The past decade has seen rapid advances in our knowledge of the pharmacotherapy of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) affecting children and adolescents. Intramural studies from the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) demonstrating the efficacy of clomipramine first appeared in the mid-1980s, although clomipramine, the first agent approved for use in pediatric populations with OCD, did not gain the approval of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) until 1989. Subsequent multisite randomized, placebo-controlled trials, many of which were industry sponsored, have also demonstrated significant efficacy in pediatric populations of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), including sertraline
(1), fluvoxamine
(2), fluoxetine
(3), and paroxetine
(4). These studies represented a major advance in the management of pediatric OCD and usefully informed clinicians who treat affected children. However, to our knowledge, no comparative treatment studies have been performed, and there is little to guide clinicians in their choices between therapeutic agents.
The conventional wisdom that all serotonin reuptake inhibitors (including clomipramine) are more or less comparably effective for children with OCD has not been investigated. Evidence of differential efficacy could, however, have important implications for patient care or for a potential commercial advantage for a drug manufacturer. In fact, evidence from several meta-analytic reviews of randomized, controlled trials of treatment for OCD in adults has suggested that, in placebo-controlled trials, clomipramine appears to be more effective than drugs with more selective serotonin uptake inhibition
(5,
6). Since children generally have a response to antiobsessional treatments similar to that of adults, it is possible that the findings of the superiority of clomipramine will also hold true in pediatric samples with OCD.
While the randomized, controlled trial has been considered the gold standard for evaluating the effects of medical interventions for decades, its significance relies on numerous factors (such as power, magnitude of observed differences, reliability of diagnosis and assessment, variability of outcome, study design, and participant inclusion and exclusion criteria, to name a few)
(6,
7). For example, some, but not all, psychometric measures of OCD severity have shown response to change with treatment in children
(8–
10). In the literature on OCD in children, both the number of randomized, controlled trials and the number of study participants do not approach those in the adult OCD literature, perhaps due to the special considerations of conducting trials involving minors
(11,
12). Underscoring this difference, the FDA requires evidence of efficacy in at least two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies to consider approval of a novel antidepressant in adults but has required only one well-conducted multisite trial demonstrating efficacy for the three agents with a current FDA indication for pediatric OCD: sertraline
(1), fluvoxamine
(2), and fluoxetine
(3).
Despite this limitation, the cumulative data accrued from randomized, controlled trials of pediatric OCD over the last 10 years, which have involved more than 1,000 youths, are now sufficient to examine the overall effect of medication treatment in this population. Quantitative meta-analysis provides a method for examining pooled effects of several studies. In this method, the result of any one randomized, controlled trial is a single data point in a population of study results. We conducted a meta-analysis to determine the pooled effect size of medication treatment versus placebo, as reported in the extant pediatric OCD literature, while examining for heterogeneity of studies and publication bias. In addition, we compared study designs, sensitivity of dependent measures, and data for individual drugs for significant differences. We hypothesized that clomipramine might show superiority over the SSRIs for treatment of pediatric OCD. To our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis undertaken for treatment studies of OCD or of SSRIs in pediatric subjects.
Method
A systematic literature review was performed for articles pertaining to the pharmacological treatment of pediatric and/or adolescent OCD. Eligible studies were identified through a search of journal abstracts in the MEDLINE and PsycINFO databases from the year 1900 to the present. Search terms included “obsessive compulsive disorder,” “clinical trial,” and “randomized controlled trial.” The search was limited to English-language articles describing studies with human subjects in child and adolescent age ranges. In addition, citations from all identified articles were individually searched in iterative fashion for any relevant studies. Studies were excluded on the basis of being open-label (three studies of fluoxetine, one study of fluvoxamine, one study of paroxetine, and one study of citalopram) or retrospective (one study of fluoxetine). To be included in this meta-analysis, studies had to be 1) randomized, 2) double-blind, 3) placebo- or active-comparator-controlled, and 4) limited to pediatric trials (subjects were age 19 years or younger). The results from one double-blind study
(13) had been previously reported by Riddle et al.
(10) and were excluded. We also excluded the study by Kurlan et al.
