FURTHER INFORMATION
Access to this interactive links box is free online.
AFFECTIVE DISTURBANCE
An abnormal or inappropriate emotion or mood.
POINT PREVALENCE
The proportion of individuals who have a phenotype at a specified point in time or within a defined timeframe (for example, 1 year).
DISABILITY ADJUSTED LIFE YEAR
The years of life that are lost due to premature mortality or disability.
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY
A psychiatric disease, or the manifestation of a psychiatric disease.
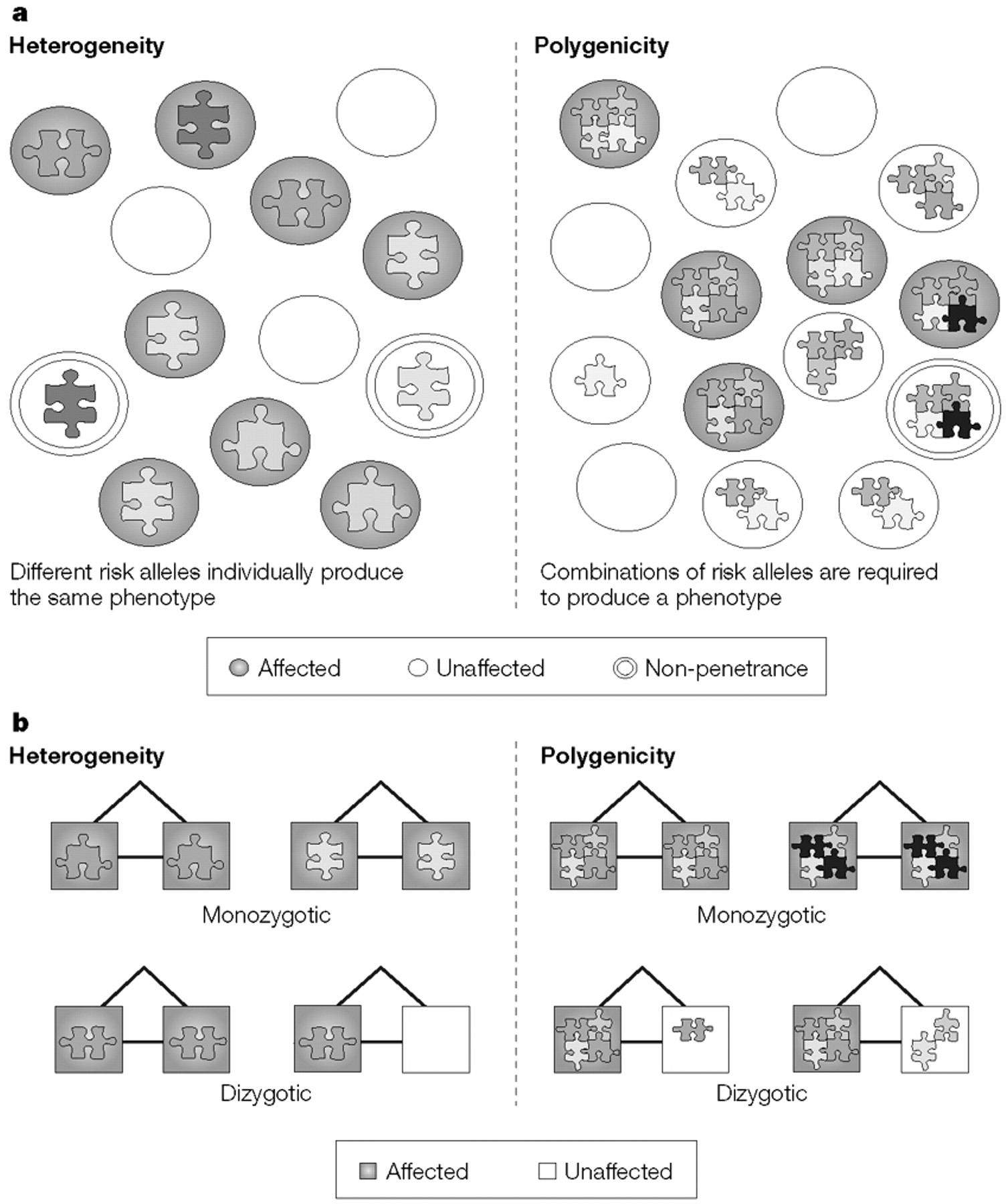
POLYGENICITY
A model of genetic determinism in which many alleles function in combination to produce a phenotype.
