial seizures of temporal lobe origin in conjunction with complementary evidence from interictal EEG (e.g., focal spike, sharp or slow wave activity over the temporal lobe), neuroimaging (e.g., temporal lobe or hippocampal atrophy), and developmental and clinical history (e.g., initial precipitating injuries such as complex febrile convulsions). Only patients who met the criteria for definite and probable temporal lobe epilepsy proceeded to study participation; patients with possible temporal lobe epilepsy were excluded. The patients were interviewed, whenever possible, in the presence of a family member or another person familiar with their epilepsy history and clinical course. Medical records from previous epilepsy-related treatments were also reviewed and abstracted by an individual who was blinded to the MRI and neuropsychological findings.
The selection criteria for the healthy comparison subjects included 1) chronological age from 18 to 60 years, 2) either a friend, significant other, or relative of the patient, 3) absence of current substance abuse, medical, or psychiatric conditions that could affect cognitive functioning, and 4) no current psychotropic medication use and no history of developmental learning disorder or loss of consciousness >5 minutes. Informed consent was obtained from each participant after the procedures were fully explained and questions were answered.
All participants underwent the following procedures: 1) standardized assessment of negative and positive symptoms, 2) comprehensive neuropsychological assessment, 3) high-resolution quantitative MRI volumetrics, and 4) self-report of depressive symptoms. Epilepsy patients also underwent the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders, Clinician Version (SCID) to determine whether they had a lifetime history of mood disorder.
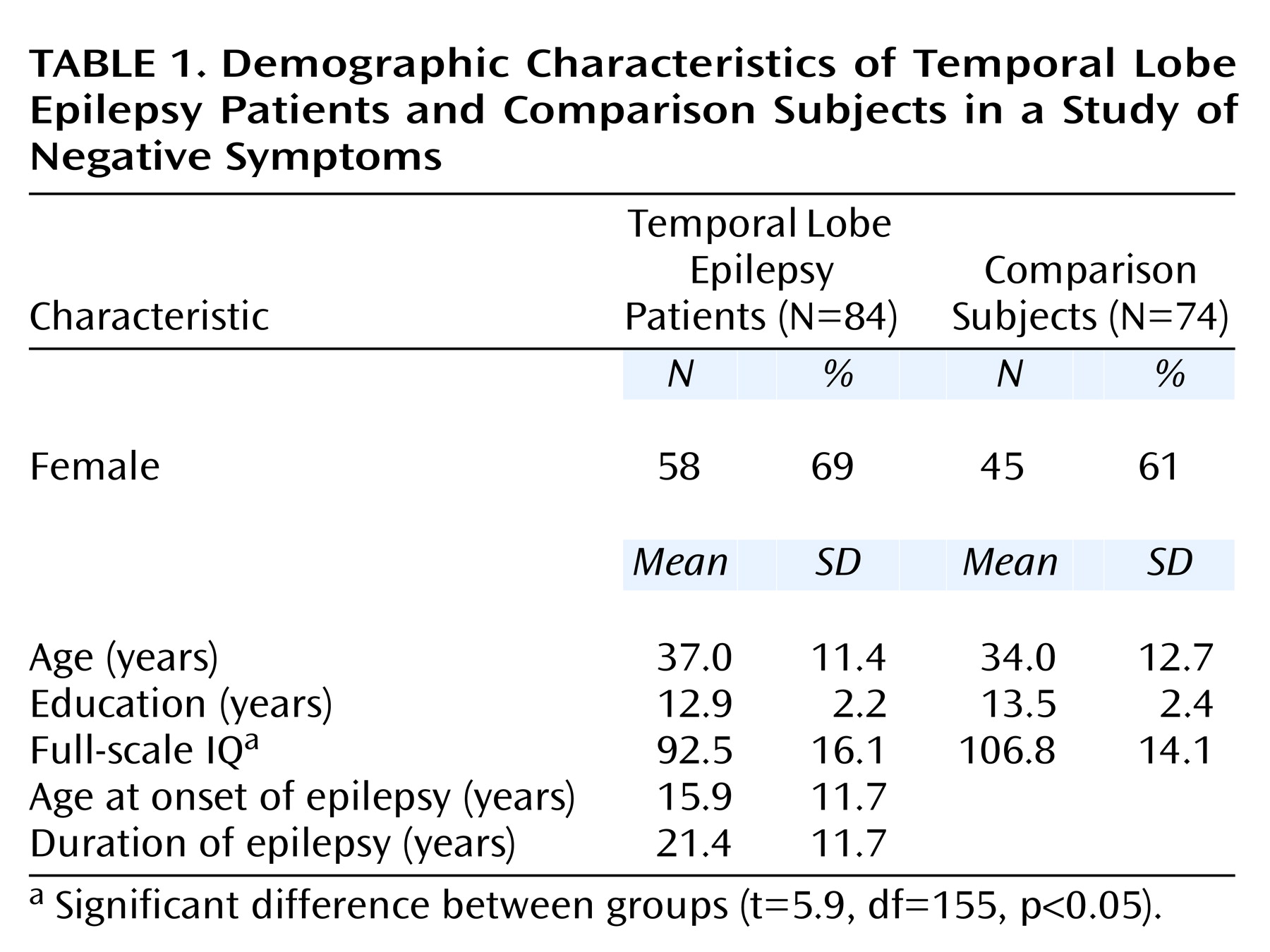
Table 1 provides the demographic and clinical features of the epilepsy patients and the comparison group. The only significant difference was a lower mean full-scale IQ in the temporal lobe epilepsy group (t=5.9, df=155, p<0.05).
