Alcohol dependence often follows a chronic, relapsing course (
2) similar to other medical disorders, such as diabetes. Despite its psychological and social antecedents, alcohol dependence, once established, is essentially a brain disorder. Without a pharmacological adjunct to psychosocial therapy, the clinical outcome is poor, with up to 70% of patients resuming drinking within 1 year (
3,
4). Thus, psychosocial intervention alone is not optimal treatment for alcohol dependence. Furthermore, it appears that brief interventions (e.g., brief behavioral compliance enhancement treatment [
5] or medical management [
6]) are sufficient to optimize an efficacious pharmacological treatment, and there is no need for more formal or intensive psychotherapy. Indeed, intensive psychotherapy has been shown to be less effective than a brief intervention plus a placebo pill for the treatment of alcohol dependence (
7). Hence, there is no longer a clinical rationale to delay starting pharmacotherapy, which can be provided with a brief psychosocial intervention in general practice.
Hazardous Drinking in Emerging Adults
Alcohol use in emerging adulthood is prevalent (
17), and much of the drinking occurring during this period could be categorized as hazardous (see case 3). Binge drinking remains frequent among college students despite increased prevention efforts over the past decade (
18,
19). Indeed, 40% of college students have binged in the previous 2 weeks, according to the College Alcohol Study surveys (
19).
Although college-age binge drinking is often viewed as a rite of passage in the transition to adulthood, hazardous drinking in emerging adults is associated with serious consequences. Approximately 1,500 to 1,700 deaths and 600,000 injuries, including 200,000 serious injuries, occur in the United States each year among college students (
20,
21). The range of health risks and psychosocial consequences due to hazardous drinking among emerging adults includes motor vehicle accidents, legal problems, personal injuries, date rape and other types of violence, unwanted or unprotected sex, sexually transmitted diseases, pregnancy, blackouts, and missed classes (
22,
23). Indeed, rates of these problems are high. In 2001, nearly 700,000 students 18 to 24 years of age were assaulted by another college student who had been drinking (
21). Over 400,000 students had unprotected sex, and 100,000 reported being too intoxicated to know whether or not they had consented to sex (
21). Short-term problems associated with drug and alcohol use in emerging adulthood include violence, depression, and unprotected sex (
19,
24). The risk for sexually transmitted diseases as a result of multiple sex partners and unprotected sex is elevated during periods such as spring break, when casual sex, impulsivity, and reduced availability of condoms are compounded with increased use of, or bingeing on, alcohol or drugs (
25). One-fourth of college students report drinking-related academic problems, such as missing classes, falling behind, performing poorly on examinations and papers, and getting lower grades (
19,
26,
27). Alcohol-related consequences are more likely among students classified as hazardous drinkers than among those classified as nonhazardous drinkers (
28).
Severe or binge drinking may have long-term negative health consequences, even among those who avoid injuries. Those who drink severely or binge drink between the ages of 18 and 24 are more likely to progress to alcohol abuse or dependence diagnoses (
29,
30). Despite being at particularly high risk, college students do not differ from non-college students in rate of meeting criteria for alcohol dependence, although results are mixed on whether the two groups differ in alcohol abuse rates (
31,
32). Because episodic severe or binge drinking and alcohol use disorders are common among all emerging adults, research on college students generalizes well to other emerging adults. However, their residence status is related to risk for diagnosis, with more alcohol abuse and less alcohol dependence occurring among students living off campus (
31).
Among college students, 31% in one large study met diagnostic criteria for alcohol abuse and 6% for alcohol dependence (
33). Emerging adults evidencing an alcohol use disorder generally have associated problems, such as alcohol-related blackouts and increased craving for alcohol (
34). The long-term effects can be serious, as severe or binge drinking during college can predict rates of alcohol use disorders up to 10 years later (
35,
36).