(14), a randomized, controlled trial of fluoxetine for obsessive-compulsive symptoms in 11 boys with Tourette’s disorder because the study included an unknown number of subjects who did not meet the full DSM criteria for OCD. The results of a recent large multisite study of paroxetine for treatment of pediatric OCD, which have been published in abstract form in the proceedings from the 2002 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association
(4) (full manuscript in preparation), were included.
For each study all dependent outcome measures reported were treated as a separate data point for entry into the analysis, with several studies providing data on more than one measure, to permit comparison between measures as well as between drugs in this population. Outcome measures included the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale
(8), the NIMH Global OCD Scale
(15), the Clinical Global Impression (CGI) of severity of illness
(16), and the Leyton Obsessional Inventory—Child Version
(17). All baseline, posttreatment, and change scores with standard deviations reported in each study were included in our analyses. Scores and standard deviations from the multisite clomipramine study
(18) were supplied by Richard Katz of the neuroscience department at Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. In some studies, standard deviations for mean change scores were not reported, and in these cases we used posttreatment scores in our analyses after determining that baseline scores were not significantly different between groups.
Statistical Analyses
Effect sizes for each dependent measure in each study were expressed as standardized mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and a pooled standardized mean difference was thus calculated for the results of all studies. The standardized mean difference is computed by taking the mean of the active drug group minus the mean of the placebo group and dividing the result by the pooled standard deviation of the groups. Studies were weighted according to the number of participants. The meta-analysis used the random effects model of DerSimonian and Laird
(19). To determine if the results of the meta-analysis were unduly influenced by any one study, we conducted a sensitivity analysis by recomputing the pooled standardized mean difference after deleting each study one at a time. We also evaluated whether these studies might be nonrepresentative of the universe of possible studies, for example, as a result of failure to publish studies that produce negative results (“publication bias”). To address this possibility, we used the method of Egger et al.
(20),
in which the standard normal deviate of the standardized mean difference is regressed on the “precision of the standardized mean difference,” defined as the inverse of the standard error of the standardized mean difference. Since precision of the standardized mean difference increases with sample size, the regression of the standard normal deviate on the precision of the standardized mean difference should have a positive slope and should run through the origin in the absence of bias (i.e., small samples with low precision have large standard errors and small standard normal deviates, whereas large samples with high precision have small standard errors and large standard normal deviates). In the presence of bias, the intercept of the regression (a) will be significantly greater than zero, as determined by the t test.
To assess the robustness of our meta-analysis, given the possibility of publication bias, we computed the fail-safe N, which is the number of studies with negative findings that would need to be combined with the studies reviewed to lead to a nonsignificant result. The larger the fail-safe N, the less likely it is that unpublished studies or future studies would overturn our result
(21).
Our meta-analysis used multiple regression to assess the degree to which the effect sizes varied with the methodological features of each study. Four covariates were used in this regression model: 1) type of dependent outcome measure, 2) type of drug, 3) type of study design, and 4) type of outcome score (change or posttreatment score). Where significant differences emerged in the omnibus analysis, pairwise comparisons were undertaken with other significant variables controlled.
