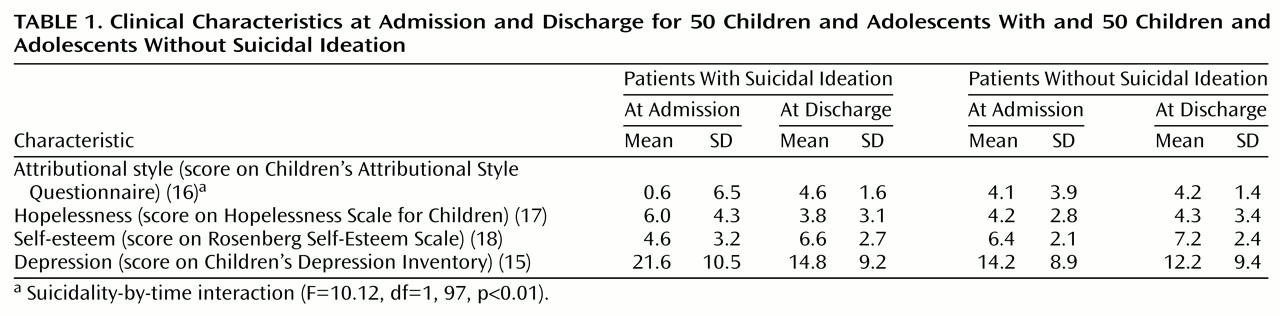
Subjects
A total of 100 subjects were selected from patients admitted to the child and adolescent inpatient units at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston. On the basis of consecutive admissions and willingness to participate, 50 subjects with and 50 subjects without suicidal ideation were selected at admission. Informed consent was obtained from a parent, and assent was obtained from the minor for participation in the study. Subject diagnoses were made by means of the DSM-IV criteria on the basis of direct interviews of the subject and a parent by means of the Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia (K-SADS) for School-Aged Children (6–18 years)—Lifetime
(14), which assesses both current and lifetime psychiatric disorders in youth.
Suicidal ideation was assessed during clinical interview by means of the Lifetime K-SADS for Adolescents, by documentation of suicidal ideation in the patient’s admission note, and by the response to item 9 on the Children’s Depression Inventory
(15). Item 9 asks whether the child has thoughts of killing himself or herself or wants to kill himself or herself. The group with suicidal ideation had documentation of suicidal ideation on the K-SADS for School-Aged Children, their admission notes, and the Children’s Depression Inventory. The comparison group had no evidence of suicidal ideation on the Lifetime K-SADS for Adolescents, their admission notes, or the Children’s Depression Inventory.
The subjects ranged in age from 7 to 17 years (mean=13.38, SD=2.67). Subjects with suicidal ideation were significantly older than the subjects without (mean=14.64 and 12.12 years, respectively) (t=5.32, df=98, p<0.01). Fifty-one percent of the subjects were male, and 49% were female. The subjects with suicidal ideation were more likely to be female (Yates’s χ2=7.84, df=1, p=0.005). The majority of the subjects were Caucasian (64%); others were African American (24%), Hispanic (10%), and Asian (1%). One subject’s ethnicity was not classified. Chi-square analyses revealed no significant differences between the subjects with and without suicidal ideation regarding ethnicity.
The principal diagnoses of the group with suicidal ideation were major depression (36%), bipolar disorder (20%), depressive disorder not otherwise specified (14%), conduct disorder (12%), substance use disorder (4%), psychotic disorder not otherwise specified (4%), organic mood disorder (4%), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (2%), acute adjustment disorder (2%), and schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type (2%). The principal diagnoses of the group without suicidal ideation included major depression (8%), bipolar disorder (32%), depressive disorder not otherwise specified (6%), conduct disorder (4%), psychotic disorder not otherwise specified (6%), PTSD (2%), acute adjustment disorder (2%), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (28%), intermittent explosive disorder (4%), undifferentiated somatoform disorder (2%), obsessive-compulsive disorder (2%), and anxiety disorder not otherwise specified (2%).
The group with suicidal ideation contained a larger number of subjects with major depression than the group without suicidal ideation (36% versus 8%) (Yates’s χ2=9.85, df=1, p=0.002). The group without suicidal ideation included several subjects with ADHD (N=14), whereas the group with suicidal ideation included none (Yates’s χ2=14.04, df=1, p=0.0002). Forty-six percent of the group with suicidal ideation had previously attempted suicide, whereas 14% of the comparison group had prior suicide attempts, which was a significant difference (Yates’s χ2=10.71, df=1, p=0.001).
During the course of hospitalization, the patients received standard treatment, including individual and family psychotherapy, group treatment, and pharmacotherapy, if clinically indicated. The mean length of hospitalization for the group with suicidal ideation was 7.98 days (SD=2.92; median=7, minimum=3, maximum=24), and the mean for the comparison group was 9.38 days (SD=3.01; median=8, minimum=2, minimum=49). This difference was nonsignificant (t=1.32, df=98, n.s.).
Measures
The Children’s Attributional Style Questionnaire
(16) is a 48-item, forced-choice measure of causal explanations for 24 positive and 24 negative events. Hypothetical events are presented, and children are requested to select the response that explains why the event happened to them. Sixteen questions pertain to each of the three attributional dimensions of internality, stability, and globality. A score of 1 is assigned to each internal, stable, or global response, and a score of 0 to each external, unstable, or specific response. There are six subscales on the Children’s Attributional Style Questionnaire, which yield a positive composite score (positive events: internal, stable, and global) and a negative composite score (negative events: internal, stable, and global). An overall score is determined by subtracting the negative composite score from the positive composite score. The lower the score, the more depressive the attributional style. The coefficient alphas for the composite positive score, composite negative score, and overall composite score are 0.71, 0.66, and 0.73, respectively. This is the most commonly used measure of attributional style in children; it is aimed at the first-grade reading level.
The Hopeless Scale for Children
(17) is a 17-item self-report questionnaire that measures feelings of hopelessness and pessimism about the future. Items are identified as either true or untrue for the patient. Scores range from 0 to 17, with a higher score reflecting greater hopelessness and pessimism about the future. This measure of hopelessness was selected because of its reasonable psychometric properties. Satisfactory internal consistency (alpha=0.97) and test-retest reliability (r=0.52) after a 6-week interval have been reported
(17).
The Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale
(18) is a 10-item self-report measure of global self-worth. Items are rated on a 4-point scale ranging from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree.” Internal consistency (alpha=0.81) and temporal stability (r=0.75) are satisfactory
(19). The Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale is a psychometrically sound measure for use with school-age children
(20,
21) and is aimed at the first-grade reading level.
The Children’s Depression Inventory
(15) is a 27-item self-report measure of depression designed for school-age children and adolescents. Its items include a wide range of depressive symptoms. Each item has three choices that are scored 0, 1, and 2, with the higher number indicative of greater severity. The total score ranges from 0 to 54. The child selects the sentence that best describes himself or herself for each item. The instrument is aimed at the first-grade reading level. This measure of depressive symptoms was selected because it has well-established reliability and validity
(22).