Following the onset of schizophrenia, an association with cigarette smoking has often been observed, with most studies reporting a 1.5–2.5-fold increase in smoking frequency compared to that of the general population and an approximately 1.5-fold increase when compared to other psychiatric diagnoses
(1–
5). The most common explanation for this association is that people suffering from schizophrenia smoke to reduce or alleviate their symptoms in some way. In support of this hypothesis, a number of studies have found improvements in selective attention and in neurophysiological deficits in people with schizophrenia following cigarette smoking
(6,
7).
However, it has also been suggested that smoking may itself be an independent risk factor for schizophrenia
(5,
8), and a number of studies have found that 85%–90% of people with schizophrenia claim to begin smoking before the onset of their illness
(1,
5,
9). However, these findings might result from recall bias or from reverse causality, whereby smoking initiation occurs during an insidious prodrome of the illness before diagnosis. The possibility that confounding is present in the studies to date is also reasonably strong given that few of them adjusted for factors such as personality or substance misuse that show strong associations with both schizophrenia and smoking
(10–
12).
Our objective in this study was to investigate whether an association exists between smoking at age 18 and subsequent development of schizophrenia within a Swedish conscript cohort while adjusting for potential confounders. We are not aware of any previously published results from a cohort study that have addressed this question.
Method
Subjects
The cohort consisted of 50,087 men (of whom 49,321 were ages 18–20) conscripted into the Swedish army during 1969–1970. Only 2%–3% of the male population were excused from conscription due to severe mental or physical handicap. The conscription procedure included tests of personality and intelligence and self-administered questionnaires on family, social background, behavior during adolescence, and substance use. Smoking was recorded as one of four categories according to the number of cigarettes smoked per day: nonsmokers, light smokers (1–10 cigarettes/day), medium smokers (11–20 cigarettes/day), and heavy smokers (>20 cigarettes/day). Only 3% of the group had data missing for one or more of the self-reported questions, while less than 2% had data missing for smoking. Details of the procedure and results of studies of its validity have been previously reported
(13).
All subjects underwent a structured interview conducted by a psychologist, and those reporting psychiatric symptoms were interviewed by a psychiatrist and given an ICD-8 diagnosis where applicable. All subjects were made anonymous, and permission to use the database was granted by the Karolinska Institute Research Ethics Committee and the Swedish Data Inspection Board. Thirty-four cases of psychosis diagnosed at conscription were excluded from the study.
Follow-Up
The Swedish National Register of Inpatient Care recorded approximately 70% of all admissions in 1970, increasing to 83% in 1973. Starting in 1974, the coverage was more than 97%. The linkage reported here was from 1970 until 1996. During the period 1984–1986, information is missing for a few counties, but this is unlikely to have affected the results in any way. Patients were given clinical diagnoses according to the Nordic version of ICD-8 (ICD-9 from 1987). Outcomes investigated were schizophrenia (codes 295.00–295.99) and other psychoses (including alcoholic, affective, drug-induced, and paranoid).
Analysis
Cox regression was used to calculate hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for schizophrenia, given a smoking history at age 18, both before and after adjustment for potential confounders. Cox regression rather than logistic regression was used, as it was possible that differential mortality in smokers and nonsmokers could bias the results. The proportional hazard assumptions were tested by examination of Nelson-Aelen cumulative hazard function plots and investigation of Schoenfeld residuals.
Previous research on this cohort found that IQ, cannabis use, personality variables concerned with interpersonal relationships and social integration, psychiatric diagnosis at conscription, and place of upbringing were all associated with schizophrenia
(14–
19). Therefore, these were included as potential confounders in the regression model. Disturbed behavior in childhood, father’s occupation, family psychiatric history, family economy, and history of alcohol problems were also considered to be potential confounders and included in the analysis.
The variable for disturbed behavior in childhood was a summed score of questions regarding truancy, misconduct marks, running away from home, and contact with police from the self-reported questionnaire. The variable relating to poor social integration as an aspect of personality was a summed score of questions regarding number of close friends, history of relationships with women, and sensitivity of the individual. These questions were selected following factor analysis of over 40 questions relating to childhood and adolescent behavior from one of the questionnaires.
