Limbic encephalitis often results from an immune-mediated reaction (autoimmune limbic encephalitis; ALE). ALE may be subdivided into paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis (PLE) and non-paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis (nPLE).
3 PLE is considered to be a rare condition, originally described by Corsellis et al.,
4 and characterized by memory disturbance, seizures, depression, irritability, and personality changes.
3 PLE is diagnosed by testing for a group of paraneoplastic autoantibodies (e.g., anti-Hu, anti-Ma, and anti-Ta antibodies) in the patient’s blood.
5 There is mounting evidence that nPLE may also be caused by antibodies against hippocampal and other limbic areas, including Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel (VGKC) complex antibodies. The potassium channels play a vital role in neuronal activity by maintaining the resting membrane potentials and producing action potentials.
Because of the nature and complexity of nPLE, a greater awareness of this condition is warranted, particularly across mental health services, in order to establish the correct diagnosis and commence early treatment. Antibody analyses are not currently performed routinely, but only in specialist centers using sophisticated and expensive methods, involving immunoprecipitation.
This systematic review aims to ascertain the clinical outcomes of VGKC-associated limbic encephalitis, exploring the clinical presentation of nPLE and correlation with VGKC levels pre- and post-treatment. It is expected that by establishing a systematic method of assessing, diagnosing, and treating VGKC-associated nPLE, the outcome and prognosis of patients with this condition could be substantially improved.
Methods
For this systematic literature review, we set out to identify all published studies on the treatment of VGKC complex antibody-associated limbic encephalitis, including case reports; case series; prospective or retrospective studies; and randomized, controlled trials.
Three scientific databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE and PsycINFO) were searched, using the following search terms or MeSH descriptors: “limbic encephalitis,” “paraneoplastic,” “voltage-gated potassium channel,” with relevant narrower subterms expanded to be included in the results.
The searches were restricted to studies on patients age 18 or above, published in English. Studies on limbic encephalitis secondary to neoplasia (i.e., paraneoplastic type) were excluded, as the treatment is targeted at the underlying tumor. Likewise, studies on nPLE associated with antibodies other than against VGKC antigens were excluded.
A data-collection sheet was designed to extract data from relevant studies that used the criteria proposed by Bien and Elger
3 for diagnosing limbic encephalitis. Data relating to individual cases were extracted and compiled in a table format, in order to identify any characteristics of the collected information, as well as perform subgroup analyses. The references of relevant studies were also searched for further relevant articles to be included in the review. Authors in the field were contacted for details on unpublished data or for clarification on published results. In general, contact was attempted with authors in order to obtain any missing information: where such information was not obtainable, the studies were excluded from our analysis.
Results
Our search retrieved a total of 56 records from the MEDLINE database, 92 from EMBASE and 91 from PsycINFO. Studies which did not include comprehensive information, such as individual patient characteristics and both pre- and post-treatment VGKC complex antibody levels, were excluded from the analyses. Contact with leading authors in the field did not provide unpublished study data, although some of the missing data in published studies were obtained through direct contact with authors.
7The systematic literature review yielded a total of 19 studies meeting inclusion criteria. All studies are presented in
Table 2. From these studies, 60 patients (of whom 46 were male) were described in sufficient detail to allow quantitative analysis.
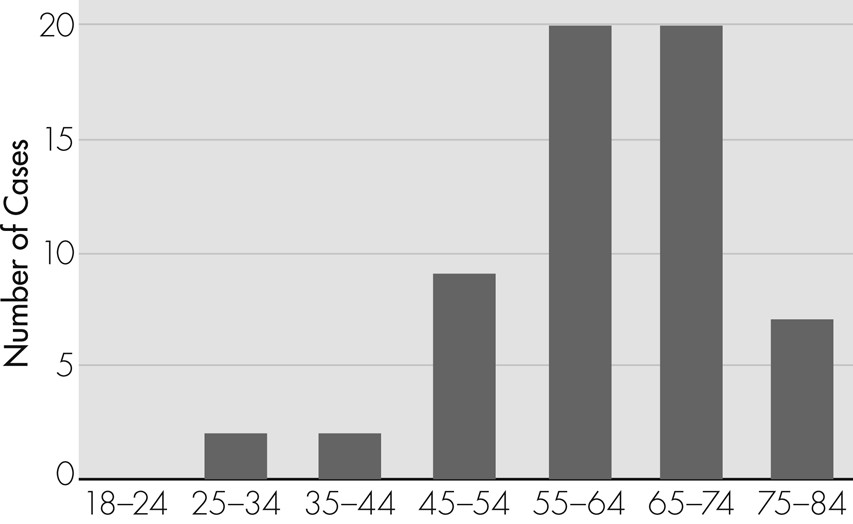
Figure 1 shows the age distribution of the 60 cases: the most frequent age-group was 55–74 years.