Diagnosis and Pharmacotherapeutic Options
The patient in case 1 is a middle-aged schoolteacher who meets DSM-IV-TR criteria for alcohol dependence. The age at onset of problem drinking could not be ascertained. The patient has a possible family history of alcohol dependence in his father and antisocial traits, as well as medical complications that include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and liver impairment. This patient has a severe form of alcohol dependence with a chronic and pervasive course. The first step in treatment should be to negotiate a drinking goal with the patient. While the gold standard for a positive treatment outcome is complete abstinence, some patients need to be helped toward this goal by setting increasingly lower levels of heavy drinking.
Given the severe nature of the patient's alcohol dependence and the fact that he is still drinking heavily and has important medical complications, my choice of pharmacotherapy would be topiramate. An additional advantage of topiramate in this patient is that because it is excreted mostly unchanged by the kidneys in the urine (
52), there would be a reduced risk of the medication worsening his developing liver impairment. Topiramate, a sulfamate-substituted fructopyranose derivative, has been shown in two large-scale randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials to improve all drinking outcomes, including a reduction of heavy drinking and a promotion of abstinence (
53,
54). Topiramate is presumed to exert its antidrinking effects by cortico-mesolimbic dopamine system modulation through the facilitation of GABA function via a nonbenzodiazepine site on the GABA
A receptor (
55) and the antagonism of glutamate activity at α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate and kainate receptors (
56). Topiramate also has been shown to decrease the medical consequences of alcohol dependence, including obesity, hypertension, liver abnormality, and high cholesterol; however, it is unknown whether this effect is independent of its antidrinking properties (
57). Topiramate is generally well tolerated, and the more common adverse events associated with its use include paresthesia, taste perversion, anorexia, and difficulty with concentration.
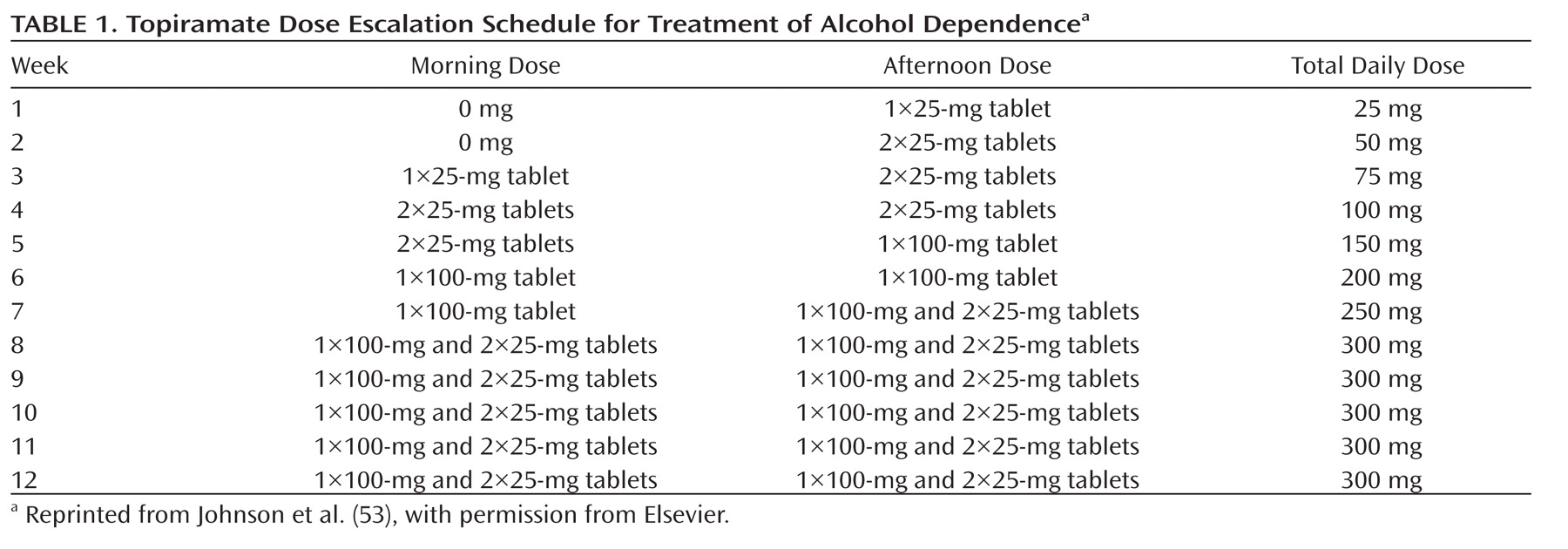
Topiramate treatment should be initiated at a dosage of 25 mg/day and titrated over 8 weeks up to 300 mg/day (
Table 1) while a brief intervention, such as brief behavioral compliance enhancement treatment, is provided on a weekly basis (
5). Care should be taken to titrate the dose of topiramate slowly, and longer dose-escalation schedules should be considered if necessary. The practitioner should be aware that topiramate's efficacy appears to be evident at dosages as low as 100 mg/day. Thus, stopping topiramate titration at this dosage may be considered if tolerability is a problem. Although the clinical trials for alcohol dependence in the United States typically report shorter-term outcomes (i.e., 3–6 months), prudent clinical practice would suggest that most patients need to be treated for 6 months to 1 year to increase the likelihood of a remission.
