Neuropsychiatric symptoms are highly prevalent among patients with Alzheimer’s disease
(1), and second-generation antipsychotics have been frequently used for their treatment
(2) . Second-generation antipsychotics, however, especially olanzapine, are associated with metabolic abnormalities, including weight gain, increased risk for diabetes mellitus, and worsening lipid profile in patients with schizophrenia
(3 –
6) .
The data regarding adverse metabolic effects of second-generation antipsychotics have been from younger or middle-aged adults, and patients with Alzheimer’s disease have not been systematically assessed. The several randomized, placebo-controlled trials of second-generation antipsychotics in Alzheimer’s disease and dementia patients, mainly residing in nursing homes, have not assessed potential metabolic changes and they were not outcomes of interest
(7,
8) . Considering that epidemiology studies indicate that weight, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia are risk factors for both cardiovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease
(9,
10), and the established relationships of second-generation antipsychotic use with cerebrovascular adverse events
(11) and deaths
(12) in patients with dementia, it is important to know whether antipsychotic treatment worsens cardiometabolic risks in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
The Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness–Alzheimer’s Disease (CATIE-AD) employed a unique design, reflecting decisions made in clinical practice, to compare the effectiveness of three second-generation antipsychotics (olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone) and placebo over 36 weeks for treating delusions and aggression in outpatients with Alzheimer’s disease and provided well-controlled longitudinal data to generate hypotheses for future testing
(13) . To assess metabolic effects of second-generation antipsychotics in these patients, we conducted a prospective analysis of CATIE-AD interventions.
Method
Study Design
CATIE-AD was a 42-site, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial designed to examine the effectiveness of second-generation antipsychotics over the course of 36 weeks in treating psychosis and agitation occurring in outpatients with Alzheimer’s disease
(13) . Briefly, four phases (phase 1, 2, 3, and an open-choice phase) were designed to reflect clinical practice and decisions in prescribing second-generation antipsychotics among patients. In phase 1, 2, or 3, if a patient did not exhibit efficacy or tolerability at a time after 2 weeks of treatment, study physicians could move the patient to the subsequent phase to receive a study medication (not placebo) differing from his or her previous treatments.
In phase 1, a total of 421 eligible patients were randomly assigned in a double-blind fashion to the olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, or placebo groups in a 2:2:2:3 ratio. After randomization, clinic visits occurred at weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, and 36. Patients doing well on their assigned treatment continued with phase 1 treatment throughout the trial. Patients who discontinued their phase 1 treatments were randomly assigned in a double-blind fashion to one of the antipsychotics or the antidepressant citalopram in phase 2. Patients who discontinued from phase 2 and entered phase 3 received randomly assigned, open-label study medications that were not previously prescribed. A patient could also directly shift from any of the three phases to the open-choice phase to receive nonstudy medications of the study physician’s choice. The length of phases 1, 2, 3, and open-choice could range from 2–36, 2–34, 2–32, and 2–34 weeks, respectively. The primary study endpoint was the time until discontinuation of treatment for any reason in phase 1
(14) . The institutional review board of each site approved the study, and all subjects or their legally authorized representatives provided written informed consent.
Current Study
The current study assessed the effects of second-generation antipsychotics on metabolic factors by a prospective analysis of the CATIE-AD trial. A total of 421 subjects (186 men, 235 women) who had a baseline and at least one postbaseline measure of metabolic factors were included. Changes in weight and other metabolic measures from baseline to the last observation were outcomes in the analysis
(3) . The duration of each second-generation antipsychotic treatment and the total duration of any second-generation antipsychotic treatment during follow-up were the exposures of interest. Analyses were conducted regardless of phase and order of treatments unless otherwise specified.
Clinical Data Collection
Participant age, gender, ethnicity, and years of education were obtained. Height, weight, blood pressure, and waist and hip circumference were measured at baseline and at each clinic visit during the trial. Body mass index (BMI) and waist/hip ratio were derived from these data. Blood pressure was measured once in a seated position at each visit.
Laboratory measurements
Blood samples were obtained at baseline and at weeks 12, 24, and 36 during the trial (regardless of phases). Serum glucose assays and plasma total cholesterol, triglyceride, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol assays were performed by Quintiles central laboratory using standard methods, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol was estimated using the Friedewald equation. The time from the last meal to the blood draw varied among patients, and we defined those blood samples obtained at least 8 hours since the last meal as fasting samples
(15) .