Assessments
Positive and negative symptoms
All patients and comparison subjects were observed and rated for positive and negative symptoms by a trained investigator using the methods developed by Andreasen and collaborators (Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms [SAPS]
[19]; Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms [SANS]
[20]). As is the convention, each symptom item was rated from absent (score=0) to severe (score=5). Items assessing inattention were not scored because attentional measures were included in the neuropsychological battery. The remaining item categories included affective flattening, alogia, apathy, and anhedonia.
Neuropsychological measures
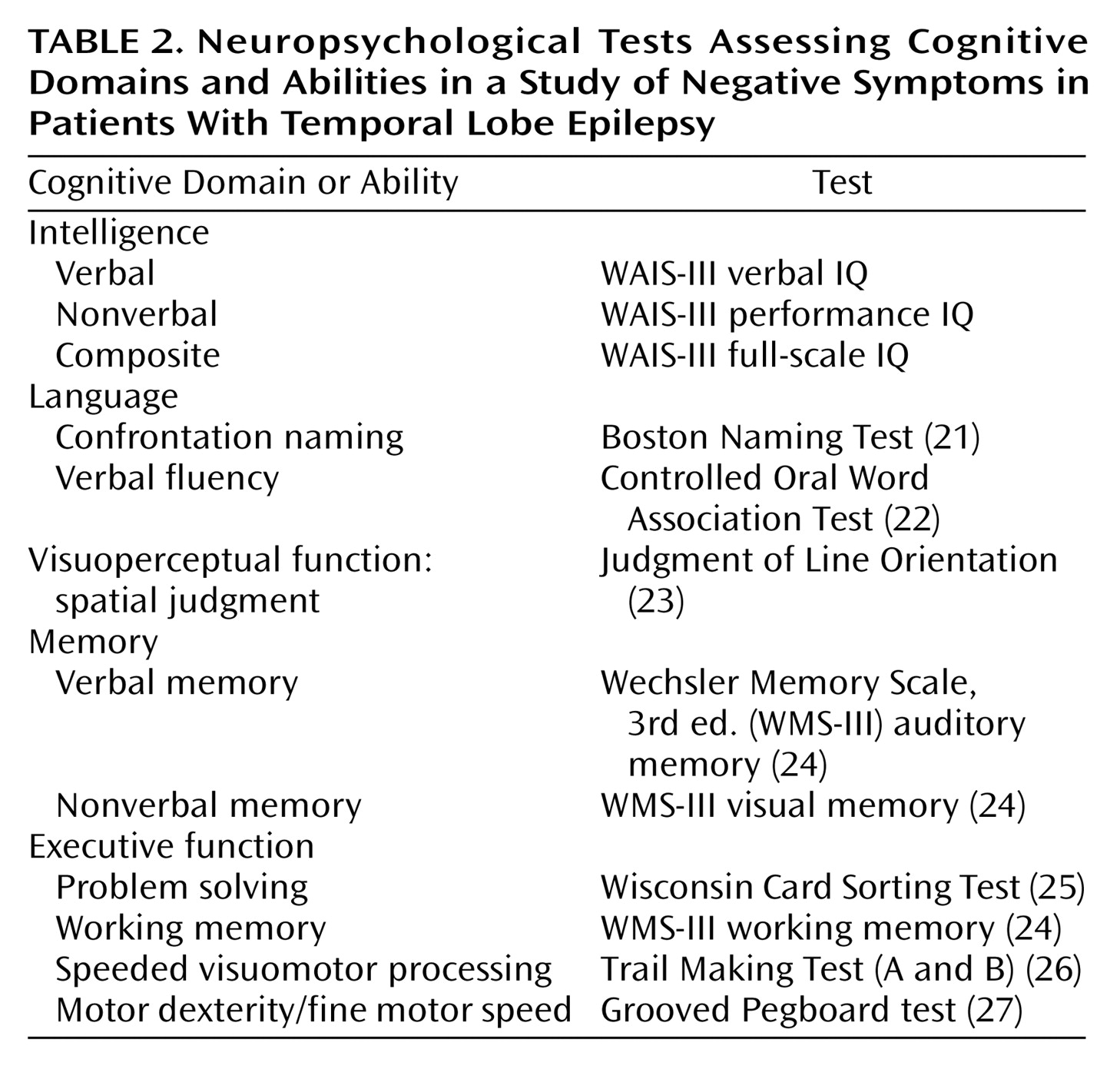
Patients and comparison subjects were administered a comprehensive neuropsychological test battery that included standard clinical measures of intelligence, language, visuoperceptual/spatial skills, memory, and executive functions.
Table 2 lists the cognitive domains and specific abilities assessed and the tests that were administered
(21–
27).
Quantitative MRI volumetrics
Images were obtained on a 1.5-T Signa scanner (General Electric, Milwaukee). Sequences acquired for each subject included 1) T1-weighted, three-dimensional spoiled gradient recall acquisition with the following parameters: TE=5, TR=24, flip angle=40, number of excitations=2, field of view=26, slice thickness=1.5 mm, slice plane=coronal, matrix=256×192; 2) proton density; and 3) T2-weighted images acquired with the following parameters: TE=36 msec (for proton density) or 96 msec (for T2), TR=3000 msec, number of excitations=1, field of view=26, slice thickness=3.0 mm, slice plane=coronal, matrix=256×192, and an echo train length=8.