Results
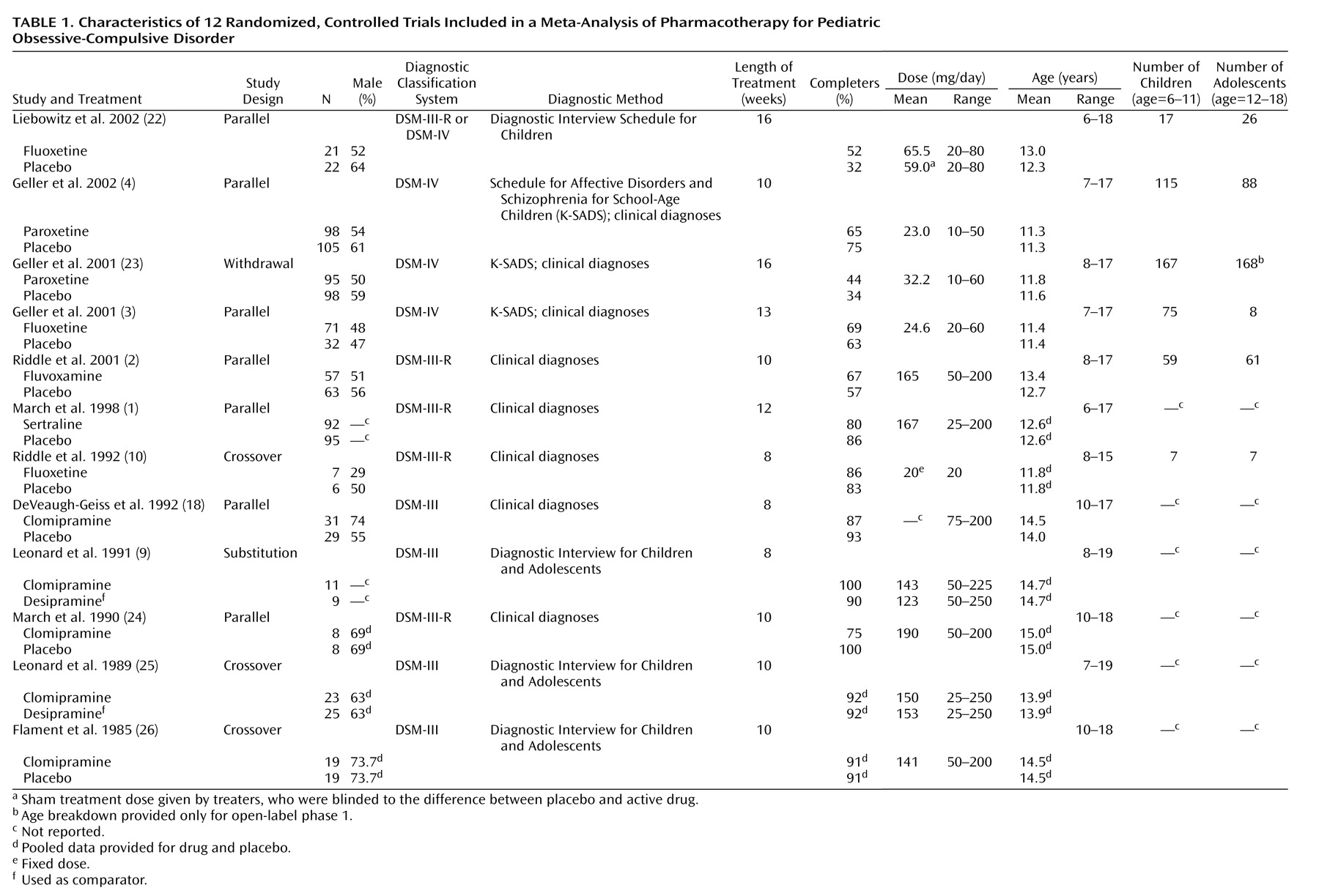
Twelve studies that included 1,044 participants met all inclusion criteria and were analyzed
(1–
4,
9,
10,
18,
22–26). Represented in the studies are four SSRIs (paroxetine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, and sertraline) and clomipramine; four study designs (parallel, withdrawal, substitution, and crossover); four dependent outcome measures (Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale, NIMH Global OCD Scale, CGI of severity, and Leyton Obsessional Inventory—Child Version); and two types of outcome scores (change and posttreatment). Study characteristics are shown in
Table 1.