HETEROGENEITY
A model of genetic determinism in which different alleles lead to the same phenotype in different individuals, but an individual allele can suffice to produce the phenotype.
HERITABILITY
An estimate of the genetic component of liability, which ranges from zero to one.
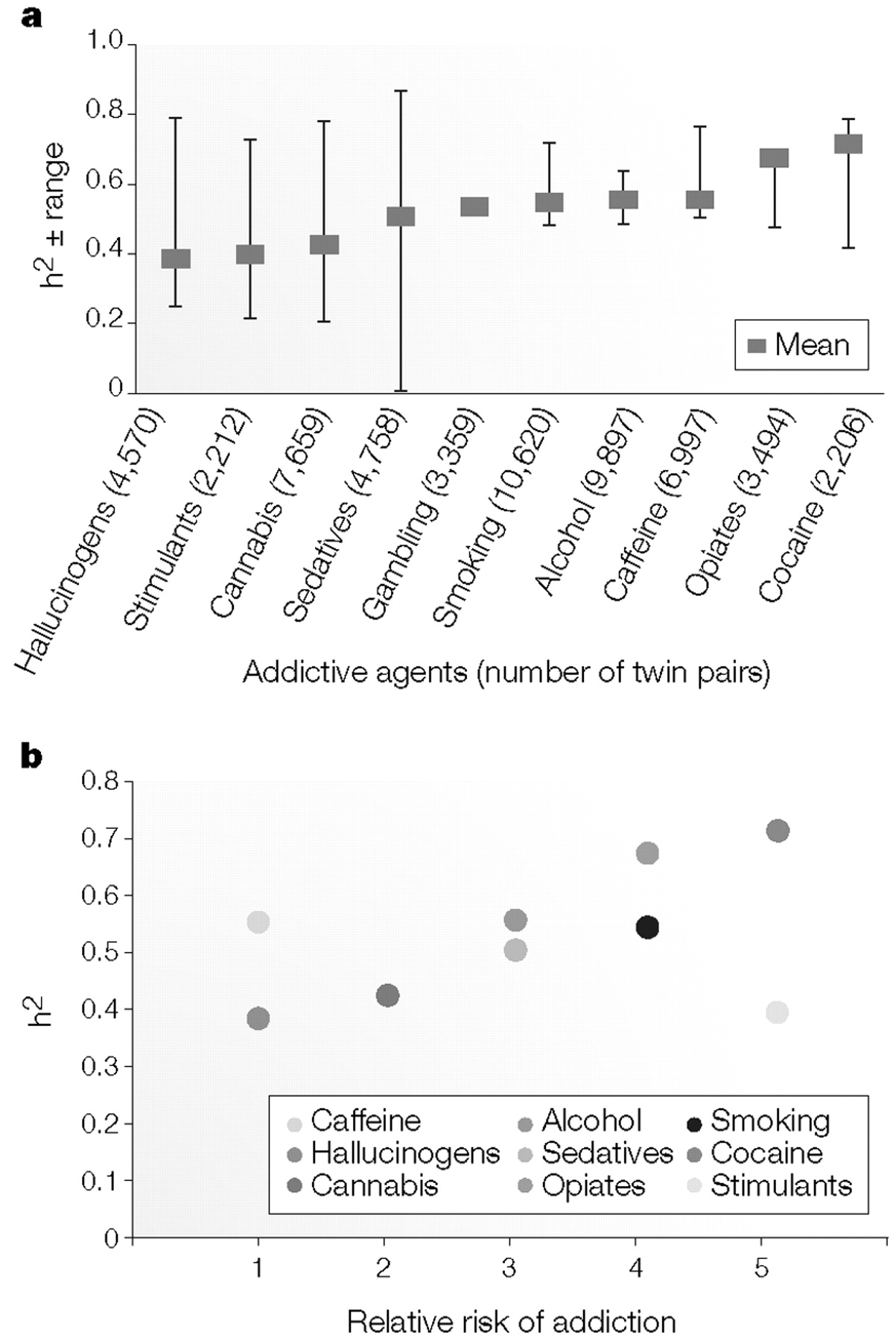
ADDICTION LIABILITY
The relative potential of an agent to lead to addiction.
