The past several years have been a time of dramatic change for substance abuse treatment nationwide. In particular, community residential facilities are assuming a larger role in the continuum of care for substance abuse patients. Many patients with more chronic, severe, and complex disorders are now being placed in community residential facilities rather than in hospital-based inpatient care (
1,
2,
3).
In the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), for example, clients recently placed in community residential facilities were more than six times as likely to misuse multiple substances and more than twice as likely to have concomitant psychiatric diagnoses than patients in earlier cohorts (
4,
5). The finding of increased severity of problems among VA substance abuse patients was consistent in studies in which treating clinicians made clinical diagnoses, in which program managers estimated the number of patients in their caseloads with dual disorders, and in which information on patients' psychiatric treatment histories was obtained from VA databases (
4,
5).
When community residential facilities have more treatment services and social activities available to patients, patients tend to participate more in treatment. In turn, greater participation results in better outcomes at discharge, especially among more impaired substance abuse patients, such as those with comorbid psychiatric diagnoses (
6,
7,
8,
9,
10). Other studies of residential substance abuse facilities (
11) and psychiatric treatment facilities (
12) reported that patients with more psychiatric impairment functioned better when the program provided more structure, such as when they were taught practical skills in preparation for release from the program. Taken together, these studies suggest that more impaired substance abuse patients have better treatment outcomes when their treatment program offers more services and structure.
We examined the extent to which community residential facilities treating substance abuse patients are providing more services and structure to meet the needs of a client population with increasingly severe problems. Specifically, we surveyed a nationwide sample of the same community residential facilities in 1995 and in 1998. We looked for changes over time in the programs' services and structure as well as changes in their organizational characteristics, such as size, patient length of stay, and staffing. We determined whether facilities that began to admit more substance abuse patients with psychiatric disorders also had more increases in services and structure than facilities that consistently limited their clientele to patients with only substance use disorders.
Methods
Sample
To conduct the 1995 survey of community residential facilities, Moos and associates (
6) obtained a list of all 305 community residential facilities nationwide that had ongoing contracts to provide services for VA patients. A total of 299 facility managers (99 percent) completed the survey. To conduct the 1998 survey of community residential facilities, we obtained an updated list containing 321 such facilities nationwide that currently had VA contracts. A total of 297 managers (93 percent) completed the second survey.
This paper focuses on 249 community residential facilities from which we had completed surveys both in 1995 and in 1998. They were all community facilities that were under contract with VA to provide residential care for substance abuse patients who had received VA inpatient or outpatient services. Although these facilities were under contract with VA, they served both veteran and nonveteran substance abuse patients.
The 1995 survey found that 81.9 percent of patients in the 249 facilities were men, 30.3 percent were between the ages of 18 and 30, 42.5 percent were between the ages of 31 and 40, 20.6 percent were between the ages of 41 and 50, and 6.6 percent were over age 50. Most of the patients were white (on average, 61.5 percent), with smaller proportions of black patients (28.2 percent) and Hispanic patients (6.1 percent). Most patients were divorced (46.7 percent) or had never married (37.3 percent). An average of 29.8 percent left school before graduating from high school, 47.2 percent had completed high school, and 23.0 percent had at least some college.
Measures
Both the 1995 and 1998 surveys contained portions of the Policies and Services Characteristics Inventory (PASCI) (
13). The PASCI yields a quantitative description of a program's policies and services so that a single program can be compared with normative samples of programs, and surveys of large numbers of programs can be used to examine the impact of program characteristics on patients' outcomes. The PASCI is descriptive rather than prescriptive; it has not been used to set standards for adequate or superior policies and services in residential treatment. In part, the PASCI obtains information about the organizational characteristics of the treatment facility such as facility size, patient length of stay, staffing, wait list features, and per diem costs. PASCI scales are internally consistent, independent, and stable (
13).
Two PASCI subscales were used in this study to assess services. The 26-item subscale on availability of health and treatment services assesses the availability of these services in the program (Cronbach's alpha=.83 in 1995 and .84 in 1998). The other subscale, the ten-item subscale on availability of social-recreational services, assesses the availability of organized activities in the program (alpha=.78 in 1995 and .79 in 1998).