Duration of study medication use
The start and end dates of each second-generation antipsychotic and placebo treatment were recorded for every patient. The duration of olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, or placebo use was calculated as the time interval between the start and end dates regardless of phase. For example, if a patient reached phase 3 at the end of the trial then the patient had switched treatment twice after the initial randomized assignment. Thus, the patient could have three duration variables to reflect the length of exposure to each second-generation antipsychotic or placebo administered during the trial. The period during which a patient received placebo, citalopram, or open-choice antipsychotic medications other than the second-generation antipsychotics did not contribute to the duration calculations for antipsychotic use.
Nonstudy medication use
The use of nonstudy medications including antihypertensive, lipid-modifying, and antidiabetic medications was assessed at each visit and recorded on medication record forms that included dose, frequency, and dates of use.
Statistical Analysis
Analysis of change in metabolic measures from baseline to the last observation was performed for all subjects who had baseline and at least one follow-up metabolic measure. Separate general linear regression models were fitted for each metabolic factor including weight, waist circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, HDL cholesterol, fasting glucose, and fasting triglycerides. The change in each metabolic factor from baseline to last observation was the dependent variable. Cumulative duration of any second-generation antipsychotic use was the primary independent variable. The regression coefficient associated with duration represents the change in the metabolic factor per week of antipsychotic use. Differences in this duration regression coefficient by gender, age group (≥80 versus <80 years), and baseline BMI (<25 kg/m 2, 25 to <30 kg/m 2, ≥30 kg/m 2 ) were tested for significance by including duration-by-gender, duration-by-age group, and duration-by-baseline BMI interaction terms.
Logistic regression was used to examine whether longer cumulative duration of second-generation antipsychotic use increases the likelihood of having clinically significant weight gain, as commonly defined as at least 7% increase from baseline. The binary dependent variable was categorized percentage weight gain (<7% and ≥7%). The independent variable was categorized cumulative duration of antipsychotic use (none, 1 day to 12 weeks, between 12 and 24 weeks, and 24–36 weeks). Age and gender were included in the model as covariates.
With regard to the effects of individual antipsychotic treatment on metabolic measures, we evaluated weekly rate of change in metabolic measures by initial assigned groups (olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, or placebo). All available follow-up visits in phase 1 were included for each subject in order to assess the effects of each individual medication treatment. Analyses of triglycerides and glucose were restricted to fasting samples and subjects whose glucose concentrations were less than 100 mg/dl with unknown fasting status. In a mixed-effects model, a metabolic factor at a given follow-up time was regressed on time since randomization (random effect), and the randomized group was modeled as a fixed effect. The main effect of treatment group examined the group difference of each metabolic measure at baseline, while the group-by-time interaction term tested whether the weekly rate of change in each metabolic measure differed across groups. Age and gender were included as covariates to control for potential confounding effects.
Study site was not used as a covariate because an unconditional means model for each metabolic factor
(16) indicated that the changes in metabolic factors did not significantly cluster by sites (the proportion of the total covariance between sites ranged from 0.004 to 0.039 compared to the sum of between- and within-site covariance).
All analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.1 software (SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.). Statistical significance was accepted at two-sided p<0.05.