ABUSE
Substance abuse is a disease that is operationally defined using objective criteria such as those issued by the American Psychatric Association and the World Health Organization.
RESILIENCY
The ability to withstand mental or physical stress.
OLIGOGENICITY
A model of genetic determinism in which a few alleles function in combination to produce a phenotype.
HAPLOTYPE
A combination of alleles at different loci on the same chromosome.
COMORBIDITY
The co-occurrence of two or more diseases in an individual or an excess of disease co-occurrence in a population.
PHENOCOPY
Describes the situation in which a phenotype of an environmental origin mimics a phenotype of a genetic origin.
GENOCOPY
Describes the situation in which a phenotype of a genetic origin mimics a phenotype of a different genetic origin.
PENETRANCE
The probability of expressing a phenotype that is determined by a genotype.
LOCUS-BASED LINKAGE
The detection of locus-to-locus or locus-to-phenotype genetic linkage. This is generally accomplished by detecting a lack of meiotic recombination in families in which alleles at one locus are observed to be in coupling (co-transmitted) or repulsion (not co-transmitted) with alleles at a second locus
LINKAGE DISEQUILIBRIUM
The excess and complementary deficit of combinations of alleles at two different loci, which is based on rarity of meiotic recombination between loci on the same chromosome.
BENZODIAZEPINE DRUGS
Structurally similar selective GABAA receptor agonists that have potent anxiolytic, sedative, central muscle relaxant and anti-epileptic properties.
QUANTITATIVE TRAIT LOCUS
A genetic locus that is identified through the statistical analysis of complex traits (such as body weight). These traits are typically affected by more than one gene and by the environment.
PHARMACODYNAMIC
Relating to the response of cells and tissues to drugs.
PHARMACOKINETIC
Relating to drug absorption, distribution or metabolism.
MANIA
A pathological elevated mood-state that is associated with mental and physical hyperactivity.
PANIC DISORDER
An anxiety disorder characterized by paroxysms of overwhelming fear with associated somatic, behavioural and cognitive symptoms.
AGORAPHOBIA
An anxiety disorder that is characterized by fear and avoidance of places from which escape might be difficult.
BULIMIA
An eating disorder that is characterized by recurrent binge eating, which is accompanied by self-induced purging and/or other inappropriate compensatory behaviours.
ALLOSTASIS
A new homeostatic (maintained) equilibrium that lies outside the normal range and is characterized by long-lasting adaptational mechanisms that are activated in response to a stressor.
CATECHOLAMINES
A class of structurally similar amine neurotransmitters, including dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline, that are derived from the amino acid tyrosine.
WISCONSIN CARD-SORT TEST
A neurocognitive test of frontal lobe function that requires the subject to switch strategies that are needed to match cards to a target.
N-BACK TEST
A neurocognitive test of frontal lobe function and working memory that requires the recall of an earlier stimulus after a new stimulus (or stimuli) has been presented.
WORKING MEMORY
A memory system that is activated for temporary storage and manipulation of information while a mental task is carried out.
WARRIOR/WORRIER MODEL
A selectionist explanation for the maintenance of COMT alleles that have counterbalancing effects in cognition versus resilience to stress and anxiety.
AMYGDALA
A complex region of the brain temporal lobe that is important in modulating emotional states.
AGONISTS
Molecules that bind to receptors and elicit signal transduction.
ANTAGONISTS
Molecules that bind to receptors and, although they do not have intrinsic action, inhibit signal transduction.