Cognitive impairment in patients with schizophrenia is ubiquitous and is considered to be core to the pathophysiology of the illness
(1). Reports of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia date back to the pioneering efforts of Kraepelin
(2) and Bleuler
(3), yet the course of these deficits over time is still unclear. Cognitive impairment has been found during the first episode of illness in schizophrenia
(4–
10), and there is evidence that these impairments continue into the chronic stages of the illness
(4,
7,
11,
12).
Moreover, several studies have reported cognitive deficits that significantly predate the onset of the illness. Jones and colleagues
(13) found that children from a 1946 birth cohort who later developed schizophrenia had lower mean scores on educational tests than did comparison subjects at ages 8, 11, and 15. The greatest deficits registered were in verbal, nonverbal, and mathematics tests, and the smallest deficits were in vocabulary and reading tests. Although cross-sectional in design, it appeared that these deficits worsened over time, with the strongest findings seen with the 15-year-old subjects.
Ambelas
(14) investigated childhood records of patients with schizophrenia who had been seen at a child guidance center and compared these records with those of children seen at the center who did not develop schizophrenia. The children who went on to develop schizophrenia had lower IQs and impaired performance in the areas of speech, language, and reading. These were children who had been seen at a child-care center and thus would have been exhibiting clinical symptoms or behavioral problems and therefore are special cases. Similarly, studies of “high-risk children,” i.e., the offspring of people with schizophrenia, have reported impairments in attention and memory
(15).
Two studies have investigated cognitive performance in large numbers of healthy male adolescents by using assessments obtained at the time of military conscription
(16,
17). Compared with subjects who did not develop psychiatric illness, the male subjects who were later diagnosed with schizophrenia had lower test scores with significant deficits in social functioning, organizational ability, and intellectual ability
(17). In addition, there was a linear relationship between risk of schizophrenia and intellectual functioning
(16,
17).
Although premorbid cognitive deficits in schizophrenia appear to be well documented, many questions still remain. For instance, to our knowledge no study to date has longitudinally evaluated premorbid cognition to assess its course over time. Also unanswered is whether these premorbid cognitive deficits are related to clinical measures of postonset illness, such as severity of symptoms or age at illness onset.
More than 30 years ago, the Department of Education at the University of Iowa pioneered the development of two standardized cognitive test batteries to be administered to all students in Iowa and many students nationwide. The Iowa Tests of Basic Skills
(18) are given to students in kindergarten through grade 8, and the Iowa Tests of Educational Development
(19) are given to students in grades 9 through 12. The purpose of the present study was to investigate premorbid cognitive functioning in patients with schizophrenia by examining their scores on these scholastic tests. The objectives of the study were to 1) document the extent and pattern of cognitive abilities; 2) assess the longitudinal course of cognitive abilities by evaluating change in scores over three periods (grades 4, 8, and 11); and 3) investigate the relationship between premorbid cognitive measures and “postmorbid” cognitive measures as well as positive, disorganized, and negative symptoms.
Method
Subjects
Subjects were 70 patients obtained from two different sources: admissions to the Mental Health Clinical Research Center and those who were participating in a prospective longitudinal study
(20). Subjects who were diagnosed with DSM-IV schizophrenia after a structured interview (the Comprehensive Assessment of Symptoms and History
[21]) were then asked if they had attended school during grades 4–11 in Iowa. Those who had were asked to provide written consent to allow release of their Iowa Tests of Basic Skills and Iowa Tests of Educational Development records. All subjects who were asked to release their scores agreed to do so. Fifty-seven were male, and 13 were female. The mean age of the patients at admission was 28.0 years (SD=6.9); the mean duration of illness was 7.8 years (SD=6.7).
The test scores for grades 4, 8, and 11 were then collected from the University of Iowa’s Department of Education and merged with demographic information and symptom ratings from the Mental Health Clinical Research Center. Data for 70 subjects with scores for at least one of the test years and Comprehensive Assessment of Symptoms and History data were used in the analyses.