Results
Baseline Subject Characteristics
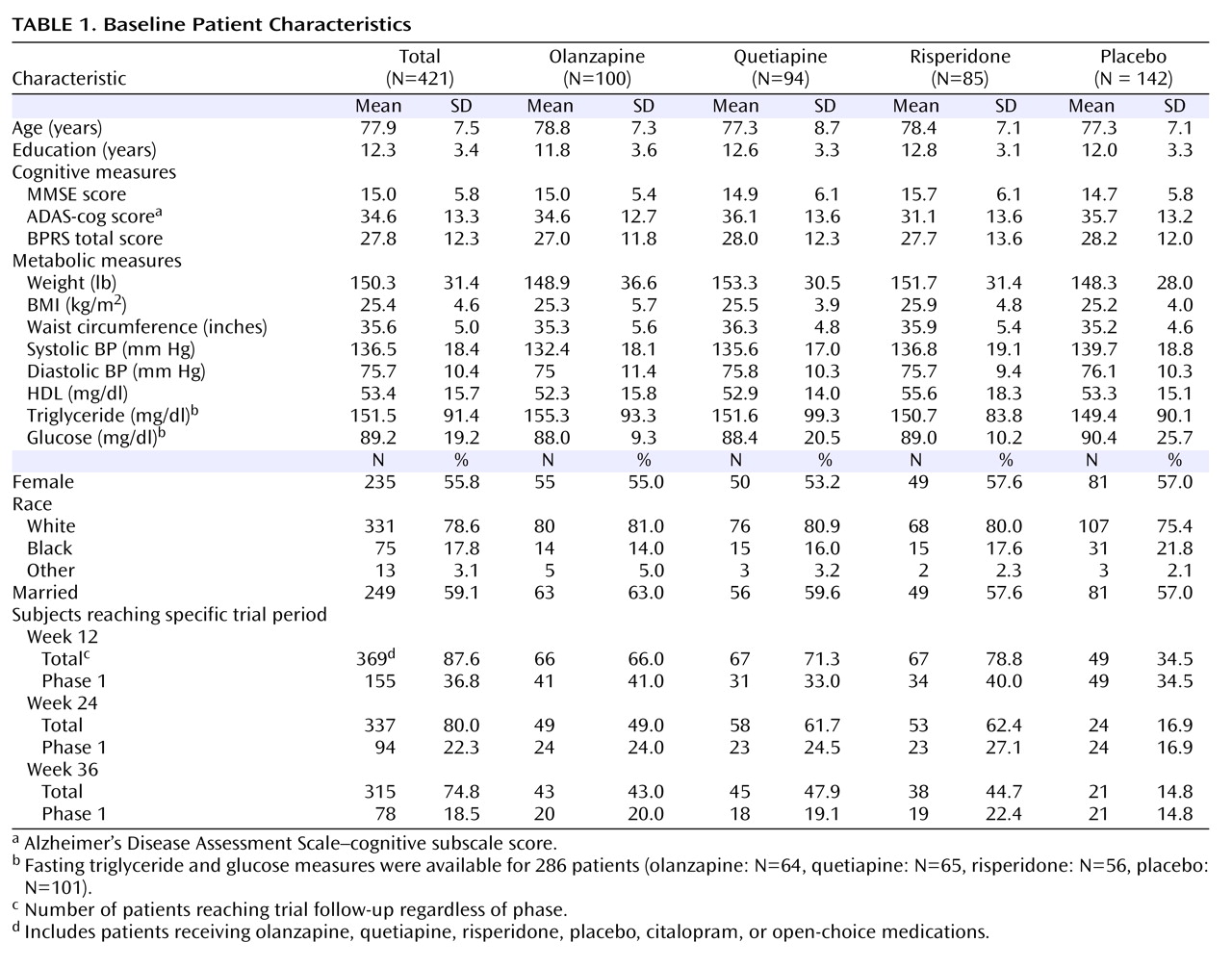
A total of 421 patients with Alzheimer’s disease were randomly assigned to four groups (olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, or placebo). Demographic, cognitive, and metabolic characteristics at randomization are summarized in
Table 1 . There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics among groups except for mean systolic blood pressure (p=0.02). The mean age at randomization was 77.9 years (range=51 to 103 years). Fifty-six percent were female, 21% were non-Caucasian, and 59% were married. On average, patients were overweight and had elevated systolic blood pressure. Almost half of the subjects (46%) were using antihypertensive agents, 60% were taking cholinesterase inhibitor or memantine antidementia medications, 24% were receiving cholesterol and triglyceride reducers, and 10% were taking oral blood glucose lowering medications at randomization.
Table 1 also includes the number of subjects reaching specific trial phases by weeks 12, 24, and 36.
Cumulative Duration of Total Second-Generation Antipsychotic Use
During the trial, 349 (83%) subjects received a second-generation antipsychotic for at least 1 day. Seventy-two subjects (17%) out of a total sample of 421 had no exposure to second-generation antipsychotics because they received placebo, citalopram, or open-choice antipsychotic medications other than the study medications. The cumulative duration of antipsychotic use ranged from 0 to 46 weeks with a median of 12.1 weeks. Among subjects who received antipsychotics for at least 1 day (N=349), 73 (21%), 63 (18%), and 61 (17%) subjects were taking olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone alone, respectively. Forty-three (12%) subjects received olanzapine and quetiapine, 42 (12%) received olanzapine and risperidone, 43 (12%) received quetiapine and risperidone, and 24 (7%) had all three second-generation antipsychotics at some time during the trial follow-up.