MRIs were acquired at the University of Wisconsin and transferred to the Image Processing Laboratory of the Mental Health Clinical Research Center at the University of Iowa, where they were processed by using a semiautomated software package (Brain Research: Analysis of Images, Networks, and Systems [BRAINS])
(28,
29). University of Iowa staff were blinded to the clinical, sociodemographic, and neuropsychological characteristics of the subjects. The T
1-weighted images were spatially normalized so that the anterior-posterior axis of the brain was realigned parallel to the anterior commissure-posterior commissure line, and the interhemispheric fissure was aligned on the other two axes. A six-point linear transformation was used to warp the standard Talairach atlas space onto the resampled image. Images from the three pulse sequences were then coregistered by using a local adaptation of automated image registration software
(30). After alignment of the image sets, the proton density and T
2 images were resampled into 1-mm cubic voxels, after which an automated algorithm classified each voxel into gray matter, white matter, CSF, blood, or “other”
(31). The brains were then “removed” from the skull by using a neural network application that had been trained on a set of manual traces
(32). Manual inspection and correction of the output of the neural network tracing was conducted. A stereotaxic method based on the Talairach atlas yields measures of the left and right frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes and the cerebellum
(33). The BRAINS software and procedures have been shown to have high interrater reliability, intrarater reliability, and scan-rescan reproducibility, particularly for the MRI indices that are the focus of the current study. MR regions of interest for this investigation included total (supratentorial) tissue volume, total white and gray matter volumes, and total CSF volume.
Depression
Current self-reported symptoms of depression were assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory. To determine lifetime and current axis I DSM-IV mood disorders, epilepsy patients were assessed with the SCID. In addition, it was determined whether any patients were exhibiting psychosis. None of the patients exhibited active psychosis; three had a past history of delusional disorder.
Results
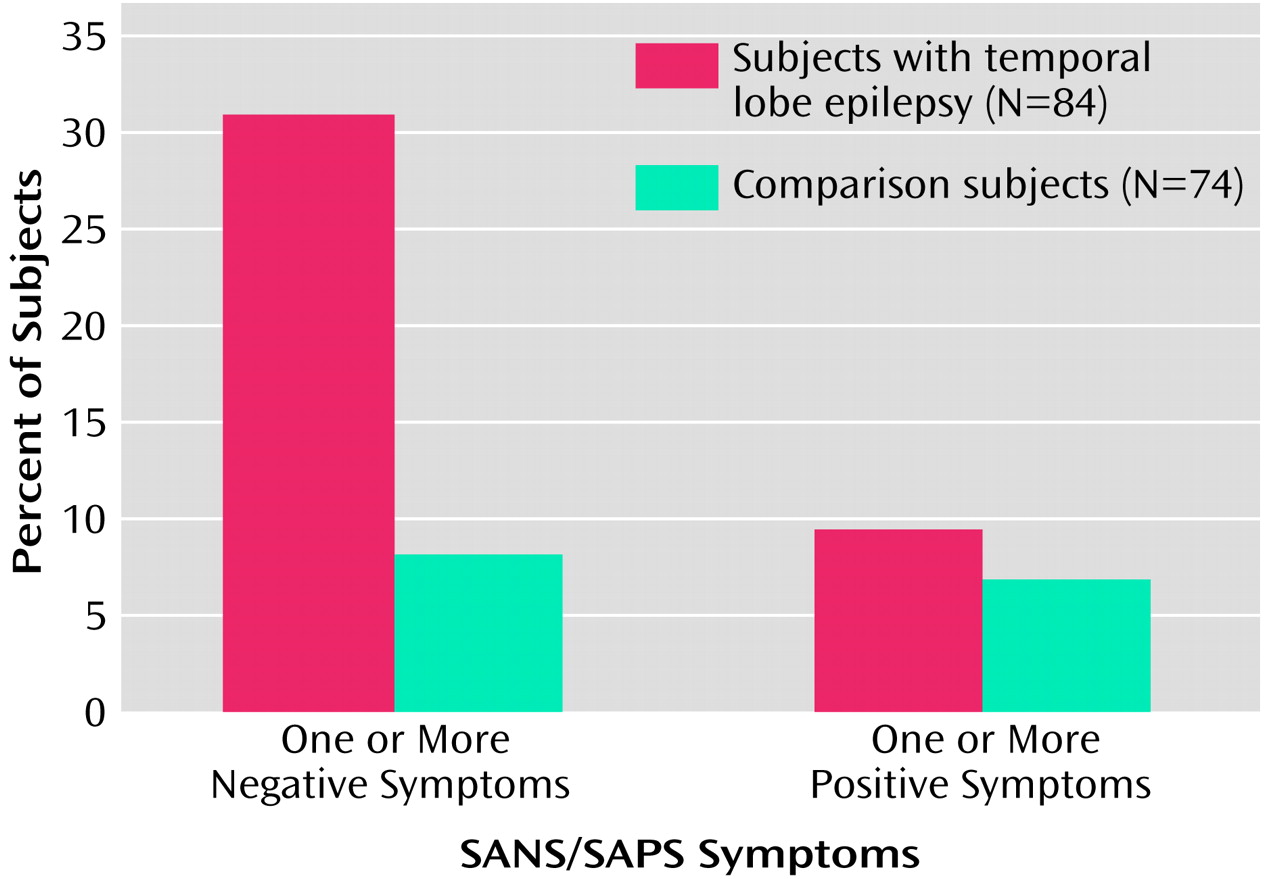
Negative and Positive Symptoms
Figure 1 shows the percentages of subjects exhibiting negative and positive symptoms in the temporal lobe epilepsy and comparison groups. A significantly greater proportion of epilepsy patients presented with one or more negative symptoms on the SANS (31.0% [N=26]), relative to the healthy comparison subjects (8.1% [N=6]) (χ
2=13.9, df=1, p<0.001). In contrast, there was no difference between groups in the proportion of subjects (9.5% [N=8] versus 6.8% [N=5]) exhibiting one or more positive symptoms on the SAPS (χ
2=0.39, df=1, p=0.53).