Standardized Test Measures
State percentile ranks for the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills and the Iowa Tests of Educational Development were used in all analyses. The percentile rank reveals the student’s relative position or rank among a group of Iowa students who were in the same grade and who were tested at the same time of year. The state percentile ranks were used instead of the national percentile ranks so as to minimize confounds from curricular sequence, emphasis, and breadth of coverage. These curricular differences vary across the nation but are more homogeneous within the state of Iowa. Furthermore, students from the state of Iowa generally rank higher than the national average
(22).
Six educational domains were created by the Iowa Department of Education when designing the standardized test batteries to measure the academic skills of students. Because the state norms are supplied for these domains, it was deemed necessary and worthwhile to use the domains provided.
Vocabulary
The vocabulary domain of both the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills and the Iowa Tests of Educational Development provides a measure of reading vocabulary. Students read a target word in context and then select the word or phrase that most closely conveys the same meaning as the target word.
Reading comprehension
This test assesses how well students can comprehend written material. In the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills, the passages to be read vary in length from a few lines to a full page and consist of fiction, poetry, social studies, science, fables, interviews, biographies, and other nonfiction. Three levels of meaning are measured: factual, inferential, and evaluative. In the Iowa Tests of Educational Development, the passages are 275 to 700 words in length and consist of five levels of meaning: factual, inferential, nonliteral, generalizing themes and ideas, and recognizing literary techniques and tone.
Language
The language tests measure fundamental skills in the use of standard written English and do not directly measure the student’s ability to write well. The Iowa Tests of Basic Skills focuses on the student’s ability to apply the guidelines for spelling, capitalization, punctuation, and usage. Usage questions ask students to evaluate which of the proposed revisions would make the passage better organized, more focused, or complete. For the Iowa Tests of Educational Development, the six areas tested are spelling, capitalization and punctuation, usage and grammar, sentence structure, organization of ideas, and expression.
Mathematics
In the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills, the mathematics component consists of two sections. The first section involves concepts and estimations. The concepts assessed include number system and numeration theory, arithmetic, geometry, measurement, fraction/decimals/percents, probability/statistics, and equations/inequalities/number sentences. Estimations include estimates using rounding, order of magnitude, front-ending, compatible numbers, and compensation. The second section examines problem solving and data interpretation. The emphasis on solving multiple-step problems increases with test level. Data interpretation ranges from reading amounts to interpreting data from a graph or a table. The mathematics section in the Iowa Tests of Educational Development measures a student’s ability to solve quantitative problems and to use appropriate mathematical reasoning. The questions require ability to perform basic arithmetic, estimations, data interpretation, and logical thinking.
Sources of information
In the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills, this domain assesses a student’s ability to use maps, diagrams, and reference materials. The Iowa Tests of Educational Development evaluates a student’s ability to use books, dictionaries, encyclopedias, maps, government sources, and periodical guides.
Composite
The composite score for both the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills and the Iowa Tests of Educational Development represents the mean of the total scores for the domains of reading ([vocabulary + reading comprehension]/2), language, mathematics, and sources of information.
Symptoms and Cognitive Test Measures
Symptoms were assessed upon admission and scored by using the Comprehensive Assessment of Symptoms and History
(21). The symptoms were classified as disorganized (bizarre behavior, positive thought disorder, inappropriate affect), psychotic (hallucinations and delusions), or negative (alogia, flattened affect, anhedonia, avolition).
Cognitive assessment occurred during a subject’s intake hospitalization at the Mental Health Clinical Research Center. Patients were tested when they were clinically stable and able to participate fully. In many cases, this was after treatment with neuroleptic medications. Patients were administered a comprehensive battery of tests that typically took 4 hours to complete. The battery included the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test
(23), from which the immediate recall, delayed recall, and recognition scores were taken; the Rey-Osterreith Complex Figure Test
(24,
25), from which the copy, immediate recall, delayed recall, and saving scores were taken; the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
(12), from which the number of categories was taken; the Word Fluency Test
(26), from which the number of words generated in 3 minutes in response to the letters C, F, and L were taken; the Stroop Color and Word Test
(27), from which the interference score was taken; and the Grooved Pegboard Test
(28). In addition, general IQs were obtained by using the WAIS-R
(29).