Weight Gain and Duration of Antipsychotic Use
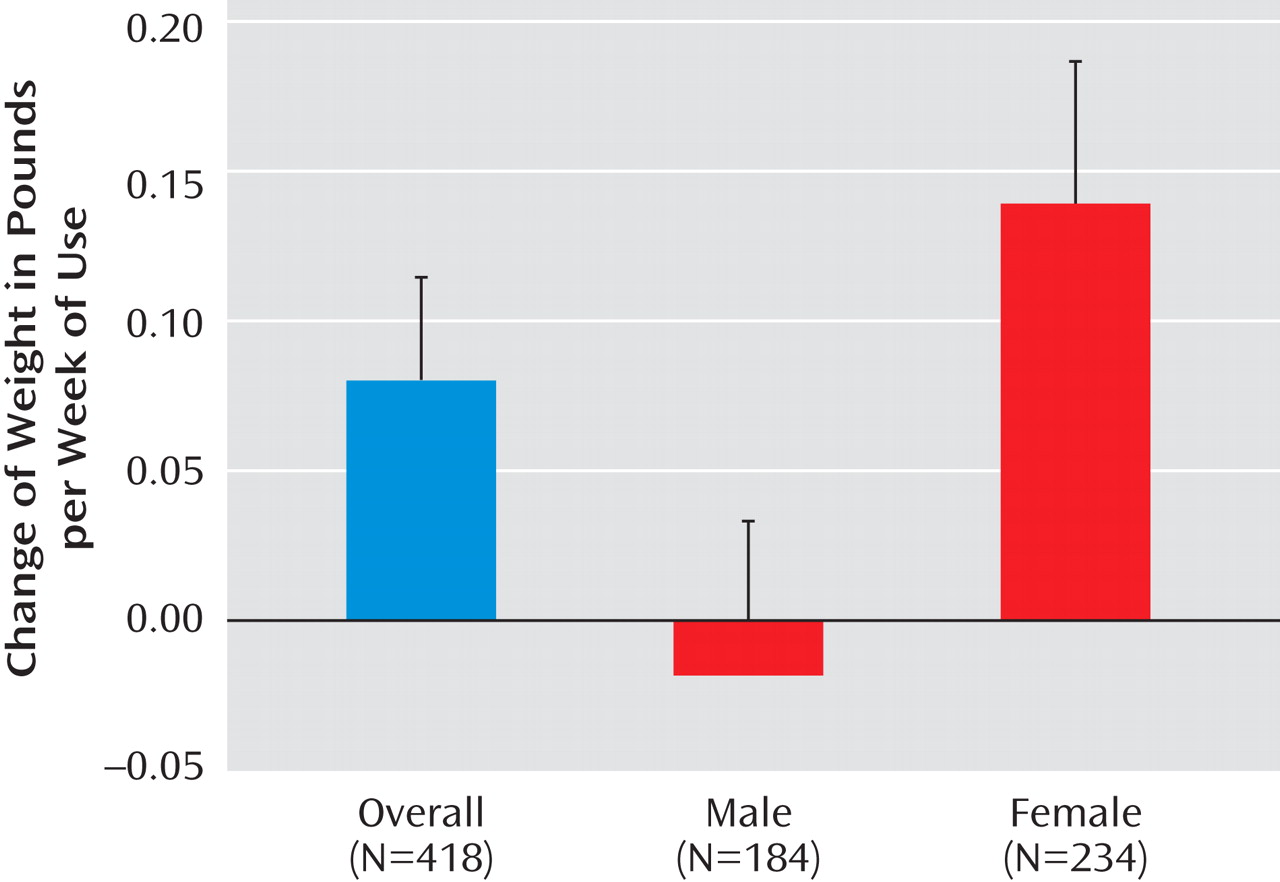
Among 418 subjects with weight measurements available at both randomization and end of trial, duration of antipsychotic use was significantly associated with weight gain after adjustment for age (p=0.02) (
Figure 1 ). As the primary independent variable in the general linear regression model, 71 of 418 subjects had no exposure (cumulative duration of zero) to second-generation antipsychotics. These subjects with no second-generation antipsychotic exposure were included in the model as the reference group. The regression coefficient associated with duration represents the additional weight change per week of antipsychotic use beyond the weight change experienced in the unexposed group. A significant interaction between duration of antipsychotic use and gender was found (p=0.008). In the overall sample, average weight gain was 0.08 pounds per week of antipsychotic use (SE=0.03). Female subjects showed a statistically significant weight gain of 0.14 pounds per week (SE=0.04) of antipsychotic use (p=0.006) while the change in weight in males was –0.02 pounds per week (SE=0.04) of antipsychotic use (p=0.64). No significant interaction between duration of antipsychotic use and age group (≥80 versus <80 years) was noted (p=0.45).
