Morphological Abnormalities of the Thalamus in Youths With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Abstract
Objective
Method
Results
Conclusion
Method
Participants
MRI Scanning and Image Analysis
Preprocessing
Whole-brain volume
Thalamus definition
Surface morphometry
Statistical Analyses
Conventional volumes
Surface morphometry
Cytoarchitectonically Defined Thalamic Atlas
Results
Conventional Volumes
Hypothesis testing
Post hoc analyses
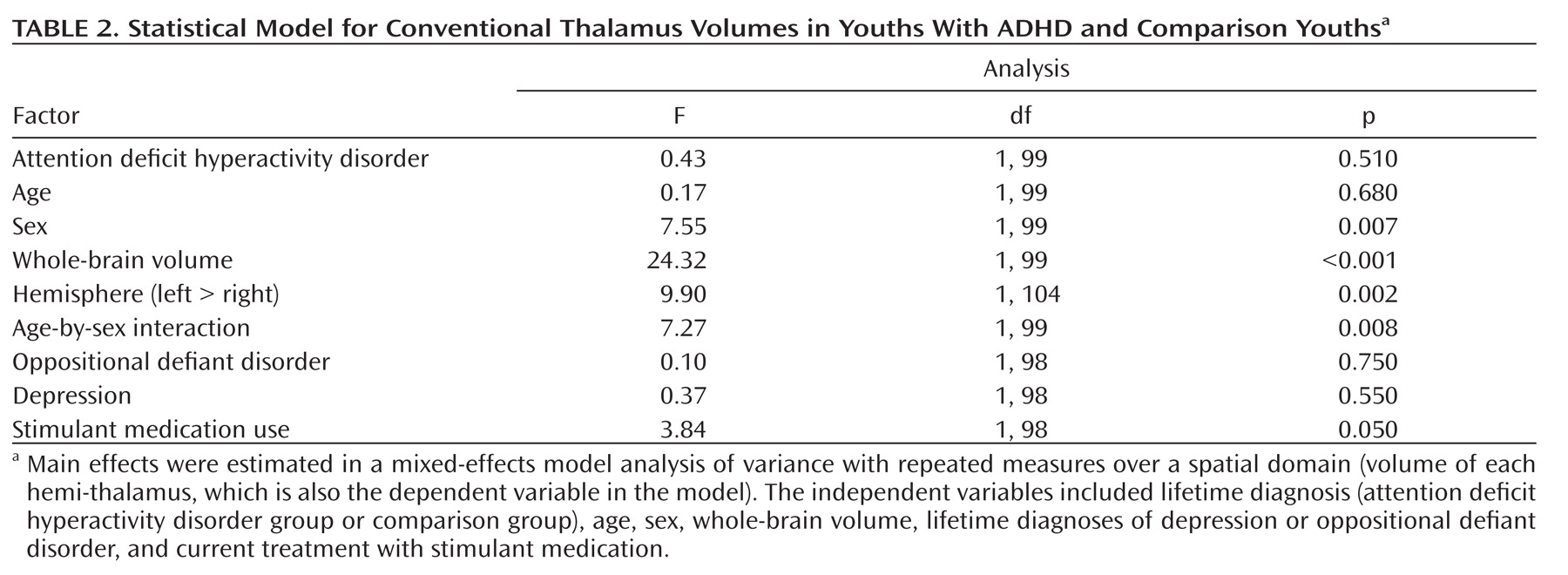
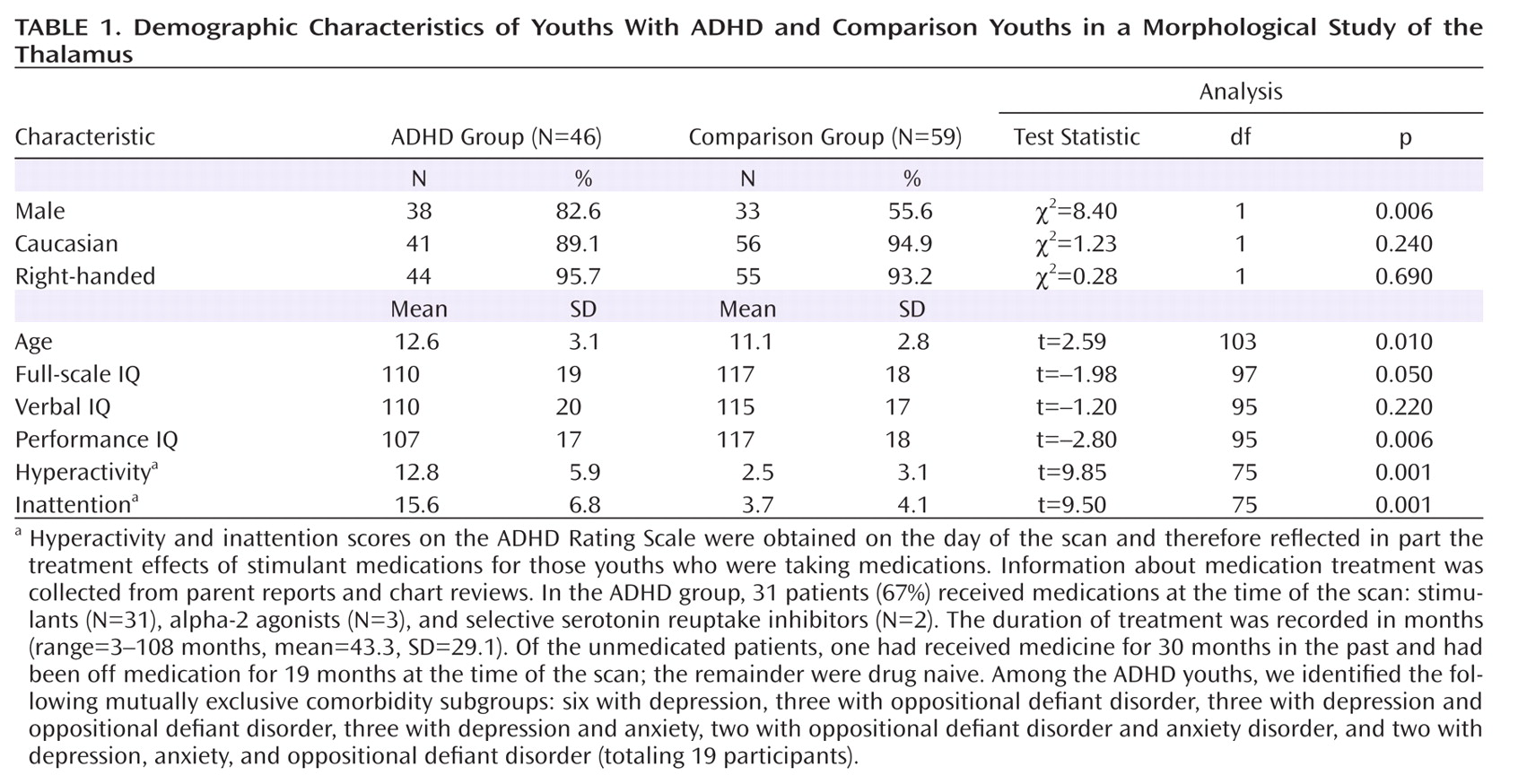
Morphological Features of the Thalamic Surface
Hypotheses testing