For subjects with a total SANS score greater than 0, the mean SANS total score for epilepsy patients was significantly higher (mean=9.5, SD=8.2, range=1–28) than for the comparison subjects (mean=2.3, SD=1.8, range=1–5) (t=2.1, df=30, p<0.05). Of the 23 epilepsy patients with one or more negative symptoms as per the SANS and no positive symptoms as per the SAPS, 15 (65%) presented with affective flattening, 14 (61%) with alogia, five (22%) with anhedonia, and four (17%) with apathy.
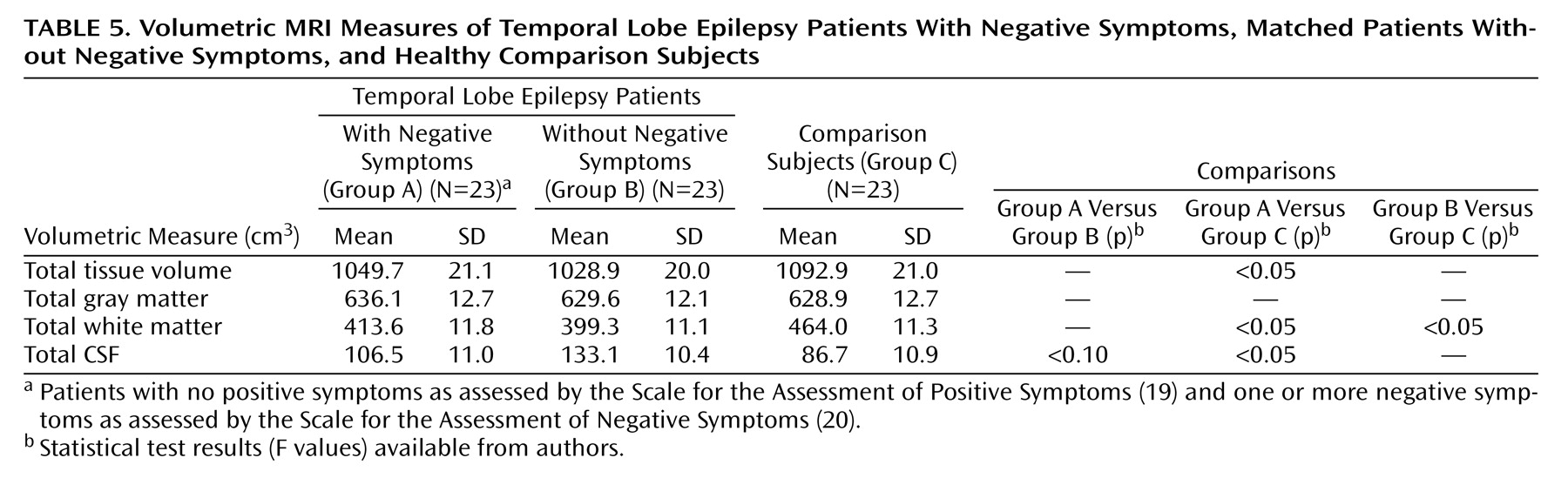
Cognition, Quantitative MRI Volumes, and Mood
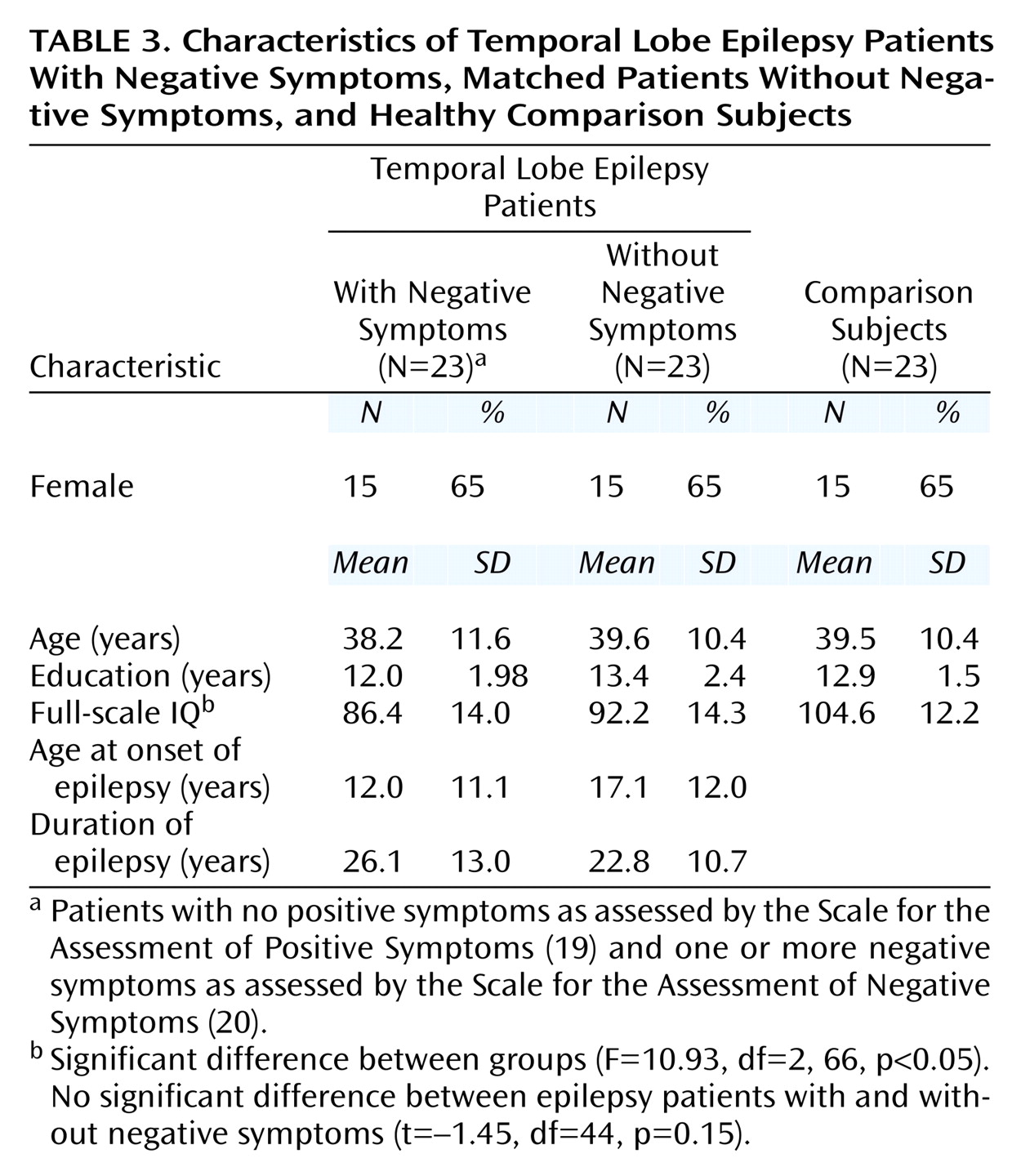
Of the 84 temporal lobe epilepsy patients, 26 received a score exceeding 0 on the SANS. Three patients in this group also received a rating of at least 1 on SAPS items representing positive or disorganized symptoms, and they were excluded to derive a temporal lobe epilepsy group with purely negative symptoms. These 23 patients with negative symptoms were matched on gender, age, and years of education with 23 epilepsy patients without negative symptoms and 23 healthy comparison subjects scoring 0 on all global ratings from the SANS/SAPS. The two patient groups were also matched on duration of epilepsy. There were no significant differences between the two epilepsy groups in full-scale IQ, although both had significantly lower full-scale IQ scores than the comparison subjects. Chi-square analyses found no differences between the two epilepsy groups in quantity of antiepileptic drug use (monotherapy versus polytherapy) (χ
2=0.04, df=1, p=0.85), presence or absence of initial precipitating insults (χ
2=0.56, df=1, p=0.46), or percentage of subjects with prescriptions for psychotropic medications (χ