Similarly, duration of antipsychotic use was associated with increase in BMI after adjustment for age (0.02 kg/m 2 per week of antipsychotic use, p=0.006), with a significant interaction between duration of antipsychotic use and gender (p=0.005). Female subjects showed a significant increase in BMI of 0.03 kg/m 2 per week of antipsychotic use (p=0.004) while male subjects did not (–0.003 kg/m 2 per week of antipsychotic use, p=0.64).
To examine whether the association between weight gain and duration of antipsychotic use was influenced by baseline BMI, we tested the interaction term duration-by-baseline BMI. Because only 14 patients (five men and nine women) were underweight at baseline (i.e., BMI<20 kg/m 2 ) we created three categories of baseline BMI: under plus normal weight (BMI<25 kg/m 2 ; women: N=125, men: N=81), overweight (from 25 to <30 kg/m 2 ; women: N=69, men: N=75), and obese (≥30 kg/m 2 ; women: N=38, men: N=24). No evidence of effect modification by baseline BMI was found (duration-by-baseline BMI, p=0.93) nor when we further tested whether baseline BMI modified the influence of gender on weight gain per week of antipsychotic use using a three-way interaction term (duration-by-gender-by-baseline BMI [p=0.43]).
Clinically Significant Weight Gain and Duration of Second-Generation Antipsychotic Use
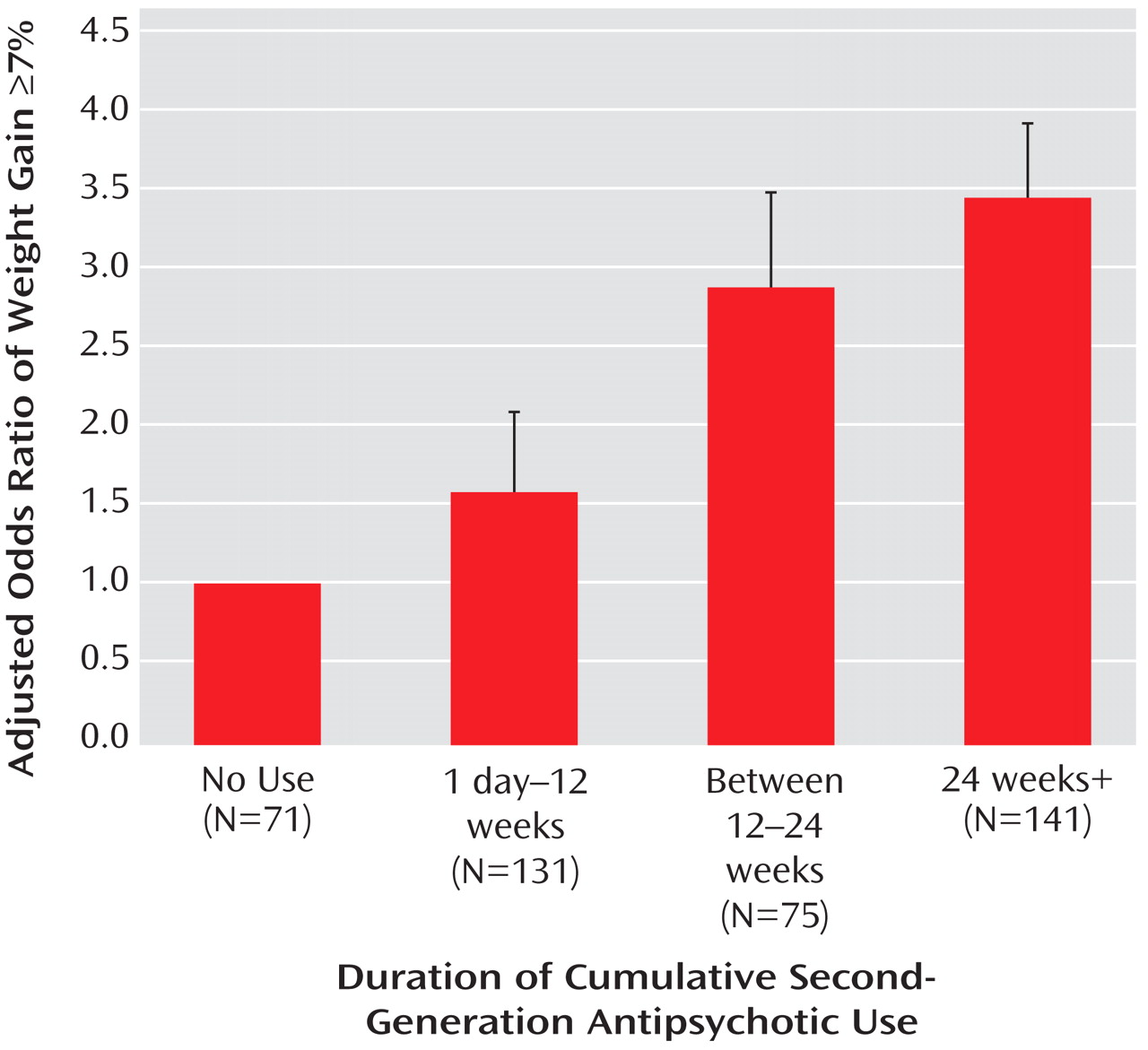
The duration-dependent association between antipsychotic use and clinically significant weight gain is presented in