Statistical Analysis
First, we looked at the mean percentile rank of the patients compared with the expected median population value in Iowa (i.e., the 50th percentile). Simple one-group F tests were used for this analysis and are reported as effect sizes (Cohen’s d).
Next, the data were analyzed by using a random regression model. This model was chosen because it allows for missing observations and gives estimations based on both the subject and group data
(30). Two models are presented. The first is an analog of a repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA), which tested whether there were differences among grades 4, 8, and 11. Another model was used to test for a simple linear decline in scores over time. Preliminary analyses indicated that a first-order auto-regressive model provided the best fit for our covariance structure and was used consistently.
There were 24 subjects with missing data for either 1 or 2 years, 16 of whom were missing data for the 11th grade. In order to assess the possibility that data were missing completely at random, demographic items from the Comprehensive Assessment of Symptoms and History for the group of patients with missing data were compared with those for two groups: 1) patients with no missing data, and 2) patients with scores for the 11th grade. These groups did not differ significantly in terms of level of education achieved, parental socioeconomic status, age at onset of illness, age at first outpatient care, age at first hospitalization, or premorbid adjustment scale score (for ages 6–12 or ages 13–21). There were no significant differences between the two groups for any of the scores on the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills for grades 4 or 8. These findings would support the notion that the data are missing completely at random.
In addition, we interviewed the faculty at the University of Iowa Department of Education about the process that led to missing data in their files. Much of the missing data throughout the state was produced by random events such as scheduling conflicts, lost records from entire schools, etc. These factors are unrelated to the subject and are not associated with the disorder that the child would face later in life. Thus, we feel comfortable that the data are missing completely at random.
Preliminary investigation revealed that there were no significant differences between male and female subjects on any of the test scores. Therefore, the male and female subjects were treated as one group throughout the analyses. Preliminary investigation also revealed that there were no significant differences between test scores of patients with illness onset before age 20 compared with those with illness onset at age 20 or older.
Pearson’s correlations were used to assess associations between variables from the standardized tests and the symptom ratings from the Comprehensive Assessment of Symptoms and History as well as neuropsychological data.
Results
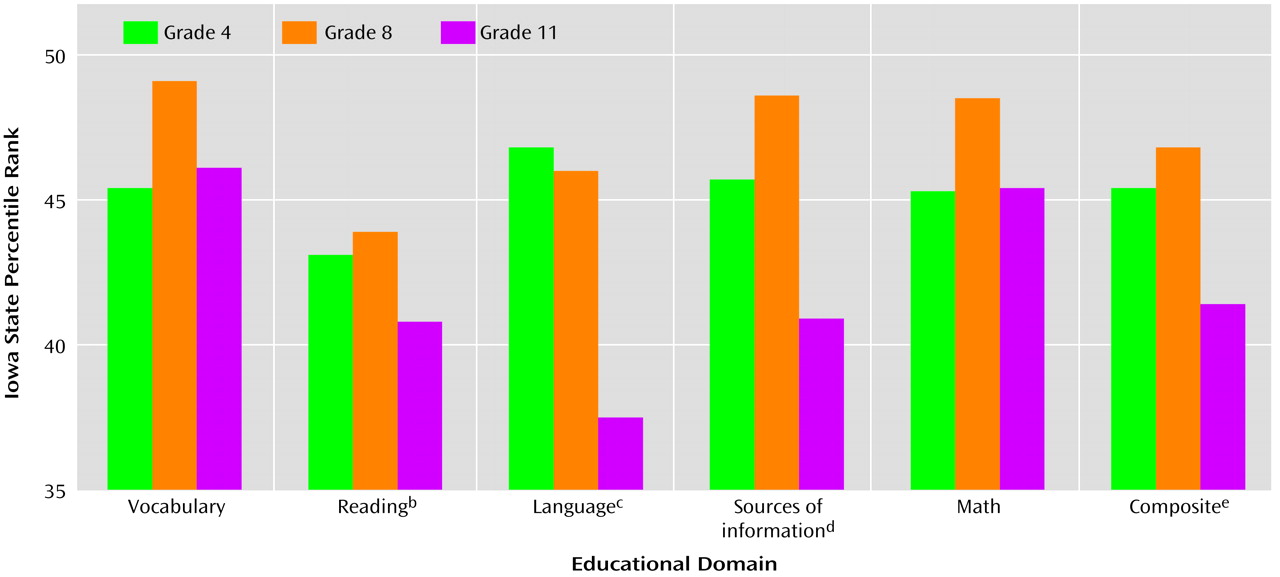
The subjects’ mean percentile rank on the domains of the scholastic standardized tests for grades 4, 8, and 11 appear in
Figure 1. In a purely descriptive manner, it is evident that these children who later developed schizophrenia fell below the state norms on every category for all three grades.
