The Hawaii Aging with HIV Cohort is a longitudinal cohort established to examine HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders in older (≥50 years old) and younger (20–39 years old) HIV-seropositive individuals. The Hawaii Aging with HIV Cohort is unique with less than 5% of the participants identified as intravenous drug users, which is lower than other cohorts.
31 –
35 Following informed consent guidelines established by the University of Hawaii Institutional Review Board, participants living in Hawaii were enrolled; we excluded those with a major psychiatric or neurologic disorder, a history of head injury with loss of consciousness greater than 1 hour, current or past opportunistic infection with brain involvement, a diagnosed learning disability, or delirium due to medications at the time of examination. For the current study, subjects who were included in the previous study were also excluded from this analysis.
36 Subjects were evaluated at entry into the cohort and yearly for 4 years. Subsequent follow-up visits were scheduled in advance at the patient’s convenience and ability to complete the neurocognitive testing in one visit in the absence of any acute medical crisis.
Participant evaluations included demographic information, medical history, neurologic examination including the United Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale to examine for extrapyramidal signs, medication/adherence history, DSM-IV-based substance abuse/dependence inventory, immunologic and virologic laboratory tests, and neuropsychiatric testing; as previously reported.
27 The 80-minute neuropsychiatric test battery, adapted from the NorthEast AIDS Dementia Cohort, assessed multiple cognitive domains affected by HIV-1 and included the following: choice and sequential reaction time from the California Computerized Assessment Package, Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT), Rey Osterreith Complex Figure (RCF) Copy and Recall, Trail Making tests A and B, WAIS-R Digit Symbol, Grooved Pegboard (dominant and nondominant hands), Verbal fluency test, Animal Naming, Boston Naming Test, the WAIS-R Digit Span (forward and backward), and Timed Gait. Depression symptomatology was assessed using the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI).
37 Normative neuropsychiatric data for individuals with a high school or greater education were derived from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study consisting of 733 HIV-1-seronegative subjects with risk profiles similar to the Hawaii cohort. For individuals with less than a high school education, normative neuropsychological data from the AIDS Link to IV Experience study (n=150) was used.
38 These two normative sets have few individuals over 54 years old. Thus, for individuals over 54, alternative published normative data were used.
39,
40 Normative data for the Rey Osterreith Complex Figure were taken from alternative published norms for individuals over 59 and the main Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study normative set for individuals under 60 years old.