Figure 2 . Relative to subjects with no use, subjects with at least 24 weeks of antipsychotic use were more likely to have clinically significant weight gain defined as at least a 7% increase from baseline. Female gender had a marginally increased likelihood for significant weight gain than male gender (odds ratio=1.79, 95% CI=0.998 to 3.211; p=0.051) with no significant interaction between duration of antipsychotic use and gender (p=0.89).
Second-Generation Antipsychotic Treatment Interruption
We modeled duration of any second-generation antipsychotic treatment as a continuous exposure in the above analysis. For patients who remained in phase 1 throughout the trial, or those who switched from one antipsychotic to another across phases, the duration variable reflects the treatment exposure without interruption. When a patient was randomly assigned to a second-generation antipsychotic in phase 1, then to citalopram in phase 2, and switched to another antipsychotic in phase 3, a gap between antipsychotic treatments occurred that might dilute the effects of treatment. Only 22 participants of a total of 83 randomly assigned to citalopram in phase 2 experienced gaps between second-generation antipsychotic treatments, i.e., received one second-generation antipsychotic in phase 1, citalopram in phase 2, and another second-generation antipsychotic in phase 3. The mean duration of citalopram use among these 22 participants was 9.7 weeks (SD=6.0), ranging from 1.1 to 21.4 weeks. To rule out the effect of treatment interruption, we further tested the association between weight gain and duration of any second-generation antipsychotic excluding these 22 participants and the results were not altered.