Analysis of differences between the median percentile rank of the state population of Iowa and the mean percentile rank of our patient group revealed that the patients’ 4th and 8th grade scores did not significantly differ from state norms for any of the variables. This suggests that in grades 4 and 8, the patients were not significantly below average for any of the categories tested on the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills. However, as seen in
Figure 1, the grade 11 scores of the patients were significantly below the median percentile rank for reading, language, sources of information, and composite scores. The effect sizes for these differences in reading (d=0.36), language (d=0.41), sources of information (d=0.35), and composite (d=0.32) scores were just below a “medium” effect (d=0.50) in Cohen’s terms. The mean scores for these domains were 9.2 (SD=30.1), 12.4 (SD=29.8), 9.1 (SD=31.7), and 8.6 (SD=29.9) percentiles below average, respectively.
In addition, within the patient group there was a significant difference among the three grades for the language and sources of information scores (
Figure 1). Further analyses of these data revealed that the sources of information scores did not differ significantly between grades 4 and 8 or between grades 4 and 11, but the scores for grade 11 were significantly lower than those for grade 8. For the language scores, there was no significant difference in scores between grades 4 and 8, but the grade 11 scores were significantly lower than those of both grade 4 and grade 8.
Finally, there was a significant linear decline in language scores across time (F=5.71, df=1, 108, p<0.04). This means that the language scores in grades 4, 8, and 11 became steadily worse.
Since none of the scores from grades 4 or 8 significantly differed from state norms, only the grade 11 scores from the Iowa Tests of Educational Development were used in the correlations with symptom and neuropsychological data. Because of the conservative nature of Bonferroni corrections, these were not used to adjust for the number of correlations. Instead, only those correlations significant at the 0.01 level or below will be discussed.
There were no significant correlations between Iowa Tests of Educational Development domain scores and age at onset of illness (r=0.06 to 0.26) or ratings of disorganized (r=0.07 to 0.24), psychotic (r=–0.04 to –0.22), or negative (r=–0.02 to –0.15) symptoms at the time of hospital admission.