2=0.39, df=1, p=0.53). One subject in each epilepsy group, with and without negative symptoms, had medication levels exceeding the normal therapeutic range; however, neither patient exhibited signs of clinical toxicity. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the two epilepsy groups and the matched comparison group are presented in
Table 3.
Neuropsychological status
Neuropsychological data were analyzed with a series of one-way analyses of variance (ANOVAs) or equivalent nonparametric tests for measures that demonstrated heterogeneity of variance.
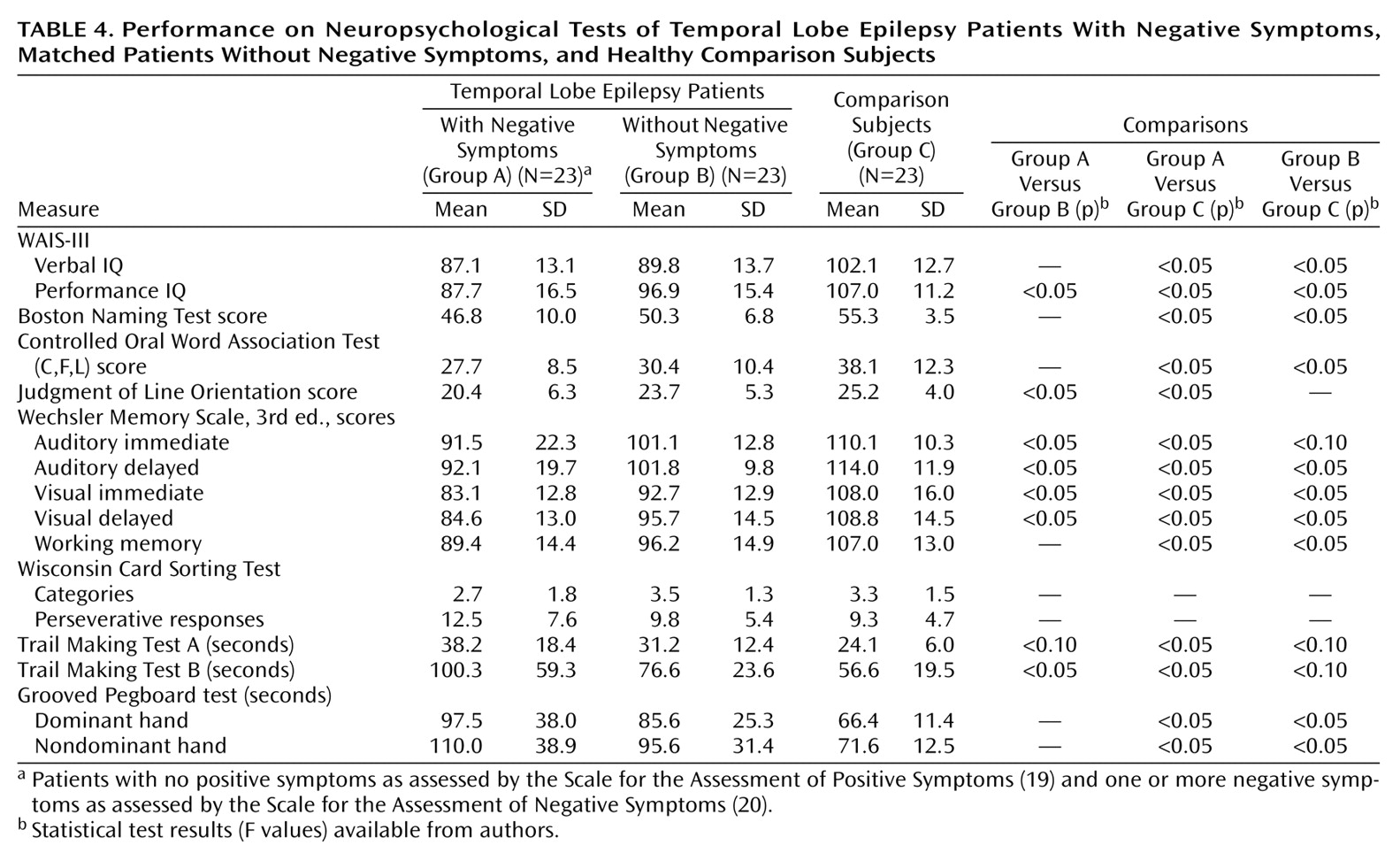
Table 4 provides the mean group scores on the cognitive tests for the epilepsy patients with and without negative symptoms and the healthy comparison subjects. ANOVAs were significant for all cognitive measures except the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. Subsequent pairwise comparisons demonstrated a significant effect of epilepsy on cognition. Both epilepsy groups had impaired performance, relative to the comparison group, across multiple neuropsychological measures. Specifically, the epilepsy patients with negative symptoms performed significantly worse than the comparison subjects on 14 of 16 cognitive measures, and the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms performed significantly worse than the comparison subjects on 10 of 16 measures, with differences on three additional measures approaching statistical significance (
Table 4). It is important to note that the epilepsy patients with negative symptoms performed significantly worse than the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms on seven measures, including tests of nonverbal intelligence, visuoperception, speeded visuomotor processing, and immediate and delayed declarative memory. When analyses were repeated by using the Beck Depression Inventory score as a covariate, only the result for Trail Making Test B and