One PASCI subscale was used to assess program structure. The 19-item structured policies subscale assesses the degree to which the program structures patients' patterns of daily living (alpha=.71 in 1995 and .73 in 1998).
Most PASCI subscale items are scored dichotomously, with 0 indicating an absence or lack of the construct assessed, and 1 indicating its presence. The item scores are then summed. To facilitate direct comparisons of raw scores, percentage scores are obtained. For example, a score of 13 on the 26-item health and treatment services subscale is given a percentage score of 50.
To compare the organizational characteristics, services, and structure of the 249 community residential facilities between 1995 and 1998, paired t tests were used for mean scores and chi square tests were used for proportions.
Results
Organizational factors, services, and policies
Organizational characteristics.
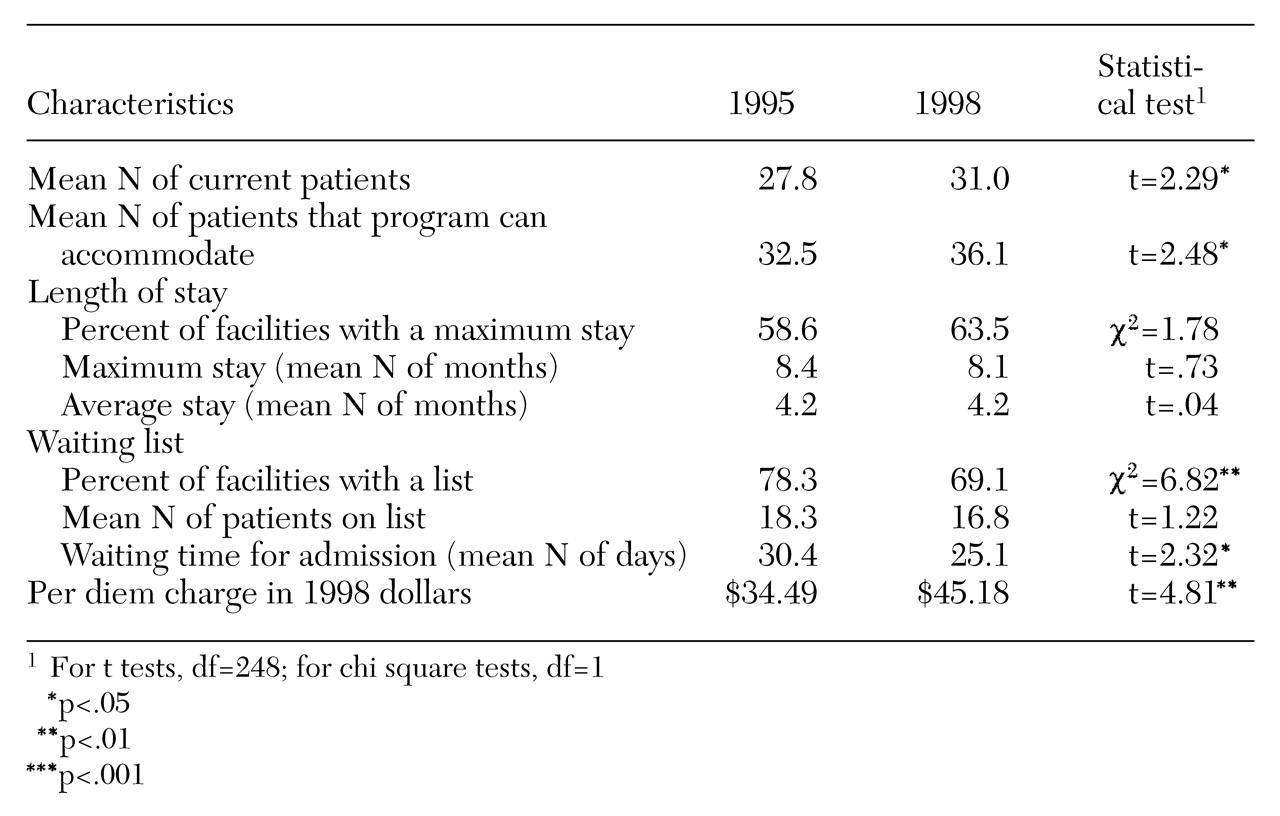
As
Table 1 shows, community residential facilities had somewhat more patients and more program capacity in 1998 than in 1995. Most facilities set a maximum length of stay in both 1995 and 1998; the average maximum length of stay allowed was about eight months. Patients' actual average length of stay was about four months in both 1995 and 1998. In 1998 facilities were less likely to have a waiting list, and patients did not wait as long to be admitted to the program. The reduced waiting time may be partly due to the larger size of the facilities in 1998. Even corrected for inflation (by converting 1995 dollars to 1998 dollars using the consumer price index), the amount patients were charged for a day of treatment was higher in 1998 than in 1995.