The subjects were also stratified into those diagnosed within 5 years of conscription (0–5 years) and those diagnosed after this time (≥5 years) in order to investigate possible effects of a prodrome at the time of conscription.
Results
Schizophrenia
Of 50,053 subjects, 362 (0.70%, 95% CI=0.65%–0.80%) were diagnosed as having schizophrenia by 1996. Data regarding smoking was missing for 12 (3.3%) of those developing schizophrenia and for 823 (1.7%) of the comparison subjects (χ
2=5.9, df=1, p=0.02). Overall, 59% (95% CI=58%–59%) of the cohort reported current smoking, which is in keeping with smoking rates for young men in Sweden during this time period
(20).
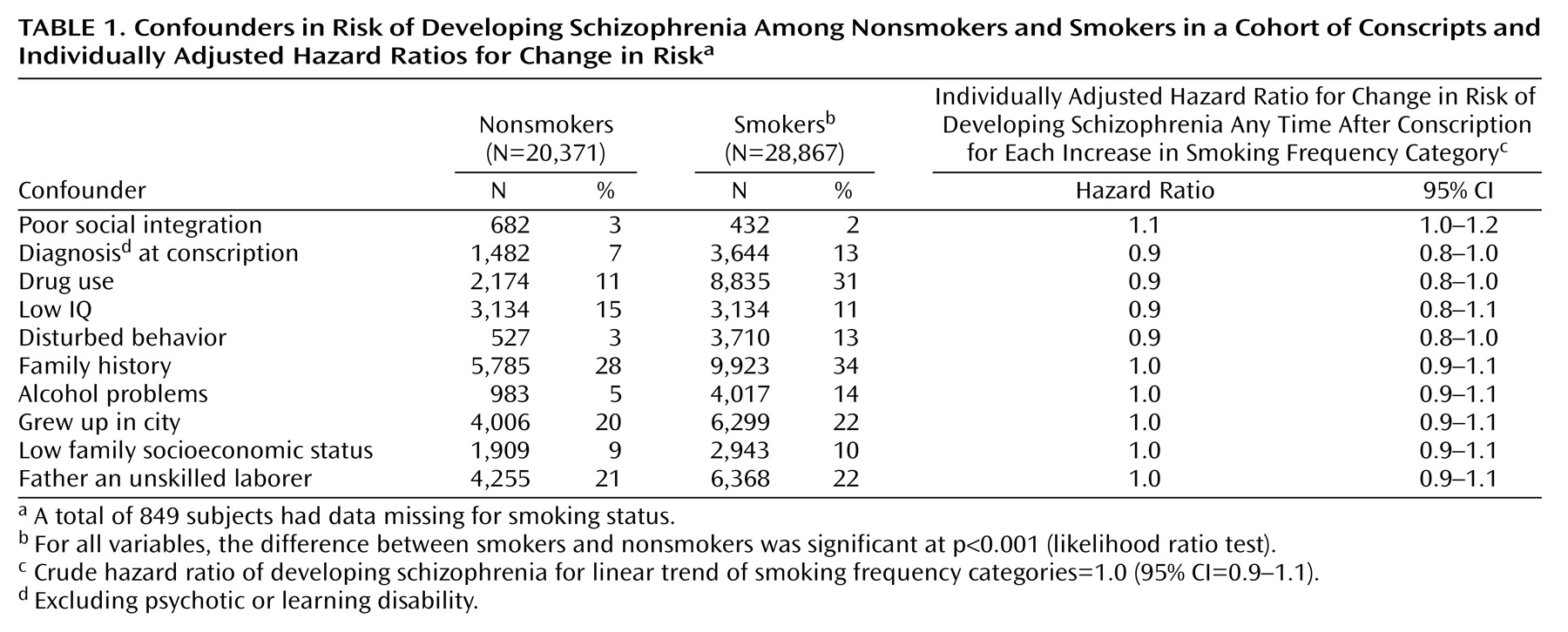
Ten variables were included as potential confounders in all the adjusted analyses, and a summary of these in relation to smoking status is presented in
Table 1. For the purposes of this table only, social integration, disturbed behavior, IQ, and family economy were treated as dichotomous variables by using the 10th percentile as a cutoff point for coding. All confounders were associated with smoking status at p<0.001. For all analyses, IQ, drug use, and poor social integration contributed most to confounding. Adjusting for family history, place of upbringing, father’s occupation, and family economy made virtually no difference to the final adjusted results.