An alternative medication treatment for this patient would be baclofen—an agonist at presynaptic GABA
B (bicuculline-insensitive) receptors that appears to act by modulation of G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRK, Kir3) to suppress cortico-mesolimbic dopamine system neurons (
58). Baclofen might be useful for this patient, as it has shown promise in treating alcohol dependence, particularly in patients with liver impairment (
59). Baclofen is excreted primarily through the kidneys. It is recommended that baclofen be titrated from a starting dosage of 5 mg three times daily in the first 3 days, and then to the ceiling dosage of 10 mg three times daily. Unlike topiramate, baclofen is administered to patients who have already become abstinent, possibly by the use of a reducing dosage of the benzodiazepine chlordiazepoxide on an outpatient basis. While baclofen might itself aid in reducing alcohol withdrawal symptoms (
60), its cessation should be gradual to avoid the emergence of withdrawal symptoms of its own, which may include confusion, hallucinations, anxiety, perceptual disturbance, and extreme muscle rigidity with or without spasticity. Common adverse events associated with baclofen administration include headaches, insomnia, nausea, hypotension, urinary frequency, and, rarely, excitement and visual abnormalities (
61).
The patient in case 2 is an elderly woman who meets DSM-IV-TR criteria for alcohol dependence. Alcohol dependence among the elderly is often underdiagnosed, and every practitioner should be diligent in inquiring about drinking habits in this age group (
62). The first step in treatment should be to negotiate a drinking goal with the patient. Because of the high association of alcohol dependence with morbidity and mortality in elderly patients, the practitioner should negotiate a goal, or a sequence of targets, that culminate in abstinence.
Given the patient's age, which may make her prone to forgetfulness, and her relative isolation, my choice of pharmacotherapy would be an injectable extended-release formulation of naltrexone (Vivitrol). After a period of abstinence (3–5 days), which might require supportive benzodiazepine treatment (e.g., a reducing dosage of chlordiazepoxide), the patient can be scheduled to receive injectable extended-release naltrexone at 380 mg/month for 4 months. The efficacy and adverse-event profile of this formulation, administered on a monthly basis, are similar to those of oral naltrexone. Pharmacotherapy should be accompanied by a brief intervention (e.g., brief behavioral compliance enhancement treatment or medical management).
Notably, while consideration would be given to adding an antidepressant such as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) to the medication regimen, it would not be appropriate to do so at present with this patient, for three reasons. First, the patient does not meet DSM-IV-TR criteria for major depression, and the reported "gloominess" is likely to lift as her drinking outcomes improve, particularly if there are fewer episodes of heavy drinking or increasing periods of abstinence. Second, SSRIs have shown added benefit in comorbid alcohol-dependent and depressed patients mainly when the symptoms of dysphoric mood are marked and accompanied by suicidal ideation (
63). Third, the patient's age at onset of problem drinking would have to be determined more accurately because SSRIs can trigger an increase (rather than a decrease) in alcohol consumption among late-onset alcoholics.