41 A similar battery with a large overlap in norms was shown to be appropriate for HIV-1-infected individuals of similar ethnic diversity.
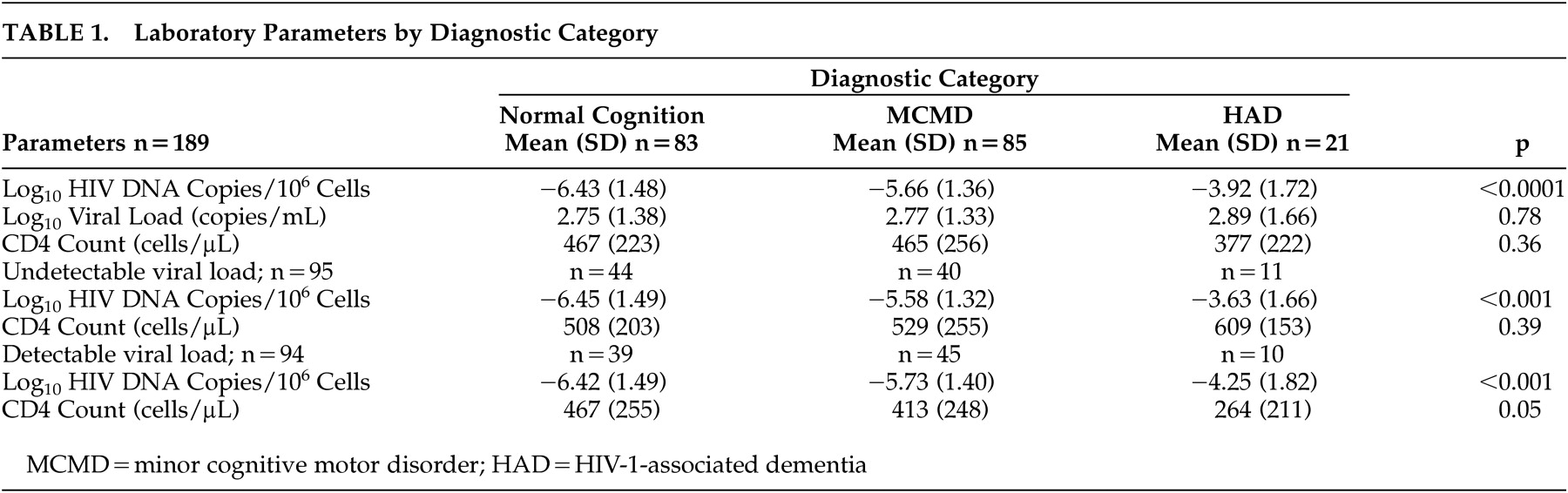
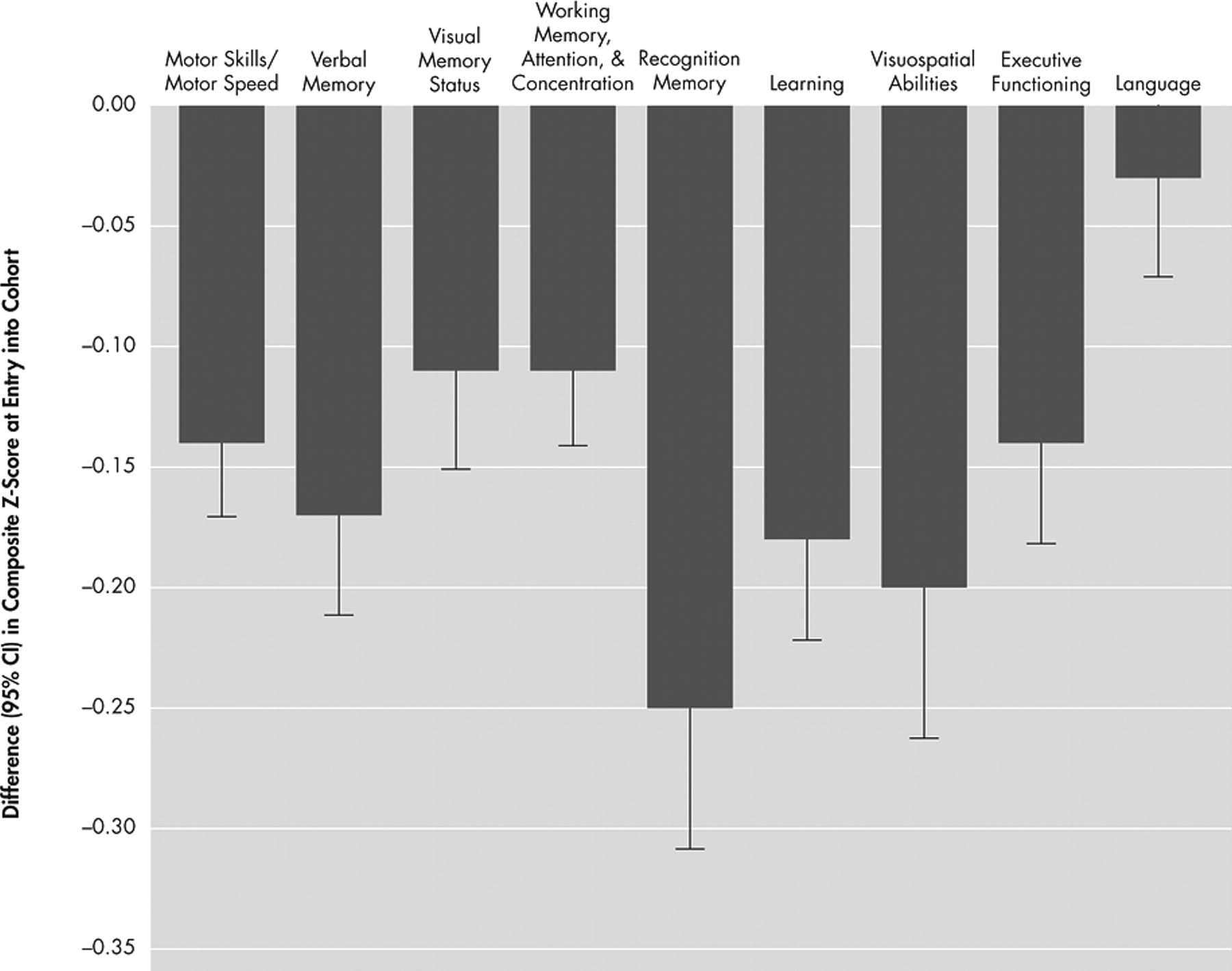
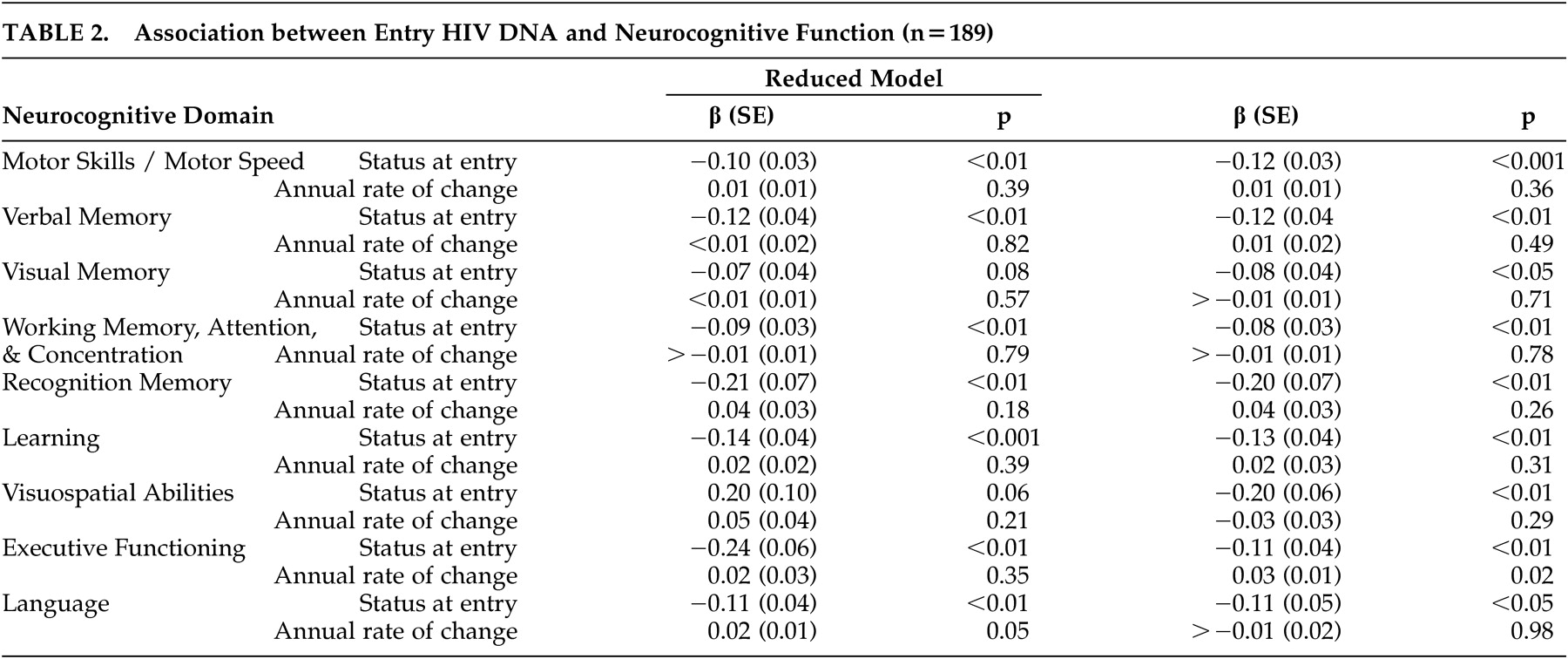
42 Various normative data were required due to the use of a comprehensive test battery and the inclusion of both younger and older subjects. The normative data were selected as the best possible dataset for this population with a long history of applications in HIV-1 research (e.g., Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study). Application of these norms was guided by the clinical neuropsychologists on the team. All test results were transformed to Z scores using appropriate age and education-matched normative data sets. Scores for cognitive domains (motor skills/motor speed; verbal memory; visual memory; working memory, attention, and concentration; learning; recognition memory; visuospatial abilities; executive functioning; language) were calculated by averaging the Z scores of the neuropsychiatric tests corresponding to the domains they were intended to measure, as previously published.
27 All patients who had research-based neurocognitive diagnoses using the American Academy of Neurology 1991 criteria (normal cognition, minor cognitive motor disorder, and HIV-1-associated dementia) without confounds (methamphetamine/cocaine use, stroke/transient ischemic attacks) who consented and donated blood for research studies were included in the analyses.
43