Before adjustment, 0.74% (95% CI=0.65%–0.85%) of smokers and 0.68% (95% CI=0.57%–0.81%) of nonsmokers developed schizophrenia during the 27-year follow-up period (hazard ratio=1.1, 95% CI=0.9–1.3, p=0.44). In the first 5 years after conscription, 0.24% of smokers and 0.14% of nonsmokers developed schizophrenia (hazard ratio=1.7, 95% CI=1.1–2.6, p=0.02). However, in the years following this initial 5-year period, 0.50% of smokers and 0.54% of nonsmokers developed schizophrenia (hazard ratio=0.9, 95% CI=0.7–1.2, p=0.61).
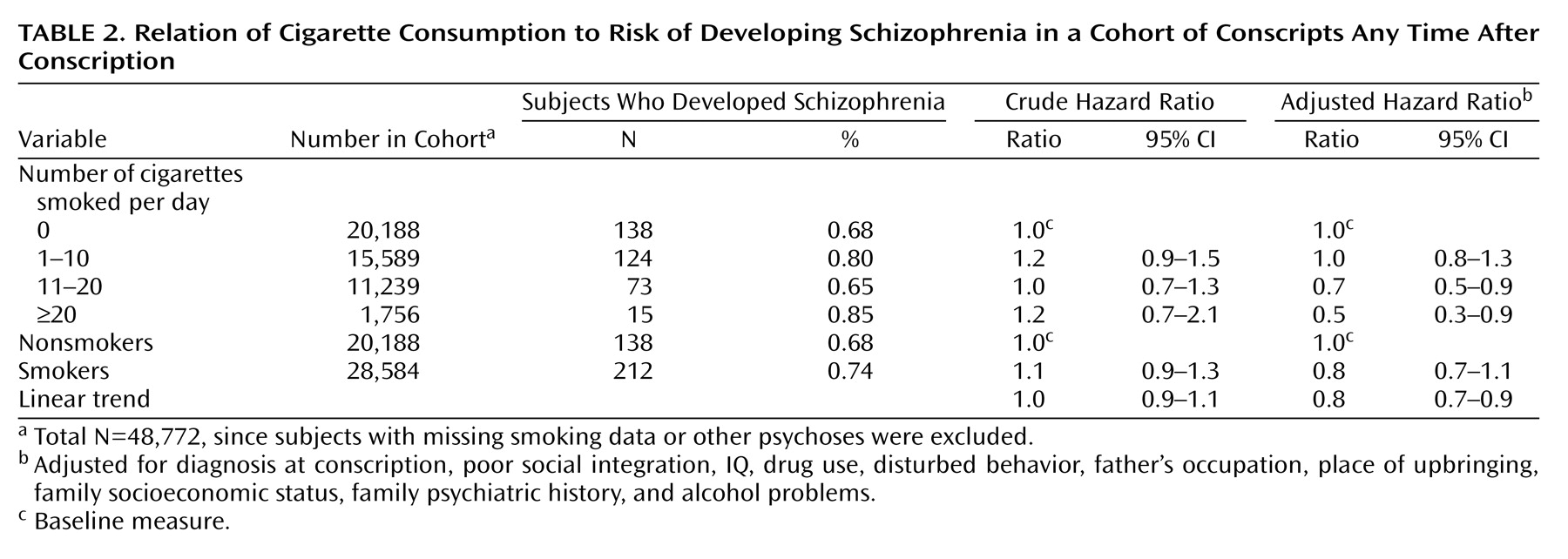
The results for all subjects who developed schizophrenia are presented in
Table 2. There was no association between smoking and schizophrenia in the crude analysis, but following adjustment for confounders, cigarette smoking at age 18 was associated with a lower risk of developing schizophrenia in both medium and heavy smokers, with an adjusted hazard ratio for linear trend across the four smoking categories of 0.8 (95% CI=0.7–0.9, p=0.002).