The patient in case 3 is an emerging adult who meets DSM-IV-TR criteria for alcohol dependence. The first step in treatment should be to educate the patient about the health risks associated with his dependence on alcohol and sensitize him to the risky behaviors in which he engages. In this age group, a motivation-based approach appears to be most useful in setting treatment goals that typically focus on reducing binge and heavy drinking episodes.
Given that the patient has a moderate severity of alcohol dependence, is still drinking, had an early onset of problem drinking, and has a strong family history, the optimal treatment option would be ondansetron, a 5-HT3 antagonist that exerts its antidrinking effects through cortico-mesolimbic dopamine system modulation. Ondansetron has been shown to improve drinking outcomes in patients with early-onset alcoholism. Adverse events are mild (usually constipation, headaches, and sedation), and the starting dosage of 4 μg/kg twice daily should be maintained throughout treatment. Unfortunately, however, ondansetron is not currently available commercially at the therapeutic dose for alcohol dependence, so it is not a practical alternative outside research treatment settings.
An alternative pharmacotherapeutic option would be the μ-opioid antagonist naltrexone, accompanied by a brief intervention provided on a weekly basis (such as medical management, which was shown to be effective in the Combined Pharmacotherapies and Behavioral Interventions for Alcohol Dependence [COMBINE] study [
7]). Naltrexone was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1994 for the treatment of alcohol dependence, and its antidrinking properties have been attributed to cortico-mesolimbic dopamine system modulation (
47). Furthermore, therapeutic response to naltrexone appears to be enhanced among those with a family history of alcoholism (
64). Naltrexone should be provided at a dose that escalates up to 100 mg/day after the patient has been abstinent for 3 to 5 days. A reducing dosage of a benzodiazepine (e.g., chlordiazepoxide) can be prescribed on an outpatient basis according to a standardized schedule (
65) to facilitate the achievement of the brief period of abstinence needed before pharmacotherapy is started. Common adverse events associated with naltrexone treatment include nausea and somnolence. Treatment should be continued for as long as possible (at least 2 months).
To date, no published study has examined exclusively the utility of pharmacotherapy coupled with a brief intervention for the treatment of alcohol dependence in emerging adults. Hence, this recommendation is an extrapolation from adult studies with overlapping populations. Notably, among emerging adults, the mainstay of treatment has been brief intervention alone. However, the severity of established alcohol dependence in this patient, rather than just alcohol abuse, suggests that additional pharmacotherapy would be needed to obtain a favorable treatment outcome.
Nevertheless, a brief motivational intervention that has been used frequently to treat college students who binge drink, the Brief Alcohol Screening and Intervention for College Students (BASICS) program (
66), may be used as the adjunct to the pharmacotherapy. The BASICS program provides personal feedback, motivation, and strategies that enhance normative drinking patterns (
67). It is typically given as a low-intensity intervention, every 2 weeks, over about 8 weeks. The BASICS program is the most well-validated motivation-based brief intervention that has been employed in treating emerging adults with alcohol-related disorders.
Clinical Monitoring
An important aspect of clinical monitoring is continuing to quantify drinking behavior and setting appropriate target goals for the reduction or cessation of alcohol consumption. Brief interventions such as medical management or brief behavioral compliance enhancement treatment offer a convenient method for setting treatment goals while providing motivation and reinforcing medication compliance. Current clinical evidence points to the use of these brief interventions with medications rather than to intensive or more formal psychotherapies as adjuncts to pharmacotherapy. Moreover, because brief interventions are more generalizable to general practice, their use with efficacious pharmacotherapies should broaden access to care.
In sum, despite the apparent disparity of presentation of the three patients described here, they all can be managed successfully by nonspecialist practitioners in an office-based practice. Any assistance needed with detoxification can be done on an outpatient basis, and hospital admission for detoxification should be considered only in extreme cases (
66), such as in patients with a previous history of seizures or delirium tremens or serious medical complications such as uncontrolled diabetes or fulminant heart disease.