the Wechsler Memory Scale auditory immediate summary score dropped from statistical significance; however, differences remained across the remaining measures. Thus, the epilepsy patients with negative symptoms exhibited more pervasive cognitive deficits than the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms, independently of the severity of depressive symptoms, suggesting that additional cognitive morbidity was associated with the presence of negative symptoms.
Quantitative MRI Volumetric Data
MRI volumetric data were analyzed by using multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA), with age, gender and height as covariates. The overall MANCOVA was significant (Hotelling’s T, F=4.69, df=6, 82, p<0.05).
Table 5 shows the mean group brain tissue and CSF volumes for the temporal lobe epilepsy and healthy comparison groups. Subsequent pairwise comparisons demonstrated that MRI volumetric differences between the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms and the comparison subjects were restricted to a lower total white matter volume in the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms. However, the epilepsy patients with negative symptoms exhibited broader volumetric abnormalities relative to the comparison subjects, with significantly smaller total tissue and white matter volumes as well as a significantly higher total CSF volume. In addition, compared to the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms, the epilepsy patients with negative symptoms had a lower total CSF volume, but the difference did not reach significance. Reanalysis of MRI volumetric data with Beck Depression Inventory scores as a covariate did not alter the findings. Reanalysis of cognitive and MRI data with the number of epilepsy medications as a covariate did not alter the findings.