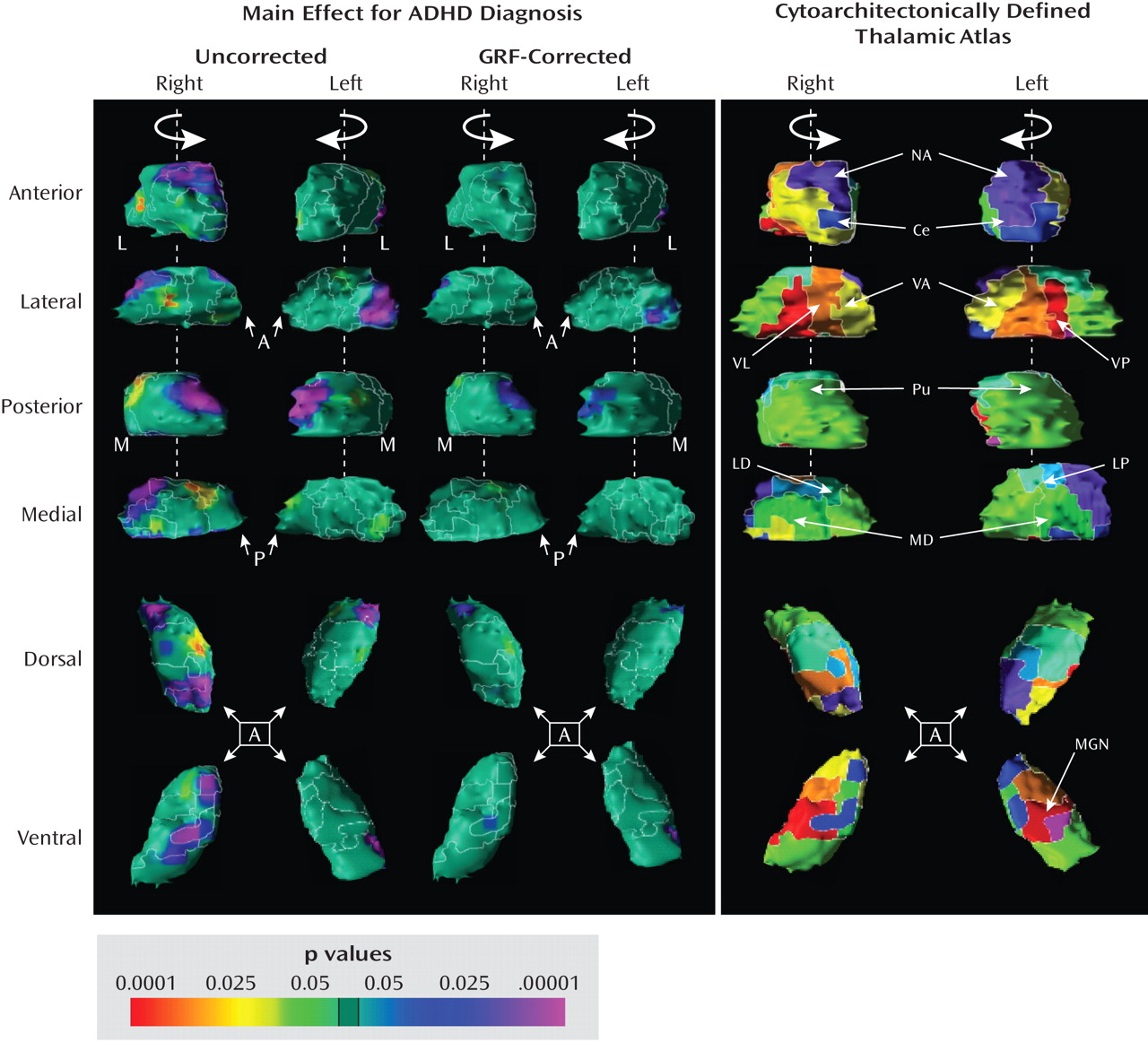
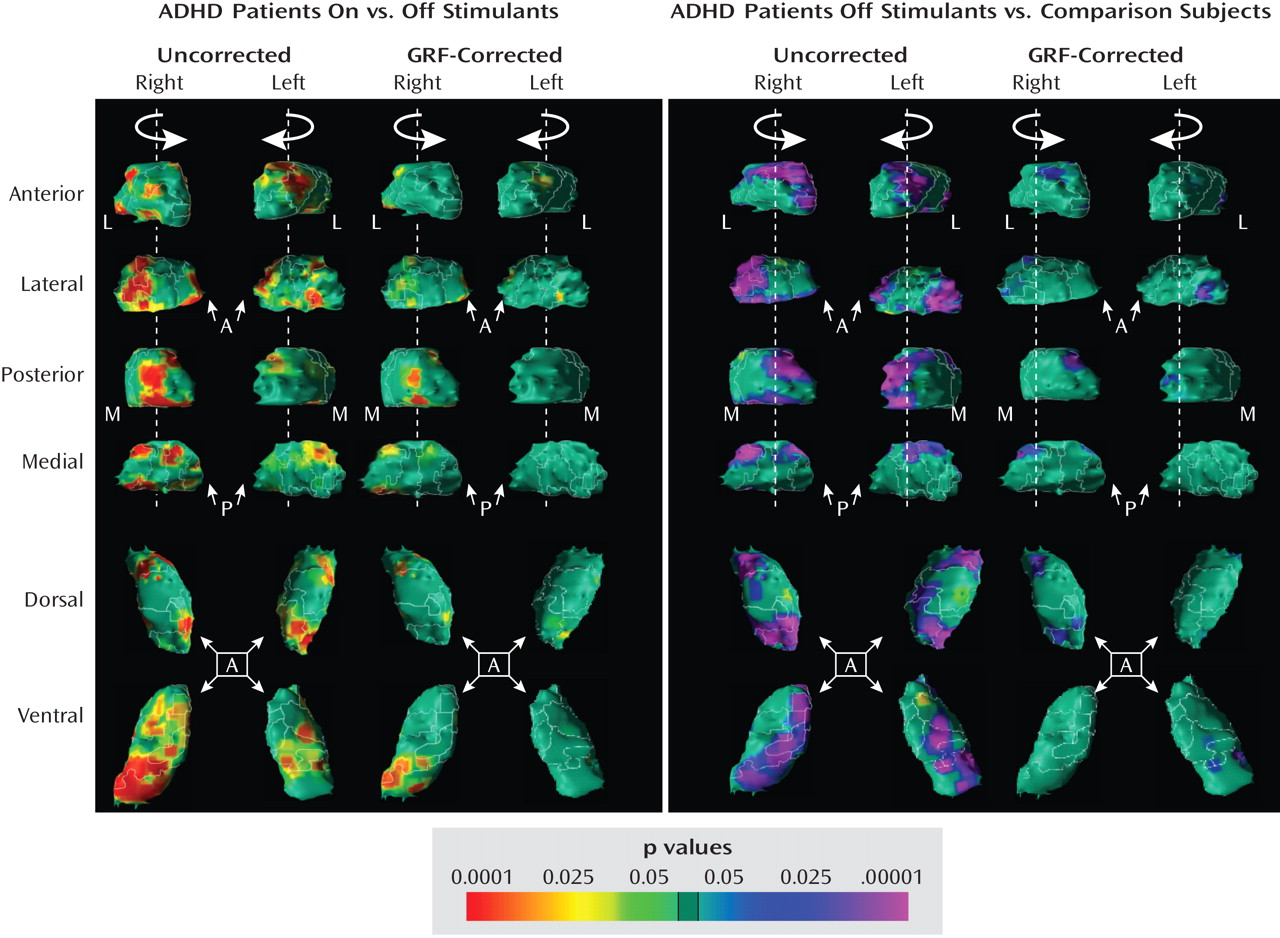
Post Hoc Analyses
Medication effects
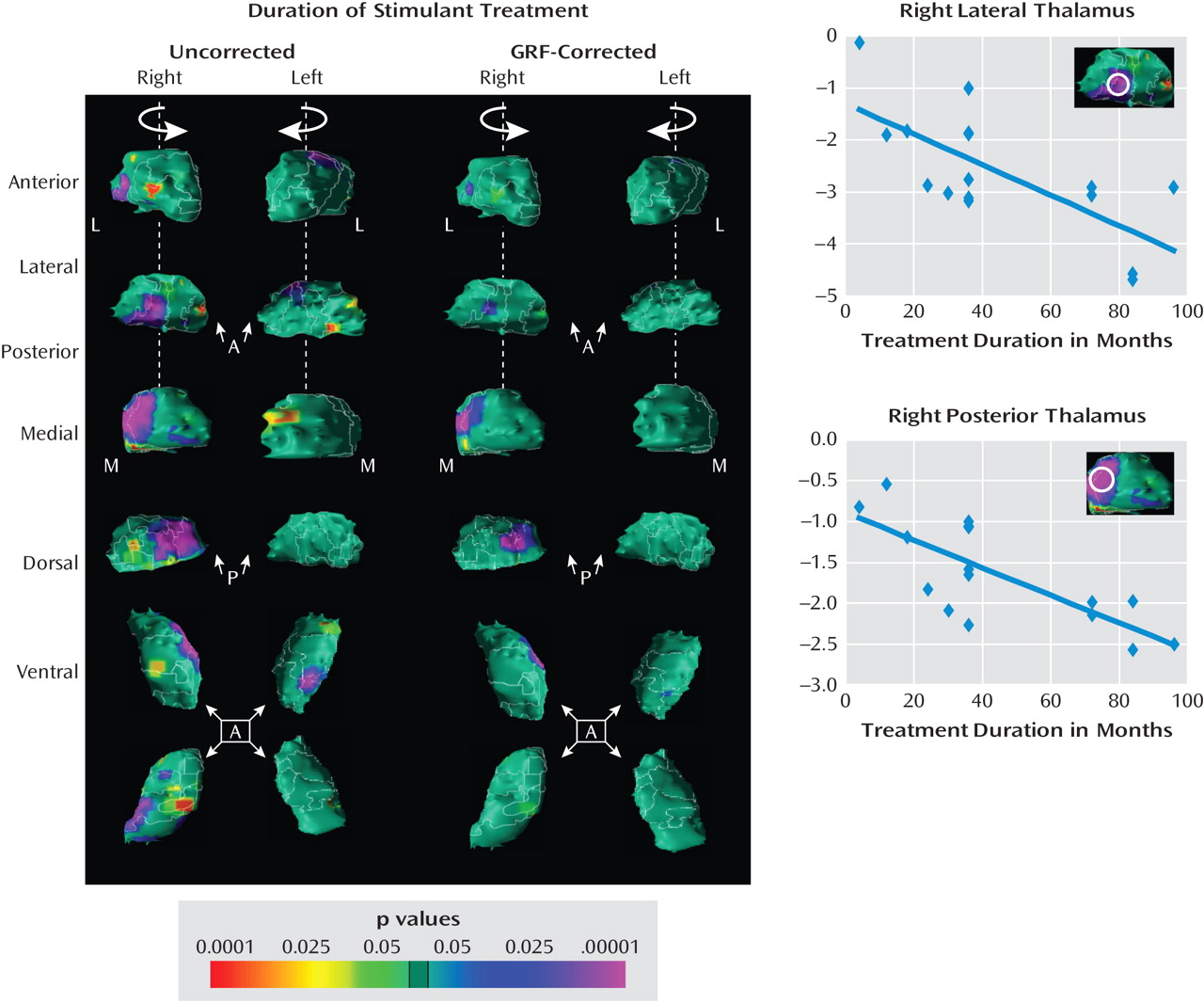
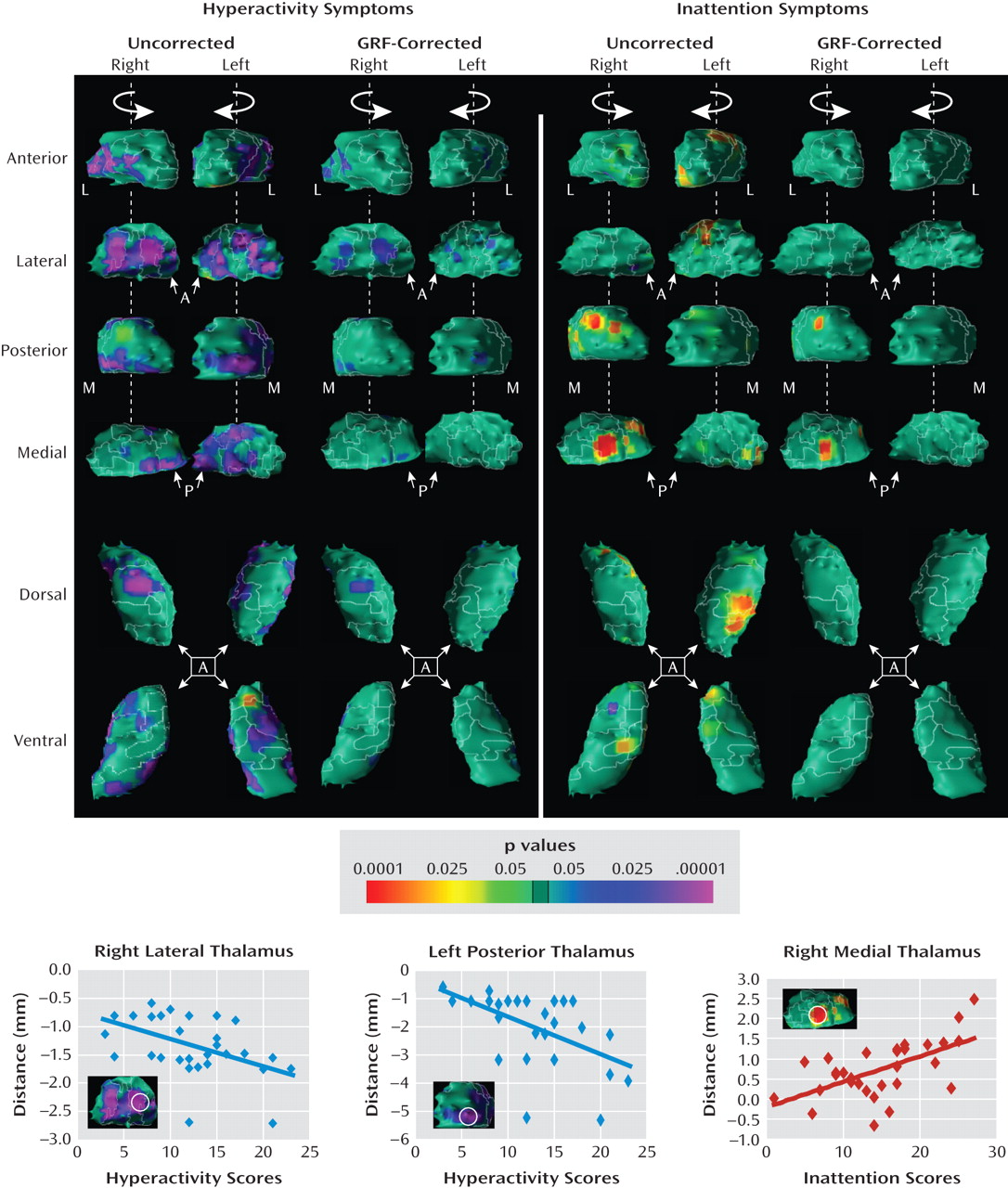
Correlations with symptom severity
Possible confounders
Discussion
The Role of the Thalamus in the Pathogenesis of ADHD
The pulvinar nucleus
The ventral lateral nucleus
Effects of Stimulant Medications on Thalamic Morphology
The Differential Association of Thalamic Nuclei With ADHD Symptom Domains
Limitations
Conclusions
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 166.40 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