Other Pharmacotherapeutic Options
Other pharmacotherapeutic choices are available that could have been provided for the patients presented here. From the list of other FDA-approved medications, disulfiram (an inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase) could have been considered. However, disulfiram treatment was not proposed because its efficacy appears to be dependent on having a partner ensure compliance with the medication regimen (
68), rendering it a "psychological pill." Its effects thus derive from the agreement of the patient to take a medication that is part of a daily pledge of abstinence. Furthermore, disulfiram has no effect in reducing the urge or propensity to drink, which newer medications, such as naltrexone, ondansetron, and topiramate, have been reported to do (
47). Acamprosate (a modulator of glutamate neurotransmission at metabotropic-5 glutamate receptors) (
69) also has received FDA approval for the treatment of alcohol dependence, principally on the basis of European studies, but the failure of two large double-blind U.S. studies has cast doubt on its efficacy (
47).
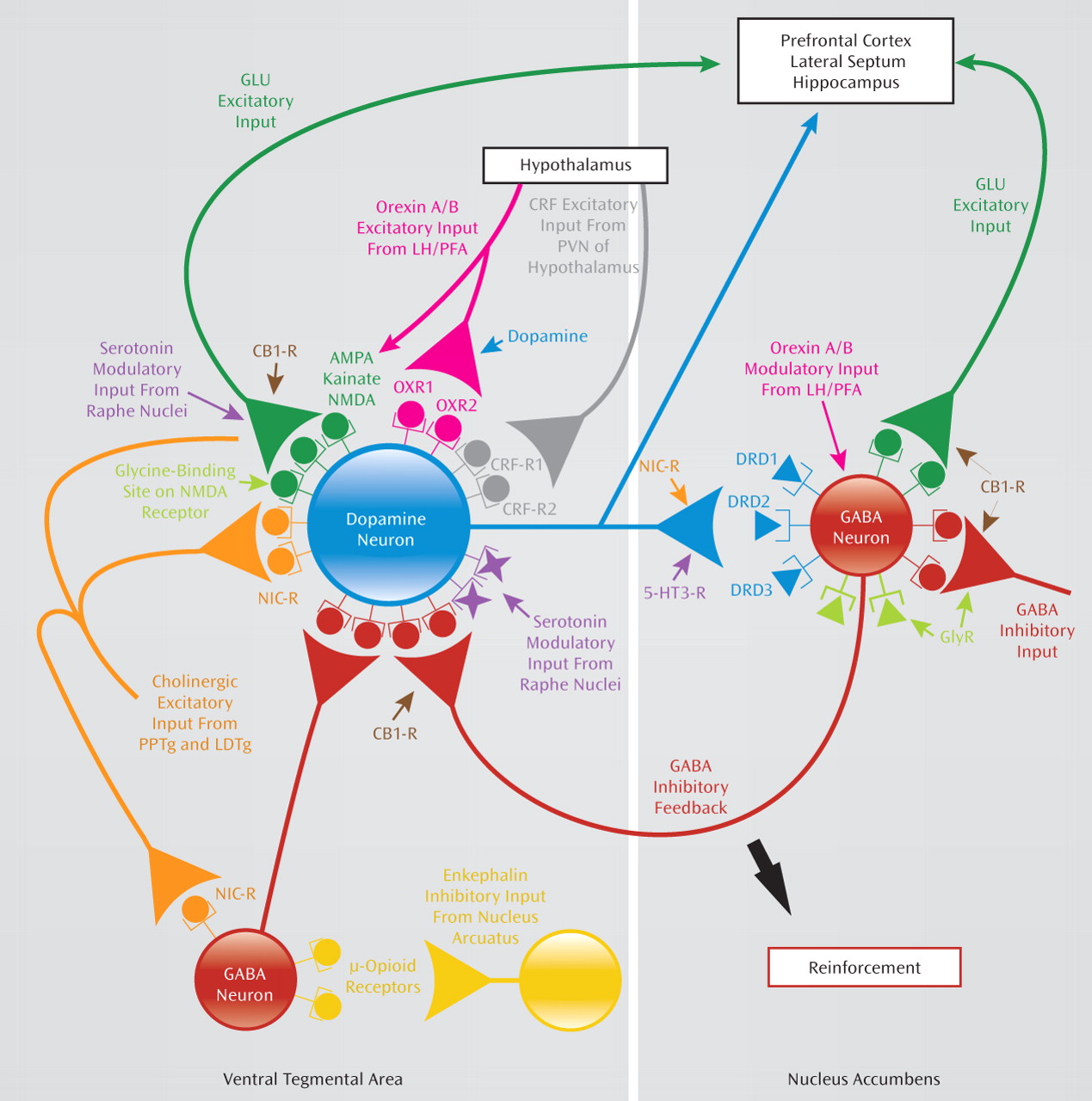
Several new molecular targets are being investigated for the treatment of alcohol dependence (see Figure 1) (
46). Apart from those already mentioned, research is being done to evaluate the efficacy of promising agents such as the neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist LY686017 (
70) and gabapentin (a modulator of voltage-gated
N-type calcium channels) (
71). Because recent double-blind trials have not found efficacy for aripiprazole (
72) or rimonabant (a cannabinoid receptor-1 antagonist) in the treatment of alcohol dependence, there is less optimism in the pursuit of these targets.