Effects of Individual Second-Generation Antipsychotic Treatment
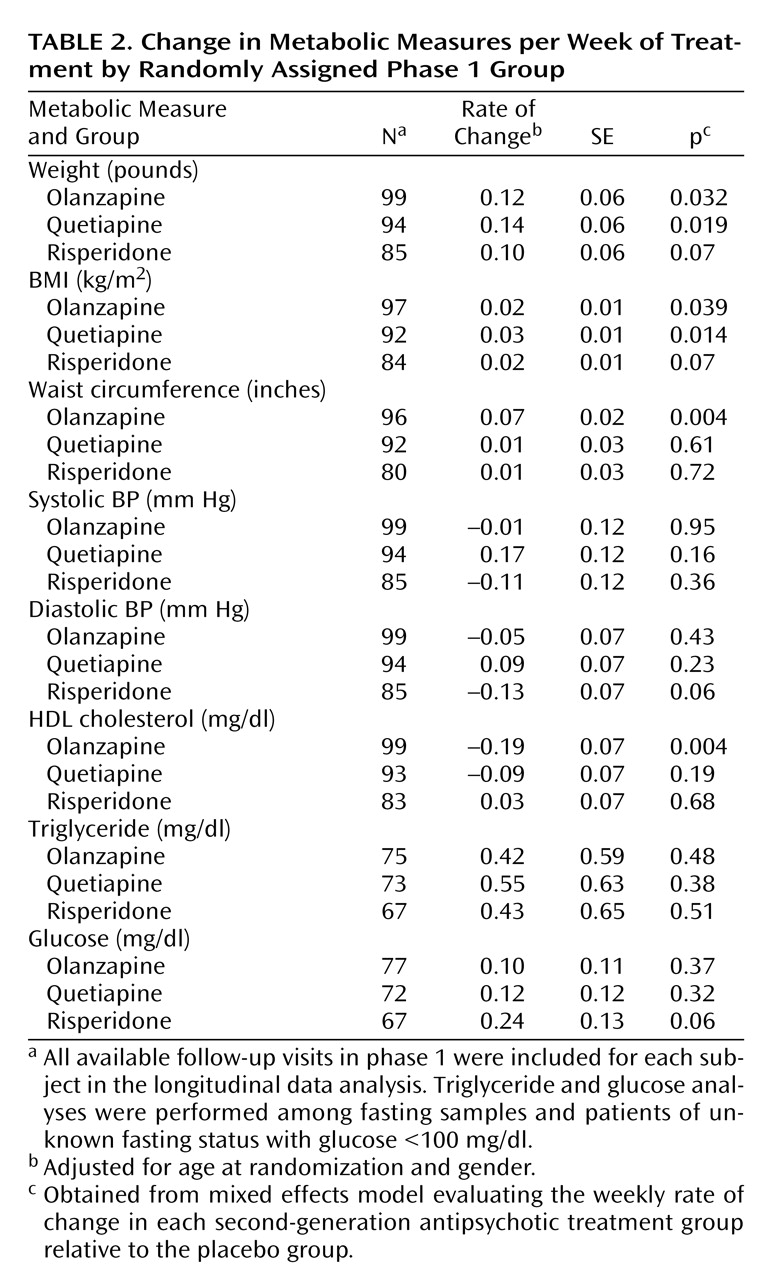
The effects of each antipsychotic treatment on the weekly rate of changes in metabolic measures are summarized in
Table 2 . For each participant, all available follow-up visits in phase 1 were included in this analysis. Multivariate mixed effects models were fitted to evaluate the weekly rate of change of each metabolic measure in relation to the treatment groups with adjustment for age and gender. At randomization, none of the metabolic measures differed among groups. Longitudinally, when compared to the placebo group, significant average weekly weight gain was observed in the olanzapine group and quetiapine group, and approached significance in the risperidone group. Similar patterns of BMI change were apparent among the three antipsychotic treatments. In addition, olanzapine treatment was significantly associated with increased waist circumference and decreased HDL cholesterol. No effects of antipsychotic treatment were noted for changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, glucose, or triglycerides.
Discussion
Clinically significant weight gain, increasing with duration of use, is associated with atypical antipsychotic treatment among outpatients with Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, an increase in waist circumference and decrease in HDL cholesterol is associated with olanzapine. The relationship of the weight gain to duration of treatment and a gender interaction makes this observation particularly compelling.
The rate of weight gain was 0.10–0.14 pounds/week and the magnitude of the gain was 1.4, 1.7, and 1.2 pounds after 12 weeks for olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone, respectively. Weight gain in older people cannot be viewed as a positive event unless it is due to increased lean muscle mass, which was unlikely to have occurred in this study that did not include a physical training intervention and observed increased waist girth. Visceral adiposity is associated with greater risks of insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and glucose intolerance and must be considered as an adverse effect rather than a benefit in these individuals.
Most data regarding adverse metabolic effects of second-generation antipsychotics have been in younger or middle-aged adults. The magnitude of the weight gain, increase in waist circumference, and change in HDL cholesterol reported in Alzheimer’s disease patients is similar to that reported from a large randomized trial in younger people with schizophrenia (mean age 41 years, 74% male, and mean BMI of 30 kg/m
2 )
(5,
6), although the Alzheimer’s disease patients had substantially lower BMI, narrower girths, and higher HDL cholesterol levels at baseline.