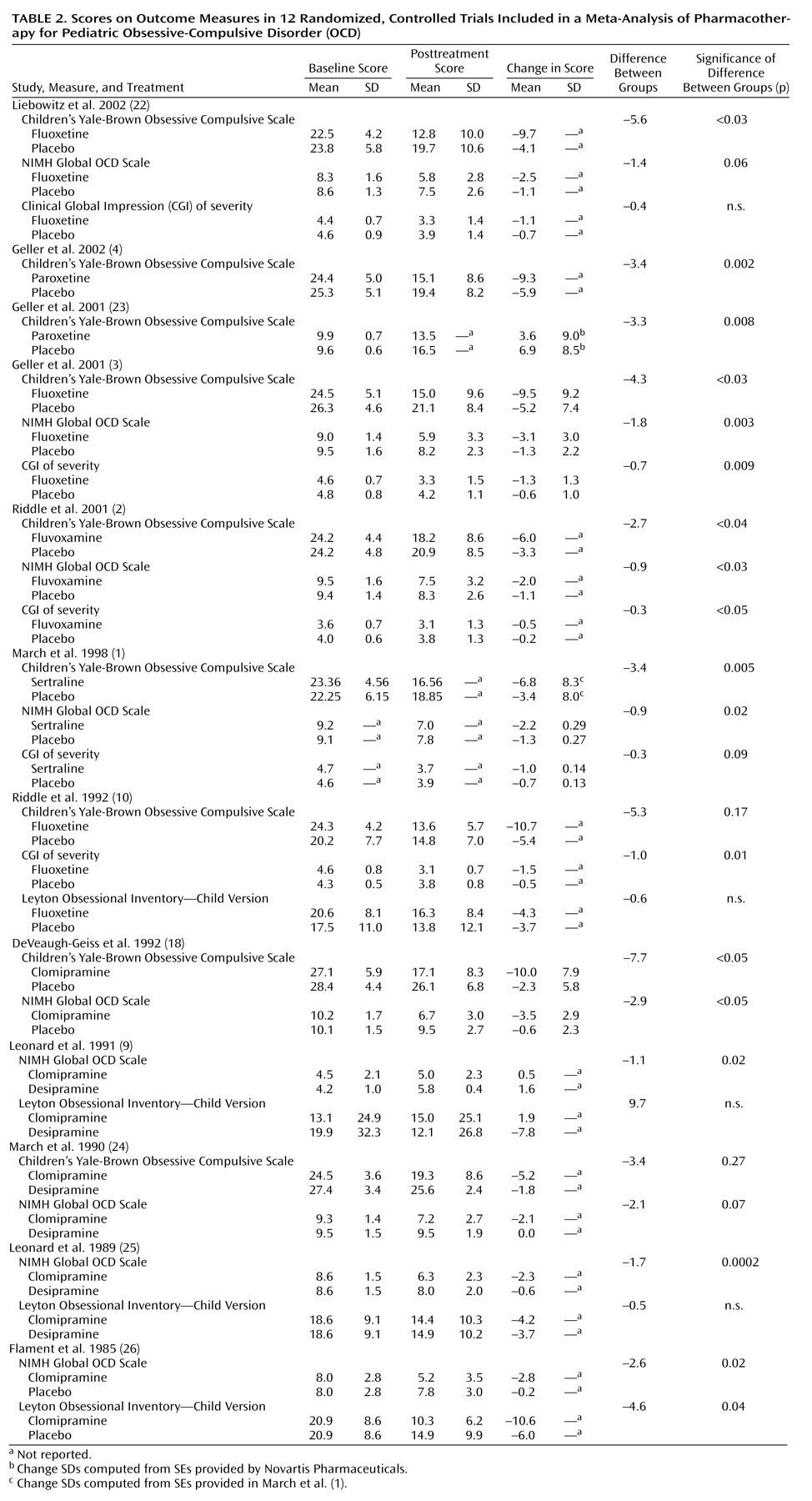
The findings from the individual studies that constitute the raw data for our analyses are shown in
Table 2.