With regard to neuropsychiatric symptoms, 58 cases (97%) presented with memory impairment, 51 (85%) with seizures, and 20 (33%) with affective changes. Neuroimaging investigations revealed baseline MRI changes in 42 cases (70%).
The three main types of treatment interventions were intravenous immunoglobulins (N=37; 62%), plasma exchange (N=30; 50%), and steroids (N=49; 82%). Only a few studies explicitly stated the sequence or duration of the different treatments administered.
All cases had increased VGKC complex antibody titers; specifically, the increase was >90% for over half of the patients. Post-treatment reductions in VGKC complex antibody levels were >90% in 28 cases (47%), >80% in 14 cases (23%), >50% in 9 cases (15%), and >10% in 6 cases (10%). Three patients (5%) had an increase in antibody levels after treatment.
As there were wide variations in the use of rating scales and outcome measures, the overall clinical outcomes were standardized and categorized into Significantly Improved (N=50; 83%), Minimally Improved (N=6; 10%), Unchanged (N=3, 5%), and Worse (N=1; 2%), based on the anchor-points of the measures used in the different studies. The presence of statistically significant changes from baseline was used as a threshold between the categories of Significantly and Minimally improved.
Neuropsychological Outcomes
Formal neuropsychological assessments before and after treatment were conducted in relatively few studies. In the study by Vincent et al.,
8 7 of 10 patients showed post-treatment changes on a range of neuropsychological tests, including Verbal and Performance Intelligence Quotient, Adult Memory and Information Processing Battery, National Adult Reading Test, Warrington Recognition Memory Test, Rey Complex Figure Test, and Graded Naming Test. However, the observed correlations between specific cognitive performance and VGKC complex antibody levels were not consistent across the 7 patients. The single case reported by Fauser et al.
9 demonstrated significant improvement across several cognitive domains, according to performances on the Verbal Learning and Memory Test, Visual and Verbal Memory Test, Diagnosticum Für Cerebralschäden, Digit Span, Visual Span, and Concentration Endurance Test, after treatment with anticonvulsants. Improvements on verbal and performance Intelligence Quotient, word and face recognition, Adult Memory and Information Processing Battery, paired-associate learning, and graded naming tests, were also reported in one out of the three cases described by Chan et al.,
10 in correlation with reduced post-treatment VGKC complex antibody levels.
Neuroradiological Outcomes
Brain MRI changes typically involved atrophy or edema of the medial temporal and limbic regions, including the hippocampus. The research papers analyzed in this study often do not describe the changes in the MRI scans after treatment. Therefore, the correlation on these changes with VGKC complex antibody levels and treatment is unclear. For example, two of the cases reported by Chan et al.
10 showed additional atrophic changes in the hippocampal areas after treatment, despite subjective improvement in cognitive functions.
Discussion
Abnormal expression of VGKC complex antibodies is one of the most recently described causes for limbic encephalitis. The possibility of VGKC complex antibody-associated limbic encephalitis should be considered as a differential diagnosis in patients presenting with subacute impairment of cognitive functions, and seizures associated with MRI changes in the limbic region. Importantly, VGKC complex antibody-associated nPLE is considered to be potentially treatable. This systematic literature review assessed the available evidence for improvement in clinical outcome in association with reduction in VGKC complex antibody levels after treatment. We found good evidence suggesting a temporal relationship between the reduction in VGKC complex antibody levels with treatment and clinical outcome, although the effects of symptoms duration on recovery are still unclear.