In the few randomized, placebo-controlled trials in Alzheimer’s disease and other dementia patients, the associations between antipsychotic use and weight change were inconsistent or not adequately reported. Although olanzapine was associated with about a 1.0-kg increase and a higher incidence of significant weight gain relative to risperidone and placebo in one 10-week outpatient trial
(17), in a 26-week trial in outpatients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease but without agitation or psychotic symptoms, a mean 1.4-kg increase in weight was not significantly greater than the placebo group
(18) . Similarly, increased weight of about 1.0 kg was associated with olanzapine in one nursing home trial
(19) but not in another
(20) . Two 10-week-long quetiapine trials in dementia patients in nursing homes did not report significant differences in weight change between the treatment and placebo groups
(21,
22) . Of four risperidone trials
(7,
23 –
25), three did not address
(23) or did not report changes in weight, BMI, or other metabolic measures
(24,
25) . The one trial that stated there was a significant increase in weight with risperidone compared to placebo provided no details
(26) . By comparison, we found significantly greater weight gain in olanzapine- and quetiapine-treated patients compared to placebo and a statistical trend for risperidone.
Women showed significant weight gain associated with antipsychotic treatment, while men did not. The female subjects were older than the male subjects (mean age=78.6 [SD=7.8] versus 76.8 [SD=6.9] years, respectively; p=0.015) and had higher HDL cholesterol (mean=58.5 [SD=15.2] versus 47.1 [SD=14.2] mg/dl; p<0.0001). At baseline, men and women were similar with regard to cognitive function, years of education, BMI, blood pressure, and fasting glucose and triglyceride levels. Because elderly women proportionally have more fat mass and less lean body mass than elderly men, they may be more susceptible to second-generation antipsychotic-associated weight gain. The difference in weight changes between women and men observed here was not reported in other studies among Alzheimer’s disease patients or the elderly and warrants further examination.
It is important to note that we observed an increasing difference in actual weight gain with continuing antipsychotic treatment over the 36-week trial. The prevalence of significant weight gain was 10%, 17%, and 20% among patients with less than 12 weeks, 12–24 weeks, and greater than 24 weeks of use compared to 7% with no use. This is particularly concerning given the association of weight gain with both cerebrovascular disease morbidity and mortality, both of which appear independently associated with antipsychotic use in dementia patients and are listed as warnings in the drugs’ labeling. Increased risk of second-generation antipsychotic-associated cerebrovascular adverse events is evident among patients with dementia
(11) . We previously reported increased risks for death with second-generation antipsychotics compared to placebo treatment in 15 randomized, placebo-controlled trials
(12) . Although some patients in the current trial may have benefited clinically from antipsychotic use in terms of particular symptom reduction (e.g., anger, aggression, and paranoid ideas), they did not benefit in performance of activities of daily living, care needs, or quality of life
(27) . Considered together, the risks of adverse events associated with longer-term use of second-generation antipsychotics must be carefully balanced against their benefits
(7,
8,
12,
14,
27) .
There are several limitations to the present study. First, the design of CATIE-AD did not allow for a parallel group comparison over 36 weeks of all patients randomized to their original (phase 1) treatment. The number of patients treated continuously with one antipsychotic over the entire trial was small (N=78), representing persons who were responding to and tolerating their initially assigned medication or placebo. Second, incomplete laboratory data due to nonfasting blood samples and 12-week assessment intervals decreased the sample size and power to assess changes in fasting glucose and triglycerides. Third, we were not able to address a potential dose effect due to the flexible dosing design. Average doses, however, in both phases 1 and 2 were from 5.5 to 5.6 (olanzapine), 56.5 to 61.1 (quetiapine), and 1.0 to 1.1 mg/day (risperidone)
(14) . These doses were generally lower than other Alzheimer’s disease trials and considerably lower than doses used to treat schizophrenia or in the CATIE schizophrenia trial
(5) .
In summary, about 20% of outpatients with Alzheimer’s disease developed significant weight gain that increased over 36 weeks with antipsychotic treatment. Patients treated with olanzapine in particular showed unfavorable changes in HDL cholesterol and abdominal girth. These are additional risks to consider when initiating and continuing antipsychotic therapy in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical trials of the atypical antipsychotics have shown modest efficacy compared to placebo in improving behavioral symptoms but adverse effects limit their overall effectiveness
(14,
27) . Alzheimer’s disease patients treated with second-generation antipsychotics should be monitored closely.