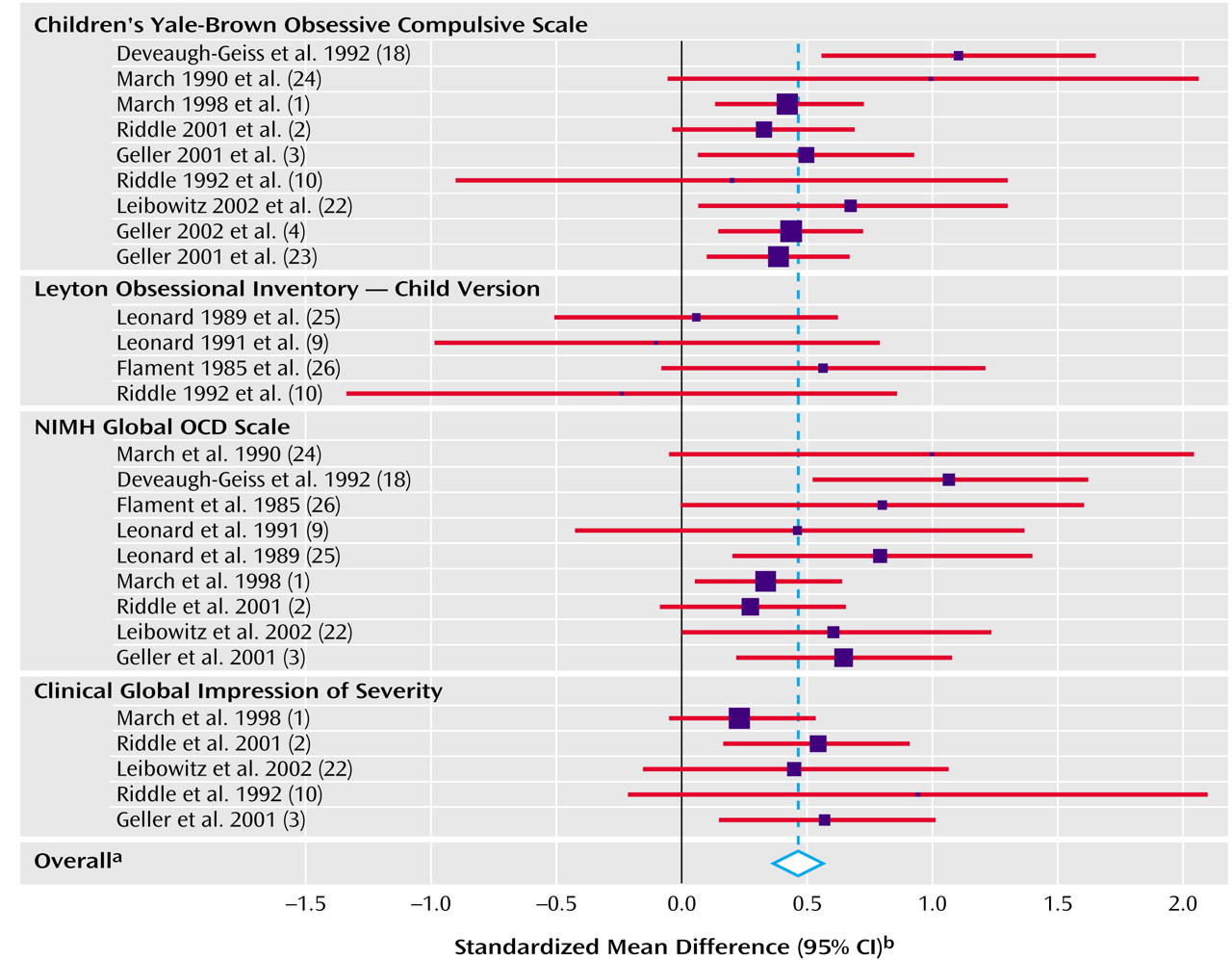
The pooled standardized mean difference across all observations was 0.46 (95% CI=0.37 to 0.55). This pooled standardized mean difference indicated a highly significant difference between drug and placebo treatment (z=9.87, p<0.001). We computed the fail-safe N to be 973. The test for heterogeneity of the standardized mean difference among the observations was not significant (χ
2=27.4, df=26, p=0.39). A graphic representation of these findings is shown as a Forest plot in
Figure 1.
