Medications and Sexual Function and Dysfunction
DEFINITION OF AND CRITERIA FOR SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION ASSOCIATED WITH MEDICATIONS
The DSM-IV-TR criteria for sexual dysfunction associated with substances and medications are outlined in Table 4-1.A substance-induced sexual dysfunction due to a prescribed treatment for a mental disorder or general medical condition must have its onset while the person is receiving the medication (e.g., antihypertensive medication). Once the treatment is discontinued, the sexual dysfunction will remit within days to several weeks (depending on the half-life of the substance). If the sexual dysfunction persists, other causes for the dysfunction should be considered. (p. 564)

ANTIDEPRESSANTS
These authors also felt that findings from the literature were not sufficiently robust to support claims of a difference in the incidence of drug-induced sexual dysfunction between existing antidepressant therapies. Nevertheless, most authors and clinicians would agree (based on some evidence) that various individual antidepressants (not groups), such as bupropion, mirtazapine, moclobemide, and nefazodone, are associated with sexual dysfunctions less frequently than the rest of antidepressants.Sexual dysfunction is widespread in the healthy non-depressed population and is a recognized symptom of depression and/or anxiety disorders (some would add also others, such as eating disorders). Sexual dysfunction has been reported with all classes of antidepressants (MAOIs, TCAs, SSRIs, SNRIs [serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors], and newer antidepressants) in patients with depression and various anxiety disorders. Numerous studies have been published, but only one used a validated sexual function rating scale and most lacked either a baseline or a placebo control or both. (p. 119)
OTHER PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATIONS
Antipsychotics
Mood stabilizers
Antianxiety medications
Stimulants and other medications used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Other medications used to treat mental disorders
NONPSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATIONS
SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND TOXINS
MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION ASSOCIATED WITH MEDICATIONS
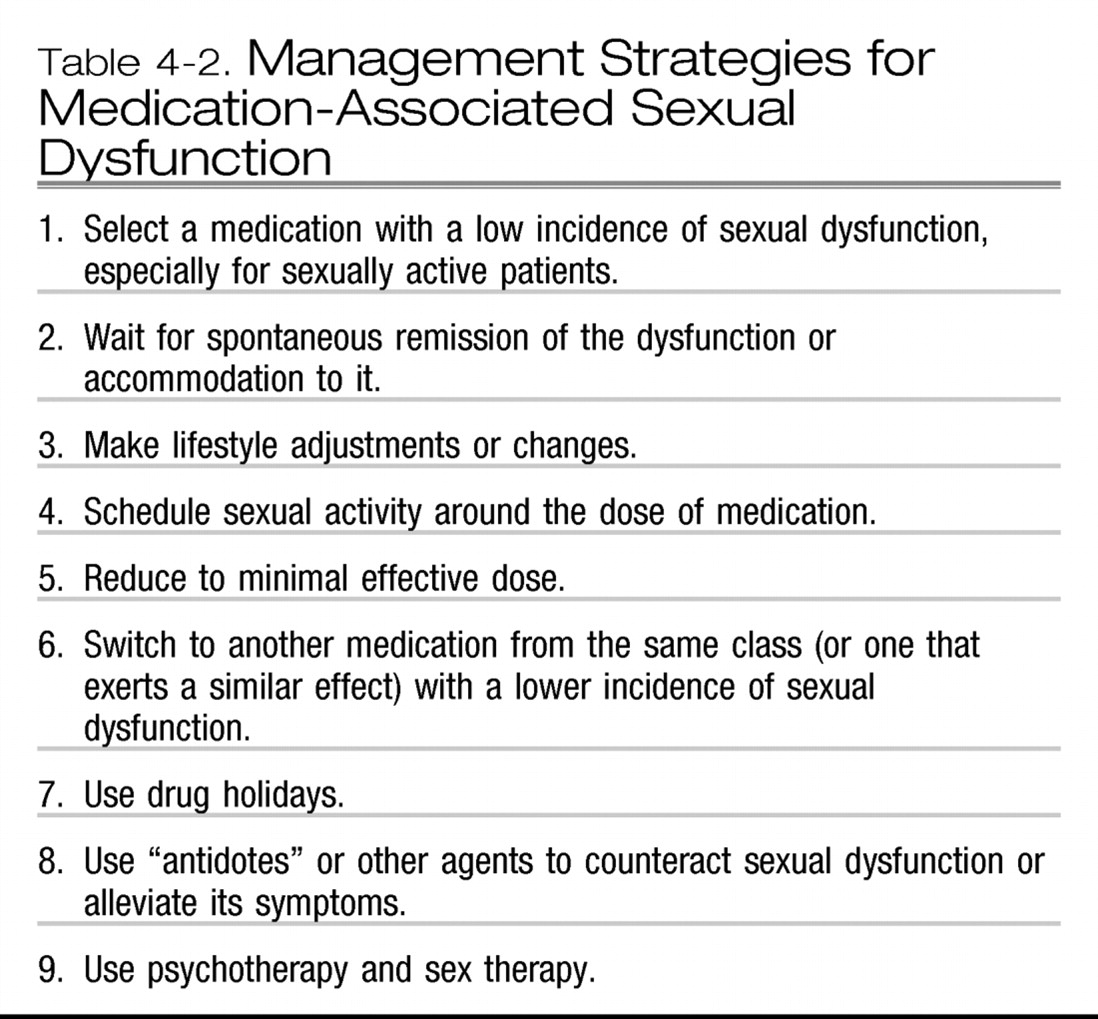
Final remark regarding the management of medication-associated sexual dysfunction
MEDICATIONS USED FOR PRIMARY SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION
Case example
KEY POINTS
REFERENCES
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBGet Access
Login options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