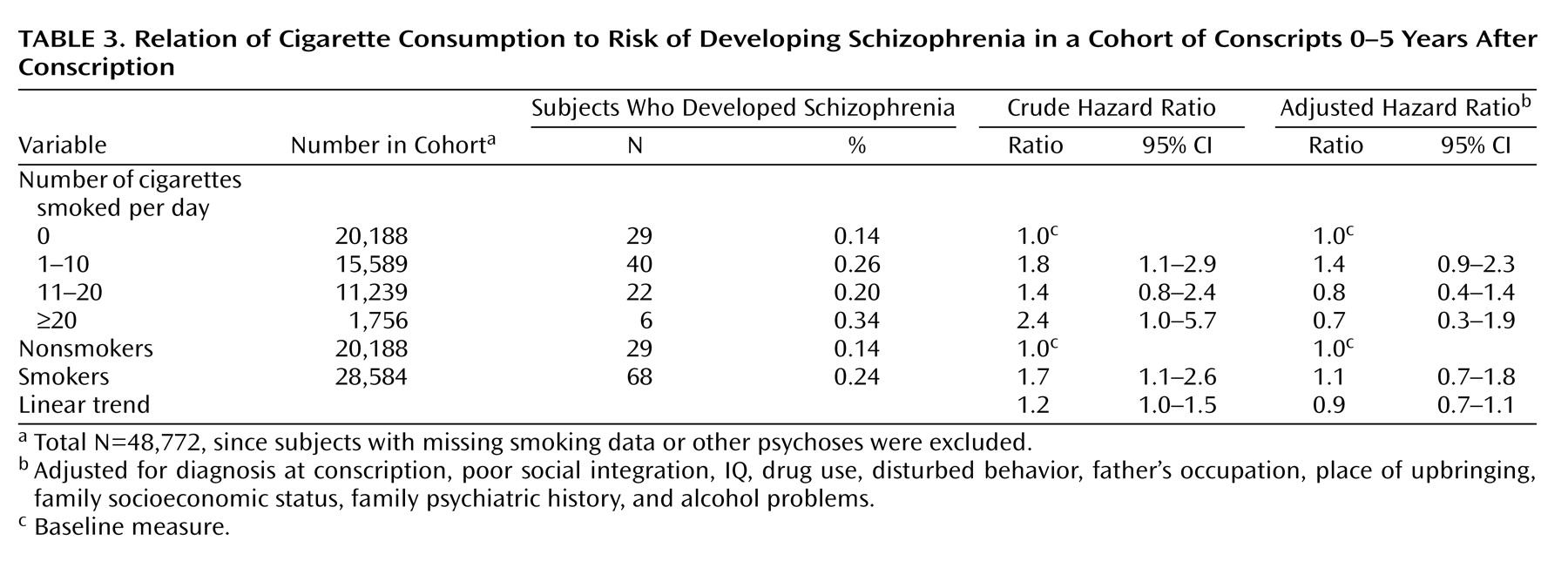
For subjects developing schizophrenia within 5 years of conscription (
Table 3), smoking was associated with a higher risk of developing schizophrenia in the crude analysis, but this association was no longer statistically significant following adjustment, with an adjusted hazard ratio for linear trend of 0.9 (95% CI=0.7–1.1, p=0.31).