With regard to neuropsychiatric symptoms, the vast majority of the reviewed cases presented with memory impairment and seizures, and about one-third with affective changes. The absence of neurological features reported in limbic encephalitis, such as neuromyotonia, could be related to local changes in the permeability of the blood–brain barrier, which determines the concentration of VGKC complex antibodies entering the central nervous system.
8 The VGKC complex structures have different components, which include the Kv1.1, Kv1.2, and Kv1.6 ion channel subunits.
12 It has been shown that sera from patients with limbic encephalitis bind preferentially to the Kv1.1 subunits, whereas sera from patients with neuromyotonia bind to the Kv1.2 and Kv1.6 subunits.
2 These variations might also explain why some patients develop CNS symptoms without peripheral neurological pathology or vice versa. Finally, the study by Iranzo et al.
13 noted an association between limbic encephalitis and REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), as immunosuppressive treatment resulted in decreased VGKC levels, with corresponding clinical improvement in both LE and RBD symptoms in 3 out of 5 patients. The authors suggested a possible pathogenic role for VGKC complex antibodies in the limbic projections to and from the brainstem, which are involved in the pathophysiology of RBD.
The most significant improvements in clinical outcomes after immunosuppressant treatment were observed in patients with VGKC complex antibody-associated nPLE presenting with affective symptoms and consistent neuroradiological changes. Of note, these patients also reported the largest decreases in antibody titers.
Although subjective improvement was often reported, when tested, the objective assessment of cognitive outcomes showed more variability; for instance, the three cases reported by Chan et al.
10 presented inconsistent post-treatment changes in their performances on the public-events questionnaire and face-recognition tests. Likewise, a case report by Chatzikonstantinou et al.,
14 which was excluded from the present review, as it did not provide sufficient data to allow quantitative analysis of the correlation between clinical outcome, neuropsychological testing, and VGKC complex antibody levels, showed a decline in the Verbal Learning and Memory Test, despite a reduction in antibody titers. This patient showed improvement in memory and overall mental state only after more aggressive therapy with intravenous immunoglobulins and azathioprine. These variations in neuropsychological outcomes may reflect individual variations in cognitive reserve, as suggested by Stern.
15 The concept of cognitive reserve is based on the hypothesis that the brain insult can be initially managed by using compensatory approaches and pre-existing cognitive processing approaches. Thus, patients with a greater cognitive reserve would be better able to cope with the same degree of brain damage, as compared with a patient with a lower cognitive reserve.
Neuroradiological findings were also characterized by variable post-treatment changes. A case report by Barajas et al.,
16 which did not present VGKC complex antibody levels and was therefore excluded from our analysis, showed partial resolution of MRI Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) hyperintensity in the hippocampal areas bilaterally after treatment. Fauser et al.
9 found a significant improvement in glucose hypermetabolism on FDG-PET after treatment, correlating with both seizure activity and overall clinical picture. Brain MRI scans showed resolution of the left hippocampal changes, which were absent in subsequent scans. The authors concluded that FDG-PET was more sensitive than MRI in visualizing changes in the limbic region at an early stage of the disease, thus providing more accurate correlations with the clinical outcome. Likewise, the case report by Chatzikonstantinou et al.
14 found that FDG-PET scans were more sensitive than MRI scans in demonstrating the development of encephalitis, as documented by bilateral hippocampal hypometabolism. It was suggested that over a longer time period, hypermetabolism may be interpreted as a sign on epileptic activity, whereas hypometabolism may be correlated with an inflammatory process.
The results of our systematic literature review suggest that there might be multiple biological mechanisms responsible for the observed clinical improvements. For example, Gast et al.
6 described a case where anticonvulsant treatment led to clinical improvement, despite a slight increase in antibody levels after treatment. The authors suggested that seizures can expose antigens by disrupting the blood–brain barrier, thus leading to more temporal lobe seizures, in a vicious cycle. Seizure control may therefore lead to decreased titres of VGKC complex antibodies along with clinical improvement. It was recommended that, in milder cases of VGKC complex antibody-associated nPLE, the decision to administer immunosuppressive treatment may be delayed, as there is some chance of spontaneous remission with seizure control.
