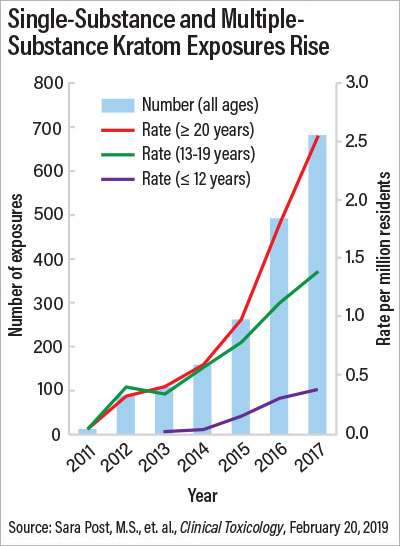
Kratom, a plant touted as a “natural opiate” and available legally in most parts of the United States, has gained popularity in recent years for its alleged ability to help with pain and the symptoms of opioid withdrawal. But those who use it may be taking a serious risk with their health, suggests a study in Clinical Toxicology.
Researchers who analyzed data from the National Poison Data System (NPDS) found that there were 1,807 kratom-related calls to U.S. poison control centers between 2011 and 2017, with 65% occurring in 2016 and 2017. Nearly a third of kratom exposures resulted in admission to a health care facility, and 11 deaths were associated with kratom use.
About 65% of the calls were regarding people who had taken kratom only. Among these single-substance exposures, 51.9% resulted in serious medical outcomes such as seizures, respiratory depression, coma, liver problems, bradycardia (slowed heart rate), and cardiac arrest. Other common side effects were agitation and irritability, tachycardia (fast heart rate), and high blood pressure. Five of the calls were for infants experiencing withdrawal after exposure to kratom in utero. The results suggest that kratom is not the benign supplement its promoters claim it to be, and it does not act like a typical opioid, said study researcher Henry A. Spiller, M.S., D.A.B.A.T., director of the Central Ohio Poison Center and an assistant professor at the Ohio State University College of Medicine.
“What we found, especially with adverse events like tachycardia and hypertension, is that it’s more like tramadol, for which one mechanism of action is serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. That’s why you see the agitation and the seizures,” Spiller said. Spiller added that kratom works like an opioid only at higher doses, when it can cause respiratory depression.
“We’re not the DEA [Drug Enforcement Administration], but people need to know there are risks to this,” Spiller added. “Natural doesn’t necessarily mean safe. Just because kratom is a plant, that doesn’t mean it can’t have adverse effects.”
Petros Levounis, M.D., M.A., an addiction psychiatrist who has treated people who use kratom, said that kratom overdose may be difficult to treat.
“Because of kratom’s complex neurotransmitter profile, naloxone may not be as effective in reversing an overdose,” said Levounis, who is a professor and chair of the Department of Psychiatry at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School.
Spiller noted a second challenge to kratom’s neurotransmitter profile. “We don’t know how many people [currently] taking kratom are taking other things like SSRIs [selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors]. If they are taking SSRIs, taking kratom may be like double dosing,” Spiller said.
In their study, Spiller and his coauthors called for more government oversight of kratom.
“The high proportions of [health care facility] admissions and serious medical outcomes highlight the need for kratom regulation by the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] to ensure quality and safety, as well as the need for more research on the effects of kratom in humans,” they wrote.
The DEA is considering listing kratom as a Schedule I drug on par with heroin or LSD, a move recommended by the Department of Health and Human Services but met with public outcry. Listing kratom as Schedule I would pose problems for research because those wishing to study it would have to register and obtain approval through the DEA, Levounis said.
“The debate about research has been around for a while. Schedule I exists to protect people from something dangerous, but the other side is that it limits access for research on it,” Levounis said. “If kratom does have some medical promise, then it should go through classic FDA approval pathways. Like cannabis, we’re far from having confidence for recommending this to patients before the research has completed its course.”
The American Association of Poison Control Centers provided the NPDS data for the study. ■
“Kratom Exposures Reported to United States Poison Control Centers: 2011–2017” can be accessed
here.