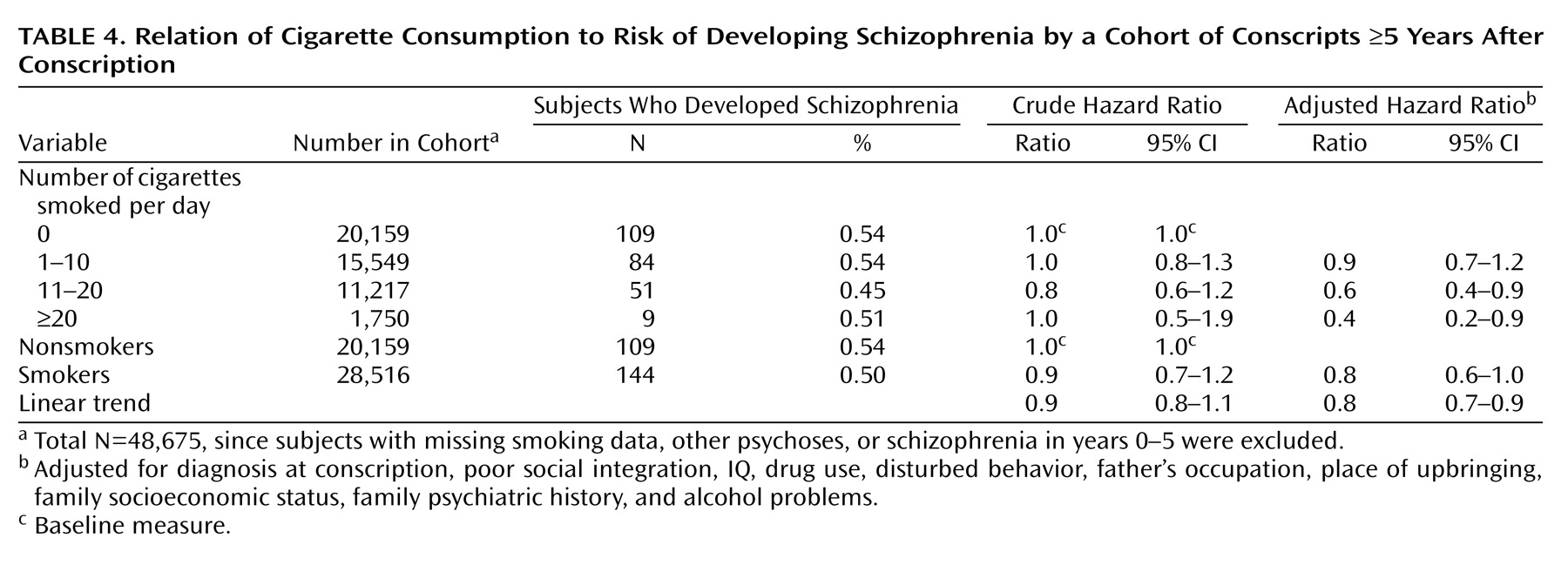
For subjects developing schizophrenia 5 years or more after conscription (
Table 4), a crude hazard ratio suggested a possible protective association of smoking. Following adjustment, there was a significant reduction in risk of developing schizophrenia in both medium and heavy smokers, with an adjusted hazard ratio for linear trend of 0.8 (95% CI=0.7–0.9, p=0.003).
Other Psychoses
The development of any psychotic illness (rather than schizophrenia, specifically) was also investigated. There were 446 subjects who received diagnoses of other (nonschizophrenia) psychoses. There was a significant increase overall in diagnosis of a psychotic illness other than schizophrenia in smokers compared to nonsmokers (linear trend crude hazard ratio=1.2, 95% CI=1.1–1.3, p<0.001), but this effect was eliminated after adjustment (linear trend adjusted hazard ratio=1.0, 95% CI=0.9–1.1, p=0.71). For subjects developing nonschizophrenia psychoses within 5 years of conscription, there was no significant association with smoking (linear trend adjusted hazard ratio=0.9, 95% CI=0.6–1.3, p=0.63). Similarly, in subjects diagnosed after the initial 5-year period, there was no suggestion of a dose-dependent protective effect of smoking (linear trend adjusted hazard ratio=1.0, 95% CI=0.9–1.2, p=0.60).
Discussion
In this study, smoking in men during late adolescence was associated with a lower risk of subsequently developing schizophrenia over a 27-year follow-up period. After adjustment, the heaviest smokers had the least risk of developing schizophrenia.
Analysis of other psychotic illnesses (including affective psychoses and substance-induced psychoses) did not show the same association with smoking, suggesting that smoking may have a rather specific effect in reducing the development of schizophrenia but not of other psychotic disorders.
In subjects developing schizophrenia in the initial 5-year period following conscription, smoking was associated with a higher risk of schizophrenia in the crude analysis but was associated with a nonsignificantly lower risk after adjustment for confounders. The small group in this restricted analysis may have reduced its statistical power. However, individuals diagnosed in the first 5 years may have already been suffering from prodromal symptoms at the time of conscription
(21) and therefore may have been smoking to alleviate those symptoms
(2).