Medication combinations, by being able to target several neurotransmitters simultaneously, also hold the promise of greater efficacy in the treatment of alcohol dependence. However, this research is in its infancy, and the early promise of combining naltrexone and acamprosate (
73) appears unlikely to pan out (
7). Other medication combinations are currently being tested, and the results of these studies are expected soon (
47).
Future Pharmacogenetic Approaches
Personalized medicine promises to optimize treatment response to ensure that patients with a given disease receive the medication that will benefit them the most. Although examination of the pharmacogenetic effects on treatment response has aroused the most clinical interest, other fields, such as metabolomics, are equally important to our understanding of the biological factors that govern sensitivity to drug effects.
In a retrospective analysis of a double-blind clinical trial of alcohol-dependent individuals of European descent who received naltrexone, Oslin et al. (
74) reported that those with one or two copies of the opioid receptor μ 1 (OPRM1) Asp40 allele, compared with their homozygous counterparts, were less likely to return to heavy drinking and had a longer time to return to heavy drinking. A similar pattern of results was reported in the COMBINE study (
75), but the size of the effect was small, and the results are contradicted by other clinical studies that have examined the role of the OPRM1 Asp40 allele in predicting treatment response to naltrexone (
76) and the μ-opioid receptor antagonist nalmefene (
77). Hence, the role of the OPRM1 Asp40 allele in predicting response to naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence remains to be established firmly.
Serotonergic function is an important mediator of mood, impulsivity, and appetitive behaviors, including alcohol consumption. Of the mechanisms controlling synaptic 5-HT concentration, perhaps the most compelling is related to the functional state of the presynaptic 5-HT transporter (5-HTT). The 5-HTT is responsible for removing 5-HT from the synaptic cleft (
78). Indeed, up to 60% of neuronal 5-HT function is gated by the 5-HTT. The 5-HTT gene is found at the SLC6A4 locus on chromosome 17q11.1–q12, and its 5′-regulatory promoter region contains a functional polymorphism known as the 5-HTT-linked polymorphic region (
79,
80). The polymorphism is an insertion/deletion mutation in which the long (L) variant has 44 base pairs that are absent in the short (S) variant. Because of the differential transcription rates between LL allelic variants compared with their SS counterparts, variation at the 5-HTT gene is an interesting candidate for examining sensitivity to alcohol and treatment response to ondansetron in alcohol-dependent individuals. It is therefore of interest that alcohol-dependent individuals who are L-allelic variants, compared with their SS counterparts, may have greater craving for alcohol (
81). Furthermore, a recent pilot study in the human laboratory has suggested that individuals with the LL genotype might be particularly responsive to ondansetron (
82). Results of the first large-scale prospective pharmacogenetic study in the alcoholism field to test whether 5-HTT gene allelic variation predicts therapeutic response to ondansetron are eagerly awaited. If the results of this study are positive, it has the potential to make a personalized approach to the treatment of alcohol dependence a reality, whereby potential responders are identified through specific genetic markers and treated with ondansetron.