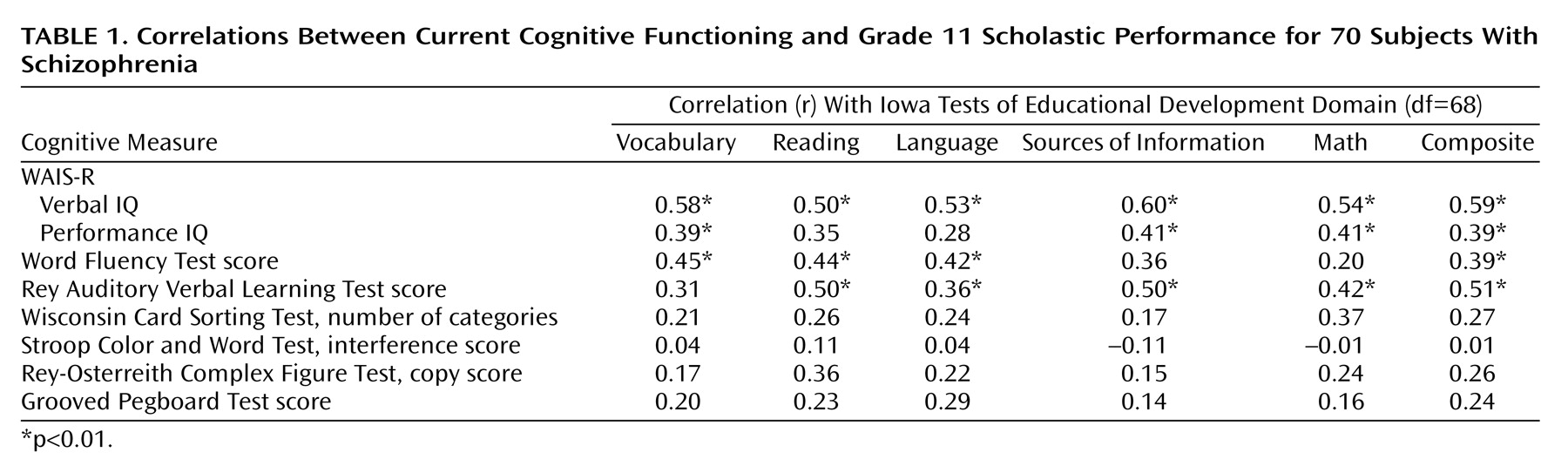
The results of the Pearson’s correlations between the neuropsychological tests carried out at the Mental Health Clinical Research Center following the onset of schizophrenia and grade 11 scores on the Iowa Tests of Educational Development are presented in
Table 1. There was a significant positive correlation between the scores for each domain and WAIS-R verbal IQ and between the scores for each domain (except language and reading) and WAIS-R performance IQ. There was a significant positive correlation between Word Fluency performance and the vocabulary, reading, language, and composite scores. This means that higher scores on the Iowa Tests of Educational Development were associated with a greater number of words produced in 60 seconds. There was a significant positive correlation between performance on the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test and all domain scores except vocabulary. This means that higher standardized test scores were related to a greater number of words correctly recalled across all trials. There were no significant correlations between Iowa Tests of Educational Development scores at grade 11 and performance on any other neuropsychological test.
Discussion
The results of this study provide evidence in support of previous findings that children who later develop schizophrenia manifest intellectual differences from peers before illness onset. These results are unique in that the patient groups included both male and female subjects, the premorbid scores were prospective and longitudinal (reflecting the childhood and adolescent stages of their lives), and multiple areas of knowledge were examined instead of using a general “intelligence” score.
For each domain of the scholastic standardized tests at each grade, the mean percentile rank for the children who later developed schizophrenia was below the 50th percentile (median state rank). However, these scores were not statistically significantly below average at grades 4 or 8. It was not until grade 11 that scores for patients fell significantly below Iowa state norms. Moreover, although the grade 11 composite score was significantly lower than the norm, some areas of cognitive functioning were more severely impaired than others. For example, grade 11 vocabulary and mathematics scores were not significantly below state norms.
Closer inspection of the pattern of scores over time reveals that in every category except language, there was actually an increase in scores in the interval between grades 4 and 8. Then, in the next interval between grades 8 and 11, four of the six measures (including composite scores) precipitously dropped to below the scores obtained in grade 4 and significantly below the state norm. Grade 8 language scores were only slightly below those of grade 4 but are unique in that they did not follow the pattern of increasing by grade 8. It is this pattern for the language scores that manifested as a statistically significant linear decline over time.
The current findings provide evidence that cognitive impairment is present before symptom onset in subjects who later develop schizophrenia. A drop in scores from grade 8 to grade 11 is not normally seen in the Iowa standardized test scores. The tests are designed so that an individual’s scores from 1 year will predict any other year. While it is true that any child can have an “off year” and decline more than would be expected, the significant decline in the scores of the students who later develop schizophrenia suggests more than just an off year. For the children who later developed schizophrenia, something was occurring between the ages of 13 (8th grade) and 16 (11th grade) that led to cognitive decline.