The central nervous system contains numerous different proteins that could be potential targets for circulating antibodies. A study by Lai et al.
17 found that antibodies from patients diagnosed with VGKC complex antibody-associated nPLE also bound to Leucine-rich Glioma Inactivated 1 (LGI1) antigen. This is a secreted neuronal protein that acts as a ligand for proteins from the protein group termed “A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease domain (ADAM),” in particular, the presynaptic ADAM 22 and postsynaptic ADAM 23, which are implicated in epileptogenesis. LGI1-binding antibodies were not found in the control group, suggesting that these antibodies might play a role in the pathogenesis of nPLE along with VGKC complex antibodies. As LGI1 is a secreted protein rather than an ion channel like VGKC, confirmation of these findings would imply that VGKC complex antibody-associated limbic encephalitis might be better categorized as “autoimmune synaptic encephalopathy,” rather than “autoimmune channelopathy.”
The reviewed literature had some methodological limitations. Although Bien and Elger
3 proposed specific diagnostic criteria for limbic encephalitis, there are currently no universally-accepted diagnostic guidelines; hence, cases might have been misdiagnosed and missed being reported in the scientific literature. Most published case reports did not present a standardized method of measuring baseline symptom severity, resulting in significant difficulties when comparing symptom severity and improvement after treatment interventions. An objective measure of the effects of treatment interventions could not always be extrapolated. In some cases, there were standardized baseline measurements, but post-treatment measurements were limited to patients’ subjective reports of improvement, leading to discharge from healthcare.
16 Finally, most of the reviewed studies did not include any specification of the targeted antigen within the VGKC complex.
Our systematic literature review strategy also had some intrinsic limitations. Most published studies on the treatment of nPLE were expected to be cited in the scientific databases used; however, it is possible that other relevant published studies were not listed in these databases. This could have been the case for some non-English literature, for example. The lack of standardized outcome measures across the studies made it impossible to conduct metaanalyses using pooled data. Instead, we performed a quantitative analysis by classifying treatment outcomes into discrete categories ranging from Significantly Improved to Worse, with risks of data oversimplification. Information about the sequence and duration of treatment interventions was often missing, making it difficult to categorize treatments into more specific groups. Authors of relevant articles were contacted for further clarifications on the published data whenever required. They were also contacted to seek negative findings or unpublished work, in an effort to minimize publication bias and missing data. A further limitation of this review is the exclusion of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis, as some cases of paraneoplastic syndromes, including limbic encephalitis, may require immunotherapy. Moreover, it is highly likely that some forms currently labeled as non-paraneoplastic might be associated with an occult tumor that could not be detected even with a thorough work-up. Hence, the border between the two is rather blurred.
As the exact pathogenesis of limbic encephalitis is still unclear and there are no therapy guidelines for this condition, patients with VGKC complex antibody-associated nPLE are currently treated with a combination of intravenous immunoglobulins, corticosteroids and plasma exchange, which appears to result in clinical improvement. However, no randomized, controlled trials currently exist to show which of these treatments, or which combinations, can lead to more favorable outcomes. In our systematic literature review, treatment with steroids was associated with the most significant reductions in plasma VGKC complex antibody levels. These findings, combined with the wide availability of steroids, suggest that these medications would be appropriate as first-line therapy. Any treatment regimen clearly requires careful and objective monitoring, with serial administration of standardized psychometric instruments along with repeated VGKC complex antibody titres. Finally, clinical outcomes should be correlated with neuroradiological and neurophysiological findings for a multimodal assessment of the pathological process and its resolution.
Although this systematic literature review showed that the most frequently affected age-group is over the age of 55, the diagnosis of nPLE is rarely considered when patients in this age-group present with subacute decline in cognitive functions. Testing for VGKC-complex antibody associated nPLE can be expensive, and an economic analysis is clearly beyond the scope of this study; however, our findings could lay the foundations for further research to determine the cost-effectiveness of investigating and treating nPLE in higher-risk clinical populations.