The community residential facilities did not differ between 1995 and 1998 in the number of full-time-equivalent staff members in various treatment positions, such as registered nurses, aides, and social workers, with one exception. In 1998 programs had more full-time-equivalent alcohol or drug addiction counselors than they did in 1995 (4.25 versus 3.59; t=2.57, df=248, p<.01).
Health and treatment services.
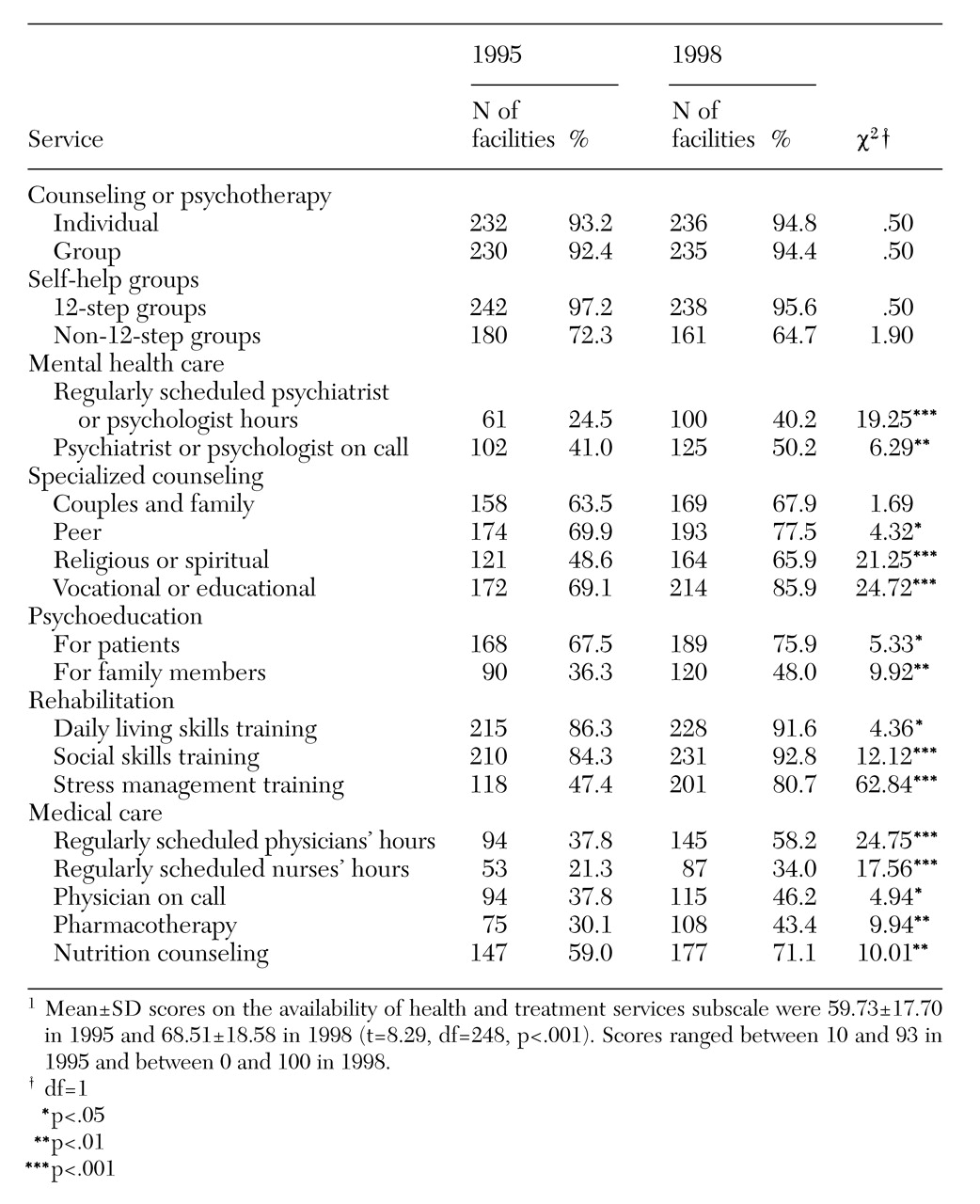
As shown in
Table 2, in both 1995 and 1998 most community residential facilities offered individual and group counseling or psychotherapy as well as 12-step and non-12-step self-help groups. In 1998 programs were more likely to have a psychiatrist or a psychologist, or both, available to patients, either on an on-call basis or by having regularly scheduled hours. Programs also were more likely in 1998 to offer specialized counseling, including peer, religious, or spiritual counseling and vocational and educational counseling. Furthermore, in 1998 programs more frequently provided psychoeducational services for both patients and their family members as well as rehabilitation services such as training in daily living skills, social skills, and stress management.