In subjects who developed schizophrenia after the first 5 years after conscription, where prodromal effects of the disorder at conscription would be reduced, statistically significant reductions in the hazard ratios for developing schizophrenia were observed for both medium and heavy smokers, with a significant reduction in the adjusted hazard ratio for linear trend. The 95% CIs for heavy smokers ranged from 0.2 to 0.9. This means that the effect of smoking heavily could result in as little as a 10% reduction in risk to as much as an 80% reduction in risk of schizophrenia. The smaller number of subjects in this subgroup is reflected in the uncertainty of the precision estimate. The CIs for linear trend of smoking in this ≥5-year group ranged from 0.7 to 0.9, indicating that, at the very least, each incremental increase in smoking was associated with a 10% reduction in the risk of schizophrenia. Although the results suggest the presence of a dose-dependent effect of smoking, the small number of subjects in the heaviest smoking group meant that the results could also be compatible with a lower risk for medium and heavy smokers that is not necessarily dose dependent.
All crude hazard ratios were reduced or even reversed after adjustment for confounders, emphasizing that smokers have a number of characteristics that are also associated with schizophrenia and that these should be adjusted in other studies that aim to investigate this relationship. IQ and drug use had the greatest effect in reducing the crude hazard ratios. Poor social integration was an exception to this rule in that adjusting for this variable increased the crude hazard ratios as a result of the positive association between smoking and greater sociability. Although we believe the questions relating to poor social integration give a reasonable estimate of sociability in our group, personality traits are difficult to measure accurately, and the possibility of residual confounding cannot be excluded.
As for alternative explanations, chance, reverse causation, and selection bias are unlikely to account for the association, given the design of the study. Outcome misclassification is also likely to be low since the diagnosis of schizophrenia in Sweden has been shown to have high specificity
(22,
23) and because over 90% of people with schizophrenia are admitted to the hospital at some point during their illness
(24).
The main limitation of this study is that data regarding exposure and confounders was only available for one point in time. Therefore, individuals who started smoking after conscription or smokers who gave up smoking after conscription would have been misclassified. Approximately 85% of smokers start smoking before the age of 19, and during the period from 1975 until 1996, approximately 20% of male smokers in Sweden stopped smoking
(20,
25). Misclassification is therefore likely to be comparatively low and nonbiased in relation to schizophrenia, given the cohort design. Nondifferential misclassification tends to reduce the size of any association toward the null, so if such misclassification were present, the size of the protective effect of smoking may be underestimated in this study. Further studies that have longitudinal data on smoking as well as data on important confounders would help to investigate this association further.
It is possible, therefore, that smoking may act as an independent protective factor for schizophrenia. Epidemiological studies suggest that smoking may also be protective in Parkinson’s disease
(26). Reports from case-control studies that smoking could also reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease are not supported by findings from cohort studies, highlighting potential problems of bias particularly inherent in case-control designs
(27).
Both in vivo and in vitro studies support a neuroprotective effect of nicotine in animal models
(28), while similar protective effects have been reported for monoamine oxidase inhibitors and related compounds that are also found in tobacco smoke
(29,
30). The neuroprotective effects of nicotine seem to be mediated by means of α4β2 and α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes
(28). Evidence supporting genetic linkage for schizophrenia has also been reported on chromosome 15 in the region of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
(31). Nicotine has widespread effects on diverse neurotransmitter pathways, including glutamatergic and dopaminergic systems, by means of activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
(28,
32). Schizophrenia is associated with both an increase in dopamine activity in the mesolimbic system (believed to underlie positive symptoms such as hallucinations) and a decrease in activity in the prefrontal cortex (that correlates with negative symptoms such as amotivation)
(33). It has been hypothesized that nicotine may reduce negative symptoms in schizophrenia by preferentially increasing dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex compared to other areas of the brain, as indeed is observed in animal models
(32,
34). Although a nonbiological explanation is possible, a biological mechanism seems more plausible for the reduced risk of schizophrenia in smokers, given the observations described.
The small number of cases of schizophrenia in the heavy smoking group means that caution must be applied to the interpretation of these results. This is particularly true given that cigarette smoking has a wide range of harmful effects on physical health that would certainly outweigh any possible beneficial effects on schizophrenia. Nevertheless, these findings may help clarify the relationship between smoking and schizophrenia and lead to an improved understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the etiology of this disorder.