Of course, one thing that is occurring between ages 13 and 16 for many subjects is adolescence. This is by no means a coincidence, as more and more evidence suggests that adolescence is a time of robust structural and functional brain changes. Moreover, these changes may underlie the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Several studies have provided evidence for a process of “pruning” in which excess or nonuseful neural connections are trimmed, leading to a decrease over time in synaptic density
(31,
32), glucose metabolism
(33), and cortical gray matter volume
(34). Feinberg
(35) was the first to suggest that schizophrenia could be due to abnormal pruning. A longitudinal study of childhood-onset schizophrenia has shown that the “normal” decrease in cortical gray matter over the ages 13–17 (seen in healthy comparison subjects) was four times greater in the patient group, leading to a significant decrement in regional cortical volume, which suggests an “overpruning”
(36). These brain changes are documented for the same period of time in which the current study shows a significant academic decline, indicating that “overpruning” of the cortex may be directly related to changes in cognitive function.
One interpretation of the current findings is that the cognitive deficits seen in the 11th grade may be due to “prodrome” or early phase of the illness rather than true premorbid deficit. However, there was no correlation between age at illness onset and scores on the Iowa Tests of Educational Development. This suggests that patients with lower scores were not necessarily closer to illness onset than patients with higher scores and supports the notion that the cognitive deficits are truly premorbid rather than prodromal or early illness. On the other hand, the distinction among premorbid, prodrome, and early illness may be artificial. The current study suggests that specific cognitive functions such as language slowly decline over time beginning in childhood. If this suggestion is correct, then the definition of illness onset becomes decidedly more complex.
The cognitive impairment seen after the diagnosis of schizophrenia is made appears to be much stronger than the premorbid cognitive deficit seen with scholastic standardized test results. The decline in language may be the first impairment to surface, and other cognitive abilities may decrease between the mid-to-late teens and the onset of psychosis. Another possibility is that the cognitive impairment seen in the first episode of schizophrenia is different from that examined by scholastic aptitude tests. Scores on the Iowa Tests of Educational Development were associated with WAIS-R verbal and performance IQs, but they were not significantly associated with all of the neuropsychological test results. Scholastic cognition may be different from neuropsychological cognition. It is likely that the cognitive domains such as reasoning and abstraction (Wisconsin Card Sorting Test), visuospatial skills (Rey-Osterreith Complex Figure Test), and inhibition (Stroop Color and Word Test) are using different cognitive skills than those used in language expression, sources of information, or reading.
One limitation of this study is the small size. There were only 70 participants with schizophrenia to compare with state norms. A second shortcoming was the lack of highly significant results. The power to detect effects, given the study group size, may not be extremely high. Power considerations only apply to negative effects. Not all our findings proved significant, but a substantial amount of significant results exists, suggesting that something is not normal in premorbid cognitive functioning in subjects who later develop schizophrenia. Further data collection for a larger patient group is currently underway.
A third limitation is that our group of patients was not a random sample. The group was a select group of individuals who developed schizophrenia in adulthood. There may be a number of factors associated with our group of children that may make them nonrepresentative, including socioeconomic status, season of birth, family history, low birth weight, etc. Since schizophrenia is likely a disease with heterogeneous etiology, it may be impossible to produce a truly matched comparison group.
Although the results of the current study provide evidence of premorbid cognitive impairment in individuals with schizophrenia, some students who went on to develop schizophrenia scored in the 90th percentile or above. Thus, not all patients diagnosed with schizophrenia show premorbid cognitive impairment, just as not all children whose standardized tests scores decline in grade 11 are destined to develop schizophrenia.
This initial investigation has provided evidence that examining scholastic achievement tests is a worthwhile investigative measure of premorbid cognitive functioning in patients with schizophrenia. Future studies are needed to explore a more fine-grained evaluation of scores between grades 8 and 11, to examine the relationship between scores and structural and functional brain measures, and to determine whether an aggregate of measures can be used to identify high-risk children who will ultimately develop schizophrenia.