Finally, in 1998 programs made medical care more available to patients by providing regularly scheduled physicians' and nurses' hours and having a physician on call. Pharmacotherapy was more commonly offered in 1998, as was nutrition counseling. On average, between 1995 and 1998 the availability of health and treatment services rose from 59.7 percent to 68.5 percent, an increase of 14.7 percent. Seventy-five percent of the programs provided more health and treatment services in 1998 than they did in 1995.
Social and recreational services.
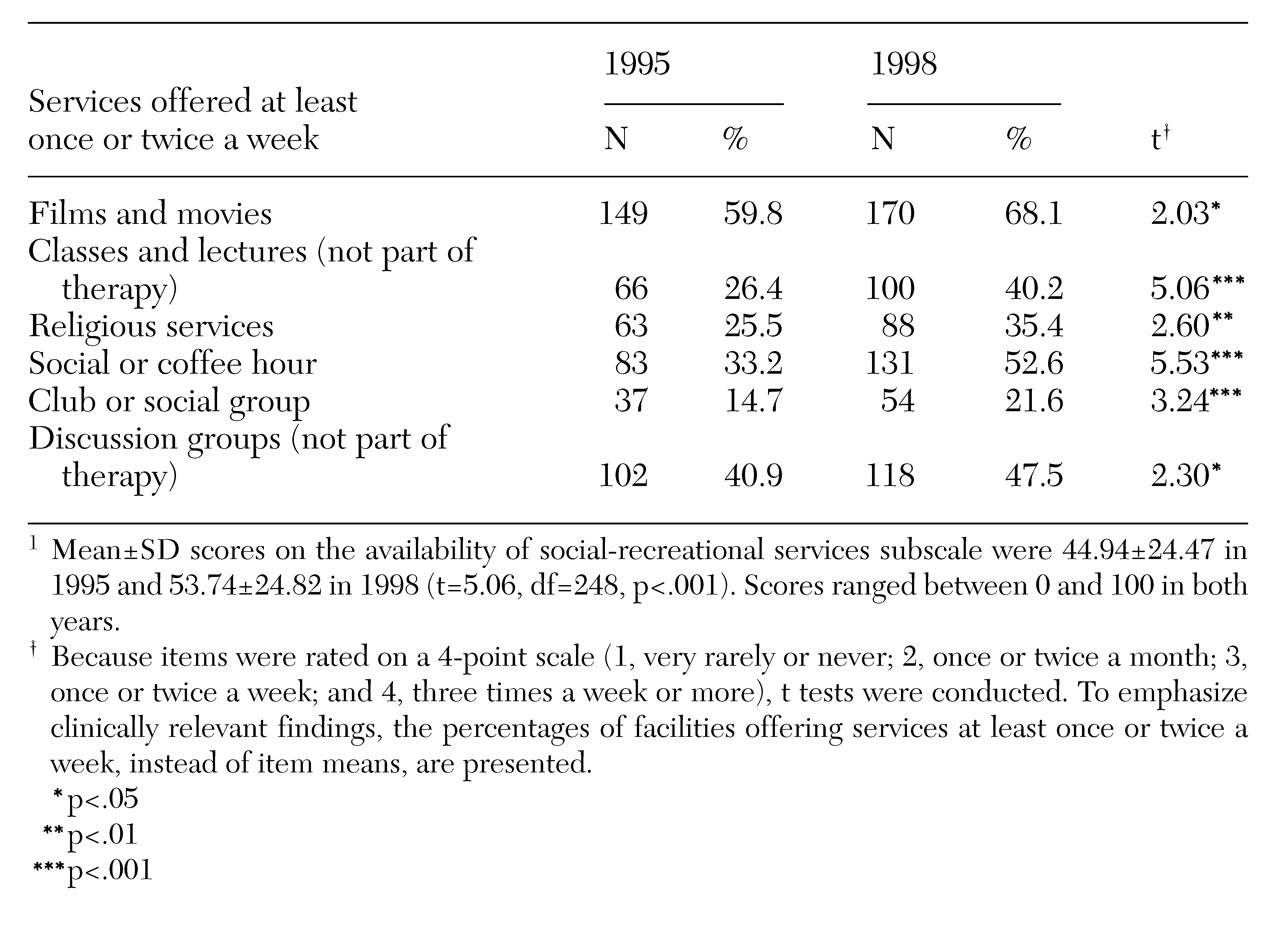
As shown in
Table 3, compared with programs in 1995, programs in 1998 were more likely to offer a number of recreational activities. The activities included those with an informational focus, such as movies, classes, lectures, and discussion groups, and those with a more purely social aim, such as social or coffee hours and clubs or social groups. In 1998 programs were more