The sensitivity analysis found that no single study accounted for the statistically significant pooled standardized mean difference; after deleting one study at a time, the pooled standardized mean difference remained statistically significant and was never less than 0.35. Egger’s test for publication bias had a positive slope and did not show significant bias since the confidence interval of the y axis intercept (a) included zero (t=1.73, df=26, p=0.10, CI=–0.15 to 1.77). Our meta-analysis regression model found no significant differences between study designs (χ2=1.89, df=3, p=0.60) or between posttreatment and change scores (χ2=0.01, df=1, p=0.91). The regression analyses did find a significant effect of type of outcome measure (χ2=11.65, df=3, p=0.009). We found significant pooled standardized mean differences for the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (standardized mean difference=0.47, 95% CI=0.33 to 0.60, z=6.81, p<0.001), the NIMH Global OCD Scale (standardized mean difference=0.56, 95% CI=0.37 to 0.75, z=5.77, p<0.001), and the CGI of severity (standardized mean difference=0.42, 95% CI=0.23 to 0.61, z=4.38, p<0.001). Each of these measures showed robust sensitivity to change with treatment. However, the Leyton Obsessional Inventory—Child Version was not sensitive to overall change in the pooled outcomes (standardized mean difference=0.15, 95% CI=–0.21 to 0.51, z=0.80, p=0.42). In pairwise comparisons the pooled standardized mean difference for the Leyton Obsessional Inventory—Child Version was significantly different from the pooled standardized mean difference for each of the other dependent measures (p<0.01 for all comparisons, multivariate regression meta-analysis).
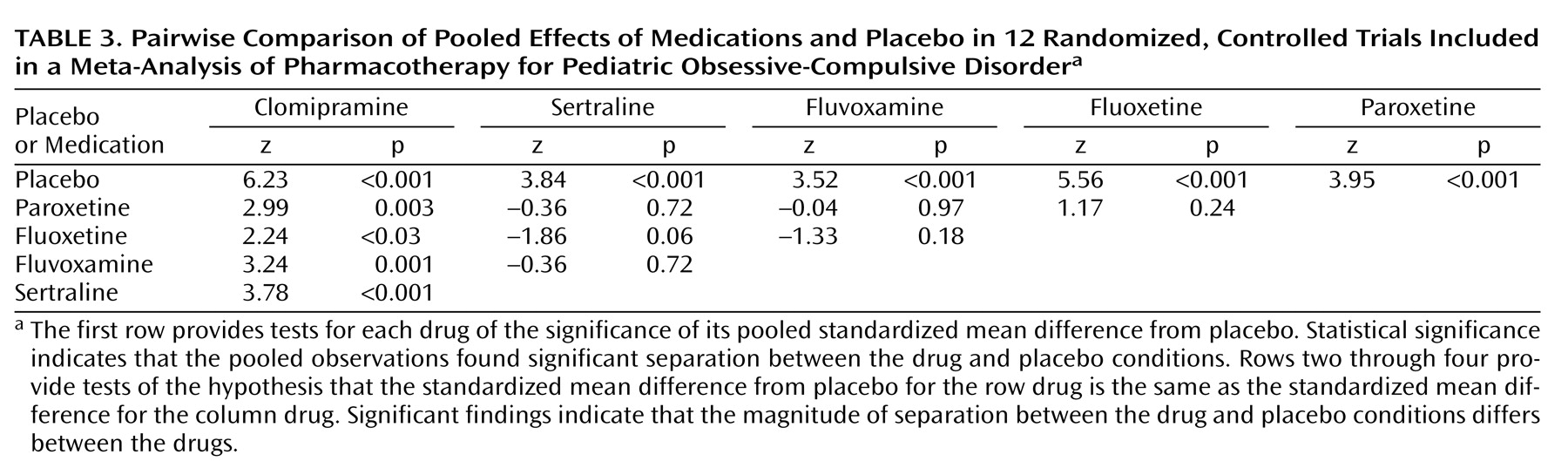
The pooled effect of each drug individually against placebo with the dependent measures controlled was highly significant (each p<0.001, test of standardized mean difference). The fail-safe Ns were 10 for paroxetine, 73 for fluoxetine, 11 for fluvoxamine, 14 for sertraline, and 120 for clomipramine. Multivariate regression meta-analysis of the drug effect with other variables controlled showed overall significance (χ
2=16.5, df=4, p=0.002), and subsequent pairwise comparisons showed that the pooled standardized mean difference for clomipramine was significantly greater than that of the other drugs (p=0.002, chi-square test), which did not differ from one another. The z scores and p values for each drug, pooled for all studies that used that drug, compared with placebo and with each other are shown in
Table 3.