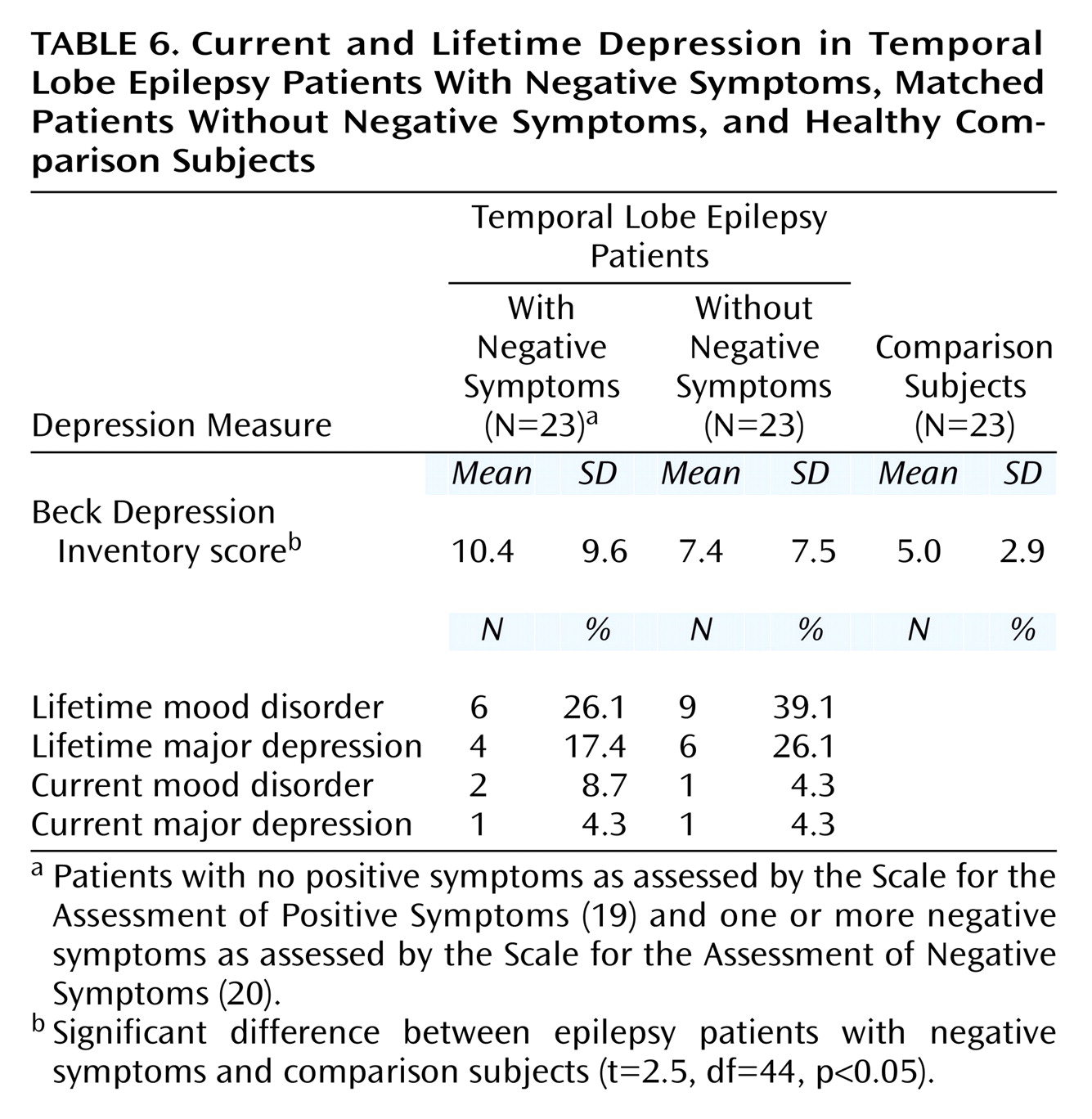
Depression
As shown in
Table 6, there was no significant difference between the two epilepsy groups in self-reported depression (Beck Depression Inventory), but the epilepsy patients with negative symptoms had a modestly higher mean Beck Depression Inventory score than the healthy comparison subjects (t=2.5, df=44, p<0.05), although the score was still not in the significantly depressed range. Further, the two temporal lobe epilepsy groups did not differ from each other in current or lifetime rate of mood disorders (χ
2=0.99, df=1, p=0.99) or major depression (χ
2=1.3, df=1, p=0.95) according to a standardized psychiatric interview (SCID). Further, none of the temporal lobe epilepsy patients was psychotic.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive investigation of the prevalence of interictal negative and positive symptoms in long-term temporal lobe epilepsy and their neuropsychological and MRI correlates. The results of this study demonstrate that negative, but not positive, symptoms occur at a higher rate in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy, relative to the rate in healthy comparison subjects. In addition, the presence of negative symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with neuropsychological deficits that exceed the cognitive morbidity associated with temporal lobe epilepsy in general. Finally, relative to healthy comparison subjects, patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and negative symptoms exhibited greater volumetric abnormalities than patients without negative symptoms.
Distribution of Negative and Positive Symptoms
Negative but not positive symptoms were more common in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (31%) than in healthy comparison subjects (8%). When negative symptoms were present, they were also more severe in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (mean SANS score=9.5) than in comparison subjects (mean=2.3). The elevated rate and severity of negative symptoms were detected in patients with long-term temporal lobe epilepsy who were nonpsychotic, suggesting that negative symptoms are not uncommon in this patient population. The presence and clinical implications of negative symptoms in patients with long-term temporal lobe epilepsy appear to have been overlooked.
Neuropsychological Correlates of Negative Symptoms
All subjects underwent comprehensive neuropsychological assessment, and, as expected, there were significant differences between the patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (with or without negative symptoms) and the healthy comparison subjects. The cognitive effects were relatively generalized in nature, evident across measures of intelligence, language, visuoperception, memory, aspects of executive functioning, and motor dexterity/speed. Although at first it may be surprising that patients with localization-related temporal lobe epilepsy exhibit relatively widespread cognitive dysfunction, this pattern has been reported previously in both children and adults with temporal lobe epilepsy
(34,
35).