likely to offer religious services on a frequent basis. On average, between the two surveys, the availability of social and recreational services increased from 44.9 percent to 53.7 percent, a rise of 19.6 percent. Fifty-nine percent of the programs provided more social and recreational services in 1998 than they did in 1995.
Structured policies.
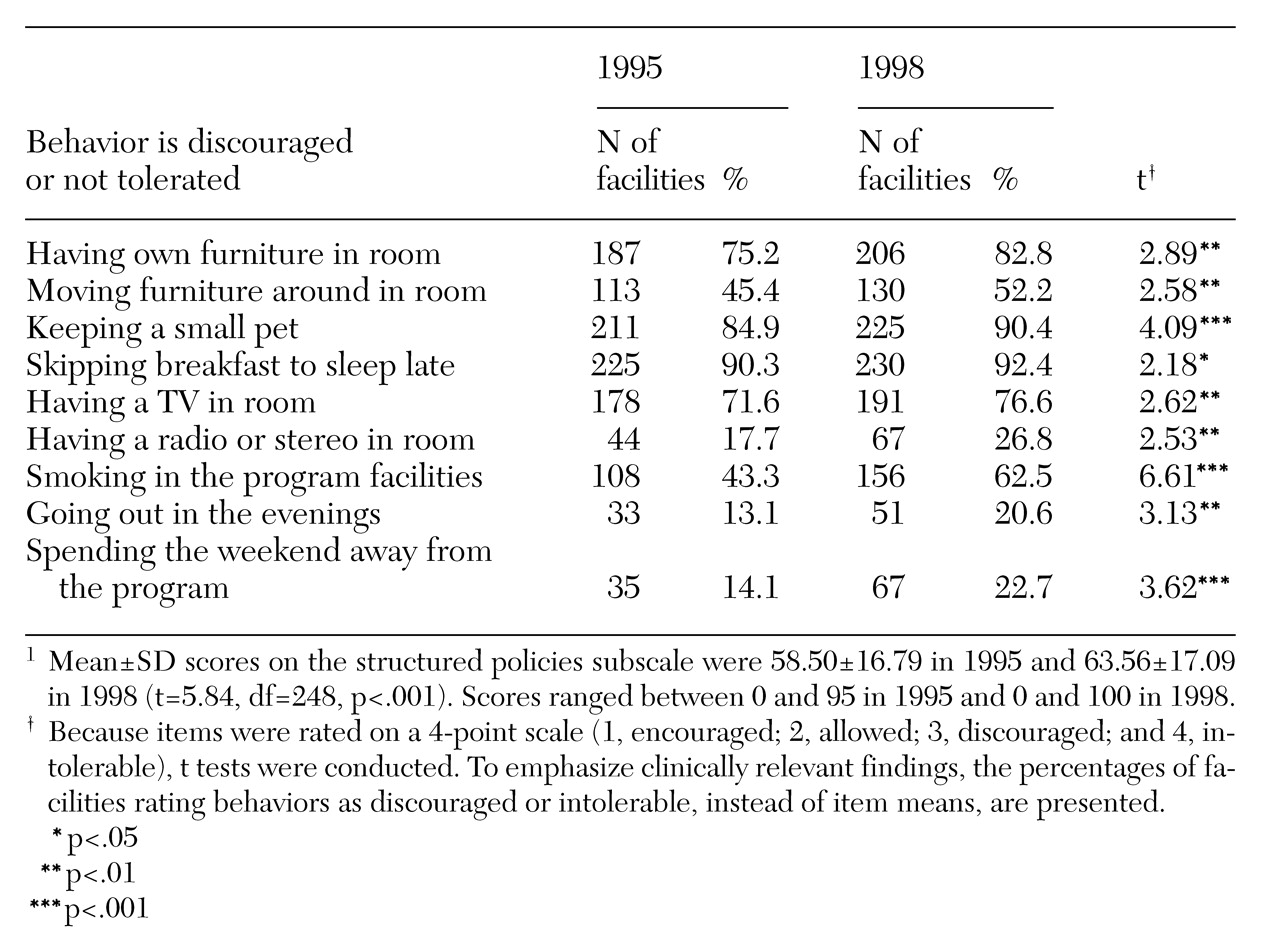
As
Table 4 indicates, in 1998 programs had become more structured than they were in 1995, in that a number of patients' behaviors were more likely to be discouraged or considered intolerable. Policies covered the type and placement of furniture in patients' rooms; televisions, radios, and stereos in patients' rooms; pets; sleeping late; smoking; and leaving the program on evenings and weekends. Programs did not change significantly between 1995 and 1998 on policies about times for waking up, bathing, and curfews. In 1998 patients were required to go to bed earlier than they were in 1995 (on average, about 10 p.m. versus 11 p.m.; t=2.38, df=248, p<.05). On average, during the three-year period, programs showed an increase of 5.1 percent in structured policies. Fifty-eight percent of the programs demonstrated increased structure.
Correlations.
Between 1995 and 1998 changes in health and treatment services showed a moderate positive correlation with changes in social and recreational services (r=.38, p<.001), but they were not associated with changes in program structure. Changes in social and recreational services had a modest positive correlation with changes in program structure (r=.16, p<.01).
Types of patients treated
In 1995 a total of 67 percent of programs (N=167) limited their admissions to patients with substance use disorders only, whereas 33 percent (N=82) also admitted patients with substance use and concomitant psychiatric disorders. In 1998 a total of 24 percent of programs (N=60) limited admissions to patients who had only substance use disorders, whereas 76 percent (N=189) also treated dual diagnosis patients. This change represents a significant shift toward treating patients with both substance abuse and psychiatric problems (χ2=12.40, df=1, p<.001).