Although we found significant effects for both the drug measure and the outcome measure, we did not find a statistically significant association between type of drug and type of outcome score (p=0.50, Fisher’s exact test). The year of study did not significantly predict the effect size (z=–1.29, p=0.20). Further, the drug effects remained significant when the year of the study was controlled (χ2=9.63, df=26, p<0.05). We examined whether the apparent superiority of clomipramine was an artifact of increasing placebo response rates over time and found no association between the year of the study and percent improvement in the placebo group (t=0.45, df=20, p=0.67). For each study we computed an odds ratio to assess the association between treatment group (drug versus placebo) and status (completer versus dropout). In each study, none of the odds ratios were significant, as indicated by their 95% confidence intervals, which included 1.0. By using meta-analysis, the pooled odds ratio across studies was 1.0, indicating no association (z=0.3, p=0.80).
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis of randomized, controlled pharmacological trials of serotonin reuptake inhibitors for treatment of OCD in children and adolescents. We found highly significant pooled effects of medication versus placebo, as well as important similarities and differences between individual drugs and differential sensitivity of quantitative measures of severity to change. An overall effect size of 0.46 equaling a difference in score of about 4 points on the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale between active and placebo treatments was found in the pooled studies, while each drug examined individually was significantly better than placebo or comparator treatments. Although differing study designs and types of change score all permitted discrimination of drug and placebo effect equally well, not all dependent measures were equally sensitive to change. Specifically, the Leyton Obsessional Inventory—Child Version alone did not show significant change with treatment, even in studies where the other scales that were used showed significant change. Finally we found that clomipramine had significantly greater effect than the other more selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in reducing OCD symptoms.
A finding that is consistent across multiple dependent measures, study designs, and different agents is more convincing than an isolated statistical effect. Our meta-analytic findings should confirm support for a role for pharmacotherapy with serotonin reuptake inhibitors in pediatric OCD patients, including preadolescent children. It is reassuring that the various study designs, which included different diagnostic classifications, diagnostic methods, and types of outcome measures, reliably and comparably separated active from placebo conditions. However, not all of the characteristics of the randomized, controlled trials that we studied fared equally well. As we have indicated, the sensitivity of the trials to drug-placebo differences was influenced by two factors: type of drug and type of outcome measure. Our findings suggest that the Leyton Obsessional Inventory—Child Version should not be used as an instrument to measure change in severity of symptoms with treatment, although it may be useful in other ways.
Although not part of our analysis, subject selection criteria may also profoundly influence outcome and are important factors in weighing the results of any study. Most of the randomized, controlled trials examined here used numerous exclusion criteria to select their samples in order to achieve homogeneous cohorts not confounded by comorbid disorders. For example, all the studies included in the analysis excluded subjects with a primary diagnosis of major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, psychosis, Tourette’s disorder, autism, eating disorders, and substance use disorders. Most studies also excluded subjects with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and no studies permitted concurrent cognitive behavior therapy or other medications. Although these exclusions may be reasonable given the purpose of these studies, whether the results obtained from these randomized, controlled medication trials apply equally to naturalistic clinical samples remains unknown. For example, several studies have suggested that treatment outcome in OCD patients may be poorer in those with comorbid tic disorders
(27,
28). As such, well-designed treatment trials that take into account the common comorbid disorders that are prevalent in children with OCD are very much needed
(23).
Although the power of pooled studies allows us to demonstrate that the effects of medication over placebo are highly significant, the magnitude of these observed effects in this analysis is nevertheless modest overall. These findings can inform researchers in design of prospective studies, including the number of participants required for sufficient power to discriminate between treatments as well as the standard against which to compare efficacy of novel treatments. From a clinical standpoint, the modest effect of medication suggests a real need for ongoing efforts at finding novel agents or augmenting strategies and evaluating the combined effects of behavioral and pharmacological treatments.