However, additional cognitive morbidity was associated with the presence of negative symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy. Compared to the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms, the patients with negative symptoms were additionally impaired on tasks of nonverbal intelligence, visuoperception, speeded visuomotor processing, and memory. Thus, negative symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy appear to have functional implications beyond characterizing interictal behavioral features. Overall, these trends are consistent with reports in the literature on schizophrenia
(2,
3,
5). More generally, these findings suggest that the presence of negative symptoms may contribute to the heterogeneity of cognitive functioning evident in temporal lobe epilepsy.
Quantitative MRI Correlates of Negative Symptoms
Relative to healthy comparison subjects, quantitative MRI volumetrics demonstrated that temporal lobe epilepsy patients with negative symptoms exhibited significantly lower total (supratentorial) tissue volume, secondary to a significant lower volume of white but not gray matter tissue, coupled with a correspondingly significantly higher level of total CSF. In contrast, the epilepsy patients without negative symptoms exhibited more limited volumetric abnormalities, with lower total white matter volumes relative to healthy comparison subjects. These findings are consistent with schizophrenia research that has shown an association between negative symptoms and diffuse cortical atrophy
(36). This diffuse atrophy is also consistent with the neuropsychological findings described earlier, which were characterized by a pattern of generalized cognitive abnormality.
Negative Symptoms and Mood
Within the schizophrenia literature, some have debated whether negative symptoms and depressive symptoms are distinct constructs. Although depression is, in general, overrepresented among patients with epilepsy
(18), we found no differences between the temporal lobe epilepsy patients with and without negative symptoms in either current self-reported depression symptoms (Beck Depression Inventory) or current or lifetime major depression or mood disorders as assessed by standardized clinical interview (SCID). Thus, the higher rate and greater severity of negative symptoms among the epilepsy patients were not merely secondary to the effects of depressed mood. Further, none of the patients or comparison subjects was actively psychotic, suggesting that the higher rate and greater severity of negative symptoms were stable features of their interictal behavior.
Study Limitations
Limitations of these findings should be noted. First, the size of the study group was modest at the level of the subgroup comparisons, particularly for comparisons of the quantitative MRI volumetrics (N=16). It is possible that more structural brain abnormalities could have been identified in a larger group of patients. More detailed lobar parcellations could also reveal regional structural abnormalities associated with negative symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy.
Second, although the frequency and severity of negative symptoms were higher in the epilepsy patients, symptom severity was below that typically reported in schizophrenia. Whereas the temporal lobe epilepsy patients with negative symptoms in our study had a mean SANS total score of 9.5 (SD=8.2), schizophrenic patients have been found to present with mean SANS scores as high as 42.4 (SD=26)
(3). However, this finding was not unexpected, given that our study group consisted of nonpsychotic temporal lobe epilepsy patients. It is worth noting that the mean SANS total score observed in the temporal lobe epilepsy group was commensurate with findings in nonpsychotic stroke patients
(13).
The concept of negative symptoms has been developed and extensively investigated primarily in relation to schizophrenia. Some studies have suggested that the concept of negative symptoms may be productively applied to neurological populations (patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer’s type, Parkinson’s disease, or stroke [
13–
15,
37]), including patients with temporal lobe epilepsy, as we suggest here. Similar to findings in schizophrenia
(38), our findings suggest that negative symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy are predictive of cognitive impairment and diffuse brain abnormality. Nevertheless, additional studies are needed to critically address the predictive significance and validity of applying the construct of negative symptoms to patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and other neurological populations. If similar brain-behavior relationships result, they would suggest that the concept of negative symptoms represents a more ubiquitous construct that has utility beyond the investigation of schizophrenia.
Finally, it is known that rates of comorbid psychiatric conditions are higher among epilepsy patients with more difficult-to-control seizures who ultimately present to tertiary care centers or university-based clinics. Thus, the rate of negative symptoms in temporal lobe epilepsy reported here may exceed rates evident in community-based groups, but this remains to be determined.
Conclusions
Patients with long-term temporal lobe epilepsy exhibited a higher frequency and greater severity of interictal negative but not positive symptoms, relative to healthy comparison subjects. Negative symptoms were not associated with psychosis, current depressive symptoms, or history of mood disorders or major depression. Negative symptoms were also found to occur independently of a broad range of clinical epilepsy variables, including age at onset of recurrent seizures, duration of epilepsy, features of antiepilepsy drug use (monotherapy versus polytherapy), use of psychotropic medications, and presence of early initial precipitating injuries. As such, these findings suggest that a distinct subset of patients with long-term temporal lobe epilepsy present with negative symptoms as a stable feature of their interictal behavior. The presence of negative symptoms was found to have implications for cognition
(2) and brain structure
(38,
39). Negative symptoms were associated with cognitive morbidity beyond that associated with temporal lobe epilepsy, particularly in the areas of nonverbal intelligence, speeded cognitive processing, memory, and aspects of executive function. In addition, quantitative MRI volumetrics revealed that patients with negative symptoms exhibited more diffuse cerebral atrophy.
Long-term temporal lobe epilepsy is a disorder that is often but not inevitably associated with an increased risk of psychosocial complications, including unemployment, decreased social interaction, problematic independent living, and dependence on government support. We plan to investigate the broader social and functional consequences of negative symptoms. In addition, it remains to be determined whether there are features of the course or etiology of epilepsy that predispose patients to negative symptoms. A clearer characterization of the cause and consequence of negative symptoms will improve understanding of the interictal complications of temporal lobe epilepsy.