Types of patients, services, and structure.
Between 1995 and 1998 a total of 116 community residential facilities changed from serving only patients with substance abuse problems to also serving patients with substance abuse and psychiatric disorders. We examined whether these facilities offered more services and had more structure in 1998, compared with the 51 facilities that served only substance abuse patients to the exclusion of dual diagnosis patients in both 1995 and 1998.
Results of t tests showed that in 1995 these two sets of programs did not differ in health and treatment services or structured policies. However, the programs that changed toward accepting dual diagnosis patients offered more social and recreational services (mean subscale score of 46.68 versus 38.63; t=1.98, df=165, p<.05). In 1998, compared with programs that accepted only substance abuse patients, programs accepting both substance abuse patients and dual diagnosis patients not only had more social and recreational services (57.03 versus 48.04; t=2.19, df=165, p<.04) but also had more health and treatment services (70.49 versus 61.69; t=2.61, df=165, p<.01) and structured policies (67.11 versus 62.33; t=2.04, df=165, p<.05).
Analysis of change scores—1995 subscale scores subtracted from the corresponding scores for 1998—showed that, compared with programs that accepted only substance abuse patients, the programs accepting substance abuse and dual diagnosis patients had larger increases in health and treatment services (17.6 percent versus 13.4 percent; t=1.9, df=165, p<.05).
Discussion and conclusions
The two surveys of a nationwide sample of 249 community residential facilities showed that programs were more likely to serve dual diagnosis patients in 1998 than in 1995 and that in 1998 programs provided more services and more structure. Facilities that changed their admission policies to admit dual diagnosis patients were most likely to have a service-intensive treatment program in 1998.
Currently, community residential facilities are more likely than they were previously to have psychiatrists and psychologists available to patients as well as specialized counseling and psychoeducational, rehabilitation, and medical services. The facilities now offer more social and recreational activities and are more likely to discourage patients from choosing individual patterns of daily living. These treatment programs are now somewhat larger, and patients do not have to wait as long to be admitted.
Although recent studies have not focused on increases in services and structure in residential substance abuse care, they have emphasized that higher levels of services and structure are beneficial for patients. For example, Nuttbrock and colleagues (
14) found that patients had better outcomes in a therapeutic community that provided psychiatric and psychological care on demand and had highly structured rules of conduct than they did in community residences that did not dispense in-house services and aimed to be less restrictive. Patients in the therapeutic community had reduced levels of substance use and psychopathology and better functioning.
Guydish and associates (
15) reported that clients in residential substance abuse programs were less likely to drop out of treatment and showed greater improvement in social problems and psychiatric symptoms than those in day treatment. The better outcomes of residential clients were attributed in part to the program's having more structure, such as strictly enforcing rules.
Results of the 1995 survey support the hypothesis of Guydish and colleagues that more program structure is related to better patient retention. Specifically, in our study more program structure was positively correlated with the percentage of patients who successfully completed treatment in 1995 (r=.24, p<.001). (This outcome was not assessed in 1998.) Thus program structure may be associated with better substance abuse treatment outcomes and psychosocial functioning because it facilitates patients' completion of recommended treatment regimens.
Our findings suggest that community facilities that contract with VA are adapting appropriately to an increasingly ill resident population by providing more services and structure. These facilities now are more likely to offer services of highly trained mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists and psychologists, and to offer regularly scheduled physicians' and nurses' hours and pharmacotherapy. Probably because of these more expensive services, per diem costs at community residential facilities have increased by more than 30 percent.
Research is needed to examine cost-effective methods of providing the increased services and structure that impaired substance abuse patients need. Although service- and structure-intensive programs may be more expensive in the short term, the long-term costs to patients and society of failing to provide adequate care may be far greater.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Health Services Research and Development Service (grant IIR-95-011) and the Mental Health Strategic Health Group Department of the Veterans Health Administration.