Despite our finding that clomipramine showed superiority over the SSRIs, it does not follow that clomipramine should be recommended as a treatment of first choice in pediatric OCD patients, due to frequent adverse events
(18) and concerns about monitoring potential arrhythmogenic effects
(29–
31). Clomipramine is less user friendly for children than the SSRIs, for which EKG and monitoring of blood levels are not routinely required, and it is usually not used as a first-line agent in uncomplicated cases. Despite these findings, our meta-analysis makes clear that clomipramine is an important drug in the armamentarium of antiobsessional medications. Although our findings are supported by a number of similar meta-analytic studies in adults, the reasons for the observed greater efficacy of clomipramine are unknown. By virtue of the fact that clomipramine was the first serotonergic agent approved for pediatric OCD, earlier subjects were essentially “medication-naive” in relation to such compounds and may have represented a different population of patients than those enrolled in later trials. Underscoring this possibility, we note that the placebo response rate in the multisite clomipramine study was only 10% but was considerably higher in subsequent randomized, controlled trials using SSRIs. However, the effect of the drug remained significant when the year of the study was included as a covariate in the analysis, and there was not a statistically significant association between the year of the study and percent improvement in the placebo groups, nor were there differences in dropout rates between active and placebo conditions in the studies either individually or collectively. Finally, we note that in adult studies, clomipramine has never shown significant superiority in direct comparison with other agents. Unfortunately, to our knowledge, there are no such head-to-head studies in the pediatric age group.
Nonetheless, clomipramine has unique pharmacodynamic properties among the serotonergic agents, since it is metabolized to desmethylclomipramine, a secondary amine tricyclic antidepressant that is identical to desipramine with a chloride atom substitution. This agent has noradrenergic properties that have been reported to be useful in the treatment of both ADHD
(32) and tic disorders
(33), so clomipramine may offer the potential advantage of targeting symptoms that are often comorbid in these children. Its wider spectrum of action as a nonselective drug with both serotonergic and noradrenergic action may be associated with its observed superiority. While the choice of a specific agent is a complex clinical decision based on many factors, these findings suggest that clomipramine should be considered for treatment or augmentation in more severe or treatment-resistant cases of pediatric OCD.
Since the SSRIs were statistically indistinguishable from each other with respect to overall effect, a decision to use any one may depend more on adverse event profiles and individual pharmacokinetic properties than on efficacy. Relevant factors to consider in the choice of a specific agent include the half-life of the compound, the presence of active metabolites, the linear or nonlinear nature of its clearance, and its capacity to inhibit various cytochrome P-450 enzymatic pathways in the liver and so produce drug interactions.
Several limitations of this study should be considered. We did not examine gender- or age-specific responses across studies because only a subset of studies provided this information and no individual studies that looked at predictors of response found differences in these factors. We were unable to examine the effect of comorbid disorders on treatment response due to the numerous exclusion criteria used. We relied on two types of outcome scores because standard deviations were not reported in some outcome measures in several studies. To reduce any possible errors, we first determined statistical equivalence of baseline measures across treatment conditions in those studies. Studies with more than one outcome measure were treated as multiple data points, potentially increasing the weight of these studies, even as the number of participants was used as the primary weighting method. However, all but two studies (N=203, 9% weight; N=193, 9% weight) had at least two outcome measures, and this method permitted an evaluation of measures that would not otherwise have been possible. Since the study selection criteria may influence the outcome of such an analysis, we included all published studies that met our inclusion criteria, including those with no significant findings, and found no evidence of publication bias. The studies were not heterogeneous, and no single study influenced our findings. Nonetheless, we could not include unpublished data that might have shown less drug efficacy (“file-drawer effect”). We were unable to compare differing doses across studies, as there are no standardized weight-based dosing guidelines for these drugs in children. All but one study used a flexible dosing regimen based on clinical response and tolerance at the investigators’ discretion. Nonetheless, the range of doses and mean doses in these studies reflected currently accepted pediatric clinical practice
(34).
To conclude, this meta-analysis showed that serotonergic medications are highly significantly superior to placebo in treating OCD in pediatric patients, with consistent findings across studies and a modest overall effect. Clomipramine, a nonselective serotonergic drug, was statistically superior to the more selective agents in reducing OCD symptoms but may not be a first-line treatment due to its pharmacokinetic properties and side effect profile. The SSRIs examined in this meta-analysis were more or less comparably effective in this population.